@@ -122,12 +122,32 @@ public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
122122第一个想法是,这三个数,两个指针?
123123
124124- 对数组排序,固定一个数 $nums[ i] $ ,然后遍历数组,并移动左右指针求和,判断是否有等于 0 的情况
125+
125126- 特例:
126127 - 排序后第一个数就大于 0,不干了
128+
127129 - 有三个需要去重的地方
128- - nums[ i] == nums[ i - 1] 直接跳过本次遍历
129- - nums[ left] == nums[ left + 1] 移动指针,即去重
130- - nums[ right] == nums[ right - 1] 移动指针
130+ - ` nums[i] == nums[i - 1] ` 直接跳过本次遍历
131+
132+ > ** 避免重复三元组:**
133+ >
134+ > - 我们从第一个元素开始遍历数组,逐步往后移动。如果当前的 ` nums[i] ` 和前一个 ` nums[i - 1] ` 相同,说明我们已经处理过以 ` nums[i - 1] ` 为起点的组合(即已经找过包含 ` nums[i - 1] ` 的三元组),此时再处理 ` nums[i] ` 会导致生成重复的三元组,因此可以跳过。
135+ > - 如果我们检查 ` nums[i] == nums[i + 1] ` ,由于 ` nums[i + 1] ` 还没有被处理,这种方式无法避免重复,并且会产生错误的逻辑。
136+
137+ - ` nums[left] == nums[left + 1] ` 移动指针,即去重
138+
139+ - ` nums[right] == nums[right - 1] ` 移动指针
140+
141+ > ** 避免重复的配对:**
142+ >
143+ > 在每次固定一个 ` nums[i] ` 后,剩下的两数之和问题通常使用双指针法来解决。双指针的左右指针 ` left ` 和 ` right ` 分别从数组的两端向中间逼近,寻找合适的配对。
144+ >
145+ > 为了** 避免相同的数字被重复使用** ,导致重复的三元组,双指针法中也需要跳过相同的元素。
146+ >
147+ > - 左指针跳过重复元素:
148+ > - 如果 ` nums[left] == nums[left + 1] ` ,说明接下来的数字与之前处理过的数字相同。为了避免生成相同的三元组,我们将 ` left ` 向右移动跳过这个重复的数字。
149+ > - 右指针跳过重复元素:
150+ > - 同样地,` nums[right] == nums[right - 1] ` 也会导致重复的配对,因此右指针也要向左移动,跳过这个重复数字。
131151
132152``` java
133153public List<List<Integer > > threeSum(int [] nums) {
@@ -143,7 +163,7 @@ public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
143163 // 排序后的第一个数字就大于0,就说明没有符合要求的结果
144164 if (nums[i] > 0 ) break ;
145165
146- // 去重, 不能是 nums[i] == nums[i +1 ],会造成遗漏
166+ // 去重, 不能是 nums[i] == nums[i +1 ],因为顺序遍历的逻辑使得前一个元素已经被处理过,而后续的元素还没有处理
147167 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) continue ;
148168 // 左右指针
149169 int l = i + 1 ;
@@ -239,27 +259,26 @@ public int maxArea(int[] height){
239259
240260```java
241261public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
242- int left = 0;
243- int right = s.length() - 1;
244- while (left < right) {
245- //这里还得加个left<right,小心while死循环,这两步就是用来过滤非字符,逗号啥的
246- while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(left))) {
247- left++;
248- }
249- while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(right))) {
250- right--;
251- }
262+ // 转换为小写并去掉非字母和数字的字符
263+ int left = 0, right = s.length() - 1;
252264
253- if (left < right) {
254- if (Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(left)) != Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(right))) {
255- return false;
256- }
257- //同时相向移动指针
258- left++;
259- right--;
265+ while (left < right) {
266+ // 忽略左边非字母和数字字符
267+ while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(left))) {
268+ left++;
269+ }
270+ // 忽略右边非字母和数字字符
271+ while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(right))) {
272+ right--;
273+ }
274+ // 比较两边字符
275+ if (Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(left)) != Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(right))) {
276+ return false;
277+ }
278+ left++;
279+ right--;
260280 }
261- }
262- return true;
281+ return true;
263282}
264283```
265284
@@ -355,7 +374,49 @@ public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
355374
356375 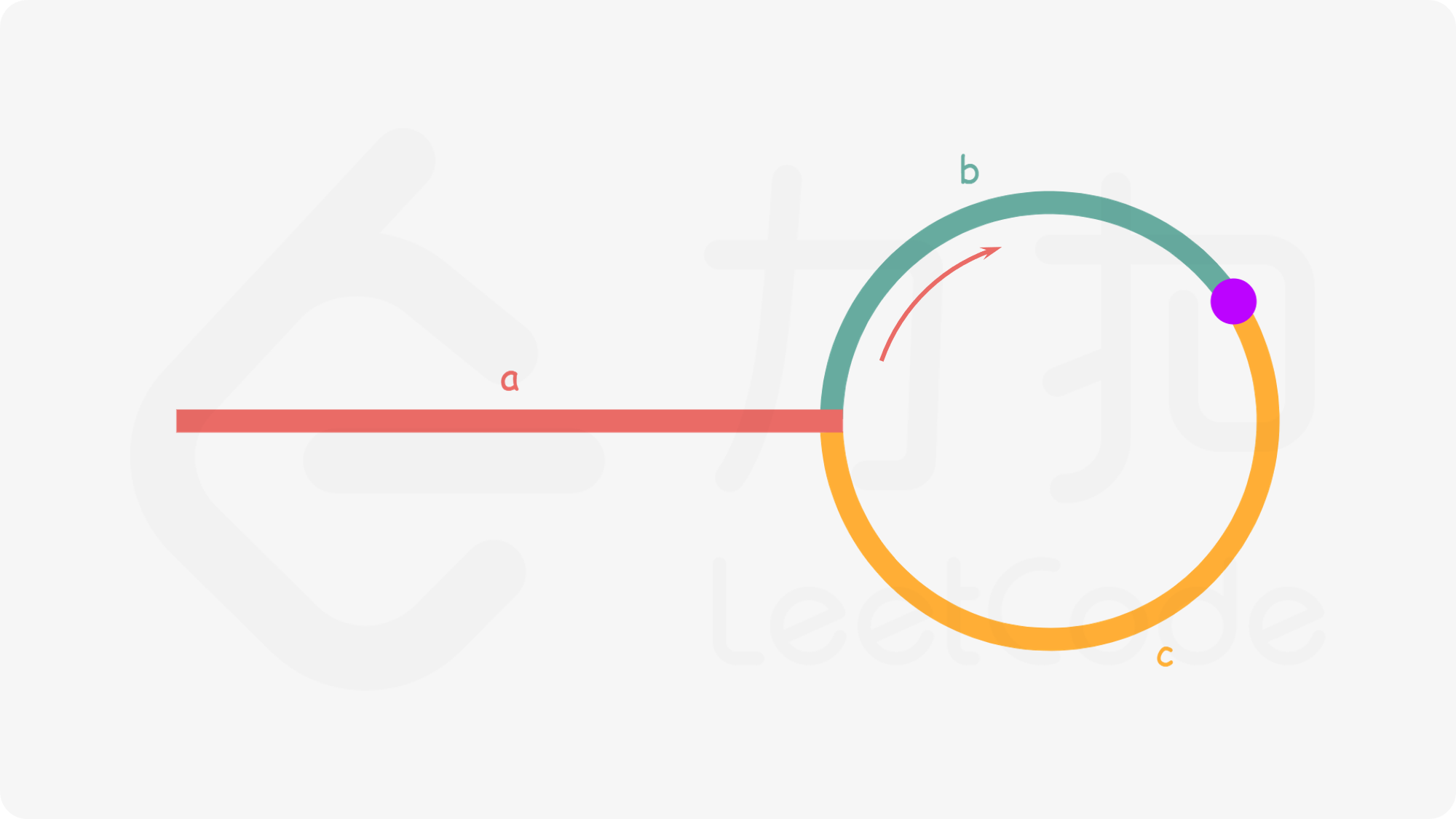
357376
377+ 1. **检测是否有环**:通过快慢指针来判断链表中是否存在环。慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步。如果链表中有环,两个指针最终会相遇;如果没有环,快指针会到达链表末尾。
358378
379+ 2. **找到环的起点**:
380+
381+ - 当快慢指针相遇时,我们已经确认链表中存在环。
382+
383+ - 从相遇点开始,慢指针保持不动,快指针回到链表头部,此时两个指针每次都走一步。两个指针会在环的起点再次相遇。
384+
385+ ```java
386+ public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
387+ if (head == null || head.next == null) {
388+ return null;
389+ }
390+
391+ ListNode slow = head;
392+ ListNode fast = head;
393+
394+ // 判断是否有环
395+ while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
396+ slow = slow.next;
397+ fast = fast.next.next;
398+ // 快慢指针相遇,说明有环
399+ if (slow == fast) {
400+ break;
401+ }
402+ }
403+
404+ // 如果没有环
405+ if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
406+ return null;
407+ }
408+
409+ // 快指针回到起点,慢指针保持在相遇点
410+ fast = head;
411+ while (fast != slow) {
412+ fast = fast.next;
413+ slow = slow.next;
414+ }
415+
416+ // 此时快慢指针相遇的地方就是环的起点
417+ return slow;
418+ }
419+ ```
359420
360421
361422
@@ -620,7 +681,7 @@ public static double getMaxAverage(int[] nums, int k) {
620681
621682### 3.2 不定长度的滑动窗口
622683
623- #### [ 无重复字符的最长子串(3) ] ( https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/ )
684+ #### [ 无重复字符的最长子串_3 ] ( https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/ )
624685
625686> 给定一个字符串 ` s ` ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 ** 最长子串** 的长度。
626687>
@@ -684,8 +745,6 @@ int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
684745
685746
686747
687-
688-
689748#### [ 最小覆盖子串(76)] ( https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/ )
690749
691750> 给你一个字符串 ` s ` 、一个字符串 ` t ` 。返回 ` s ` 中涵盖 ` t ` 所有字符的最小子串。如果 ` s ` 中不存在涵盖 ` t ` 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 ` "" ` 。
@@ -717,7 +776,7 @@ int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
717776
718777```java
719778public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
720- // 两个map,window 代表字符字符出现的次数 ,need 记录所需字符出现次数
779+ // 两个map,window 记录窗口中的字符频率 ,need 记录t中字符的频率
721780 HashMap<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();
722781 HashMap<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();
723782
@@ -783,7 +842,11 @@ public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
783842> 解释:s2 包含 s1 的排列之一 ("ba").
784843> ```
785844
786- 思路:和上一题基本一致,只是 移动 `left` 缩小窗口的时机是窗口大小大于 `t.length()` 时,当发现 `valid == need.size()` 时,就说明窗口中就是一个合法的排列
845+ 思路:
846+
847+ 通过滑动窗口(Sliding Window)和字符频率统计来解决
848+
849+ 和上一题基本一致,只是 移动 `left` 缩小窗口的时机是窗口大小大于 `t.length()` 时,当发现 `valid == need.size()` 时,就说明窗口中就是一个合法的排列
787850
788851```java
789852class Solution {
@@ -962,11 +1025,59 @@ public int characterReplacement(String s, int k) {
9621025
9631026## 四、其他双指针问题
9641027
965- #### [88. 合并两个有序数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/)
1028+ #### [最长回文子串_5](https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/)
1029+
1030+ > 给你一个字符串 `s`,找到 `s` 中最长的 回文子串。
1031+
1032+ ```java
1033+ public static String longestPalindrome(String s){
1034+ //处理边界
1035+ if(s == null || s.length() < 2){
1036+ return s;
1037+ }
1038+
1039+ //初始化start和maxLength变量,用来记录最长回文子串的起始位置和长度
1040+ int start = 0, maxLength = 0;
9661041
1042+ //遍历每个字符
1043+ for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
1044+ //以当前字符为中心的奇数长度回文串
1045+ int len1 = centerExpand(s, i, i);
1046+ //以当前字符和下一个字符之间的中心的偶数长度回文串
1047+ int len2 = centerExpand(s, i, i+1);
9671048
1049+ int len = Math.max(len1, len2);
9681050
969- ### [下一个排列_31](https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-permutation/)
1051+ //当前找到的回文串大于之前的记录,更新start和maxLength
1052+ if(len > maxLength){
1053+ // i 是当前扩展的中心位置, len 是找到的回文串的总长度,我们要用这两个值计算出起始位置 start
1054+ // (len - 1)/2 为什么呢,计算中心到回文串起始位置的距离, 为什么不用 len/2, 这里考虑的是奇数偶数的通用性,比如'abcba' 和 'abba' 或者 'cabbad',巧妙的同时处理两种,不需要分别考虑
1055+ start = i - (len - 1)/2;
1056+ maxLength = len;
1057+ }
1058+
1059+ }
1060+
1061+ return s.substring(start, start + maxLength);
1062+ }
1063+
1064+ private static int centerExpand(String s, int left, int right){
1065+ while(left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)){
1066+ left --;
1067+ right ++;
1068+ }
1069+ //这个的含义: 假设扩展过程中,left 和 right 已经超出了回文返回, 此时回文范围是 (left+1,right-1), 那么回文长度= (right-1)-(left+1)+1=right-left-1
1070+ return right - left - 1;
1071+ }
1072+ ```
1073+
1074+
1075+
1076+ #### [ 合并两个有序数组_88] ( https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/ )
1077+
1078+
1079+
1080+ #### [ 下一个排列_31] ( https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-permutation/ )
9701081
9711082> 整数数组的一个 ** 排列** 就是将其所有成员以序列或线性顺序排列。
9721083>
@@ -1039,7 +1150,7 @@ private void reverse(int[] nums, int start){
10391150
10401151
10411152
1042- ### [ 颜色分类_75] ( https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-colors/ )
1153+ #### [ 颜色分类_75] ( https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-colors/ )
10431154
10441155> 给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色、共 ` n ` 个元素的数组 ` nums ` ,** [ 原地] ( https://baike.baidu.com/item/原地算法 ) ** 对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
10451156>
@@ -1062,7 +1173,7 @@ private void reverse(int[] nums, int start){
10621173- `mid` 表示当前处理的元素索引。
10631174- `high` 表示蓝色 (2) 的边界,指向的元素是 2 的位置,把所有 2 放在 `high` 的右边。
10641175
1065- #### 算法步骤:
1176+ ** 算法步骤:**
10661177
106711781. 初始化:`low = 0`,`mid = 0`,`high = nums.length - 1`。
106811792. 当 `mid <= high` 时,进行以下判断:
@@ -1136,6 +1247,87 @@ private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
11361247
11371248
11381249
1250+ #### [ 排序链表_148] ( https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-list/description/ )
1251+
1252+ > 给你链表的头结点 ` head ` ,请将其按 ** 升序** 排列并返回 ** 排序后的链表** 。
1253+ >
1254+ > ```
1255+ > 输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
1256+ > 输出:[1,2,3,4]
1257+ > ```
1258+
1259+ **Approach**: 要将链表排序,并且时间复杂度要求为 O(nlogn)O(n \log n)O(nlogn),这提示我们需要使用 **归并排序**。归并排序的特点就是时间复杂度是 O(nlogn)O(n \log n)O(nlogn),并且它在链表上的表现很好,因为链表的分割和合并操作相对容易。
1260+
1261+ 具体实现步骤:
1262+
1263+ 1. **分割链表**:我们可以使用 **快慢指针** 来找到链表的中点,从而将链表一分为二。
1264+ 2. **递归排序**:分别对左右两部分链表进行排序。
1265+ 3. **合并有序链表**:最后将两个已经排序好的链表合并成一个有序链表。
1266+
1267+ ```java
1268+
1269+ public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
1270+ // base case: if the list is empty or contains a single element, it's already sorted
1271+ if (head == null || head.next == null) {
1272+ return head;
1273+ }
1274+
1275+ // Step 1: split the linked list into two halves
1276+ ListNode mid = getMiddle(head);
1277+ // right 为链表右半部分的头结点
1278+ ListNode right = mid.next;
1279+ mid.next = null; //断开
1280+
1281+ // Step 2: recursively sort both halves
1282+ ListNode leftSorted = sortList(head);
1283+ ListNode rightSorted = sortList(right);
1284+
1285+ // Step 3: merge the sorted halves
1286+ return mergeTwoLists(leftSorted, rightSorted);
1287+ }
1288+
1289+ // Helper method to find the middle node of the linked list
1290+ private ListNode getMiddle(ListNode head) {
1291+ ListNode slow = head;
1292+ ListNode fast = head;
1293+
1294+ while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
1295+ slow = slow.next;
1296+ fast = fast.next.next;
1297+ }
1298+
1299+ return slow;
1300+ }
1301+
1302+ // Helper method to merge two sorted linked lists
1303+ private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
1304+ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
1305+ ListNode current = dummy;
1306+
1307+ while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
1308+ if (l1.val < l2.val) {
1309+ current.next = l1;
1310+ l1 = l1.next;
1311+ } else {
1312+ current.next = l2;
1313+ l2 = l2.next;
1314+ }
1315+ current = current.next;
1316+ }
1317+
1318+ // Append the remaining elements of either list
1319+ if (l1 != null) {
1320+ current.next = l1;
1321+ } else {
1322+ current.next = l2;
1323+ }
1324+
1325+ return dummy.next;
1326+ }
1327+ ```
1328+
1329+
1330+
11391331### 总结
11401332
11411333区间不同的定义决定了不同的初始化逻辑、遍历过程中的逻辑。
0 commit comments