, val: i32) -> i32 {
@@ -317,7 +388,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-Swift:
+### Swift:
```swift
func removeElement(_ nums: inout [Int], _ val: Int) -> Int {
@@ -333,7 +404,8 @@ func removeElement(_ nums: inout [Int], _ val: Int) -> Int {
}
```
-PHP:
+### PHP:
+
```php
class Solution {
/**
@@ -357,7 +429,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-C:
+### C:
+
```c
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
int slow = 0;
@@ -373,7 +446,8 @@ int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
}
```
-Kotlin:
+### Kotlin:
+
```kotlin
fun removeElement(nums: IntArray, `val`: Int): Int {
var slowIndex = 0 // 初始化慢指针
@@ -384,7 +458,8 @@ fun removeElement(nums: IntArray, `val`: Int): Int {
}
```
-Scala:
+### Scala:
+
```scala
object Solution {
def removeElement(nums: Array[Int], `val`: Int): Int = {
@@ -400,7 +475,8 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-C#:
+### C#:
+
```csharp
public class Solution {
public int RemoveElement(int[] nums, int val) {
@@ -415,7 +491,29 @@ public class Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List nums, int val) {
+ //相向双指针法
+ var left = 0;
+ var right = nums.length - 1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ //寻找左侧的val,将其被右侧非val覆盖
+ if (nums[left] == val) {
+ while (nums[right] == val&&left<=right) {
+ right--;
+ if (right < 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ nums[left] = nums[right--];
+ } else {
+ left++;
+ }
+ }
+ //覆盖后可以将0至left部分视为所需部分
+ return left;
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md" "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2757130c8a..ef8a6c58e6
--- "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
+++ "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List nums, int val) {
+ //相向双指针法
+ var left = 0;
+ var right = nums.length - 1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ //寻找左侧的val,将其被右侧非val覆盖
+ if (nums[left] == val) {
+ while (nums[right] == val&&left<=right) {
+ right--;
+ if (right < 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ nums[left] = nums[right--];
+ } else {
+ left++;
+ }
+ }
+ //覆盖后可以将0至left部分视为所需部分
+ return left;
+}
+
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md" "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2757130c8a..ef8a6c58e6
--- "a/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
+++ "b/problems/0028.\345\256\236\347\216\260strStr.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 在一个串中查找是否出现过另一个串,这是KMP的看家本领。
@@ -27,16 +25,16 @@
当 needle 是空字符串时,我们应当返回什么值呢?这是一个在面试中很好的问题。
对于本题而言,当 needle 是空字符串时我们应当返回 0 。这与C语言的 strstr() 以及 Java的 indexOf() 定义相符。
+## 算法公开课
-# 思路
-
-本题是KMP 经典题目。
-
-以下文字如果看不进去,可以看我的B站视频:
+本题是KMP 经典题目。以下文字如果看不进去,可以看[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
* [帮你把KMP算法学个通透!B站(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd/)
* [帮你把KMP算法学个通透!(求next数组代码篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx)
+
+## 思路
+
KMP的经典思想就是:**当出现字符串不匹配时,可以记录一部分之前已经匹配的文本内容,利用这些信息避免从头再去做匹配。**
本篇将以如下顺序来讲解KMP,
@@ -60,13 +58,13 @@ KMP的经典思想就是:**当出现字符串不匹配时,可以记录一部
读完本篇可以顺便把leetcode上28.实现strStr()题目做了。
-# 什么是KMP
+### 什么是KMP
说到KMP,先说一下KMP这个名字是怎么来的,为什么叫做KMP呢。
因为是由这三位学者发明的:Knuth,Morris和Pratt,所以取了三位学者名字的首字母。所以叫做KMP
-# KMP有什么用
+### KMP有什么用
KMP主要应用在字符串匹配上。
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ KMP的主要思想是**当出现字符串不匹配时,可以知道一部分之
下面Carl就带大家把KMP的精髓,next数组弄清楚。
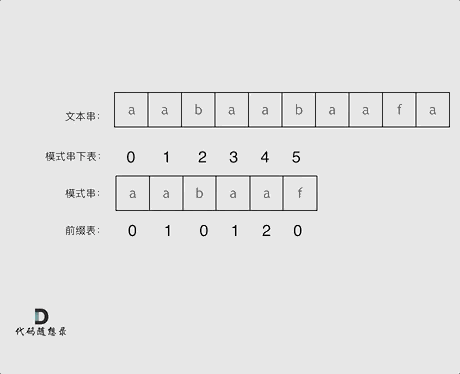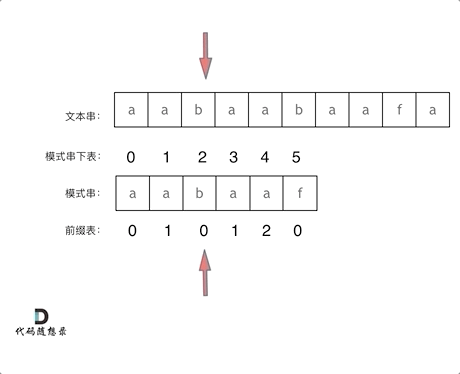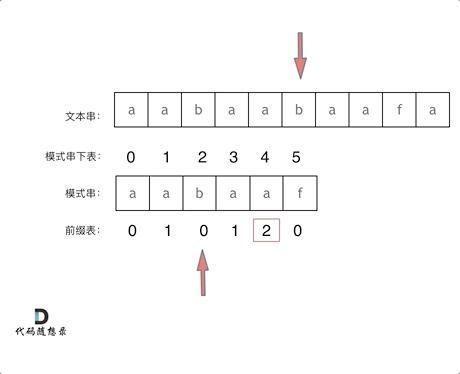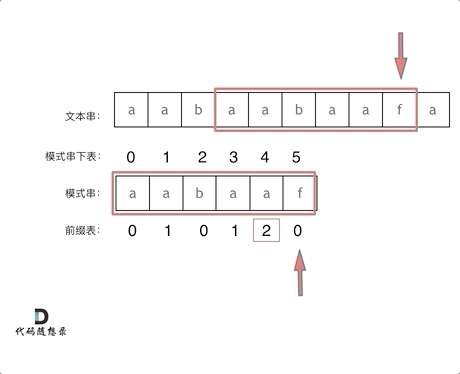
-# 什么是前缀表
+### 什么是前缀表
写过KMP的同学,一定都写过next数组,那么这个next数组究竟是个啥呢?
@@ -108,7 +106,7 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
如动画所示:
-
+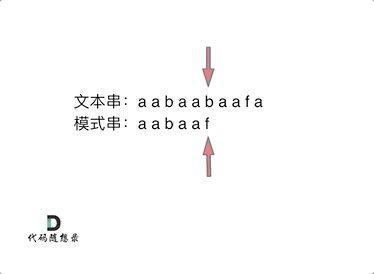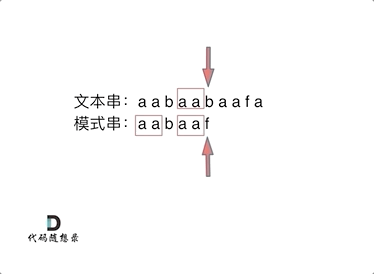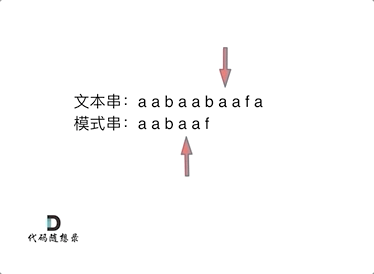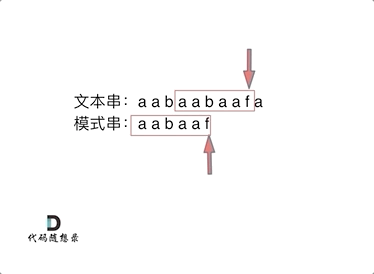
动画里,我特意把 子串`aa` 标记上了,这是有原因的,大家先注意一下,后面还会说到。
@@ -122,7 +120,7 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
那么什么是前缀表:**记录下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
-# 最长公共前后缀?
+### 最长公共前后缀
文章中字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**。
@@ -144,16 +142,16 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
等等.....。
-# 为什么一定要用前缀表
+### 为什么一定要用前缀表
这就是前缀表,那为啥就能告诉我们 上次匹配的位置,并跳过去呢?
回顾一下,刚刚匹配的过程在下标5的地方遇到不匹配,模式串是指向f,如图:
- +
+ 然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
-
然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
- +
+ 以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -163,21 +161,21 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
**很多介绍KMP的文章或者视频并没有把为什么要用前缀表?这个问题说清楚,而是直接默认使用前缀表。**
-# 如何计算前缀表
+### 如何计算前缀表
接下来就要说一说怎么计算前缀表。
如图:
-
以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -163,21 +161,21 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
**很多介绍KMP的文章或者视频并没有把为什么要用前缀表?这个问题说清楚,而是直接默认使用前缀表。**
-# 如何计算前缀表
+### 如何计算前缀表
接下来就要说一说怎么计算前缀表。
如图:
- +
+ 长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
-
长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
- +
+ 长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
-
长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
- +
+ 长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
-
长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
- +
+ 可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -205,9 +203,9 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
最后就在文本串中找到了和模式串匹配的子串了。
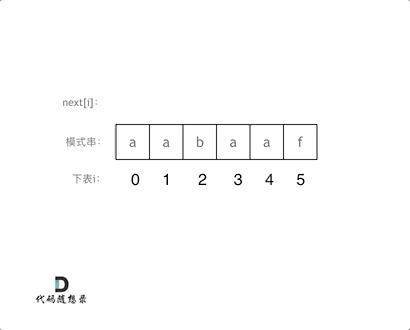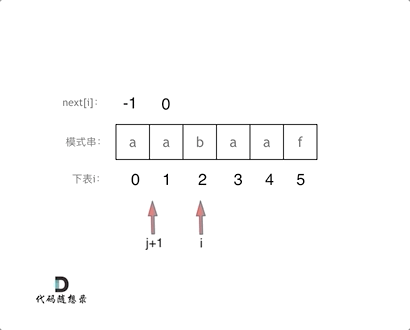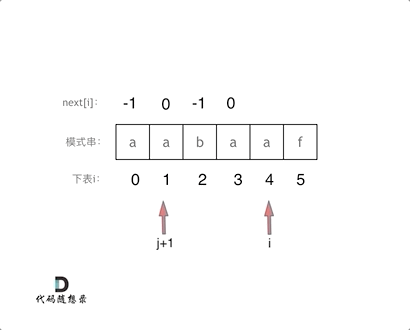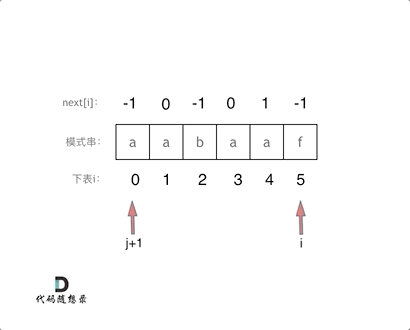
-# 前缀表与next数组
+### 前缀表与next数组
-很多KMP算法的时间都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
+很多KMP算法的实现都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减一(右移一位,初始位置为-1)之后作为next数组。
@@ -217,7 +215,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
后面我会提供两种不同的实现代码,大家就明白了。
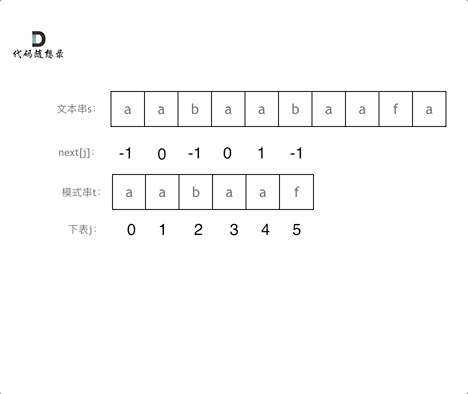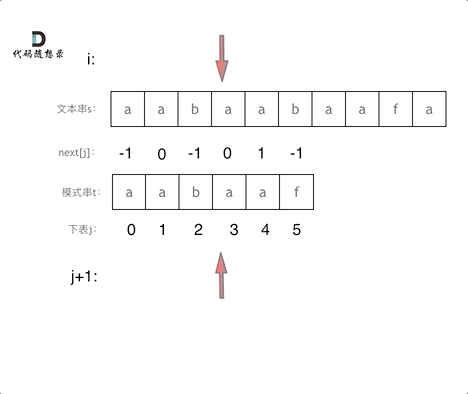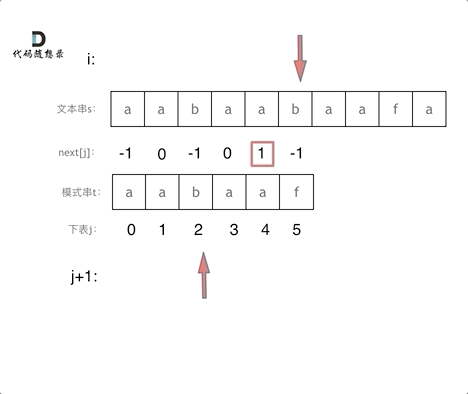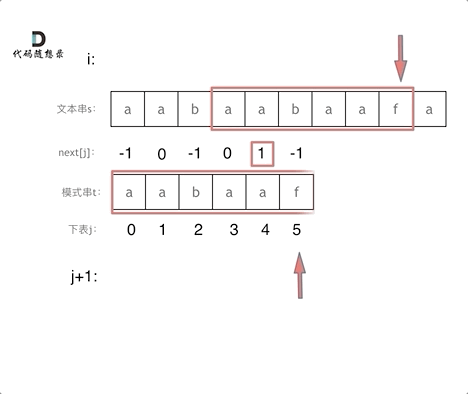
-# 使用next数组来匹配
+### 使用next数组来匹配
**以下我们以前缀表统一减一之后的next数组来做演示**。
@@ -227,9 +225,9 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
-# 时间复杂度分析
+### 时间复杂度分析
其中n为文本串长度,m为模式串长度,因为在匹配的过程中,根据前缀表不断调整匹配的位置,可以看出匹配的过程是O(n),之前还要单独生成next数组,时间复杂度是O(m)。所以整个KMP算法的时间复杂度是O(n+m)的。
@@ -239,7 +237,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
都知道使用KMP算法,一定要构造next数组。
-# 构造next数组
+### 构造next数组
我们定义一个函数getNext来构建next数组,函数参数为指向next数组的指针,和一个字符串。 代码如下:
@@ -334,11 +332,11 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
-# 使用next数组来做匹配
+### 使用next数组来做匹配
在文本串s里 找是否出现过模式串t。
@@ -403,7 +401,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
此时所有逻辑的代码都已经写出来了,力扣 28.实现strStr 题目的整体代码如下:
-# 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
+### 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -425,8 +423,8 @@ public:
if (needle.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
- int next[needle.size()];
- getNext(next, needle);
+ vector next(needle.size());
+ getNext(&next[0], needle);
int j = -1; // // 因为next数组里记录的起始位置为-1
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.size(); i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
while(j >= 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j + 1]) { // 不匹配
@@ -444,8 +442,10 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n + m)
+* 空间复杂度: O(m), 只需要保存字符串needle的前缀表
-# 前缀表(不减一)C++实现
+### 前缀表(不减一)C++实现
那么前缀表就不减一了,也不右移的,到底行不行呢?
@@ -522,8 +522,8 @@ public:
if (needle.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
- int next[needle.size()];
- getNext(next, needle);
+ vector next(needle.size());
+ getNext(&next[0], needle);
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.size(); i++) {
while(j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j]) {
@@ -540,8 +540,11 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n + m)
+* 空间复杂度: O(m)
+
-# 总结
+## 总结
我们介绍了什么是KMP,KMP可以解决什么问题,然后分析KMP算法里的next数组,知道了next数组就是前缀表,再分析为什么要是前缀表而不是什么其他表。
@@ -558,8 +561,39 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
+### Java:
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ /**
+ 牺牲空间,换取最直白的暴力法
+ 时间复杂度 O(n * m)
+ 空间 O(n + m)
+ */
+ public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
+ // 获取 haystack 和 needle 的长度
+ int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
+ // 将字符串转换为字符数组,方便索引操作
+ char[] s = haystack.toCharArray(), p = needle.toCharArray();
+
+ // 遍历 haystack 字符串
+ for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
+ // 初始化匹配的指针
+ int a = i, b = 0;
+ // 循环检查 needle 是否在当前位置开始匹配
+ while (b < m && s[a] == p[b]) {
+ // 如果当前字符匹配,则移动指针
+ a++;
+ b++;
+ }
+ // 如果 b 等于 m,说明 needle 已经完全匹配,返回当前位置 i
+ if (b == m) return i;
+ }
-Java:
+ // 如果遍历完毕仍未找到匹配的子串,则返回 -1
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -686,9 +720,69 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python3:
+### Python3:
+(版本一)前缀表(减一)
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getNext(self, next, s):
+ j = -1
+ next[0] = j
+ for i in range(1, len(s)):
+ while j >= 0 and s[i] != s[j+1]:
+ j = next[j]
+ if s[i] == s[j+1]:
+ j += 1
+ next[i] = j
+
+ def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
+ if not needle:
+ return 0
+ next = [0] * len(needle)
+ self.getNext(next, needle)
+ j = -1
+ for i in range(len(haystack)):
+ while j >= 0 and haystack[i] != needle[j+1]:
+ j = next[j]
+ if haystack[i] == needle[j+1]:
+ j += 1
+ if j == len(needle) - 1:
+ return i - len(needle) + 1
+ return -1
+```
+(版本二)前缀表(不减一)
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getNext(self, next: List[int], s: str) -> None:
+ j = 0
+ next[0] = 0
+ for i in range(1, len(s)):
+ while j > 0 and s[i] != s[j]:
+ j = next[j - 1]
+ if s[i] == s[j]:
+ j += 1
+ next[i] = j
+
+ def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
+ if len(needle) == 0:
+ return 0
+ next = [0] * len(needle)
+ self.getNext(next, needle)
+ j = 0
+ for i in range(len(haystack)):
+ while j > 0 and haystack[i] != needle[j]:
+ j = next[j - 1]
+ if haystack[i] == needle[j]:
+ j += 1
+ if j == len(needle):
+ return i - len(needle) + 1
+ return -1
+```
+
+
+(版本三)暴力法
```python
-//暴力解法:
class Solution(object):
def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
"""
@@ -702,104 +796,24 @@ class Solution(object):
return i
return -1
```
+(版本四)使用 index
```python
-// 方法一
-class Solution:
- def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
- a = len(needle)
- b = len(haystack)
- if a == 0:
- return 0
- next = self.getnext(a,needle)
- p=-1
- for j in range(b):
- while p >= 0 and needle[p+1] != haystack[j]:
- p = next[p]
- if needle[p+1] == haystack[j]:
- p += 1
- if p == a-1:
- return j-a+1
- return -1
-
- def getnext(self,a,needle):
- next = ['' for i in range(a)]
- k = -1
- next[0] = k
- for i in range(1, len(needle)):
- while (k > -1 and needle[k+1] != needle[i]):
- k = next[k]
- if needle[k+1] == needle[i]:
- k += 1
- next[i] = k
- return next
-```
-
-```python
-// 方法二
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
- a = len(needle)
- b = len(haystack)
- if a == 0:
- return 0
- i = j = 0
- next = self.getnext(a, needle)
- while(i < b and j < a):
- if j == -1 or needle[j] == haystack[i]:
- i += 1
- j += 1
- else:
- j = next[j]
- if j == a:
- return i-j
- else:
+ try:
+ return haystack.index(needle)
+ except ValueError:
return -1
-
- def getnext(self, a, needle):
- next = ['' for i in range(a)]
- j, k = 0, -1
- next[0] = k
- while(j < a-1):
- if k == -1 or needle[k] == needle[j]:
- k += 1
- j += 1
- next[j] = k
- else:
- k = next[k]
- return next
```
-
+(版本五)使用 find
```python
-// 前缀表(不减一)Python实现
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
- if len(needle) == 0:
- return 0
- next = self.getNext(needle)
- j = 0
- for i in range(len(haystack)):
- while j >= 1 and haystack[i] != needle[j]:
- j = next[j-1]
- if haystack[i] == needle[j]:
- j += 1
- if j == len(needle):
- return i - len(needle) + 1
- return -1
-
- def getNext(self, needle):
- next = [0] * len(needle)
- j = 0
- next[0] = j
- for i in range(1, len(needle)):
- while j >= 1 and needle[i] != needle[j]:
- j = next[j-1]
- if needle[i] == needle[j]:
- j += 1
- next[i] = j
- return next
+ return haystack.find(needle)
+
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
// 方法一:前缀表使用减1实现
@@ -887,7 +901,7 @@ func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
}
```
-JavaScript版本
+### JavaScript:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -975,7 +989,7 @@ var strStr = function (haystack, needle) {
};
```
-TypeScript版本:
+### TypeScript:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -1052,7 +1066,7 @@ function strStr(haystack: string, needle: string): number {
}
```
-Swift 版本
+### Swift:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -1212,7 +1226,7 @@ func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
```
-PHP:
+### PHP:
> 前缀表统一减一
```php
@@ -1288,7 +1302,7 @@ function getNext(&$next, $s){
}
```
-Rust:
+### Rust:
> 前缀表统一不减一
```Rust
@@ -1309,7 +1323,6 @@ impl Solution {
pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
let (haystack_len, needle_len) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
- if haystack_len == 0 { return 0; }
if haystack_len < needle_len { return -1;}
let (haystack, needle) = (haystack.chars().collect::>(), needle.chars().collect::>());
let mut next: Vec = vec![0; haystack_len];
@@ -1350,9 +1363,6 @@ impl Solution {
next
}
pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
- if needle.is_empty() {
- return 0;
- }
if haystack.len() < needle.len() {
return -1;
}
@@ -1378,8 +1388,133 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -205,9 +203,9 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
最后就在文本串中找到了和模式串匹配的子串了。
-# 前缀表与next数组
+### 前缀表与next数组
-很多KMP算法的时间都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
+很多KMP算法的实现都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减一(右移一位,初始位置为-1)之后作为next数组。
@@ -217,7 +215,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
后面我会提供两种不同的实现代码,大家就明白了。
-# 使用next数组来匹配
+### 使用next数组来匹配
**以下我们以前缀表统一减一之后的next数组来做演示**。
@@ -227,9 +225,9 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
-# 时间复杂度分析
+### 时间复杂度分析
其中n为文本串长度,m为模式串长度,因为在匹配的过程中,根据前缀表不断调整匹配的位置,可以看出匹配的过程是O(n),之前还要单独生成next数组,时间复杂度是O(m)。所以整个KMP算法的时间复杂度是O(n+m)的。
@@ -239,7 +237,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
都知道使用KMP算法,一定要构造next数组。
-# 构造next数组
+### 构造next数组
我们定义一个函数getNext来构建next数组,函数参数为指向next数组的指针,和一个字符串。 代码如下:
@@ -334,11 +332,11 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
-# 使用next数组来做匹配
+### 使用next数组来做匹配
在文本串s里 找是否出现过模式串t。
@@ -403,7 +401,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
此时所有逻辑的代码都已经写出来了,力扣 28.实现strStr 题目的整体代码如下:
-# 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
+### 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -425,8 +423,8 @@ public:
if (needle.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
- int next[needle.size()];
- getNext(next, needle);
+ vector next(needle.size());
+ getNext(&next[0], needle);
int j = -1; // // 因为next数组里记录的起始位置为-1
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.size(); i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
while(j >= 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j + 1]) { // 不匹配
@@ -444,8 +442,10 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n + m)
+* 空间复杂度: O(m), 只需要保存字符串needle的前缀表
-# 前缀表(不减一)C++实现
+### 前缀表(不减一)C++实现
那么前缀表就不减一了,也不右移的,到底行不行呢?
@@ -522,8 +522,8 @@ public:
if (needle.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
- int next[needle.size()];
- getNext(next, needle);
+ vector next(needle.size());
+ getNext(&next[0], needle);
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.size(); i++) {
while(j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j]) {
@@ -540,8 +540,11 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n + m)
+* 空间复杂度: O(m)
+
-# 总结
+## 总结
我们介绍了什么是KMP,KMP可以解决什么问题,然后分析KMP算法里的next数组,知道了next数组就是前缀表,再分析为什么要是前缀表而不是什么其他表。
@@ -558,8 +561,39 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
+### Java:
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ /**
+ 牺牲空间,换取最直白的暴力法
+ 时间复杂度 O(n * m)
+ 空间 O(n + m)
+ */
+ public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
+ // 获取 haystack 和 needle 的长度
+ int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
+ // 将字符串转换为字符数组,方便索引操作
+ char[] s = haystack.toCharArray(), p = needle.toCharArray();
+
+ // 遍历 haystack 字符串
+ for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
+ // 初始化匹配的指针
+ int a = i, b = 0;
+ // 循环检查 needle 是否在当前位置开始匹配
+ while (b < m && s[a] == p[b]) {
+ // 如果当前字符匹配,则移动指针
+ a++;
+ b++;
+ }
+ // 如果 b 等于 m,说明 needle 已经完全匹配,返回当前位置 i
+ if (b == m) return i;
+ }
-Java:
+ // 如果遍历完毕仍未找到匹配的子串,则返回 -1
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -686,9 +720,69 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python3:
+### Python3:
+(版本一)前缀表(减一)
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getNext(self, next, s):
+ j = -1
+ next[0] = j
+ for i in range(1, len(s)):
+ while j >= 0 and s[i] != s[j+1]:
+ j = next[j]
+ if s[i] == s[j+1]:
+ j += 1
+ next[i] = j
+
+ def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
+ if not needle:
+ return 0
+ next = [0] * len(needle)
+ self.getNext(next, needle)
+ j = -1
+ for i in range(len(haystack)):
+ while j >= 0 and haystack[i] != needle[j+1]:
+ j = next[j]
+ if haystack[i] == needle[j+1]:
+ j += 1
+ if j == len(needle) - 1:
+ return i - len(needle) + 1
+ return -1
+```
+(版本二)前缀表(不减一)
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getNext(self, next: List[int], s: str) -> None:
+ j = 0
+ next[0] = 0
+ for i in range(1, len(s)):
+ while j > 0 and s[i] != s[j]:
+ j = next[j - 1]
+ if s[i] == s[j]:
+ j += 1
+ next[i] = j
+
+ def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
+ if len(needle) == 0:
+ return 0
+ next = [0] * len(needle)
+ self.getNext(next, needle)
+ j = 0
+ for i in range(len(haystack)):
+ while j > 0 and haystack[i] != needle[j]:
+ j = next[j - 1]
+ if haystack[i] == needle[j]:
+ j += 1
+ if j == len(needle):
+ return i - len(needle) + 1
+ return -1
+```
+
+
+(版本三)暴力法
```python
-//暴力解法:
class Solution(object):
def strStr(self, haystack, needle):
"""
@@ -702,104 +796,24 @@ class Solution(object):
return i
return -1
```
+(版本四)使用 index
```python
-// 方法一
-class Solution:
- def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
- a = len(needle)
- b = len(haystack)
- if a == 0:
- return 0
- next = self.getnext(a,needle)
- p=-1
- for j in range(b):
- while p >= 0 and needle[p+1] != haystack[j]:
- p = next[p]
- if needle[p+1] == haystack[j]:
- p += 1
- if p == a-1:
- return j-a+1
- return -1
-
- def getnext(self,a,needle):
- next = ['' for i in range(a)]
- k = -1
- next[0] = k
- for i in range(1, len(needle)):
- while (k > -1 and needle[k+1] != needle[i]):
- k = next[k]
- if needle[k+1] == needle[i]:
- k += 1
- next[i] = k
- return next
-```
-
-```python
-// 方法二
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
- a = len(needle)
- b = len(haystack)
- if a == 0:
- return 0
- i = j = 0
- next = self.getnext(a, needle)
- while(i < b and j < a):
- if j == -1 or needle[j] == haystack[i]:
- i += 1
- j += 1
- else:
- j = next[j]
- if j == a:
- return i-j
- else:
+ try:
+ return haystack.index(needle)
+ except ValueError:
return -1
-
- def getnext(self, a, needle):
- next = ['' for i in range(a)]
- j, k = 0, -1
- next[0] = k
- while(j < a-1):
- if k == -1 or needle[k] == needle[j]:
- k += 1
- j += 1
- next[j] = k
- else:
- k = next[k]
- return next
```
-
+(版本五)使用 find
```python
-// 前缀表(不减一)Python实现
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
- if len(needle) == 0:
- return 0
- next = self.getNext(needle)
- j = 0
- for i in range(len(haystack)):
- while j >= 1 and haystack[i] != needle[j]:
- j = next[j-1]
- if haystack[i] == needle[j]:
- j += 1
- if j == len(needle):
- return i - len(needle) + 1
- return -1
-
- def getNext(self, needle):
- next = [0] * len(needle)
- j = 0
- next[0] = j
- for i in range(1, len(needle)):
- while j >= 1 and needle[i] != needle[j]:
- j = next[j-1]
- if needle[i] == needle[j]:
- j += 1
- next[i] = j
- return next
+ return haystack.find(needle)
+
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
// 方法一:前缀表使用减1实现
@@ -887,7 +901,7 @@ func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
}
```
-JavaScript版本
+### JavaScript:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -975,7 +989,7 @@ var strStr = function (haystack, needle) {
};
```
-TypeScript版本:
+### TypeScript:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -1052,7 +1066,7 @@ function strStr(haystack: string, needle: string): number {
}
```
-Swift 版本
+### Swift:
> 前缀表统一减一
@@ -1212,7 +1226,7 @@ func strStr(_ haystack: String, _ needle: String) -> Int {
```
-PHP:
+### PHP:
> 前缀表统一减一
```php
@@ -1288,7 +1302,7 @@ function getNext(&$next, $s){
}
```
-Rust:
+### Rust:
> 前缀表统一不减一
```Rust
@@ -1309,7 +1323,6 @@ impl Solution {
pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
let (haystack_len, needle_len) = (haystack.len(), needle.len());
- if haystack_len == 0 { return 0; }
if haystack_len < needle_len { return -1;}
let (haystack, needle) = (haystack.chars().collect::>(), needle.chars().collect::>());
let mut next: Vec = vec![0; haystack_len];
@@ -1350,9 +1363,6 @@ impl Solution {
next
}
pub fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
- if needle.is_empty() {
- return 0;
- }
if haystack.len() < needle.len() {
return -1;
}
@@ -1378,8 +1388,133 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+>前缀表统一不减一
+```csharp
+public int StrStr(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(needle))
+ return 0;
+
+ if (needle.Length > haystack.Length || string.IsNullOrEmpty(haystack))
+ return -1;
+
+ return KMP(haystack, needle);
+}
+
+public int KMP(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = GetNext(needle);
+ int i = 0, j = 0;
+ while (i < haystack.Length)
+ {
+ if (haystack[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ i++;
+ j++;
+ }
+ if (j == needle.Length)
+ return i-j;
+ else if (i < haystack.Length && haystack[i] != needle[j])
+ if (j != 0)
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+public int[] GetNext(string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = new int[needle.Length];
+ next[0] = 0;
+ int i = 1, j = 0;
+ while (i < needle.Length)
+ {
+ if (needle[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ next[i++] = ++j;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ if (j == 0)
+ {
+ next[i++] = 0;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+```
+
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 34aa1086c0..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+>前缀表统一不减一
+```csharp
+public int StrStr(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(needle))
+ return 0;
+
+ if (needle.Length > haystack.Length || string.IsNullOrEmpty(haystack))
+ return -1;
+
+ return KMP(haystack, needle);
+}
+
+public int KMP(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = GetNext(needle);
+ int i = 0, j = 0;
+ while (i < haystack.Length)
+ {
+ if (haystack[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ i++;
+ j++;
+ }
+ if (j == needle.Length)
+ return i-j;
+ else if (i < haystack.Length && haystack[i] != needle[j])
+ if (j != 0)
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+public int[] GetNext(string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = new int[needle.Length];
+ next[0] = 0;
+ int i = 1, j = 0;
+ while (i < needle.Length)
+ {
+ if (needle[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ next[i++] = ++j;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ if (j == 0)
+ {
+ next[i++] = 0;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+```
+
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 34aa1086c0..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -34,7 +32,7 @@
* 输出:[1]
-# 思路
+## 思路
一些同学可能手动写排列的顺序,都没有写对,那么写程序的话思路一定是有问题的了,我这里以1234为例子,把全排列都列出来。可以参考一下规律所在:
@@ -69,7 +67,7 @@
以求1243为例,流程如图:
- +
+ 对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -92,9 +90,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -159,7 +157,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+### Python
>直接使用sorted()会开辟新的空间并返回一个新的list,故补充一个原地反转函数
```python
class Solution:
@@ -191,7 +189,7 @@ class Solution:
"""
```
-## Go
+### Go
```go
//卡尔的解法
@@ -216,7 +214,7 @@ func reverse(a []int,begin,end int){
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
//卡尔的解法(吐槽一下JavaScript的sort和其他语言的不太一样,只想到了拷贝数组去排序再替换原数组来实现nums的[i + 1, nums.length)升序排序)
@@ -268,7 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
-
对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -92,9 +90,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -159,7 +157,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+### Python
>直接使用sorted()会开辟新的空间并返回一个新的list,故补充一个原地反转函数
```python
class Solution:
@@ -191,7 +189,7 @@ class Solution:
"""
```
-## Go
+### Go
```go
//卡尔的解法
@@ -216,7 +214,7 @@ func reverse(a []int,begin,end int){
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
//卡尔的解法(吐槽一下JavaScript的sort和其他语言的不太一样,只想到了拷贝数组去排序再替换原数组来实现nums的[i + 1, nums.length)升序排序)
@@ -268,7 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e58a870d8..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e58a870d8..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
@@ -233,14 +231,14 @@ class Solution {
if (index == -1) { // nums 中不存在 target,直接返回 {-1, -1}
return new int[] {-1, -1}; // 匿名数组
}
- // nums 中存在 targe,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
+ // nums 中存在 target,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
int left = index;
int right = index;
// 向左滑动,找左边界
while (left - 1 >= 0 && nums[left - 1] == nums[index]) { // 防止数组越界。逻辑短路,两个条件顺序不能换
left--;
}
- // 向左滑动,找右边界
+ // 向右滑动,找右边界
while (right + 1 < nums.length && nums[right + 1] == nums[index]) { // 防止数组越界。
right++;
}
@@ -329,6 +327,67 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+### C#
+
+```csharp
+public int[] SearchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
+
+ var leftBorder = GetLeftBorder(nums, target);
+ var rightBorder = GetRightBorder(nums, target);
+
+ if (leftBorder == -2 || rightBorder == -2) {
+ return new int[] {-1, -1};
+ }
+
+ if (rightBorder - leftBorder >=2) {
+ return new int[] {leftBorder + 1, rightBorder - 1};
+ }
+
+ return new int[] {-1, -1};
+
+}
+
+public int GetLeftBorder(int[] nums, int target){
+ var left = 0;
+ var right = nums.Length - 1;
+ var leftBorder = -2;
+
+ while (left <= right) {
+ var mid = (left + right) / 2;
+
+ if (target <= nums[mid]) {
+ right = mid - 1;
+ leftBorder = right;
+ }
+ else {
+ left = mid + 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ return leftBorder;
+}
+
+public int GetRightBorder(int[] nums, int target){
+ var left = 0;
+ var right = nums.Length - 1;
+ var rightBorder = -2;
+
+ while (left <= right) {
+ var mid = (left + right) / 2;
+
+ if (target >= nums[mid]) {
+ left = mid + 1;
+ rightBorder = left;
+ }
+ else {
+ right = mid - 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ return rightBorder;
+}
+```
+
### Python
@@ -389,7 +448,7 @@ class Solution:
return -1
index = binarySearch(nums, target)
if index == -1:return [-1, -1] # nums 中不存在 target,直接返回 {-1, -1}
- # nums 中存在 targe,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
+ # nums 中存在 target,则左右滑动指针,来找到符合题意的区间
left, right = index, index
# 向左滑动,找左边界
while left -1 >=0 and nums[left - 1] == target: left -=1
@@ -739,8 +798,58 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+### C
+```c
+int searchLeftBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录leftBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int leftBorder = -1;
+ // 边界为[left, right]
+ while (left <= right) {
+ // 更新middle值,等同于middle = (left + right) / 2
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将左边界设为middle,并向左继续寻找左边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ leftBorder = middle;
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return leftBorder;
+}
+int searchRightBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录rightBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int rightBorder = -1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将右边界设为middle,并向右继续寻找右边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ rightBorder = middle;
+ left = middle + 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return rightBorder;
+}
+
+int* searchRange(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
+ int leftBorder = searchLeftBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+ int rightBorder = searchRightBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+
+ // 定义返回数组及数组大小
+ *returnSize = 2;
+ int *resNums = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
+ resNums[0] = leftBorder;
+ resNums[1] = rightBorder;
+ return resNums;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4d9ee74fb2..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
+### C
+```c
+int searchLeftBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录leftBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int leftBorder = -1;
+ // 边界为[left, right]
+ while (left <= right) {
+ // 更新middle值,等同于middle = (left + right) / 2
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将左边界设为middle,并向左继续寻找左边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ leftBorder = middle;
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return leftBorder;
+}
+int searchRightBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录rightBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int rightBorder = -1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将右边界设为middle,并向右继续寻找右边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ rightBorder = middle;
+ left = middle + 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return rightBorder;
+}
+
+int* searchRange(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
+ int leftBorder = searchLeftBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+ int rightBorder = searchRightBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+
+ // 定义返回数组及数组大小
+ *returnSize = 2;
+ int *resNums = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
+ resNums[0] = leftBorder;
+ resNums[1] = rightBorder;
+ return resNums;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4d9ee74fb2..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
@@ -16,18 +16,22 @@
你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
示例 1:
+
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 5
* 输出: 2
-示例 2:
+示例 2:
+
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 2
* 输出: 1
示例 3:
+
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 7
* 输出: 4
示例 4:
+
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 0
* 输出: 0
@@ -37,7 +41,7 @@
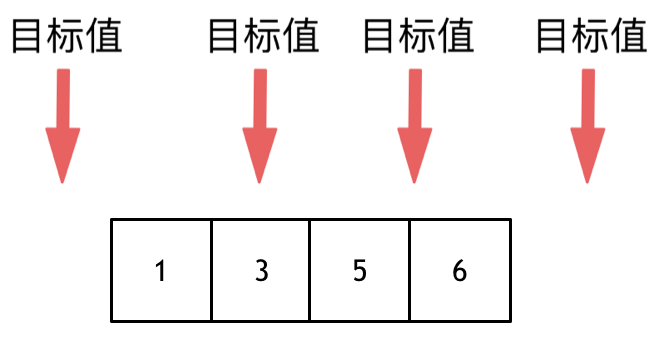
这道题目,要在数组中插入目标值,无非是这四种情况。
-
+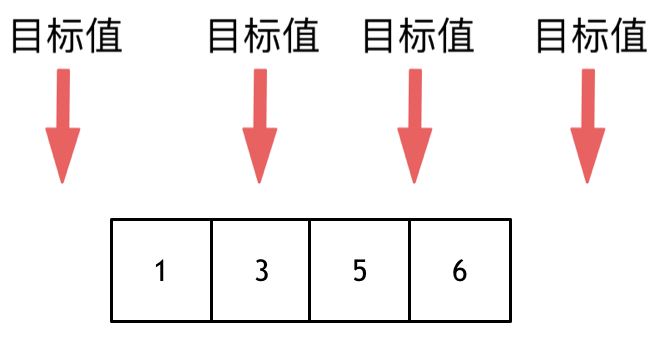
* 目标值在数组所有元素之前
* 目标值等于数组中某一个元素
@@ -78,13 +82,14 @@ public:
效率如下:
-
+
### 二分法
-既然暴力解法的时间复杂度是$O(n)$,就要尝试一下使用二分查找法。
+既然暴力解法的时间复杂度是O(n),就要尝试一下使用二分查找法。
-
+
+
大家注意这道题目的前提是数组是有序数组,这也是使用二分查找的基础条件。
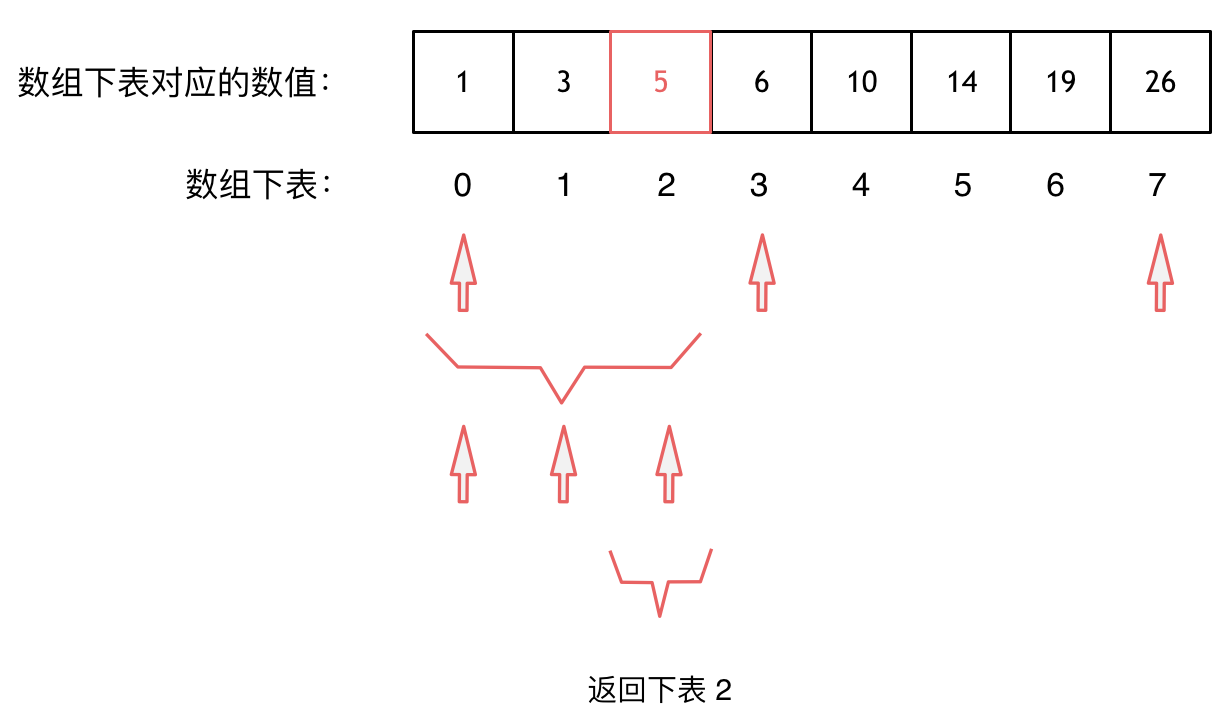
@@ -94,7 +99,7 @@ public:
大体讲解一下二分法的思路,这里来举一个例子,例如在这个数组中,使用二分法寻找元素为5的位置,并返回其下标。
-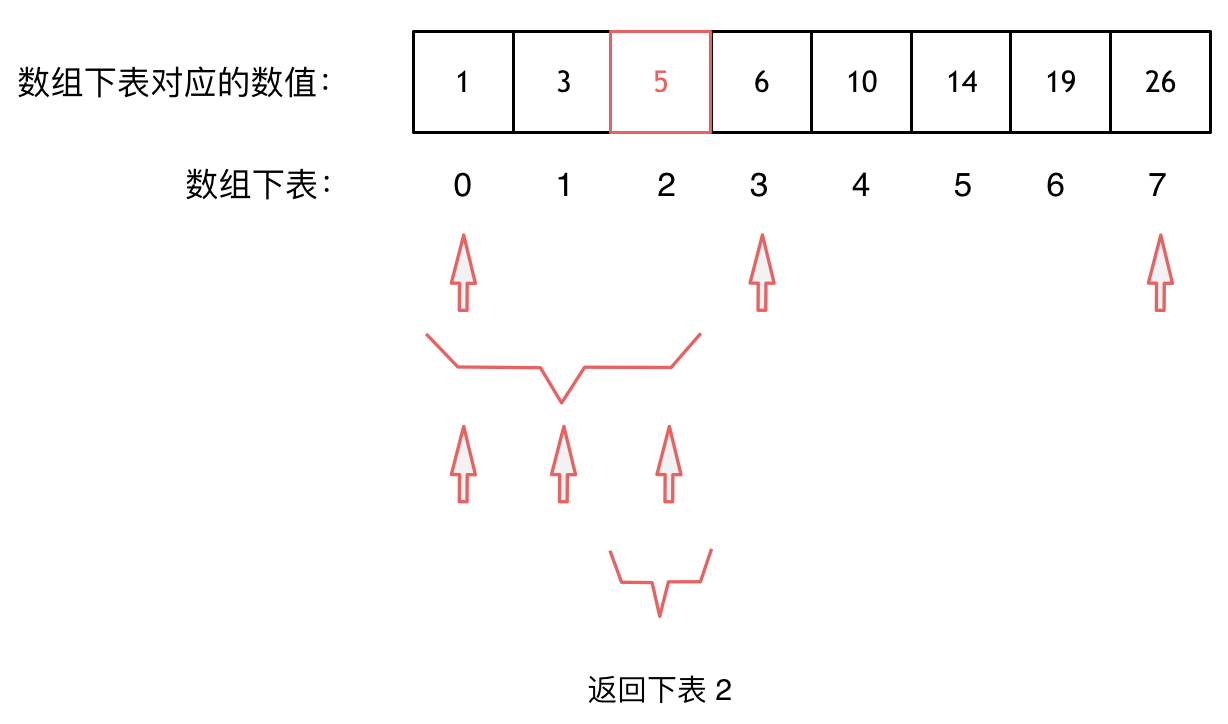
+
二分查找涉及的很多的边界条件,逻辑比较简单,就是写不好。
@@ -145,7 +150,7 @@ public:
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
效率如下:
-
+
### 二分法第二种写法
@@ -184,8 +189,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(\log n)$
-* 时间复杂度:$O(1)$
+* 时间复杂度:O(log n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(1)
## 总结
@@ -199,7 +204,7 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-### Java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -226,11 +231,12 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+
```java
//第二种二分法:左闭右开
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
- int right = nums.length;
+ int right = nums.length;
while (left < right) { //左闭右开 [left, right)
int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[middle] > target) {
@@ -250,6 +256,37 @@ public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
+### C#
+
+```go
+public int SearchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
+
+ var left = 0;
+ var right = nums.Length - 1;
+
+ while (left <= right) {
+
+ var curr = (left + right) / 2;
+
+ if (nums[curr] == target)
+ {
+ return curr;
+ }
+
+ if (target > nums[curr]) {
+ left = curr + 1;
+ }
+ else {
+ right = curr - 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ return left;
+}
+```
+
+
+
### Golang
```go
@@ -266,7 +303,7 @@ func searchInsert(nums []int, target int) int {
left = mid + 1
}
}
- return len(nums)
+ return right+1
}
```
@@ -274,24 +311,26 @@ func searchInsert(nums []int, target int) int {
```rust
impl Solution {
- pub fn search_insert(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
- let mut left = 0;
- let mut right = nums.len();
- while left < right {
+ pub fn search_insert(nums: Vec, target: i32) -> i32 {
+ use std::cmp::Ordering::{Equal, Greater, Less};
+ let (mut left, mut right) = (0, nums.len() as i32 - 1);
+ while left <= right {
let mid = (left + right) / 2;
- match nums[mid].cmp(&target) {
- Ordering::Less => left = mid + 1,
- Ordering::Equal => return ((left + right) / 2) as i32,
- Ordering::Greater => right = mid,
+ match nums[mid as usize].cmp(&target) {
+ Less => left = mid + 1,
+ Equal => return mid,
+ Greater => right = mid - 1,
}
}
- ((left + right) / 2) as i32
+ right + 1
}
}
```
-### Python
+### Python
+
```python
+# 第一种二分法: [left, right]左闭右闭区间
class Solution:
def searchInsert(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
@@ -308,7 +347,28 @@ class Solution:
return right + 1
```
-### JavaScript
+```python
+# 第二种二分法: [left, right)左闭右开区间
+class Solution:
+ def searchInsert(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
+ left = 0
+ right = len(nums)
+
+ while (left < right):
+ middle = (left + right) // 2
+
+ if nums[middle] > target:
+ right = middle
+ elif nums[middle] < target:
+ left = middle + 1
+ else:
+ return middle
+
+ return right
+```
+
+### JavaScript
+
```js
var searchInsert = function (nums, target) {
let l = 0, r = nums.length - 1, ans = nums.length;
@@ -350,7 +410,7 @@ function searchInsert(nums: number[], target: number): number {
};
```
-### Swift
+### Swift
```swift
// 暴力法
@@ -383,7 +443,9 @@ func searchInsert(_ nums: [Int], _ target: Int) -> Int {
return right + 1
}
```
+
### Scala
+
```scala
object Solution {
def searchInsert(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Int = {
@@ -404,7 +466,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-### PHP
+### PHP
```php
// 二分法(1):[左闭右闭]
@@ -429,11 +491,13 @@ function searchInsert($nums, $target)
return $r + 1;
}
```
+
### C
+
```c
//版本一 [left, right]左闭右闭区间
int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
- //左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize-1]
+ //左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize-1]
int left =0;
int mid =0;
int right = numsSize - 1;
@@ -451,14 +515,15 @@ int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
}
}
//数组中未找到target元素
- //target在数组所有元素之后,[left, right]是右闭区间,需要返回 right +1
+ //target在数组所有元素之后,[left, right]是右闭区间,需要返回 right +1
return right + 1;
}
```
+
```c
//版本二 [left, right]左闭右开区间
int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
- //左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize)
+ //左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize)
int left =0;
int mid =0;
int right = numsSize;
@@ -481,7 +546,4 @@ int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18a96d581b..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18a96d581b..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-如果对回溯法理论还不清楚的同学,可以先看这个视频[视频来了!!带你学透回溯算法(理论篇)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/wDd5azGIYWjbU0fdua_qBg)
+
+> 如果对回溯法理论还不清楚的同学,可以先看这个视频[视频来了!!带你学透回溯算法(理论篇)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/wDd5azGIYWjbU0fdua_qBg)
# 37. 解数独
@@ -14,29 +13,28 @@
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
一个数独的解法需遵循如下规则:
-数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
-数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
-数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
-空白格用 '.' 表示。
+数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
+数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
+数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
+空白格用 '.' 表示。
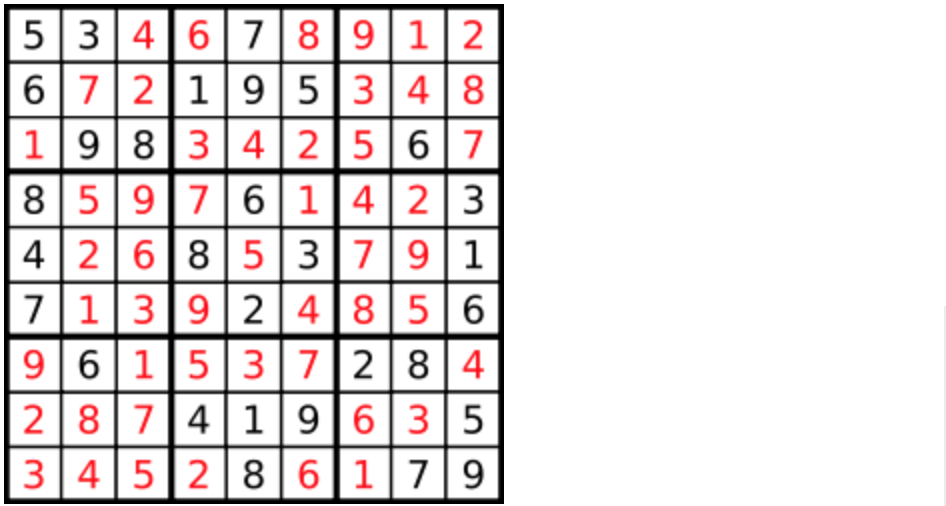
-
+
一个数独。
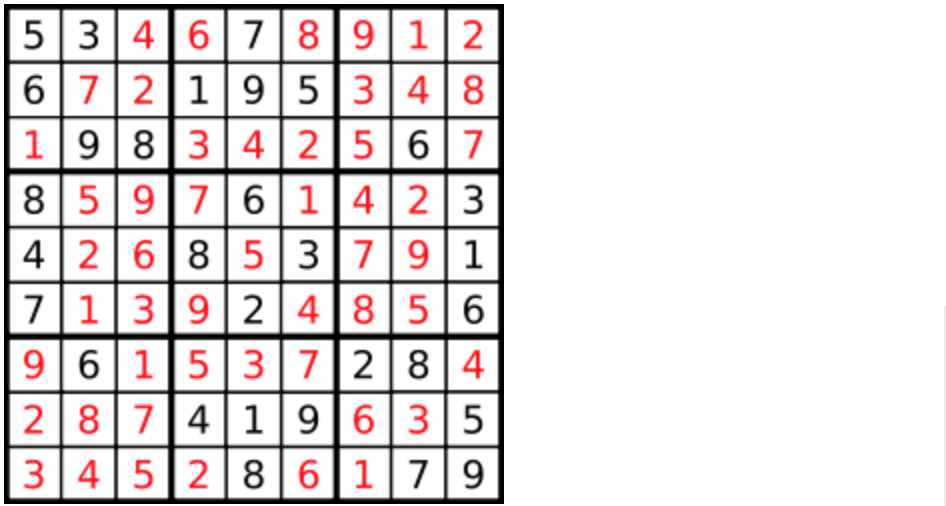
-
+
答案被标成红色。
提示:
+
* 给定的数独序列只包含数字 1-9 和字符 '.' 。
* 你可以假设给定的数独只有唯一解。
* 给定数独永远是 9x9 形式的。
-# 算法公开课
-
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[回溯算法二维递归?解数独不过如此!| LeetCode:37. 解数独](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1TW4y1471V/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-
+## 算法公开课
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[回溯算法二维递归?解数独不过如此!| LeetCode:37. 解数独](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1TW4y1471V/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@
因为这个树形结构太大了,我抽取一部分,如图所示:
-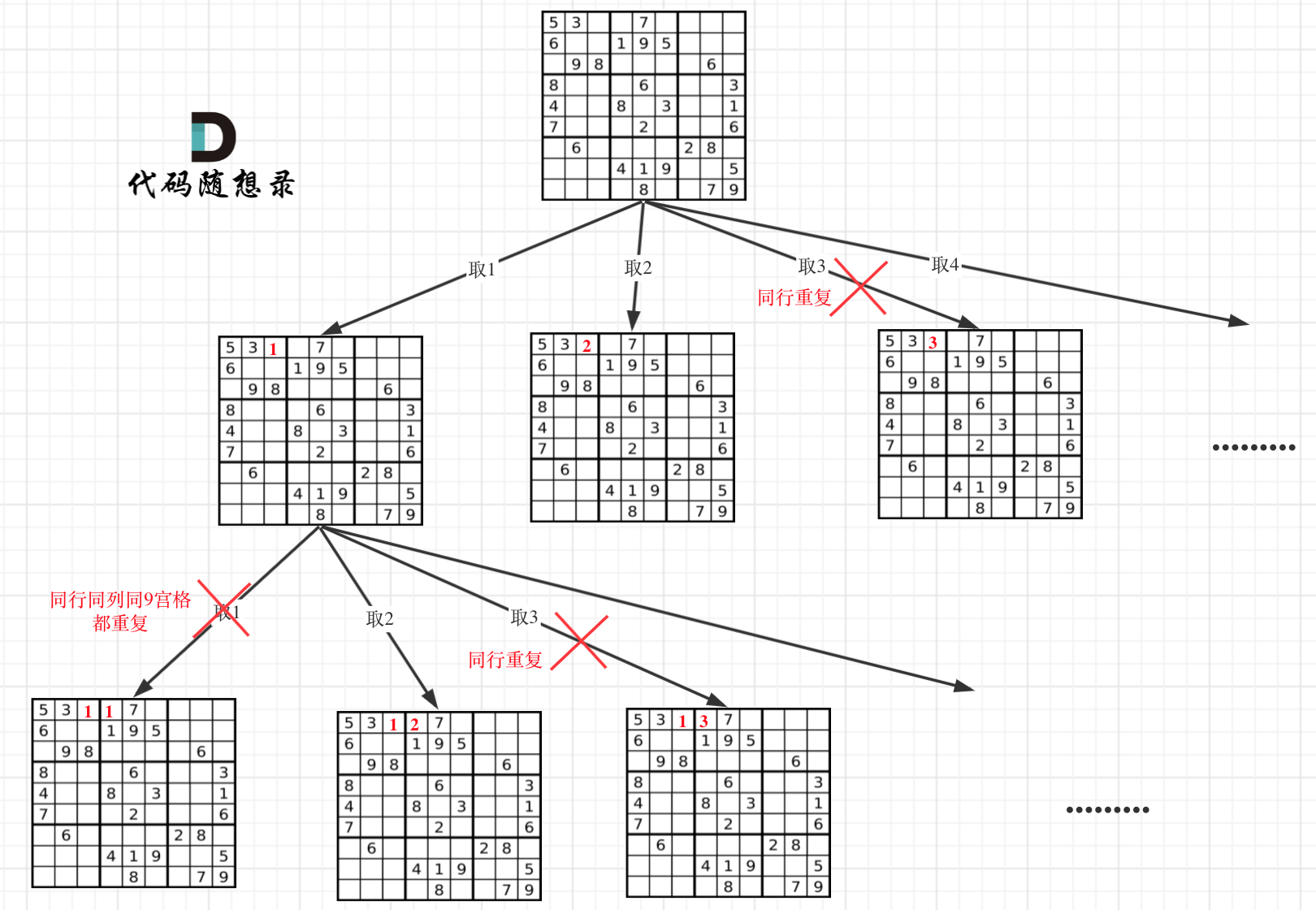
+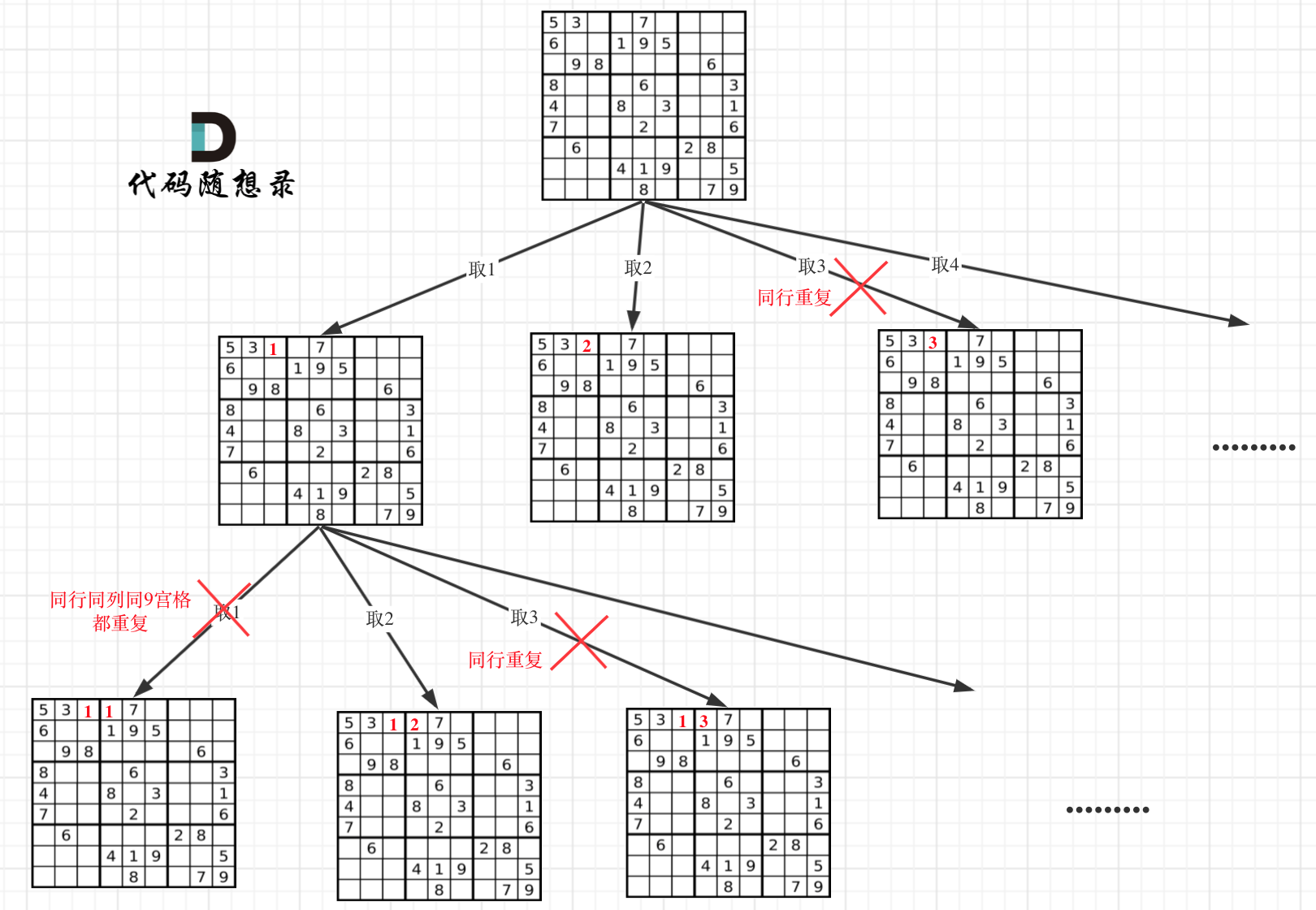
### 回溯三部曲
@@ -85,9 +83,9 @@ bool backtracking(vector>& board)
* 递归单层搜索逻辑
-
+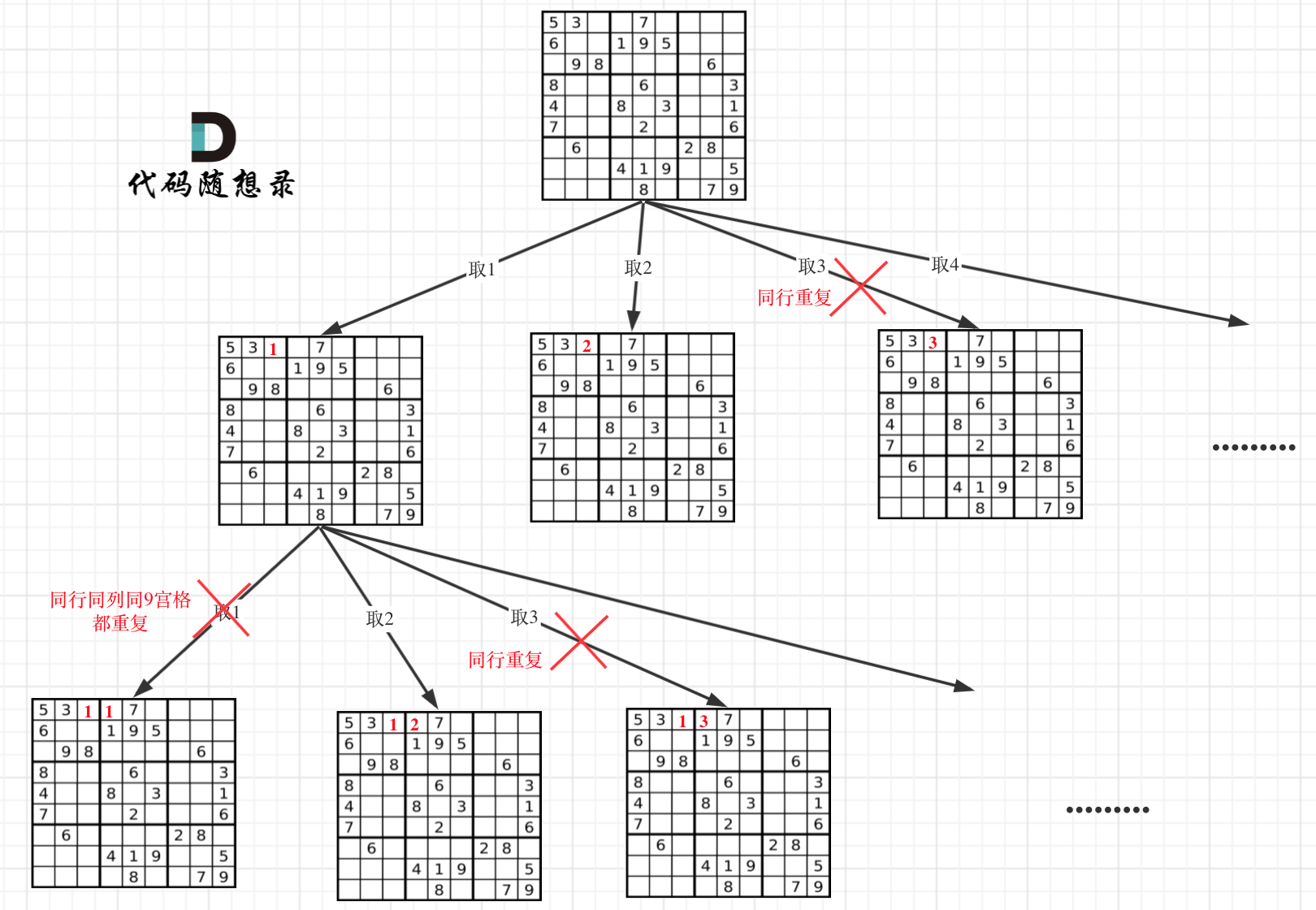
-在树形图中可以看出我们需要的是一个二维的递归(也就是两个for循环嵌套着递归)
+在树形图中可以看出我们需要的是一个二维的递归 (一行一列)
**一个for循环遍历棋盘的行,一个for循环遍历棋盘的列,一行一列确定下来之后,递归遍历这个位置放9个数字的可能性!**
@@ -171,8 +169,8 @@ bool backtracking(vector>& board) {
board[i][j] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销k
}
}
- return false; // 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false
- }
+ return false; // 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false
+ }
}
}
return true; // 遍历完没有返回false,说明找到了合适棋盘位置了
@@ -223,7 +221,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-### Java
+### Java
+解法一:
```java
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
@@ -290,51 +289,134 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+解法二(bitmap标记)
+```
+class Solution{
+ int[] rowBit = new int[9];
+ int[] colBit = new int[9];
+ int[] square9Bit = new int[9];
+
+ public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
+ // 1 10 11
+ for (int y = 0; y < board.length; y++) {
+ for (int x = 0; x < board[y].length; x++) {
+ int numBit = 1 << (board[y][x] - '1');
+ rowBit[y] ^= numBit;
+ colBit[x] ^= numBit;
+ square9Bit[(y / 3) * 3 + x / 3] ^= numBit;
+ }
+ }
+ backtrack(board, 0);
+ }
+
+ public boolean backtrack(char[][] board, int n) {
+ if (n >= 81) {
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ // 快速算出行列编号 n/9 n%9
+ int row = n / 9;
+ int col = n % 9;
+
+ if (board[row][col] != '.') {
+ return backtrack(board, n + 1);
+ }
+
+ for (char c = '1'; c <= '9'; c++) {
+ int numBit = 1 << (c - '1');
+ if (!isValid(numBit, row, col)) continue;
+ {
+ board[row][col] = c; // 当前的数字放入到数组之中,
+ rowBit[row] ^= numBit; // 第一行rowBit[0],第一个元素eg: 1 , 0^1=1,第一个元素:4, 100^1=101,...
+ colBit[col] ^= numBit;
+ square9Bit[(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3] ^= numBit;
+ }
+ if (backtrack(board, n + 1)) return true;
+ {
+ board[row][col] = '.'; // 不满足条件,回退成'.'
+ rowBit[row] &= ~numBit; // 第一行rowBit[0],第一个元素eg: 1 , 101&=~1==>101&111111110==>100
+ colBit[col] &= ~numBit;
+ square9Bit[(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3] &= ~numBit;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+
+
+ boolean isValid(int numBit, int row, int col) {
+ // 左右
+ if ((rowBit[row] & numBit) > 0) return false;
+ // 上下
+ if ((colBit[col] & numBit) > 0) return false;
+ // 9宫格: 快速算出第n个九宫格,编号[0,8] , 编号=(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3
+ if ((square9Bit[(row / 3) * 3 + col / 3] & numBit) > 0) return false;
+ return true;
+ }
+
+}
+
+```
+### Python
-### Python
```python
class Solution:
def solveSudoku(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
- self.backtracking(board)
-
- def backtracking(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
- # 若有解,返回True;若无解,返回False
- for i in range(len(board)): # 遍历行
- for j in range(len(board[0])): # 遍历列
- # 若空格内已有数字,跳过
- if board[i][j] != '.': continue
- for k in range(1, 10):
- if self.is_valid(i, j, k, board):
- board[i][j] = str(k)
- if self.backtracking(board): return True
- board[i][j] = '.'
- # 若数字1-9都不能成功填入空格,返回False无解
- return False
- return True # 有解
-
- def is_valid(self, row: int, col: int, val: int, board: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
- # 判断同一行是否冲突
- for i in range(9):
- if board[row][i] == str(val):
- return False
- # 判断同一列是否冲突
- for j in range(9):
- if board[j][col] == str(val):
- return False
- # 判断同一九宫格是否有冲突
- start_row = (row // 3) * 3
- start_col = (col // 3) * 3
- for i in range(start_row, start_row + 3):
- for j in range(start_col, start_col + 3):
- if board[i][j] == str(val):
- return False
- return True
+ row_used = [set() for _ in range(9)]
+ col_used = [set() for _ in range(9)]
+ box_used = [set() for _ in range(9)]
+ for row in range(9):
+ for col in range(9):
+ num = board[row][col]
+ if num == ".":
+ continue
+ row_used[row].add(num)
+ col_used[col].add(num)
+ box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3].add(num)
+ self.backtracking(0, 0, board, row_used, col_used, box_used)
+
+ def backtracking(
+ self,
+ row: int,
+ col: int,
+ board: List[List[str]],
+ row_used: List[List[int]],
+ col_used: List[List[int]],
+ box_used: List[List[int]],
+ ) -> bool:
+ if row == 9:
+ return True
+
+ next_row, next_col = (row, col + 1) if col < 8 else (row + 1, 0)
+ if board[row][col] != ".":
+ return self.backtracking(
+ next_row, next_col, board, row_used, col_used, box_used
+ )
+
+ for num in map(str, range(1, 10)):
+ if (
+ num not in row_used[row]
+ and num not in col_used[col]
+ and num not in box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3]
+ ):
+ board[row][col] = num
+ row_used[row].add(num)
+ col_used[col].add(num)
+ box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3].add(num)
+ if self.backtracking(
+ next_row, next_col, board, row_used, col_used, box_used
+ ):
+ return True
+ board[row][col] = "."
+ row_used[row].remove(num)
+ col_used[col].remove(num)
+ box_used[(row // 3) * 3 + col // 3].remove(num)
+ return False
```
-### Go
+### Go
```go
func solveSudoku(board [][]byte) {
@@ -392,7 +474,8 @@ func isvalid(row, col int, k byte, board [][]byte) bool {
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
+
```Javascript
var solveSudoku = function(board) {
function isValid(row, col, val, board) {
@@ -433,7 +516,7 @@ var solveSudoku = function(board) {
if (backTracking()) {
return true
}
-
+
board[i][j] = `.`
}
}
@@ -444,7 +527,7 @@ var solveSudoku = function(board) {
}
backTracking(board)
return board
-
+
};
```
@@ -543,7 +626,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-### C
+### C
```C
bool isValid(char** board, int row, int col, int k) {
@@ -660,9 +743,10 @@ func solveSudoku(_ board: inout [[Character]]) {
### Scala
详细写法:
+
```scala
object Solution {
-
+
def solveSudoku(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Unit = {
backtracking(board)
}
@@ -692,7 +776,7 @@ object Solution {
return false
}
}
-
+
// 列
for (j <- 0 until 9) {
if (board(x)(j) == value) {
@@ -717,9 +801,10 @@ object Solution {
```
遵循Scala至简原则写法:
+
```scala
object Solution {
-
+
def solveSudoku(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Unit = {
backtracking(board)
}
@@ -751,8 +836,58 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public void SolveSudoku(char[][] board)
+ {
+ BackTracking(board);
+ }
+ public bool BackTracking(char[][] board)
+ {
+ for (int i = 0; i < board.Length; i++)
+ {
+ for (int j = 0; j < board[0].Length; j++)
+ {
+ if (board[i][j] != '.') continue;
+ for (char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++)
+ {
+ if (IsValid(board, i, j, k))
+ {
+ board[i][j] = k;
+ if (BackTracking(board)) return true;
+ board[i][j] = '.';
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+ public bool IsValid(char[][] board, int row, int col, char val)
+ {
+ for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
+ {
+ if (board[i][col] == val) return false;
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
+ {
+ if (board[row][i] == val) return false;
+ }
+ int startRow = (row / 3) * 3;
+ int startCol = (col / 3) * 3;
+ for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; i++)
+ {
+ for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; j++)
+ {
+ if (board[i][j] == val) return false;
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a3c62c53dd..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,45 +1,47 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a3c62c53dd..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,45 +1,47 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
# 39. 组合总和
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/)
-给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
+给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
-candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
+candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
-* 所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
-* 解集不能包含重复的组合。
+* 所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
+* 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
+
* 输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
* 所求解集为:
-[
+ [
[7],
[2,2,3]
-]
+ ]
+
+示例 2:
-示例 2:
* 输入:candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
* 所求解集为:
-[
- [2,2,2,2],
- [2,3,3],
- [3,5]
-]
+ [
+ [2,2,2,2],
+ [2,3,3],
+ [3,5]
+ ]
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[Leetcode:39. 组合总和讲解](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-
-# 思路
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[Leetcode:39. 组合总和讲解](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+## 思路
题目中的**无限制重复被选取,吓得我赶紧想想 出现0 可咋办**,然后看到下面提示:1 <= candidates[i] <= 200,我就放心了。
@@ -48,12 +50,12 @@ candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
本题搜索的过程抽象成树形结构如下:
-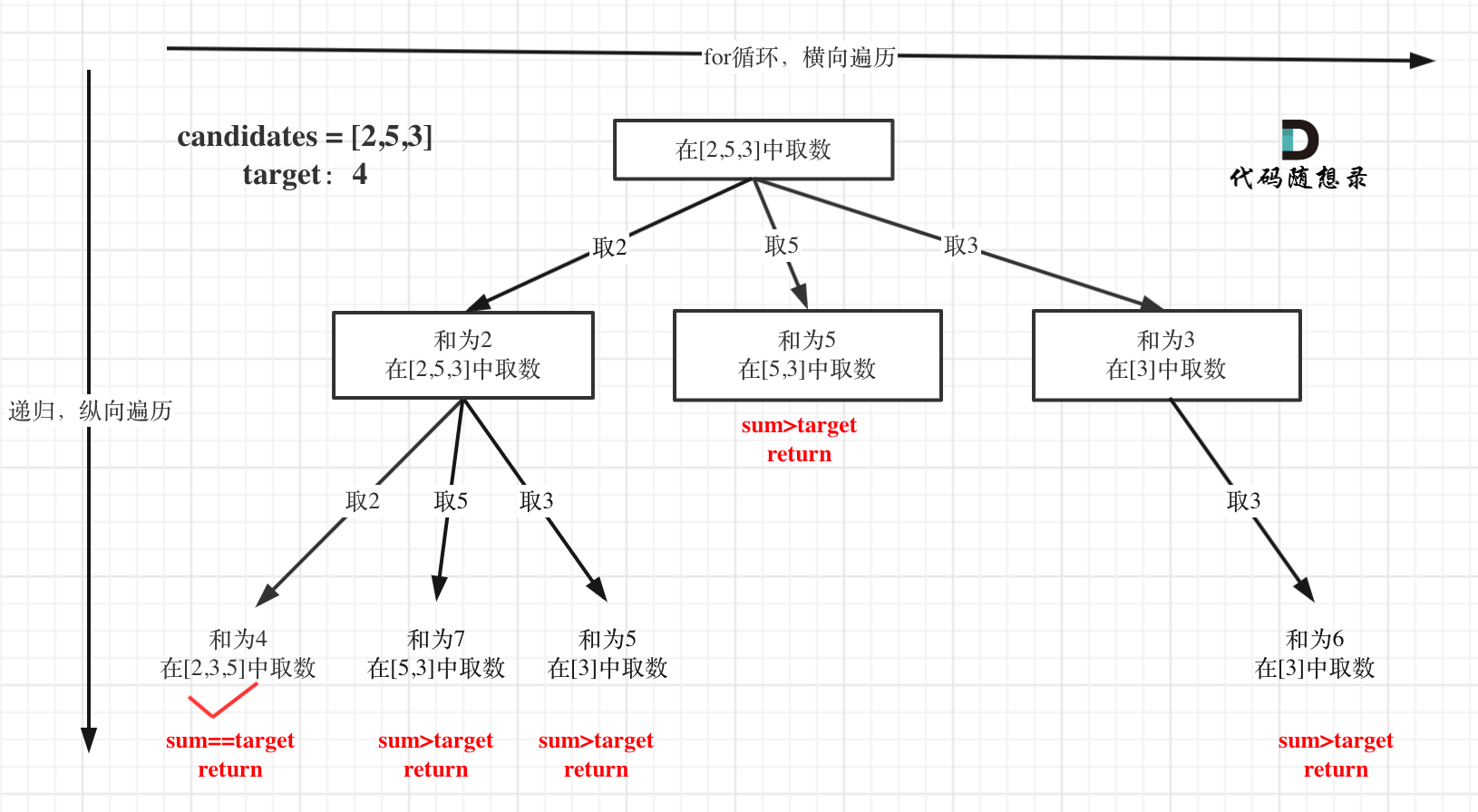
+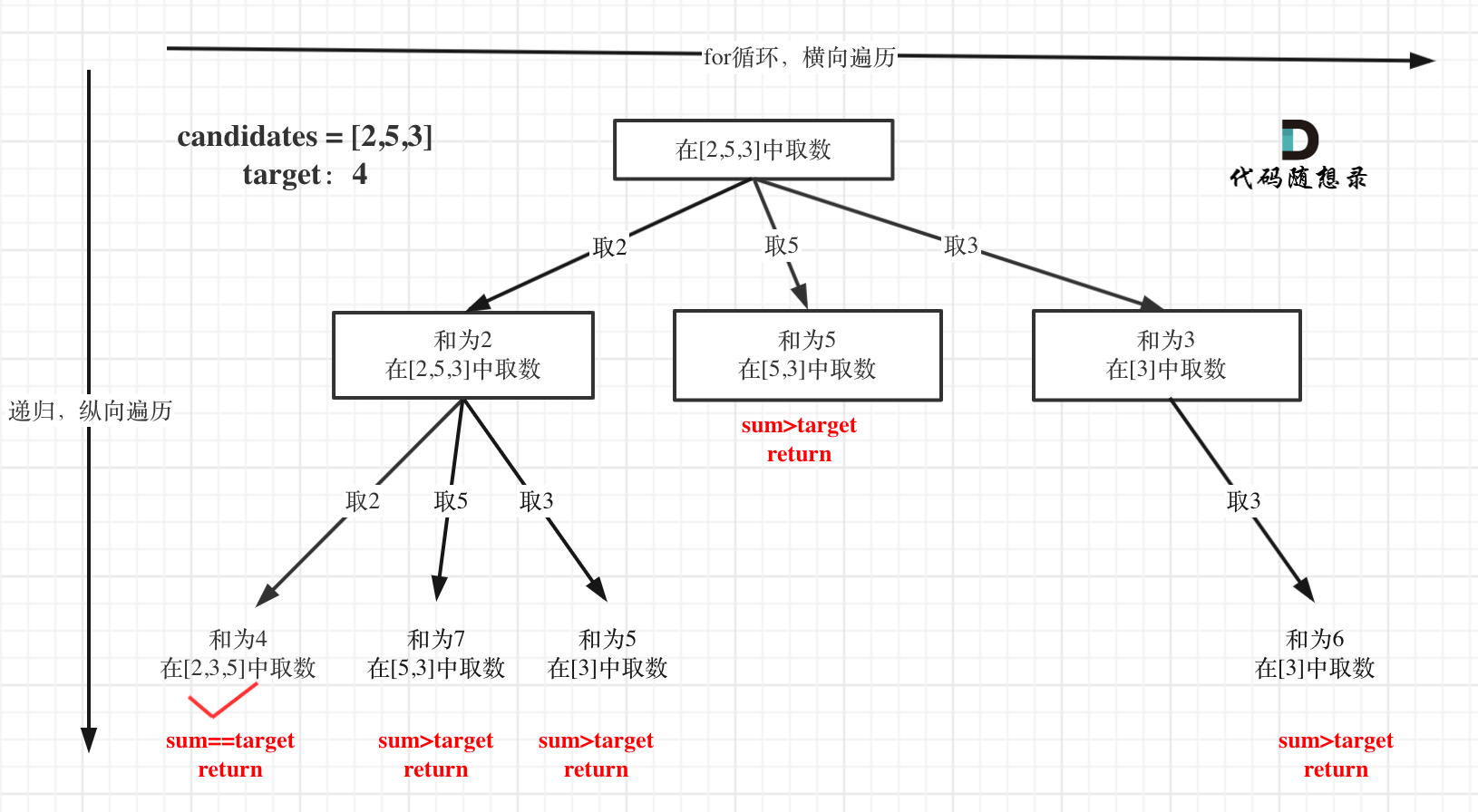
注意图中叶子节点的返回条件,因为本题没有组合数量要求,仅仅是总和的限制,所以递归没有层数的限制,只要选取的元素总和超过target,就返回!
而在[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)和[216.组合总和III](https://programmercarl.com/0216.组合总和III.html) 中都可以知道要递归K层,因为要取k个元素的组合。
-## 回溯三部曲
+### 回溯三部曲
* 递归函数参数
@@ -69,7 +71,7 @@ candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
如果是多个集合取组合,各个集合之间相互不影响,那么就不用startIndex,例如:[17.电话号码的字母组合](https://programmercarl.com/0017.电话号码的字母组合.html)
-**注意以上我只是说求组合的情况,如果是排列问题,又是另一套分析的套路,后面我再讲解排列的时候就重点介绍**。
+**注意以上我只是说求组合的情况,如果是排列问题,又是另一套分析的套路,后面我在讲解排列的时候会重点介绍**。
代码如下:
@@ -83,7 +85,7 @@ void backtracking(vector& candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex)
在如下树形结构中:
-
+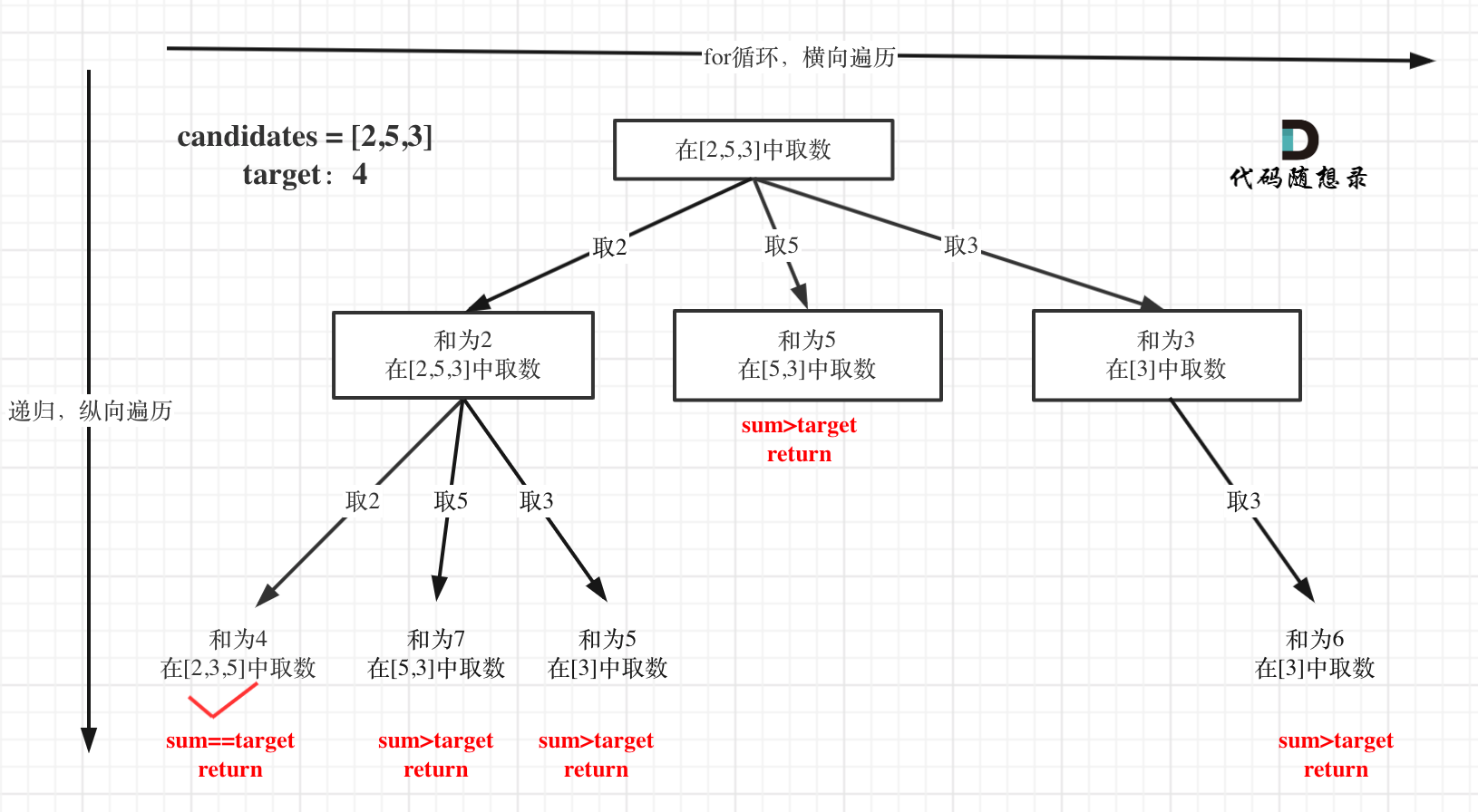
从叶子节点可以清晰看到,终止只有两种情况,sum大于target和sum等于target。
@@ -152,11 +154,11 @@ public:
};
```
-## 剪枝优化
+### 剪枝优化
在这个树形结构中:
-
+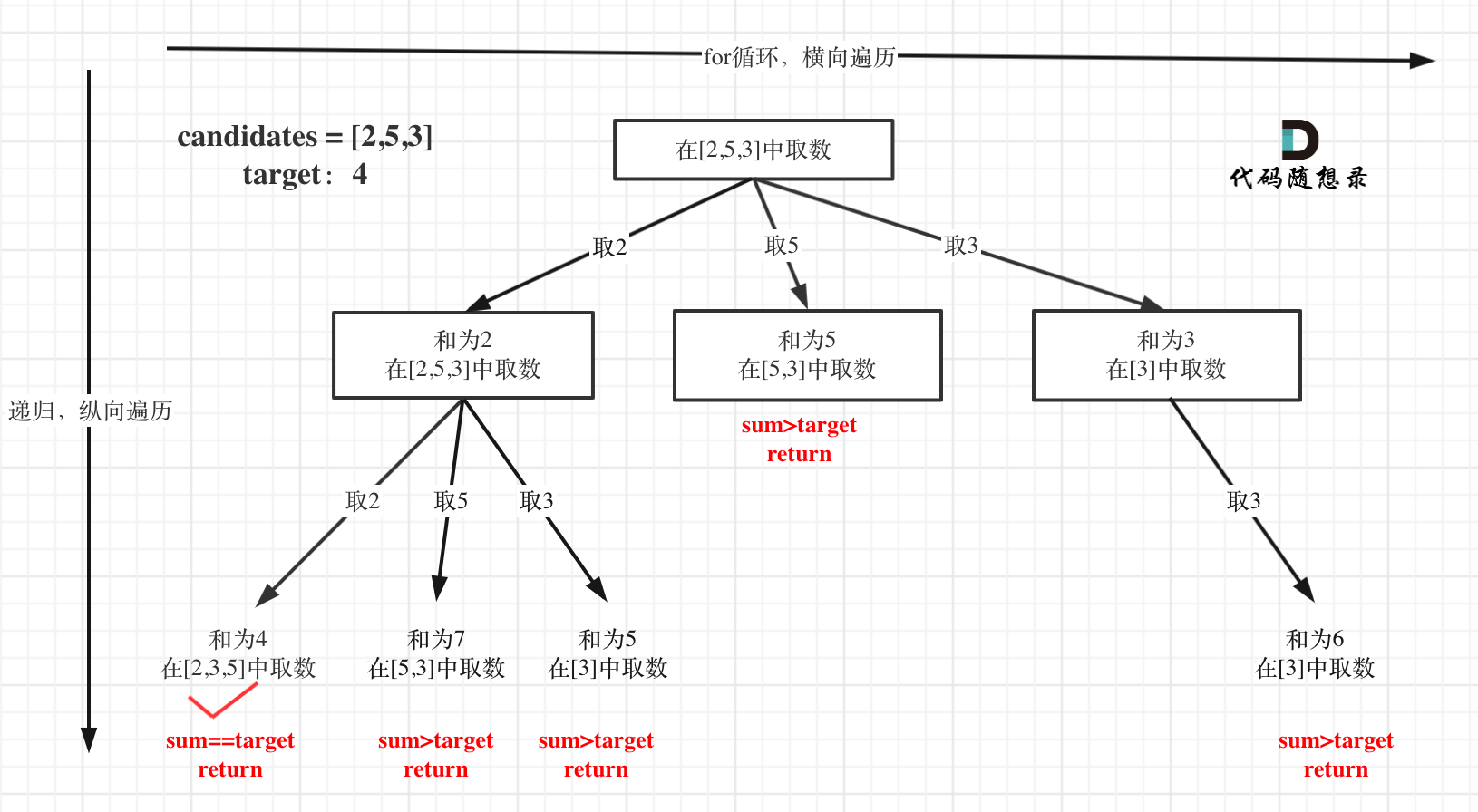
以及上面的版本一的代码大家可以看到,对于sum已经大于target的情况,其实是依然进入了下一层递归,只是下一层递归结束判断的时候,会判断sum > target的话就返回。
@@ -169,7 +171,7 @@ public:
如图:
-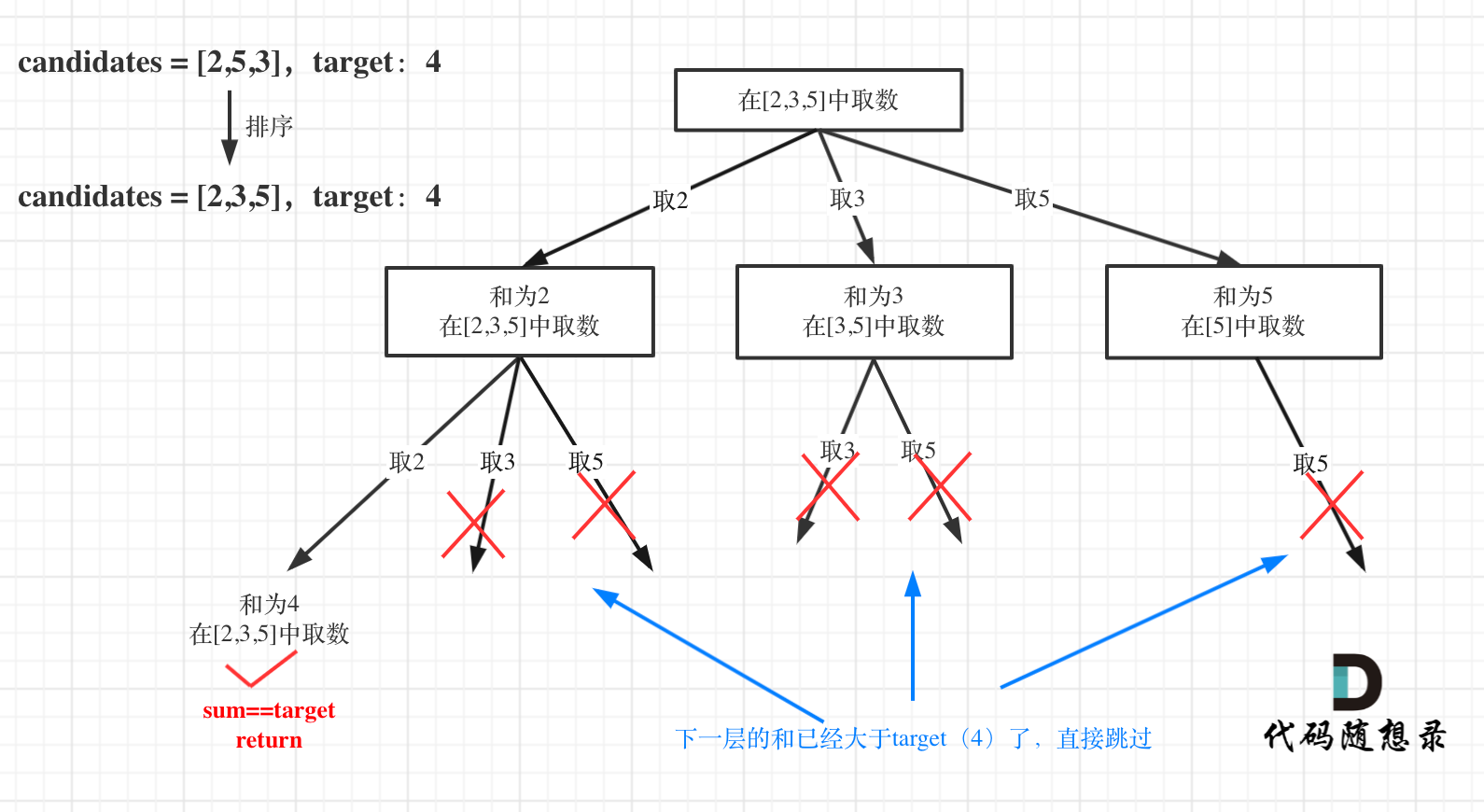
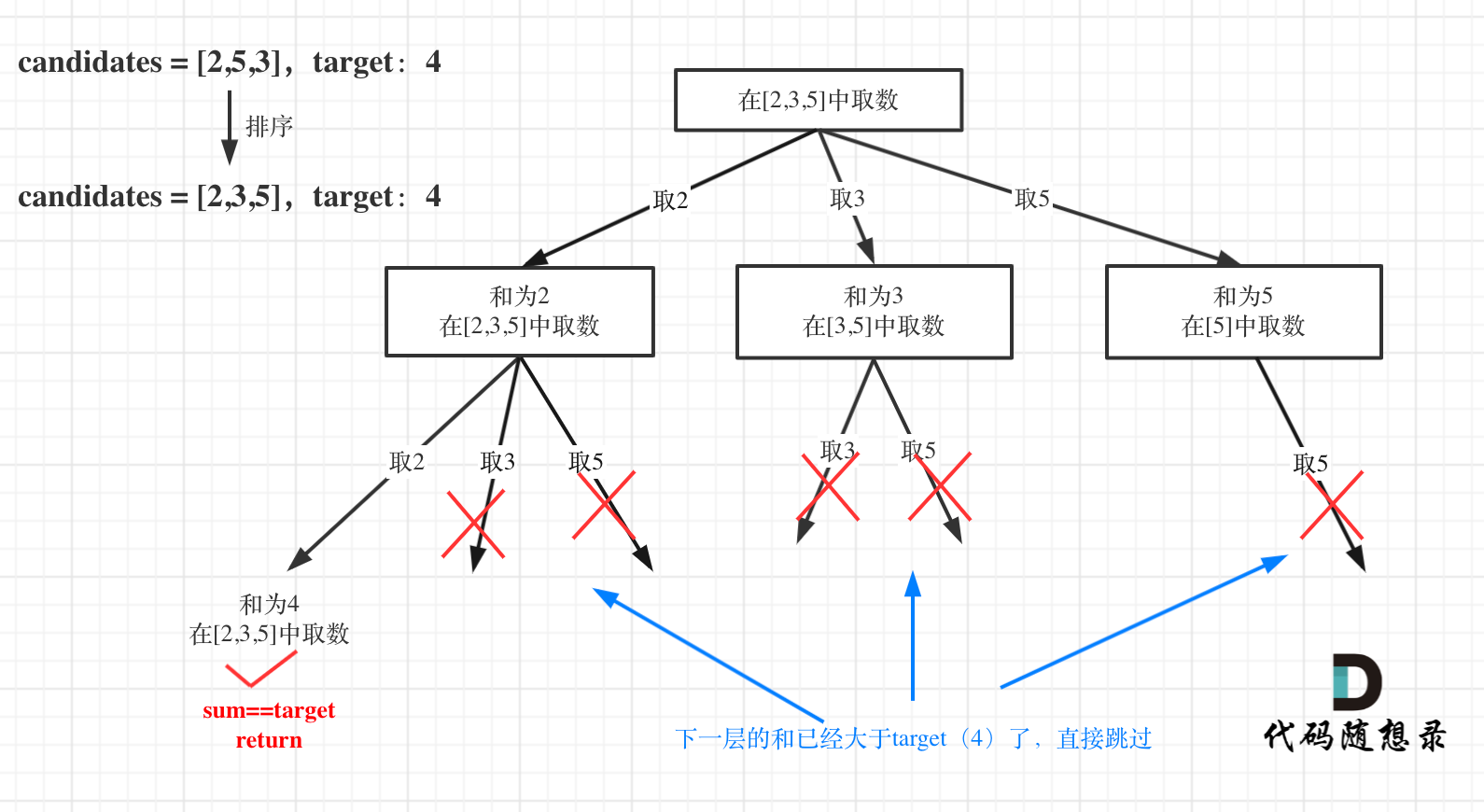
+
for循环剪枝代码如下:
@@ -210,8 +212,10 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n),注意这只是复杂度的上界,因为剪枝的存在,真实的时间复杂度远小于此
+* 空间复杂度: O(target)
-# 总结
+## 总结
本题和我们之前讲过的[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)、[216.组合总和III](https://programmercarl.com/0216.组合总和III.html)有两点不同:
@@ -232,10 +236,11 @@ public:
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
+
+### Java
-## Java
```Java
// 剪枝优化
class Solution {
@@ -264,76 +269,107 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
-**回溯**
+### Python
+
+回溯(版本一)
+
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.path = []
- self.paths = []
- def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- '''
- 因为本题没有组合数量限制,所以只要元素总和大于target就算结束
- '''
- self.path.clear()
- self.paths.clear()
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0)
- return self.paths
-
- def backtracking(self, candidates: List[int], target: int, sum_: int, start_index: int) -> None:
- # Base Case
- if sum_ == target:
- self.paths.append(self.path[:]) # 因为是shallow copy,所以不能直接传入self.path
+ def backtracking(self, candidates, target, total, startIndex, path, result):
+ if total > target:
+ return
+ if total == target:
+ result.append(path[:])
return
- if sum_ > target:
- return
-
- # 单层递归逻辑
- for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
- sum_ += candidates[i]
- self.path.append(candidates[i])
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum_, i) # 因为无限制重复选取,所以不是i+1
- sum_ -= candidates[i] # 回溯
- self.path.pop() # 回溯
+
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
+ total += candidates[i]
+ path.append(candidates[i])
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i, path, result) # 不用i+1了,表示可以重复读取当前的数
+ total -= candidates[i]
+ path.pop()
+
+ def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):
+ result = []
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, [], result)
+ return result
+
```
-**剪枝回溯**
+
+回溯剪枝(版本一)
+
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.path = []
- self.paths = []
+ def backtracking(self, candidates, target, total, startIndex, path, result):
+ if total == target:
+ result.append(path[:])
+ return
+
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
+ if total + candidates[i] > target:
+ break
+ total += candidates[i]
+ path.append(candidates[i])
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i, path, result)
+ total -= candidates[i]
+ path.pop()
+
+ def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):
+ result = []
+ candidates.sort() # 需要排序
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, [], result)
+ return result
+
+```
+
+回溯(版本二)
+
+```python
+class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- '''
- 因为本题没有组合数量限制,所以只要元素总和大于target就算结束
- '''
- self.path.clear()
- self.paths.clear()
+ result =[]
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, [], result)
+ return result
+ def backtracking(self, candidates, target, startIndex, path, result):
+ if target == 0:
+ result.append(path[:])
+ return
+ if target < 0:
+ return
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
+ path.append(candidates[i])
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, path, result)
+ path.pop()
- # 为了剪枝需要提前进行排序
- candidates.sort()
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0)
- return self.paths
+```
+
+回溯剪枝(版本二)
- def backtracking(self, candidates: List[int], target: int, sum_: int, start_index: int) -> None:
- # Base Case
- if sum_ == target:
- self.paths.append(self.path[:]) # 因为是shallow copy,所以不能直接传入self.path
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+ result =[]
+ candidates.sort()
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, [], result)
+ return result
+ def backtracking(self, candidates, target, startIndex, path, result):
+ if target == 0:
+ result.append(path[:])
return
- # 单层递归逻辑
- # 如果本层 sum + condidates[i] > target,就提前结束遍历,剪枝
- for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
- if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
- return
- sum_ += candidates[i]
- self.path.append(candidates[i])
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum_, i) # 因为无限制重复选取,所以不是i-1
- sum_ -= candidates[i] # 回溯
- self.path.pop() # 回溯
+
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
+ if target - candidates[i] < 0:
+ break
+ path.append(candidates[i])
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, path, result)
+ path.pop()
+
```
-## Go
+### Go
+
主要在于递归中传递下一个数字
```go
@@ -366,7 +402,7 @@ func dfs(candidates []int, start int, target int) {
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
var combinationSum = function(candidates, target) {
@@ -392,7 +428,7 @@ var combinationSum = function(candidates, target) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
```typescript
function combinationSum(candidates: number[], target: number): number[][] {
@@ -418,12 +454,12 @@ function combinationSum(candidates: number[], target: number): number[][] {
};
```
-## Rust
+### Rust
```Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec>, path: &mut Vec, candidates: &Vec, target: i32, mut sum: i32, start_index: usize) {
- if sum == target {
+ if sum == target {
result.push(path.to_vec());
return;
}
@@ -447,7 +483,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-## C
+### C
```c
int* path;
@@ -503,7 +539,7 @@ int** combinationSum(int* candidates, int candidatesSize, int target, int* retur
}
```
-## Swift
+### Swift
```swift
func combinationSum(_ candidates: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -532,7 +568,7 @@ func combinationSum(_ candidates: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [[Int]] {
}
```
-## Scala
+### Scala
```scala
object Solution {
@@ -560,9 +596,66 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> CombinationSum(int[] candidates, int target)
+ {
+ BackTracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int[] candidates, int target, int start, int sum)
+ {
+ if (sum > target) return;
+ if (sum == target)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i < candidates.Length; i++)
+ {
+ sum += candidates[i];
+ path.Add(candidates[i]);
+ BackTracking(candidates, target, i, sum);
+ sum -= candidates[i];
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 剪枝优化
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> CombinationSum(int[] candidates, int target)
+ {
+ Array.Sort(candidates);
+ BackTracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int[] candidates, int target, int start, int sum)
+ {
+ if (sum > target) return;
+ if (sum == target)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i < candidates.Length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++)
+ {
+ sum += candidates[i];
+ path.Add(candidates[i]);
+ BackTracking(candidates, target, i, sum);
+ sum -= candidates[i];
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 415fdb605f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 415fdb605f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-> 这篇可以说是全网把组合问题如何去重,讲的最清晰的了!
-
# 40.组合总和II
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/)
@@ -41,13 +37,11 @@ candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
]
```
-# 算法公开课
-
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[回溯算法中的去重,树层去重树枝去重,你弄清楚了没?| LeetCode:40.组合总和II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12V4y1V73A),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-
+## 算法公开课
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[回溯算法中的去重,树层去重树枝去重,你弄清楚了没?| LeetCode:40.组合总和II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12V4y1V73A),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-# 思路
+## 思路
这道题目和[39.组合总和](https://programmercarl.com/0039.组合总和.html)如下区别:
@@ -82,11 +76,11 @@ candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
选择过程树形结构如图所示:
-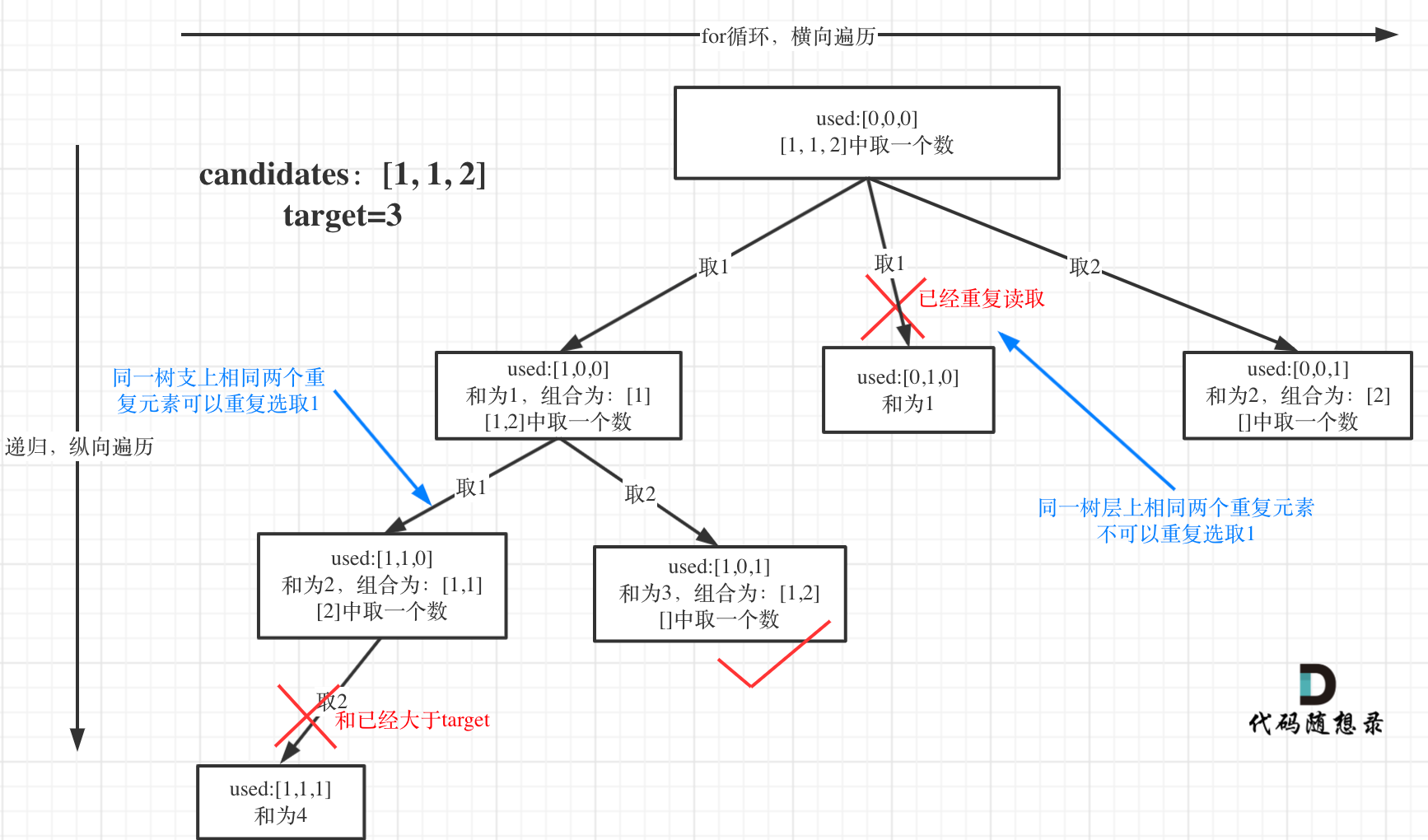
+
可以看到图中,每个节点相对于 [39.组合总和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FLg8G6EjVcxBjwCbzpACPw)我多加了used数组,这个used数组下面会重点介绍。
-## 回溯三部曲
+### 回溯三部曲
* **递归函数参数**
@@ -132,7 +126,7 @@ if (sum == target) {
这块比较抽象,如图:
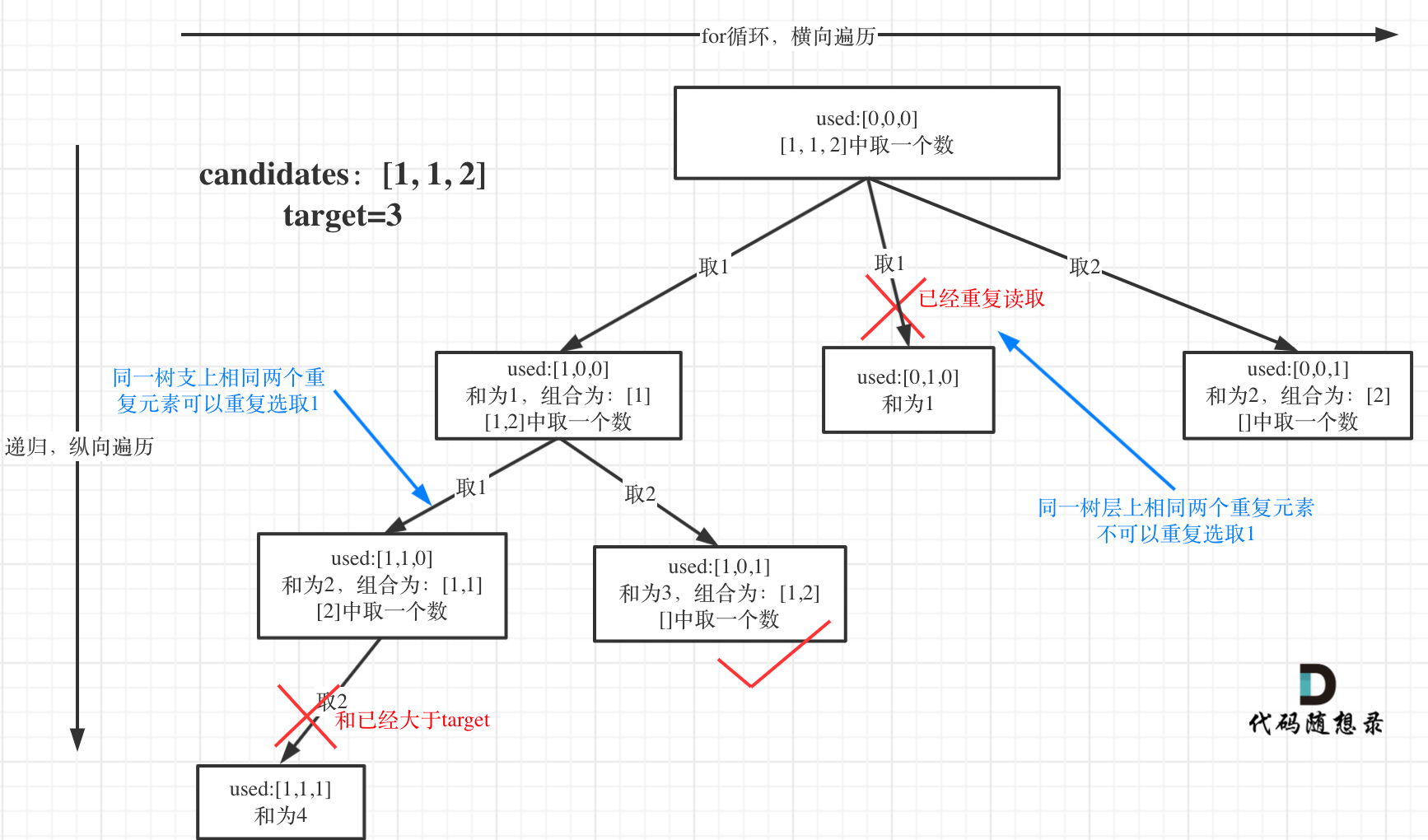
-
+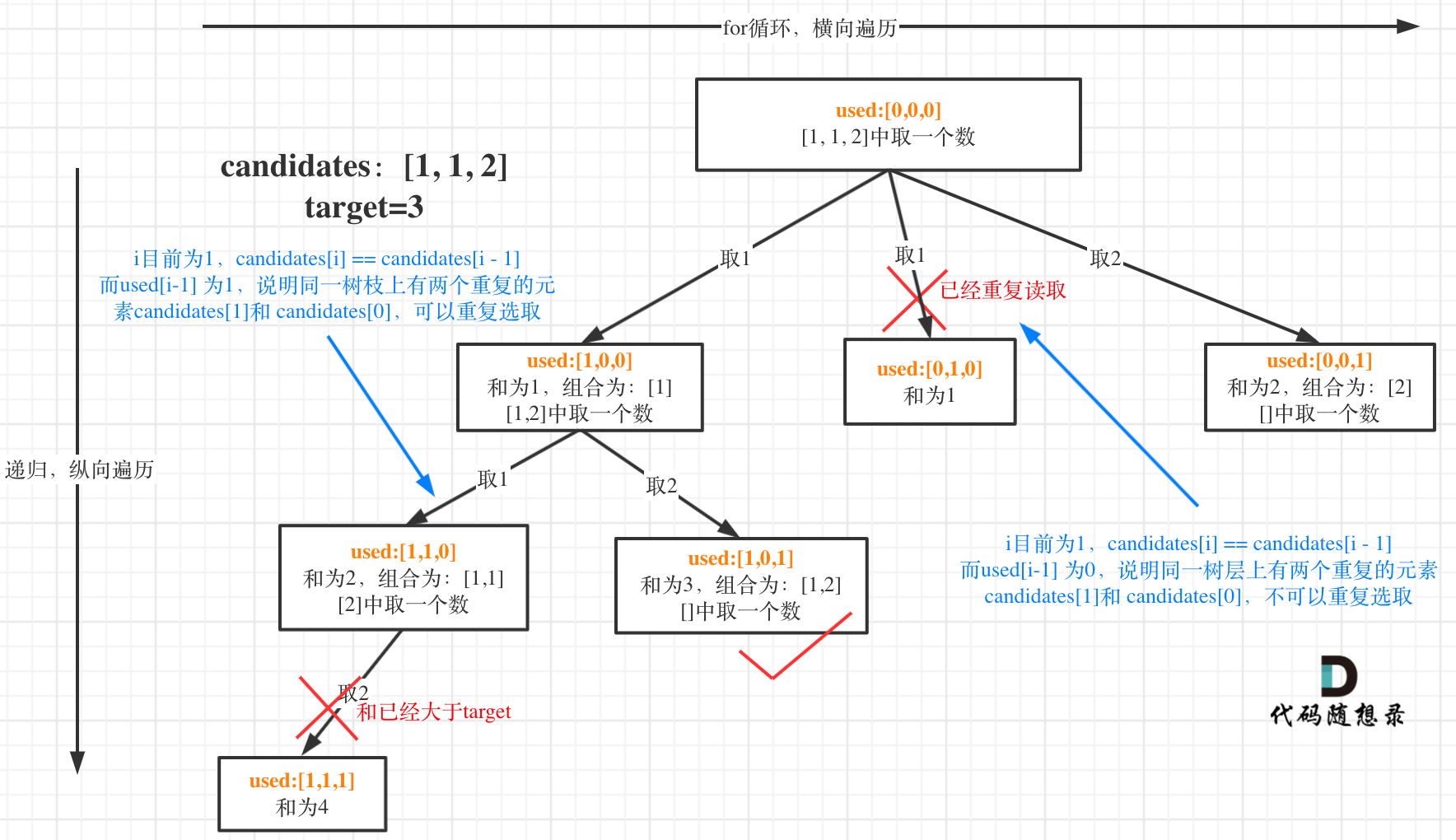
我在图中将used的变化用橘黄色标注上,可以看出在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
@@ -143,7 +137,7 @@ if (sum == target) {
而 used[i - 1] == true,说明是进入下一层递归,去下一个数,所以是树枝上,如图所示:
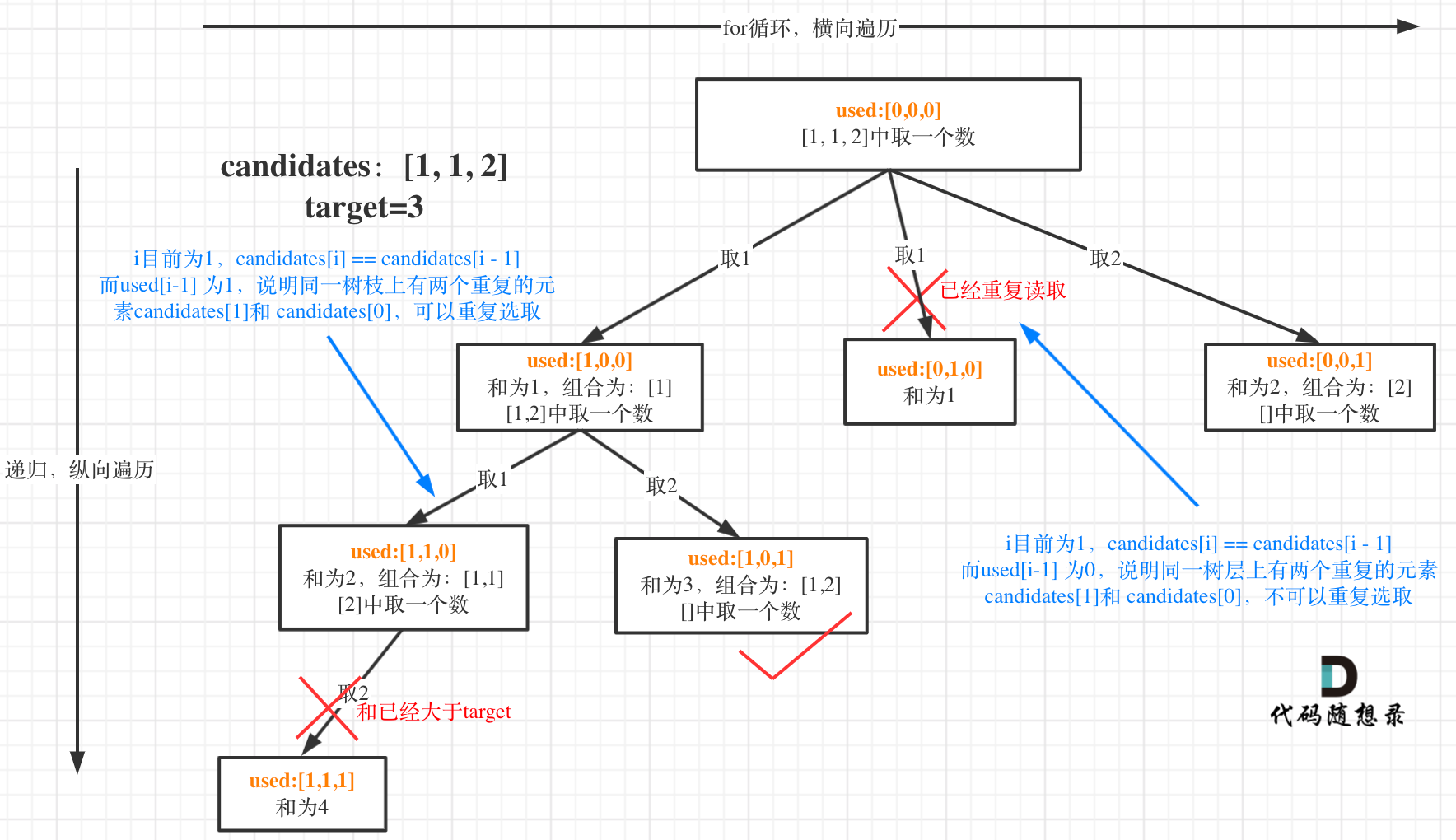
-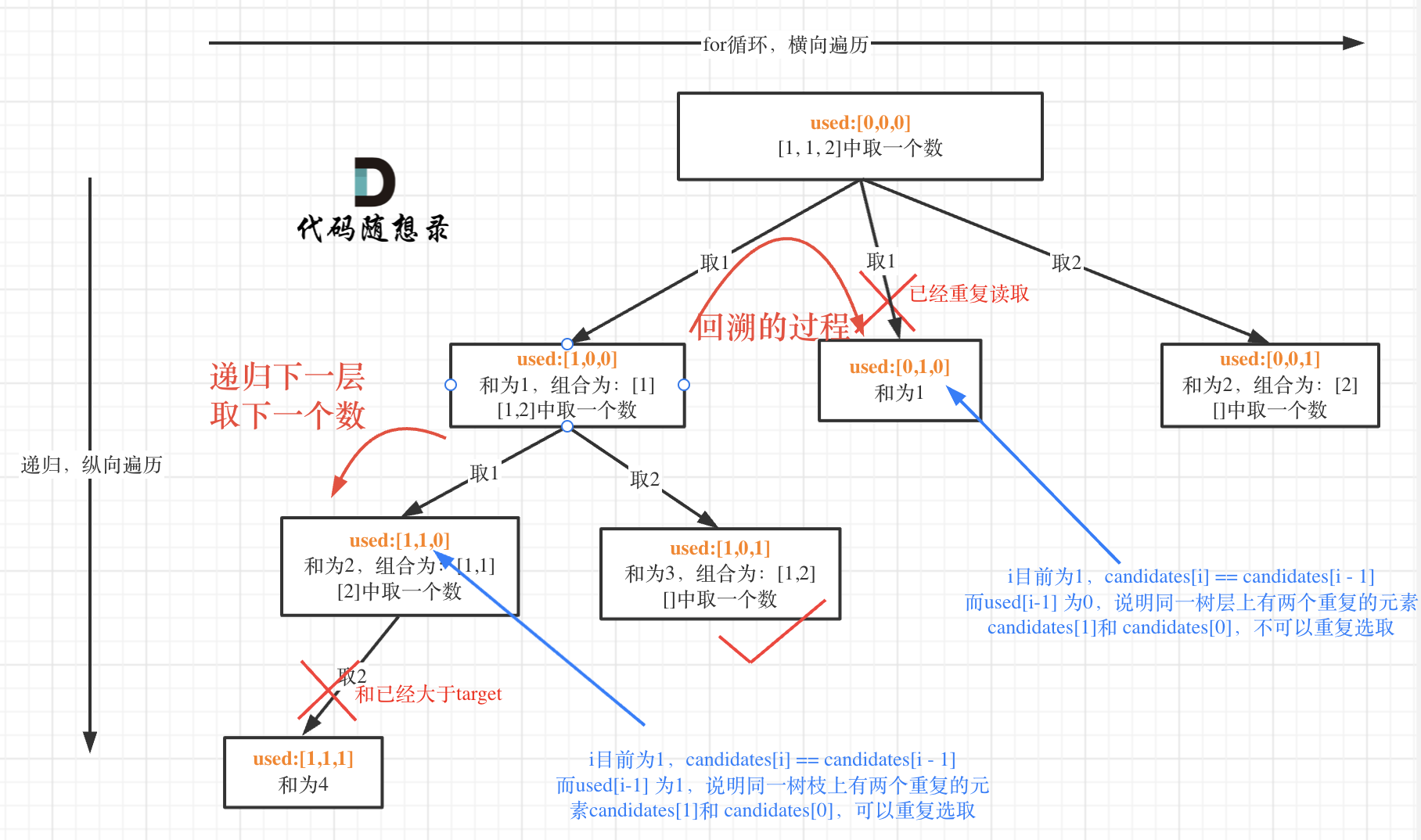
+
**这块去重的逻辑很抽象,网上搜的题解基本没有能讲清楚的,如果大家之前思考过这个问题或者刷过这道题目,看到这里一定会感觉通透了很多!**
@@ -214,8 +208,10 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
-## 补充
+### 补充
这里直接用startIndex来去重也是可以的, 就不用used数组了。
@@ -255,7 +251,7 @@ public:
```
-# 总结
+## 总结
本题同样是求组合总和,但就是因为其数组candidates有重复元素,而要求不能有重复的组合,所以相对于[39.组合总和](https://programmercarl.com/0039.组合总和.html)难度提升了不少。
@@ -263,14 +259,10 @@ public:
所以Carl有必要把去重的这块彻彻底底的给大家讲清楚,**就连“树层去重”和“树枝去重”都是我自创的词汇,希望对大家理解有帮助!**
+## 其他语言版本
-
-
-# 其他语言版本
-
-
-## Java
+### Java
**使用标记数组**
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -353,95 +345,94 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
-**回溯+巧妙去重(省去使用used**
+### Python
+回溯
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.paths = []
- self.path = []
- def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- '''
- 类似于求三数之和,求四数之和,为了避免重复组合,需要提前进行数组排序
- '''
- self.paths.clear()
- self.path.clear()
- # 必须提前进行数组排序,避免重复
- candidates.sort()
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0)
- return self.paths
- def backtracking(self, candidates: List[int], target: int, sum_: int, start_index: int) -> None:
- # Base Case
- if sum_ == target:
- self.paths.append(self.path[:])
+ def backtracking(self, candidates, target, total, startIndex, path, result):
+ if total == target:
+ result.append(path[:])
return
-
- # 单层递归逻辑
- for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
- # 剪枝,同39.组合总和
- if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
- return
-
- # 跳过同一树层使用过的元素
- if i > start_index and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]:
+
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
+ if i > startIndex and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]:
continue
-
- sum_ += candidates[i]
- self.path.append(candidates[i])
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum_, i+1)
- self.path.pop() # 回溯,为了下一轮for loop
- sum_ -= candidates[i] # 回溯,为了下一轮for loop
+
+ if total + candidates[i] > target:
+ break
+
+ total += candidates[i]
+ path.append(candidates[i])
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i + 1, path, result)
+ total -= candidates[i]
+ path.pop()
+
+ def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
+ result = []
+ candidates.sort()
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, [], result)
+ return result
+
```
-**回溯+去重(使用used)**
+回溯 使用used
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.paths = []
- self.path = []
- self.used = []
- def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- '''
- 类似于求三数之和,求四数之和,为了避免重复组合,需要提前进行数组排序
- 本题需要使用used,用来标记区别同一树层的元素使用重复情况:注意区分递归纵向遍历遇到的重复元素,和for循环遇到的重复元素,这两者的区别
- '''
- self.paths.clear()
- self.path.clear()
- self.usage_list = [False] * len(candidates)
- # 必须提前进行数组排序,避免重复
- candidates.sort()
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0)
- return self.paths
- def backtracking(self, candidates: List[int], target: int, sum_: int, start_index: int) -> None:
- # Base Case
- if sum_ == target:
- self.paths.append(self.path[:])
+ def backtracking(self, candidates, target, total, startIndex, used, path, result):
+ if total == target:
+ result.append(path[:])
return
-
- # 单层递归逻辑
- for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
- # 剪枝,同39.组合总和
- if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
- return
-
- # 检查同一树层是否出现曾经使用过的相同元素
- # 若数组中前后元素值相同,但前者却未被使用(used == False),说明是for loop中的同一树层的相同元素情况
- if i > 0 and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1] and self.usage_list[i-1] == False:
+
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(candidates)):
+ # 对于相同的数字,只选择第一个未被使用的数字,跳过其他相同数字
+ if i > startIndex and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] and not used[i - 1]:
continue
- sum_ += candidates[i]
- self.path.append(candidates[i])
- self.usage_list[i] = True
- self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum_, i+1)
- self.usage_list[i] = False # 回溯,为了下一轮for loop
- self.path.pop() # 回溯,为了下一轮for loop
- sum_ -= candidates[i] # 回溯,为了下一轮for loop
+ if total + candidates[i] > target:
+ break
+
+ total += candidates[i]
+ path.append(candidates[i])
+ used[i] = True
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, total, i + 1, used, path, result)
+ used[i] = False
+ total -= candidates[i]
+ path.pop()
+
+ def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
+ used = [False] * len(candidates)
+ result = []
+ candidates.sort()
+ self.backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, used, [], result)
+ return result
+
```
+回溯优化
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+ candidates.sort()
+ results = []
+ self.combinationSumHelper(candidates, target, 0, [], results)
+ return results
-## Go
+ def combinationSumHelper(self, candidates, target, index, path, results):
+ if target == 0:
+ results.append(path[:])
+ return
+ for i in range(index, len(candidates)):
+ if i > index and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]:
+ continue
+ if candidates[i] > target:
+ break
+ path.append(candidates[i])
+ self.combinationSumHelper(candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1, path, results)
+ path.pop()
+```
+### Go
主要在于如何在回溯中去重
**使用used数组**
@@ -517,7 +508,7 @@ func dfs(candidates []int, start int, target int) {
}
}
```
-## javaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
/**
@@ -587,7 +578,7 @@ var combinationSum2 = function(candidates, target) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
```typescript
function combinationSum2(candidates: number[], target: number): number[][] {
@@ -618,7 +609,7 @@ function combinationSum2(candidates: number[], target: number): number[][] {
};
```
-## Rust
+### Rust
```Rust
impl Solution {
@@ -653,7 +644,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-## C
+### C
```c
int* path;
@@ -715,7 +706,7 @@ int** combinationSum2(int* candidates, int candidatesSize, int target, int* retu
}
```
-## Swift
+### Swift
```swift
func combinationSum2(_ candidates: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -748,7 +739,7 @@ func combinationSum2(_ candidates: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [[Int]] {
```
-## Scala
+### Scala
```scala
object Solution {
@@ -778,8 +769,37 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public List> res = new List>();
+ public List path = new List();
+ public IList> CombinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target)
+ {
+
+ Array.Sort(candidates);
+ BackTracking(candidates, target, 0, 0);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int[] candidates, int target, int start, int sum)
+ {
+ if (sum > target) return;
+ if (sum == target)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i < candidates.Length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++)
+ {
+ if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) continue;
+ sum += candidates[i];
+ path.Add(candidates[i]);
+ BackTracking(candidates, target, i + 1, sum);
+ sum -= candidates[i];
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8ea81234cc..62fbe270b7
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8ea81234cc..62fbe270b7
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-> 这个图就是大厂面试经典题目,接雨水! 最常青藤的一道题,面试官百出不厌!
-# 42. 接雨水
+
+
+# 42. 接雨水
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
@@ -15,8 +14,7 @@
示例 1:
-
-
+
* 输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
* 输出:6
* 解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
@@ -26,27 +24,32 @@
* 输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
* 输出:9
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[单调栈,经典来袭!LeetCode:42.接雨水](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1uD4y1u75P/),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
-# 思路
+## 思路
接雨水问题在面试中还是常见题目的,有必要好好讲一讲。
本文深度讲解如下三种方法:
-* 双指针法
-* 动态规划
+
+* 暴力解法
+* 双指针优化
* 单调栈
-## 暴力解法
+### 暴力解法
本题暴力解法也是也是使用双指针。
首先要明确,要按照行来计算,还是按照列来计算。
按照行来计算如图:
-
+
按照列来计算如图:
-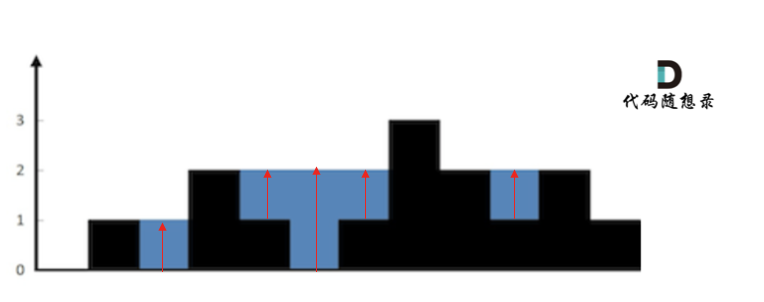
+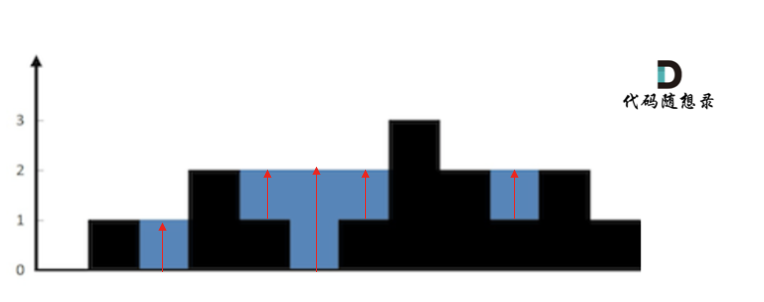
一些同学在实现的时候,很容易一会按照行来计算一会按照列来计算,这样就会越写越乱。
@@ -58,7 +61,7 @@
这句话可以有点绕,来举一个理解,例如求列4的雨水高度,如图:
-
+
列4 左侧最高的柱子是列3,高度为2(以下用lHeight表示)。
@@ -72,7 +75,7 @@
此时求出了列4的雨水体积。
-一样的方法,只要从头遍历一遍所有的列,然后求出每一列雨水的体积,相加之后就是总雨水的体积了。
+一样的方法,只要从头遍历一遍所有的列,然后求出每一列雨水的体积,相加之后就是总雨水的体积了。
首先从头遍历所有的列,并且**要注意第一个柱子和最后一个柱子不接雨水**,代码如下:
@@ -132,9 +135,9 @@ public:
因为每次遍历列的时候,还要向两边寻找最高的列,所以时间复杂度为O(n^2),空间复杂度为O(1)。
-力扣后面修改了后台测试数据,所以以上暴力解法超时了。
+力扣后面修改了后台测试数据,所以以上暴力解法超时了。
-## 双指针优化
+### 双指针优化
在暴力解法中,我们可以看到只要记录左边柱子的最高高度 和 右边柱子的最高高度,就可以计算当前位置的雨水面积,这就是通过列来计算。
@@ -181,9 +184,9 @@ public:
};
```
-## 单调栈解法
+### 单调栈解法
-关于单调栈的理论基础,单调栈适合解决什么问题,单调栈的工作过程,大家可以先看这题讲解 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
+关于单调栈的理论基础,单调栈适合解决什么问题,单调栈的工作过程,大家可以先看这题讲解 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
单调栈就是保持栈内元素有序。和[栈与队列:单调队列](https://programmercarl.com/0239.滑动窗口最大值.html)一样,需要我们自己维持顺序,没有现成的容器可以用。
@@ -191,13 +194,13 @@ public:
而接雨水这道题目,我们正需要寻找一个元素,右边最大元素以及左边最大元素,来计算雨水面积。
-### 准备工作
+#### 准备工作
那么本题使用单调栈有如下几个问题:
1. 首先单调栈是按照行方向来计算雨水,如图:
-
+
知道这一点,后面的就可以理解了。
@@ -211,11 +214,11 @@ public:
如图:
-
+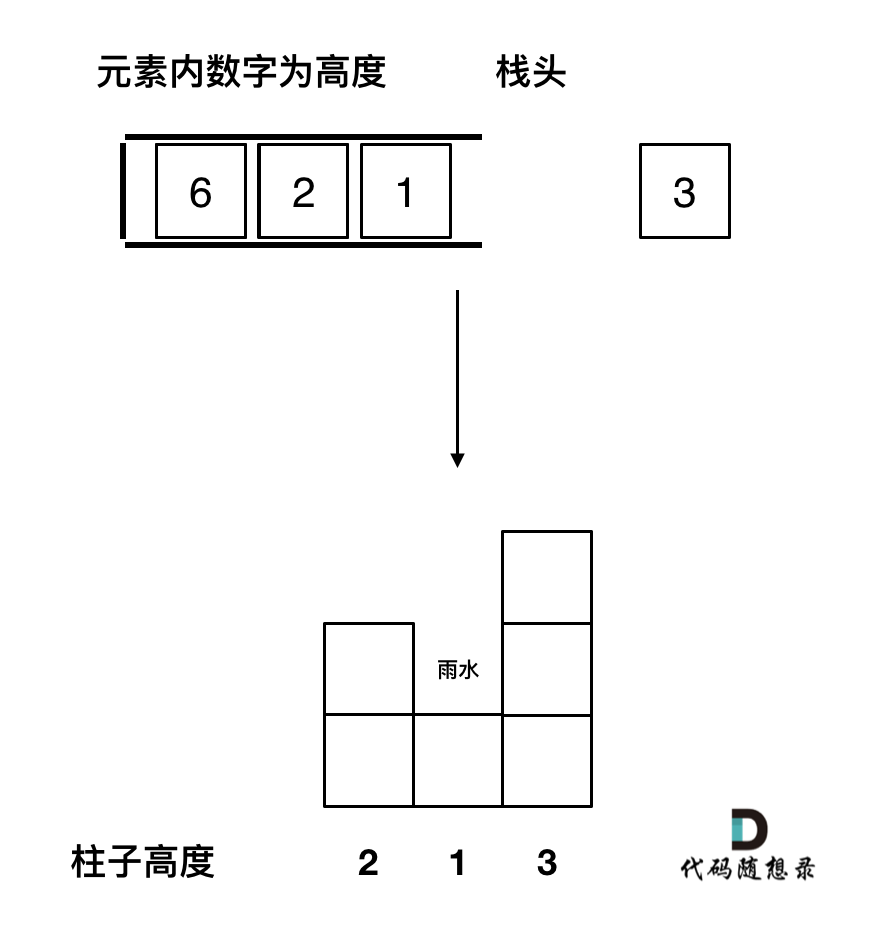
关于单调栈的顺序给大家一个总结: [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html) 中求一个元素右边第一个更大元素,单调栈就是递增的,[84.柱状图中最大的矩形](https://programmercarl.com/0084.柱状图中最大的矩形.html)求一个元素右边第一个更小元素,单调栈就是递减的。
-3. 遇到相同高度的柱子怎么办。
+3. 遇到相同高度的柱子怎么办。
遇到相同的元素,更新栈内下标,就是将栈里元素(旧下标)弹出,将新元素(新下标)加入栈中。
@@ -225,7 +228,7 @@ public:
如图所示:
-
+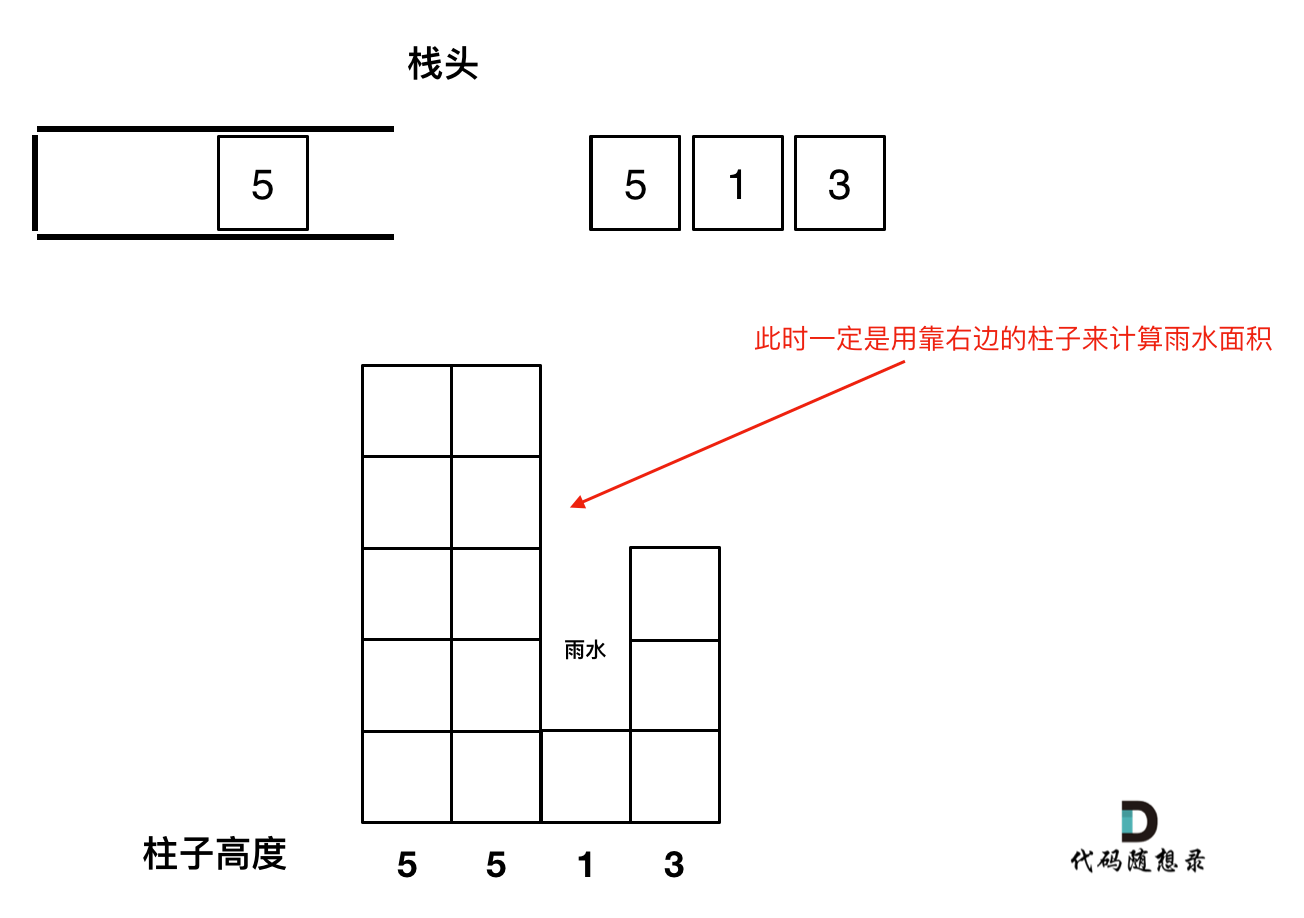
4. 栈里要保存什么数值
@@ -233,7 +236,7 @@ public:
长就是通过柱子的高度来计算,宽是通过柱子之间的下标来计算,
-那么栈里有没有必要存一个pair类型的元素,保存柱子的高度和下标呢。
+那么栈里有没有必要存一个pair类型的元素,保存柱子的高度和下标呢。
其实不用,栈里就存放下标就行,想要知道对应的高度,通过height[stack.top()] 就知道弹出的下标对应的高度了。
@@ -245,17 +248,17 @@ stack st; // 存着下标,计算的时候用下标对应的柱子高度
明确了如上几点,我们再来看处理逻辑。
-### 单调栈处理逻辑
+#### 单调栈处理逻辑
-以下操作过程其实和 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html) 也是一样的,建议先做 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
+以下操作过程其实和 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html) 也是一样的,建议先做 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
-以下逻辑主要就是三种情况
+以下逻辑主要就是三种情况
-* 情况一:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度小于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] < height[st.top()]
-* 情况二:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度等于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] == height[st.top()]
-* 情况三:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] > height[st.top()]
+* 情况一:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度小于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] < height[st.top()]
+* 情况二:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度等于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] == height[st.top()]
+* 情况三:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] > height[st.top()]
-先将下标0的柱子加入到栈中,`st.push(0);`。 栈中存放我们遍历过的元素,所以先将下标0加进来。
+先将下标0的柱子加入到栈中,`st.push(0);`。 栈中存放我们遍历过的元素,所以先将下标0加进来。
然后开始从下标1开始遍历所有的柱子,`for (int i = 1; i < height.size(); i++)`。
@@ -278,9 +281,9 @@ if (height[i] == height[st.top()]) { // 例如 5 5 1 7 这种情况
}
```
-如果当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度,此时就出现凹槽了,如图所示:
+如果当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度,此时就出现凹槽了,如图所示:
-
+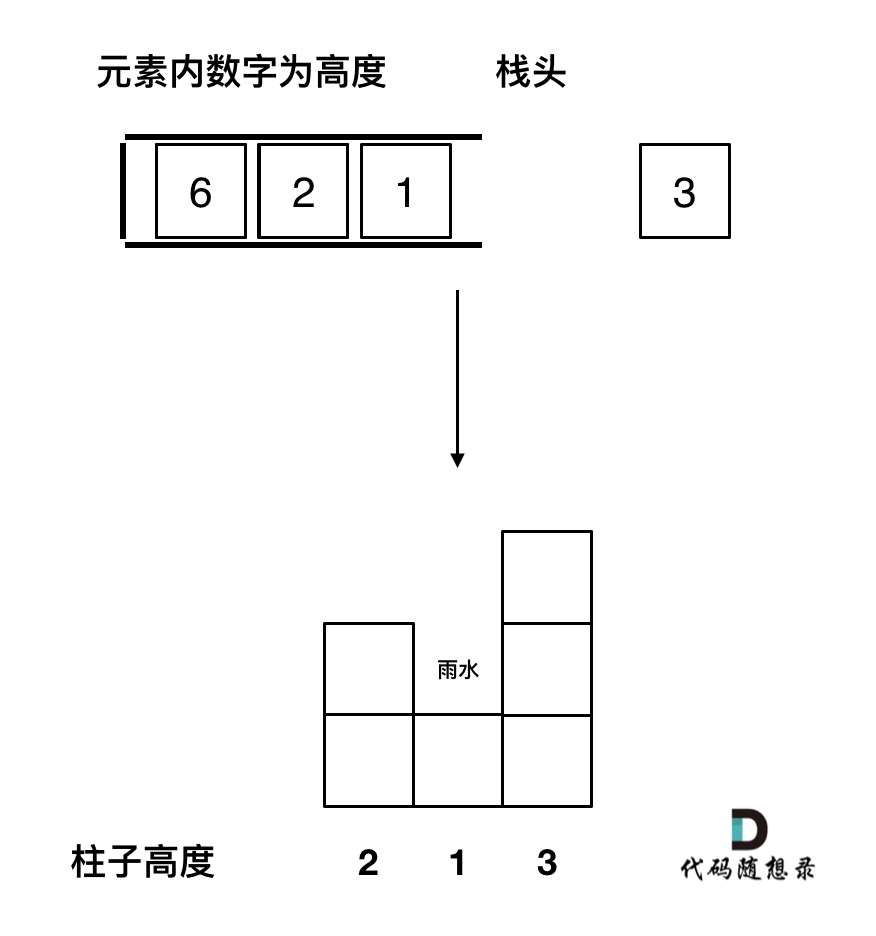
取栈顶元素,将栈顶元素弹出,这个就是凹槽的底部,也就是中间位置,下标记为mid,对应的高度为height[mid](就是图中的高度1)。
@@ -290,7 +293,7 @@ if (height[i] == height[st.top()]) { // 例如 5 5 1 7 这种情况
此时大家应该可以发现其实就是**栈顶和栈顶的下一个元素以及要入栈的元素,三个元素来接水!**
-那么雨水高度是 min(凹槽左边高度, 凹槽右边高度) - 凹槽底部高度,代码为:`int h = min(height[st.top()], height[i]) - height[mid];`
+那么雨水高度是 min(凹槽左边高度, 凹槽右边高度) - 凹槽底部高度,代码为:`int h = min(height[st.top()], height[i]) - height[mid];`
雨水的宽度是 凹槽右边的下标 - 凹槽左边的下标 - 1(因为只求中间宽度),代码为:`int w = i - st.top() - 1 ;`
@@ -373,11 +376,12 @@ public:
精简之后的代码,大家就看不出去三种情况的处理了,貌似好像只处理的情况三,其实是把情况一和情况二融合了。 这样的代码不太利于理解。
-## 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-### Java:
+### Java:
暴力解法:
+
```java
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
@@ -385,7 +389,7 @@ class Solution {
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
// 第一个柱子和最后一个柱子不接雨水
if (i==0 || i== height.length - 1) continue;
-
+
int rHeight = height[i]; // 记录右边柱子的最高高度
int lHeight = height[i]; // 记录左边柱子的最高高度
for (int r = i+1; r < height.length; r++) {
@@ -404,6 +408,7 @@ class Solution {
```
双指针:
+
```java
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
@@ -411,15 +416,15 @@ class Solution {
if (length <= 2) return 0;
int[] maxLeft = new int[length];
int[] maxRight = new int[length];
-
+
// 记录每个柱子左边柱子最大高度
maxLeft[0] = height[0];
for (int i = 1; i< length; i++) maxLeft[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxLeft[i-1]);
-
+
// 记录每个柱子右边柱子最大高度
maxRight[length - 1] = height[length - 1];
for(int i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) maxRight[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxRight[i+1]);
-
+
// 求和
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
@@ -431,14 +436,42 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+双指针优化
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int trap(int[] height) {
+ if (height.length <= 2) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // 从两边向中间寻找最值
+ int maxLeft = height[0], maxRight = height[height.length - 1];
+ int l = 1, r = height.length - 2;
+ int res = 0;
+ while (l <= r) {
+ // 不确定上一轮是左边移动还是右边移动,所以两边都需更新最值
+ maxLeft = Math.max(maxLeft, height[l]);
+ maxRight = Math.max(maxRight, height[r]);
+ // 最值较小的一边所能装的水量已定,所以移动较小的一边。
+ if (maxLeft < maxRight) {
+ res += maxLeft - height[l ++];
+ } else {
+ res += maxRight - height[r --];
+ }
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
单调栈法
+
```java
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height){
int size = height.length;
if (size <= 2) return 0;
-
+
// in the stack, we push the index of array
// using height[] to access the real height
Stack stack = new Stack();
@@ -458,7 +491,7 @@ class Solution {
int heightAtIdx = height[index];
while (!stack.isEmpty() && (heightAtIdx > height[stackTop])){
int mid = stack.pop();
-
+
if (!stack.isEmpty()){
int left = stack.peek();
@@ -472,7 +505,7 @@ class Solution {
stack.push(index);
}
}
-
+
return sum;
}
}
@@ -481,6 +514,7 @@ class Solution {
### Python:
暴力解法:
+
```Python
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
@@ -495,32 +529,35 @@ class Solution:
for k in range(i+2,len(height)):
if height[k] > rHight:
rHight = height[k]
- res1 = min(lHight,rHight) - height[i]
+ res1 = min(lHight,rHight) - height[i]
if res1 > 0:
res += res1
return res
```
双指针:
+
```python
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
leftheight, rightheight = [0]*len(height), [0]*len(height)
-
+
leftheight[0]=height[0]
for i in range(1,len(height)):
leftheight[i]=max(leftheight[i-1],height[i])
rightheight[-1]=height[-1]
for i in range(len(height)-2,-1,-1):
rightheight[i]=max(rightheight[i+1],height[i])
-
+
result = 0
for i in range(0,len(height)):
summ = min(leftheight[i],rightheight[i])-height[i]
result += summ
return result
```
+
单调栈
+
```Python
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
@@ -565,8 +602,8 @@ class Solution:
result += h * w
stack.append(i)
return result
-
-# 单调栈压缩版
+
+# 单调栈压缩版
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
stack = [0]
@@ -586,7 +623,7 @@ class Solution:
```
-### Go
+### Go:
```go
func trap(height []int) int {
@@ -601,7 +638,7 @@ func trap(height []int) int {
}
left++
} else {
- if height[right] > rightMax {
+ if height[right] > rightMax {
rightMax = height[right] // //设置右边最高柱子
} else {
res += rightMax - height[right] // //左边必定有柱子挡水,所以,遇到所有值小于等于rightMax的,全部加入水池
@@ -652,6 +689,7 @@ func min(a,b int)int{
```
单调栈解法
+
```go
func trap(height []int) int {
if len(height) <= 2 {
@@ -689,6 +727,45 @@ func min(x, y int) int {
}
```
+单调栈压缩版:
+
+```go
+func trap(height []int) int {
+ stack := make([]int, 0)
+ res := 0
+
+ // 无需事先将第一个柱子的坐标入栈,因为它会在该for循环的最后入栈
+ for i := 0; i < len(height); i ++ {
+ // 满足栈不为空并且当前柱子高度大于栈顶对应的柱子高度的情况时
+ for len(stack) > 0 && height[stack[len(stack) - 1]] < height[i] {
+ // 获得凹槽高度
+ mid := height[stack[len(stack) - 1]]
+ // 凹槽坐标出栈
+ stack = stack[: len(stack) - 1]
+
+ // 如果栈不为空则此时栈顶元素为左侧柱子坐标
+ if len(stack) > 0 {
+ // 求得雨水高度
+ h := min(height[i], height[stack[len(stack) - 1]]) - mid
+ // 求得雨水宽度
+ w := i - stack[len(stack) - 1] - 1
+ res += h * w
+ }
+ }
+ // 如果栈为空或者当前柱子高度小于等于栈顶对应的柱子高度时入栈
+ stack = append(stack, i)
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func min(x, y int) int {
+ if x < y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
### JavaScript:
```javascript
@@ -791,7 +868,7 @@ var trap = function(height) {
};
```
-### TypeScript
+### TypeScript:
暴力解法:
@@ -896,12 +973,12 @@ int trap(int* height, int heightSize) {
while (left < right) { //两个指针重合就结束
leftMax = fmax(leftMax, height[left]);
rightMax = fmax(rightMax, height[right]);
- if (leftMax < rightMax) {
+ if (leftMax < rightMax) {
ans += leftMax - height[left]; //这里考虑的是下标为left的“底”能装多少水
++left;//指针的移动次序是这个方法的关键
//这里左指针右移是因为左“墙”较矮,左边这一片实际情况下的盛水量是受制于这个矮的左“墙”的
//而较高的右边在实际情况下的限制条件可能不是当前的左“墙”,比如限制条件可能是右“墙”,就能装更高的水,
- }
+ }
else {
ans += rightMax - height[right]; //同理,考虑下标为right的元素
--right;
@@ -914,8 +991,103 @@ int trap(int* height, int heightSize) {
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
+### Rust:
+
+双指针
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn trap(height: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let n = height.len();
+ let mut max_left = vec![0; height.len()];
+ let mut max_right = vec![0; height.len()];
+ max_left.iter_mut().zip(max_right.iter_mut().rev()).enumerate().fold((0, 0), |(lm, rm), (idx, (x, y))| {
+ let lmax = lm.max(height[idx]);
+ let rmax = rm.max(height[n - 1 - idx]);
+ *x = lmax; *y = rmax;
+ (lmax, rmax)
+ });
+ height.iter().enumerate().fold(0, |acc, (idx, x)| {
+ let h = max_left[idx].min(max_right[idx]);
+ if h > 0 { h - x + acc } else { acc }
+ })
+ }
+}
+```
+
+单调栈
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn trap(height: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let mut stack = vec![];
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ for (right_pos, &right_h) in height.iter().enumerate() {
+ while !stack.is_empty() && height[*stack.last().unwrap()] <= right_h {
+ let mid_pos = stack.pop().unwrap();
+ if !stack.is_empty() {
+ let left_pos = *stack.last().unwrap();
+ let left_h = height[left_pos];
+ let top = std::cmp::min(left_h, right_h);
+ if top > height[mid_pos] {
+ ans += (top - height[mid_pos]) * (right_pos - left_pos - 1) as i32;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ stack.push(right_pos);
+ }
+ ans
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Rust
+
+双指针
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn trap(height: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let n = height.len();
+ let mut max_left = vec![0; height.len()];
+ let mut max_right = vec![0; height.len()];
+ max_left.iter_mut().zip(max_right.iter_mut().rev()).enumerate().fold((0, 0), |(lm, rm), (idx, (x, y))| {
+ let lmax = lm.max(height[idx]);
+ let rmax = rm.max(height[n - 1 - idx]);
+ *x = lmax; *y = rmax;
+ (lmax, rmax)
+ });
+ height.iter().enumerate().fold(0, |acc, (idx, x)| {
+ let h = max_left[idx].min(max_right[idx]);
+ if h > 0 { h - x + acc } else { acc }
+ })
+ }
+}
+```
+
+单调栈
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn trap(height: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let mut stack = vec![];
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ for (right_pos, &right_h) in height.iter().enumerate() {
+ while !stack.is_empty() && height[*stack.last().unwrap()] <= right_h {
+ let mid_pos = stack.pop().unwrap();
+ if !stack.is_empty() {
+ let left_pos = *stack.last().unwrap();
+ let left_h = height[left_pos];
+ let top = std::cmp::min(left_h, right_h);
+ if top > height[mid_pos] {
+ ans += (top - height[mid_pos]) * (right_pos - left_pos - 1) as i32;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ stack.push(right_pos);
+ }
+ ans
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d4f2e6ea78..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d4f2e6ea78..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+> 相对于[贪心算法:跳跃游戏](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/606_N9j8ACKCODoCbV1lSA)难了不少,做好心理准备!
-> 相对于[贪心算法:跳跃游戏](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/606_N9j8ACKCODoCbV1lSA)难了不少,做好心里准备!
-
-# 45.跳跃游戏II
+# 45.跳跃游戏 II
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/jump-game-ii/)
@@ -18,13 +15,17 @@
你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
示例:
-* 输入: [2,3,1,1,4]
-* 输出: 2
-* 解释: 跳到最后一个位置的最小跳跃数是 2。从下标为 0 跳到下标为 1 的位置,跳 1 步,然后跳 3 步到达数组的最后一个位置。
+
+- 输入: [2,3,1,1,4]
+- 输出: 2
+- 解释: 跳到最后一个位置的最小跳跃数是 2。从下标为 0 跳到下标为 1 的位置,跳 1 步,然后跳 3 步到达数组的最后一个位置。
说明:
假设你总是可以到达数组的最后一个位置。
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[贪心算法,最少跳几步还得看覆盖范围 | LeetCode: 45.跳跃游戏 II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y24y1r7XZ),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -32,13 +33,13 @@
但思路是相似的,还是要看最大覆盖范围。
-本题要计算最小步数,那么就要想清楚什么时候步数才一定要加一呢?
+本题要计算最少步数,那么就要想清楚什么时候步数才一定要加一呢?
-贪心的思路,局部最优:当前可移动距离尽可能多走,如果还没到终点,步数再加一。整体最优:一步尽可能多走,从而达到最小步数。
+贪心的思路,局部最优:当前可移动距离尽可能多走,如果还没到终点,步数再加一。整体最优:一步尽可能多走,从而达到最少步数。
思路虽然是这样,但在写代码的时候还不能真的能跳多远就跳多远,那样就不知道下一步最远能跳到哪里了。
-**所以真正解题的时候,要从覆盖范围出发,不管怎么跳,覆盖范围内一定是可以跳到的,以最小的步数增加覆盖范围,覆盖范围一旦覆盖了终点,得到的就是最小步数!**
+**所以真正解题的时候,要从覆盖范围出发,不管怎么跳,覆盖范围内一定是可以跳到的,以最小的步数增加覆盖范围,覆盖范围一旦覆盖了终点,得到的就是最少步数!**
**这里需要统计两个覆盖范围,当前这一步的最大覆盖和下一步最大覆盖**。
@@ -46,18 +47,18 @@
如图:
-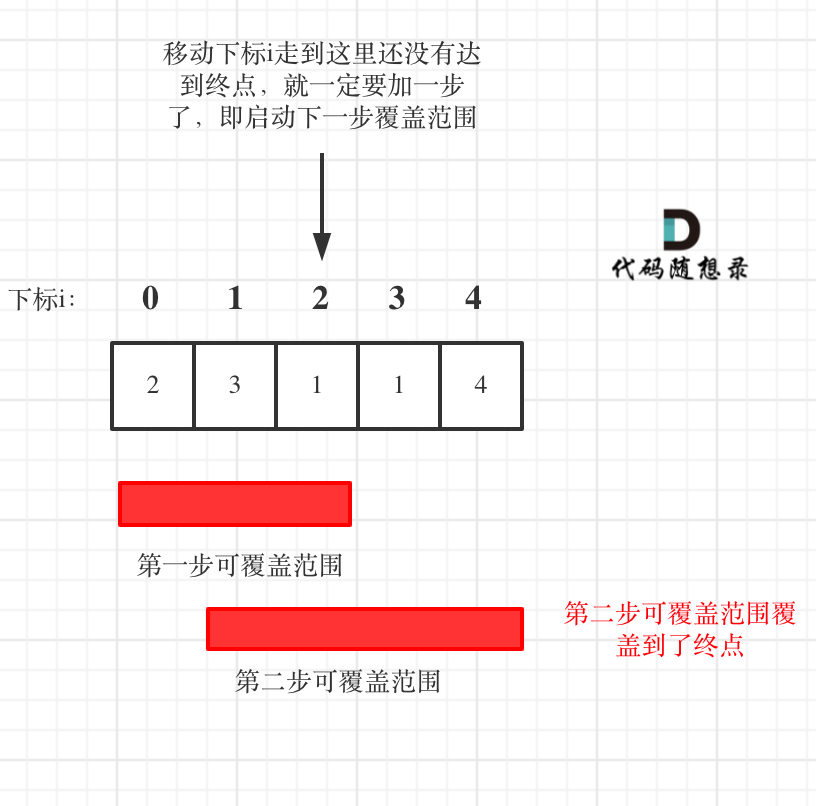
+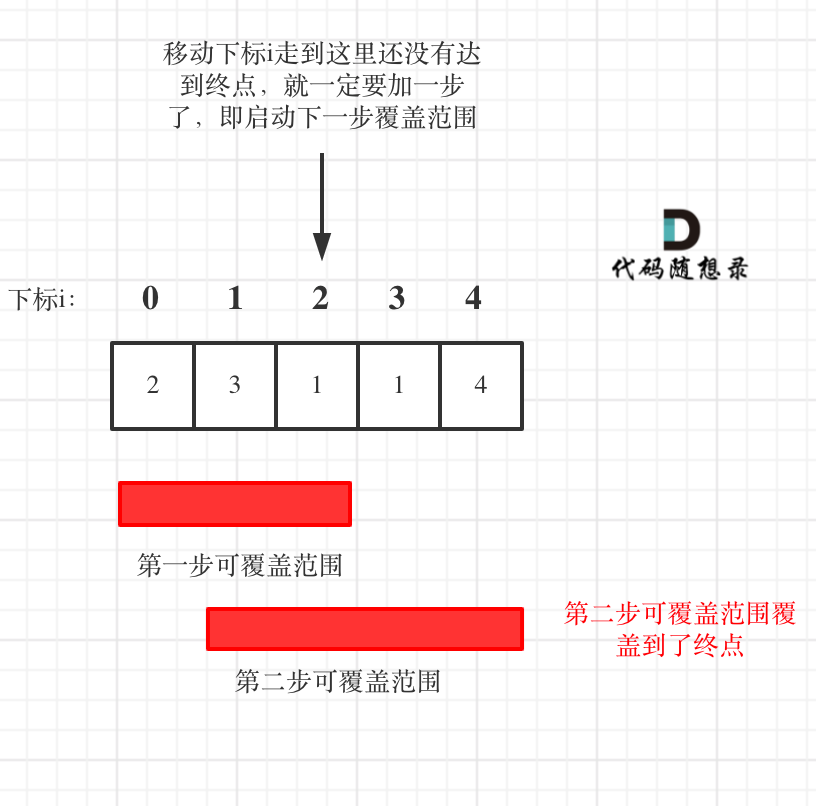
**图中覆盖范围的意义在于,只要红色的区域,最多两步一定可以到!(不用管具体怎么跳,反正一定可以跳到)**
-## 方法一
+### 方法一
从图中可以看出来,就是移动下标达到了当前覆盖的最远距离下标时,步数就要加一,来增加覆盖距离。最后的步数就是最少步数。
这里还是有个特殊情况需要考虑,当移动下标达到了当前覆盖的最远距离下标时
-* 如果当前覆盖最远距离下标不是是集合终点,步数就加一,还需要继续走。
-* 如果当前覆盖最远距离下标就是是集合终点,步数不用加一,因为不能再往后走了。
+- 如果当前覆盖最远距离下标不是是集合终点,步数就加一,还需要继续走。
+- 如果当前覆盖最远距离下标就是是集合终点,步数不用加一,因为不能再往后走了。
C++代码如下:(详细注释)
@@ -73,11 +74,9 @@ public:
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
nextDistance = max(nums[i] + i, nextDistance); // 更新下一步覆盖最远距离下标
if (i == curDistance) { // 遇到当前覆盖最远距离下标
- if (curDistance < nums.size() - 1) { // 如果当前覆盖最远距离下标不是终点
- ans++; // 需要走下一步
- curDistance = nextDistance; // 更新当前覆盖最远距离下标(相当于加油了)
- if (nextDistance >= nums.size() - 1) break; // 下一步的覆盖范围已经可以达到终点,结束循环
- } else break; // 当前覆盖最远距到达集合终点,不用做ans++操作了,直接结束
+ ans++; // 需要走下一步
+ curDistance = nextDistance; // 更新当前覆盖最远距离下标(相当于加油了)
+ if (nextDistance >= nums.size() - 1) break; // 当前覆盖最远距到达集合终点,不用做ans++操作了,直接结束
}
}
return ans;
@@ -85,22 +84,26 @@ public:
};
```
-## 方法二
+* 时间复杂度: O(n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(1)
+
+
+### 方法二
依然是贪心,思路和方法一差不多,代码可以简洁一些。
**针对于方法一的特殊情况,可以统一处理**,即:移动下标只要遇到当前覆盖最远距离的下标,直接步数加一,不考虑是不是终点的情况。
-想要达到这样的效果,只要让移动下标,最大只能移动到nums.size - 2的地方就可以了。
+想要达到这样的效果,只要让移动下标,最大只能移动到 nums.size - 2 的地方就可以了。
-因为当移动下标指向nums.size - 2时:
+因为当移动下标指向 nums.size - 2 时:
-* 如果移动下标等于当前覆盖最大距离下标, 需要再走一步(即ans++),因为最后一步一定是可以到的终点。(题目假设总是可以到达数组的最后一个位置),如图:
-
+- 如果移动下标等于当前覆盖最大距离下标, 需要再走一步(即 ans++),因为最后一步一定是可以到的终点。(题目假设总是可以到达数组的最后一个位置),如图:
+ 
-* 如果移动下标不等于当前覆盖最大距离下标,说明当前覆盖最远距离就可以直接达到终点了,不需要再走一步。如图:
+- 如果移动下标不等于当前覆盖最大距离下标,说明当前覆盖最远距离就可以直接达到终点了,不需要再走一步。如图:
-
+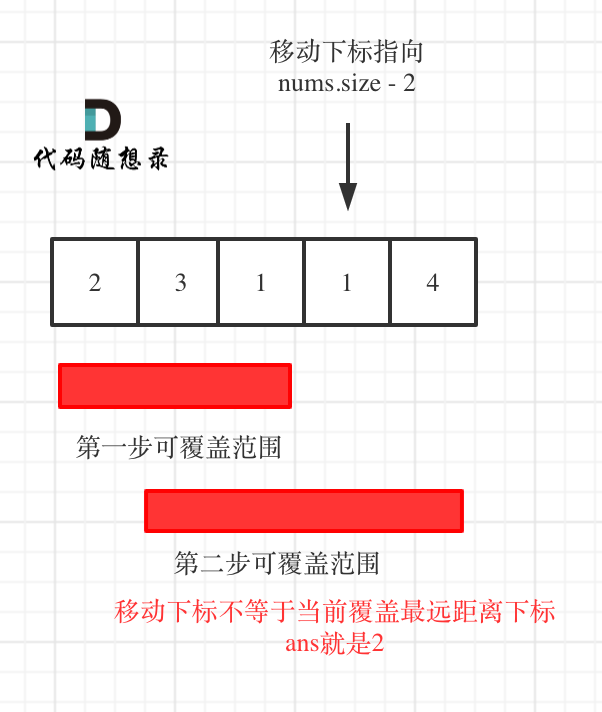
代码如下:
@@ -124,9 +127,14 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(1)
+
+
+
可以看出版本二的代码相对于版本一简化了不少!
-**其精髓在于控制移动下标i只移动到nums.size() - 2的位置**,所以移动下标只要遇到当前覆盖最远距离的下标,直接步数加一,不用考虑别的了。
+**其精髓在于控制移动下标 i 只移动到 nums.size() - 2 的位置**,所以移动下标只要遇到当前覆盖最远距离的下标,直接步数加一,不用考虑别的了。
## 总结
@@ -134,13 +142,12 @@ public:
但代码又十分简单,贪心就是这么巧妙。
-理解本题的关键在于:**以最小的步数增加最大的覆盖范围,直到覆盖范围覆盖了终点**,这个范围内最小步数一定可以跳到,不用管具体是怎么跳的,不纠结于一步究竟跳一个单位还是两个单位。
-
+理解本题的关键在于:**以最小的步数增加最大的覆盖范围,直到覆盖范围覆盖了终点**,这个范围内最少步数一定可以跳到,不用管具体是怎么跳的,不纠结于一步究竟跳一个单位还是两个单位。
## 其他语言版本
+### Java
-### Java
```Java
// 版本一
class Solution {
@@ -196,56 +203,114 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python
-
+贪心(版本一)
```python
class Solution:
- def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- if len(nums) == 1: return 0
- ans = 0
- curDistance = 0
- nextDistance = 0
+ def jump(self, nums):
+ if len(nums) == 1:
+ return 0
+
+ cur_distance = 0 # 当前覆盖最远距离下标
+ ans = 0 # 记录走的最大步数
+ next_distance = 0 # 下一步覆盖最远距离下标
+
for i in range(len(nums)):
- nextDistance = max(i + nums[i], nextDistance)
- if i == curDistance:
- if curDistance != len(nums) - 1:
- ans += 1
- curDistance = nextDistance
- if nextDistance >= len(nums) - 1: break
+ next_distance = max(nums[i] + i, next_distance) # 更新下一步覆盖最远距离下标
+ if i == cur_distance: # 遇到当前覆盖最远距离下标
+ ans += 1 # 需要走下一步
+ cur_distance = next_distance # 更新当前覆盖最远距离下标(相当于加油了)
+ if next_distance >= len(nums) - 1: # 当前覆盖最远距离达到数组末尾,不用再做ans++操作,直接结束
+ break
+
return ans
+
```
+贪心(版本二)
```python
-# 贪心版本二
class Solution:
- def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- if len(nums) == 1:
+ def jump(self, nums):
+ cur_distance = 0 # 当前覆盖的最远距离下标
+ ans = 0 # 记录走的最大步数
+ next_distance = 0 # 下一步覆盖的最远距离下标
+
+ for i in range(len(nums) - 1): # 注意这里是小于len(nums) - 1,这是关键所在
+ next_distance = max(nums[i] + i, next_distance) # 更新下一步覆盖的最远距离下标
+ if i == cur_distance: # 遇到当前覆盖的最远距离下标
+ cur_distance = next_distance # 更新当前覆盖的最远距离下标
+ ans += 1
+
+ return ans
+
+```
+贪心(版本三) 类似‘55-跳跃游戏’写法
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def jump(self, nums) -> int:
+ if len(nums)==1: # 如果数组只有一个元素,不需要跳跃,步数为0
return 0
- curDistance, nextDistance = 0, 0
- step = 0
- for i in range(len(nums)-1):
- nextDistance = max(nextDistance, nums[i]+i)
- if i == curDistance:
- curDistance = nextDistance
- step += 1
- return step
+
+ i = 0 # 当前位置
+ count = 0 # 步数计数器
+ cover = 0 # 当前能够覆盖的最远距离
+
+ while i <= cover: # 当前位置小于等于当前能够覆盖的最远距离时循环
+ for i in range(i, cover+1): # 遍历从当前位置到当前能够覆盖的最远距离之间的所有位置
+ cover = max(nums[i]+i, cover) # 更新当前能够覆盖的最远距离
+ if cover >= len(nums)-1: # 如果当前能够覆盖的最远距离达到或超过数组的最后一个位置,直接返回步数+1
+ return count+1
+ count += 1 # 每一轮遍历结束后,步数+1
+
+
```
+动态规划
```python
-# 动态规划做法
-class Solution:
+class Solution:
def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- result = [10**4+1]*len(nums)
- result[0]=0
- for i in range(len(nums)):
- for j in range(nums[i]+1):
- if i+j i32 {
- if a > b { a } else { b }
- }
pub fn jump(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- if nums.len() == 0 { return 0; }
- let mut cur_distance: i32 = 0;
- let mut ans: i32 = 0;
- let mut next_distance: i32 = 0;
- for i in 0..nums.len() {
- next_distance = Self::max(nums[i] + i as i32, next_distance);
- if i as i32 == cur_distance {
- if cur_distance != (nums.len() - 1) as i32 {
+ if nums.len() == 1 {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ let mut cur_distance = 0;
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut next_distance = 0;
+ for (i, &n) in nums.iter().enumerate().take(nums.len() - 1) {
+ next_distance = (n as usize + i).max(next_distance);
+ if i == cur_distance {
+ if cur_distance < nums.len() - 1 {
ans += 1;
cur_distance = next_distance;
- if next_distance == (nums.len() - 1) as i32 { break; }
+ if next_distance >= nums.len() - 1 {
+ break;
+ };
+ } else {
+ break;
}
- else { break; }
}
}
ans
@@ -405,16 +472,16 @@ impl Solution {
```Rust
//版本二
impl Solution {
- fn max(a: i32, b:i32) -> i32 {
- if a > b { a } else { b }
- }
pub fn jump(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let mut cur_distance: i32 = 0;
- let mut ans: i32 = 0;
- let mut next_distance: i32 = 0;
- for i in 0..nums.len() - 1 {
- next_distance = Self::max(nums[i] + i as i32, next_distance);
- if i as i32 == cur_distance {
+ if nums.len() == 1 {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ let mut cur_distance = 0;
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut next_distance = 0;
+ for (i, &n) in nums.iter().enumerate().take(nums.len() - 1) {
+ next_distance = (n as usize + i).max(next_distance);
+ if i == cur_distance {
cur_distance = next_distance;
ans += 1;
}
@@ -423,9 +490,53 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int jump(int* nums, int numsSize) {
+ if(numsSize == 1){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int count = 0;
+ // 记录当前能走的最远距离
+ int curDistance = 0;
+ // 记录下一步能走的最远距离
+ int nextDistance = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++){
+ nextDistance = max(i + nums[i], nextDistance);
+ // 下标到了当前的最大距离
+ if(i == nextDistance){
+ count++;
+ curDistance = nextDistance;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+### C#
+
+```csharp
+// 版本二
+public class Solution
+{
+ public int Jump(int[] nums)
+ {
+ int cur = 0, next = 0, step = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length - 1; i++)
+ {
+ next = Math.Max(next, i + nums[i]);
+ if (i == cur)
+ {
+ cur = next;
+ step++;
+ }
+ }
+ return step;
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 86bc704d4b..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 86bc704d4b..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 46.全排列
@@ -24,9 +22,9 @@
]
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[组合与排列的区别,回溯算法求解的时候,有何不同?| LeetCode:46.全排列](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19v4y1S79W/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[组合与排列的区别,回溯算法求解的时候,有何不同?| LeetCode:46.全排列](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19v4y1S79W/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -42,7 +40,8 @@
我以[1,2,3]为例,抽象成树形结构如下:
-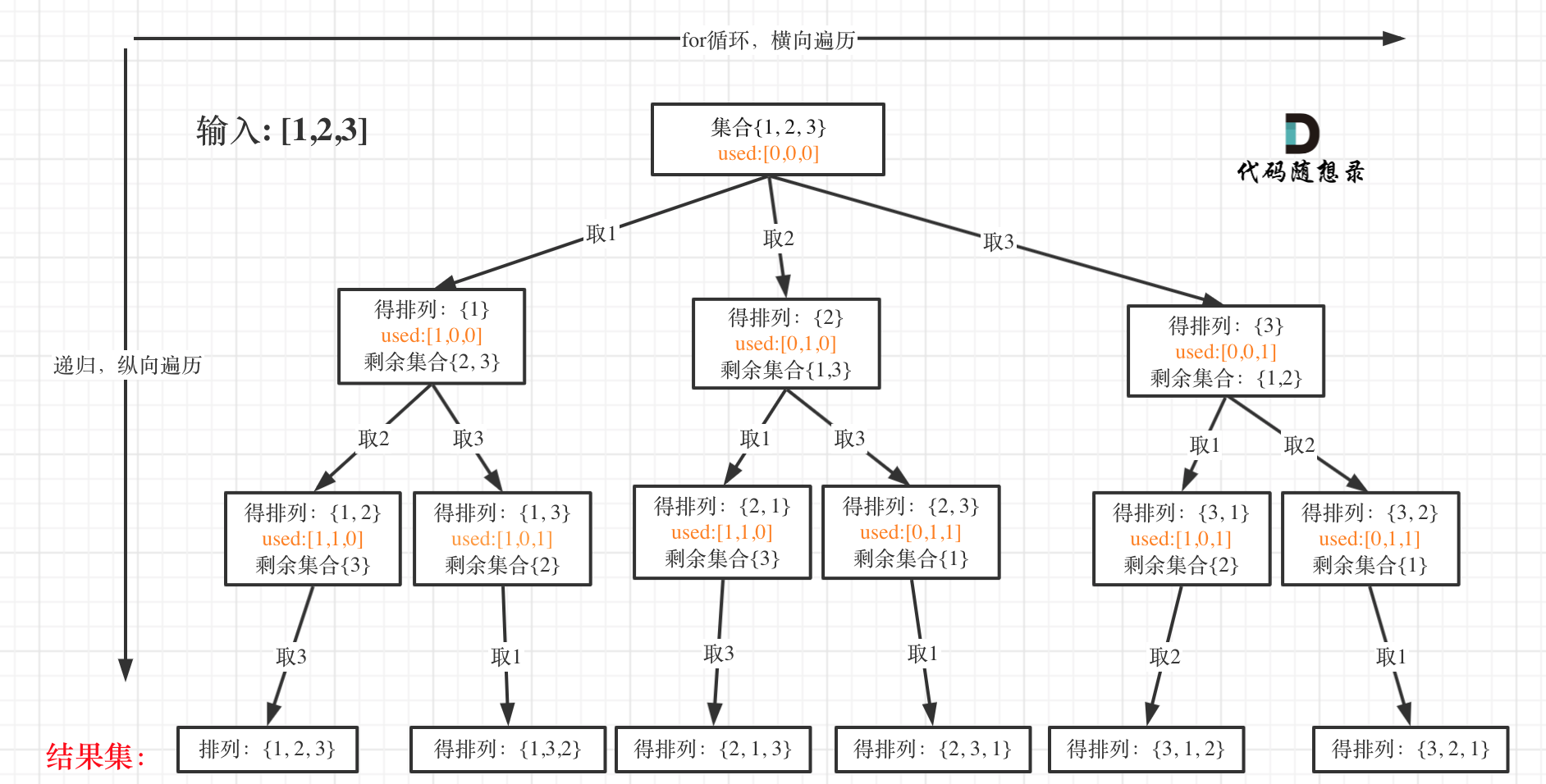
+
+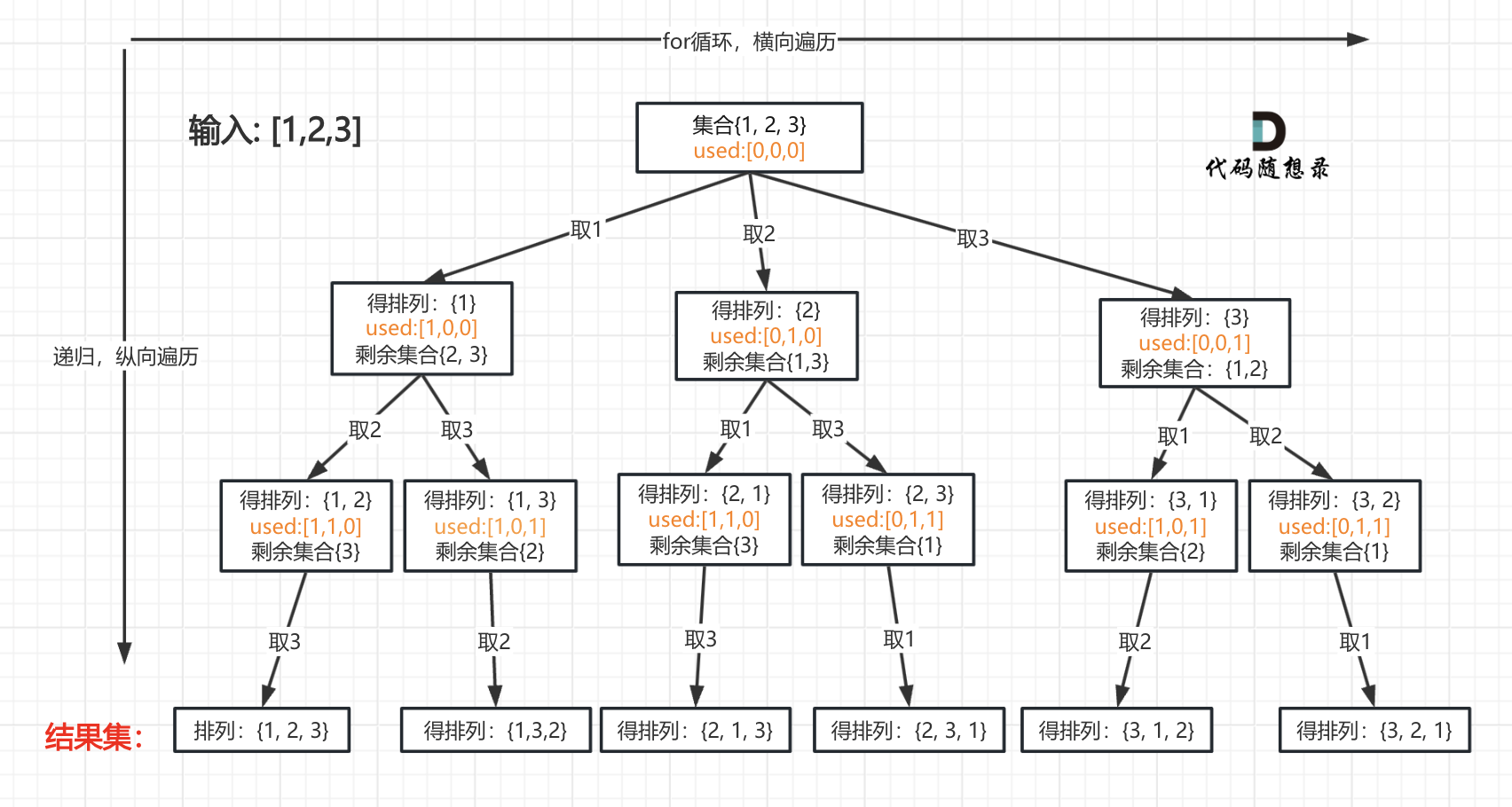
### 回溯三部曲
@@ -54,7 +53,7 @@
但排列问题需要一个used数组,标记已经选择的元素,如图橘黄色部分所示:
-
+
代码如下:
@@ -66,7 +65,7 @@ void backtracking (vector& nums, vector& used)
* 递归终止条件
-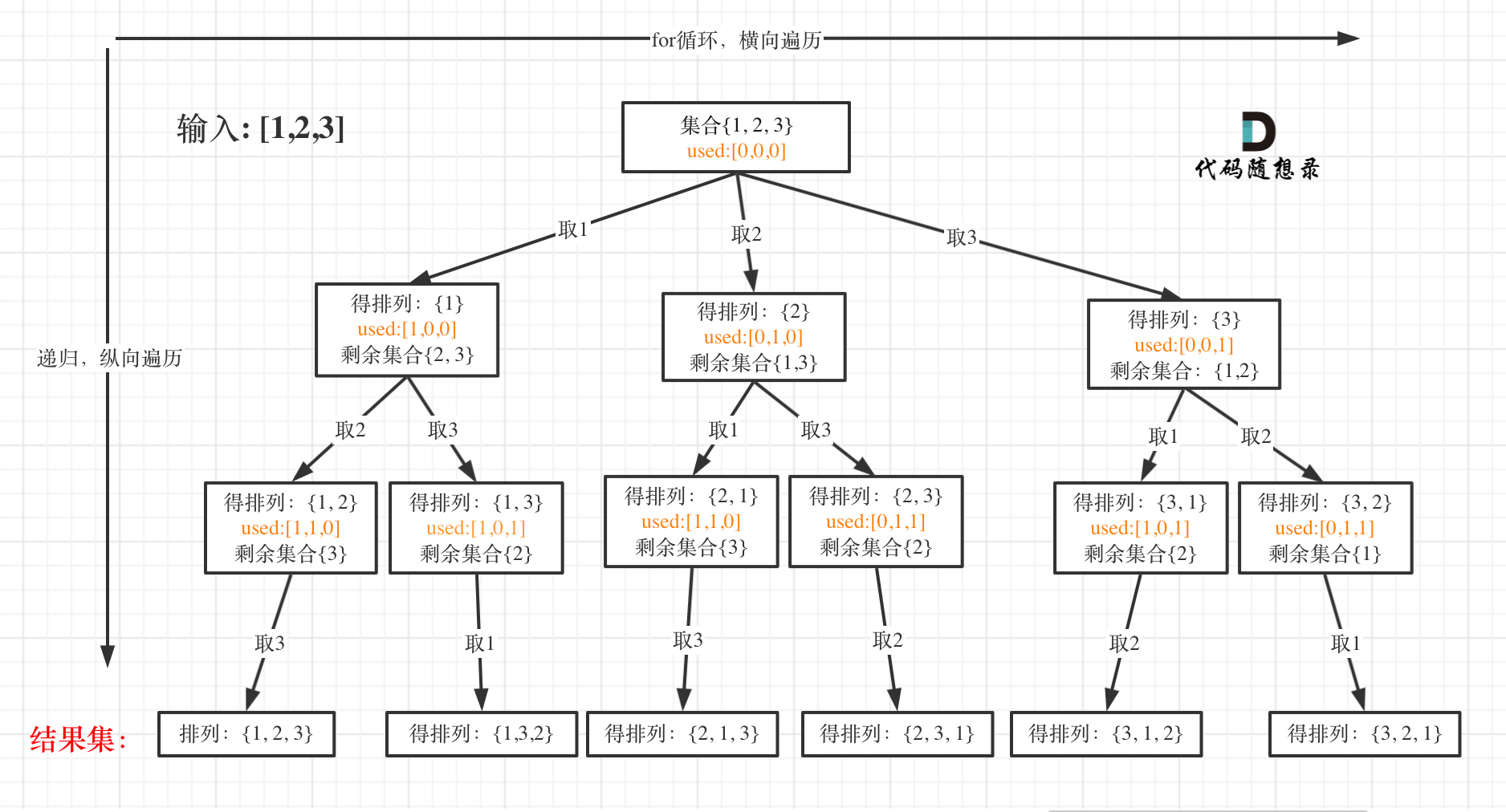
+
可以看出叶子节点,就是收割结果的地方。
@@ -136,6 +135,8 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n!)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
## 总结
@@ -198,6 +199,7 @@ class Solution {
public void backtrack(int[] nums, LinkedList path) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
+ return;
}
for (int i =0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果path中已有,则跳过
@@ -213,68 +215,27 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python
-**回溯**
+回溯 使用used
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.path = []
- self.paths = []
-
- def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
- '''
- 因为本题排列是有序的,这意味着同一层的元素可以重复使用,但同一树枝上不能重复使用(usage_list)
- 所以处理排列问题每层都需要从头搜索,故不再使用start_index
- '''
- usage_list = [False] * len(nums)
- self.backtracking(nums, usage_list)
- return self.paths
-
- def backtracking(self, nums: List[int], usage_list: List[bool]) -> None:
- # Base Case本题求叶子节点
- if len(self.path) == len(nums):
- self.paths.append(self.path[:])
+ def permute(self, nums):
+ result = []
+ self.backtracking(nums, [], [False] * len(nums), result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, nums, path, used, result):
+ if len(path) == len(nums):
+ result.append(path[:])
return
-
- # 单层递归逻辑
- for i in range(0, len(nums)): # 从头开始搜索
- # 若遇到self.path里已收录的元素,跳过
- if usage_list[i] == True:
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ if used[i]:
continue
- usage_list[i] = True
- self.path.append(nums[i])
- self.backtracking(nums, usage_list) # 纵向传递使用信息,去重
- self.path.pop()
- usage_list[i] = False
-```
-**回溯+丢掉usage_list**
-```python
-class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.path = []
- self.paths = []
-
- def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
- '''
- 因为本题排列是有序的,这意味着同一层的元素可以重复使用,但同一树枝上不能重复使用
- 所以处理排列问题每层都需要从头搜索,故不再使用start_index
- '''
- self.backtracking(nums)
- return self.paths
-
- def backtracking(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
- # Base Case本题求叶子节点
- if len(self.path) == len(nums):
- self.paths.append(self.path[:])
- return
+ used[i] = True
+ path.append(nums[i])
+ self.backtracking(nums, path, used, result)
+ path.pop()
+ used[i] = False
- # 单层递归逻辑
- for i in range(0, len(nums)): # 从头开始搜索
- # 若遇到self.path里已收录的元素,跳过
- if nums[i] in self.path:
- continue
- self.path.append(nums[i])
- self.backtracking(nums)
- self.path.pop()
```
### Go
@@ -309,7 +270,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, cur int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```js
@@ -525,8 +486,37 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> Permute(int[] nums)
+ {
+ var used = new bool[nums.Length];
+ BackTracking(nums, used);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int[] nums, bool[] used)
+ {
+ if (path.Count == nums.Length)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
+ {
+ if (used[i]) continue;
+ used[i] = true;
+ path.Add(nums[i]);
+ BackTracking(nums, used);
+ used[i] = false;
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3eb99948ea..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3eb99948ea..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
# 47.全排列 II
@@ -12,23 +12,26 @@
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例 1:
+
* 输入:nums = [1,1,2]
* 输出:
-[[1,1,2],
- [1,2,1],
- [2,1,1]]
+ [[1,1,2],
+ [1,2,1],
+ [2,1,1]]
示例 2:
+
* 输入:nums = [1,2,3]
* 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
提示:
+
* 1 <= nums.length <= 8
* -10 <= nums[i] <= 10
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[回溯算法求解全排列,如何去重?| LeetCode:47.全排列 II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1R84y1i7Tm/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[回溯算法求解全排列,如何去重?| LeetCode:47.全排列 II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1R84y1i7Tm/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -45,7 +48,7 @@
我以示例中的 [1,1,2]为例 (为了方便举例,已经排序)抽象为一棵树,去重过程如图:
-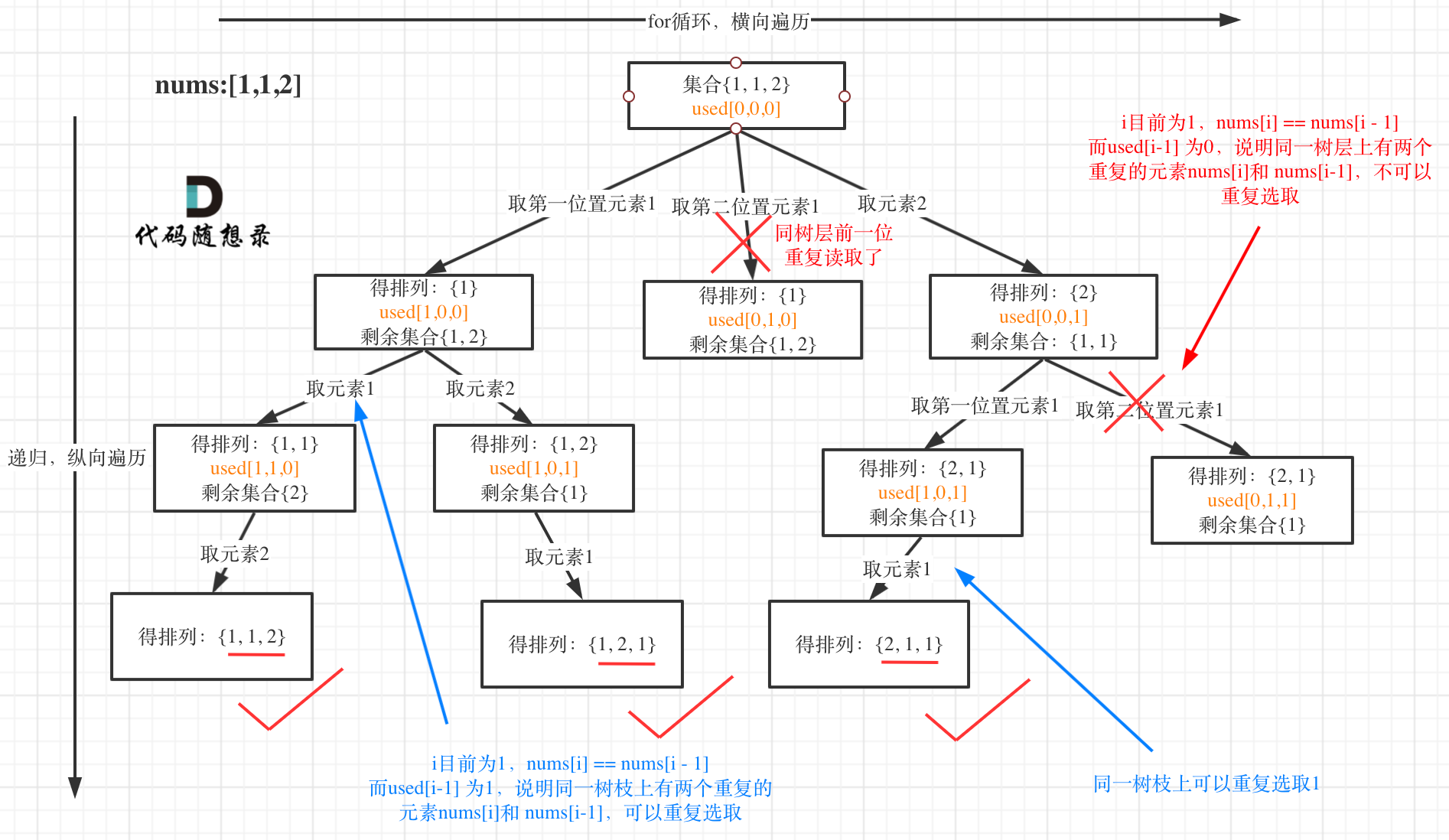
+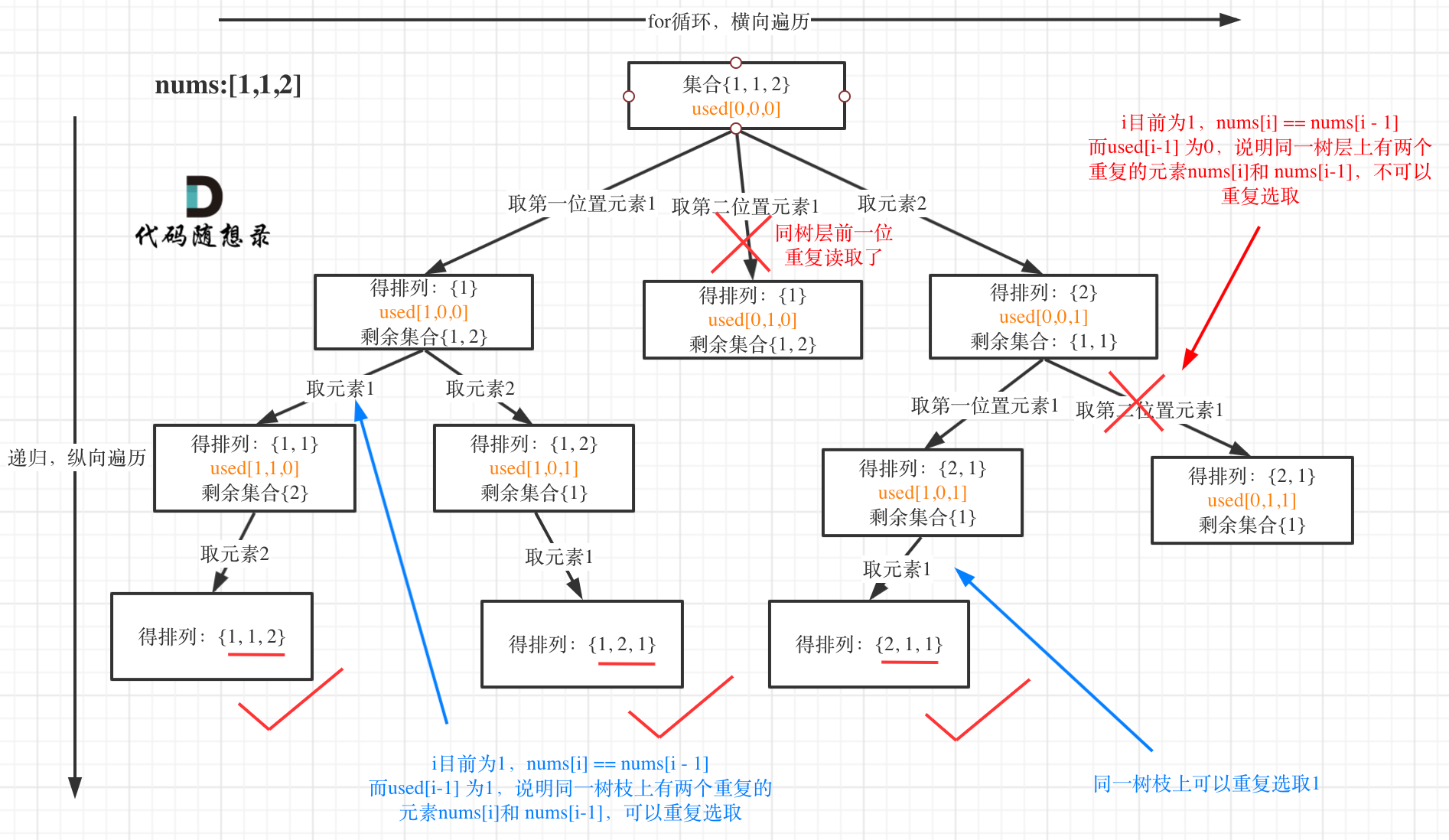
图中我们对同一树层,前一位(也就是nums[i-1])如果使用过,那么就进行去重。
@@ -53,7 +56,7 @@
在[46.全排列](https://programmercarl.com/0046.全排列.html)中已经详细讲解了排列问题的写法,在[40.组合总和II](https://programmercarl.com/0040.组合总和II.html) 、[90.子集II](https://programmercarl.com/0090.子集II.html)中详细讲解了去重的写法,所以这次我就不用回溯三部曲分析了,直接给出代码,如下:
-## C++代码
+
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -68,7 +71,7 @@ private:
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝nums[i - 1]使用过
- // used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层nums[i - 1]使用过
+ // used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层nums[i - 1]使用过
// 如果同一树层nums[i - 1]使用过则直接跳过
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
@@ -93,7 +96,11 @@ public:
}
};
+// 时间复杂度: 最差情况所有元素都是唯一的。复杂度和全排列1都是 O(n! * n) 对于 n 个元素一共有 n! 中排列方案。而对于每一个答案,我们需要 O(n) 去复制最终放到 result 数组
+// 空间复杂度: O(n) 回溯树的深度取决于我们有多少个元素
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n! * n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
## 拓展
@@ -123,23 +130,26 @@ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == true) {
树层上去重(used[i - 1] == false),的树形结构如下:
-
+
树枝上去重(used[i - 1] == true)的树型结构如下:
-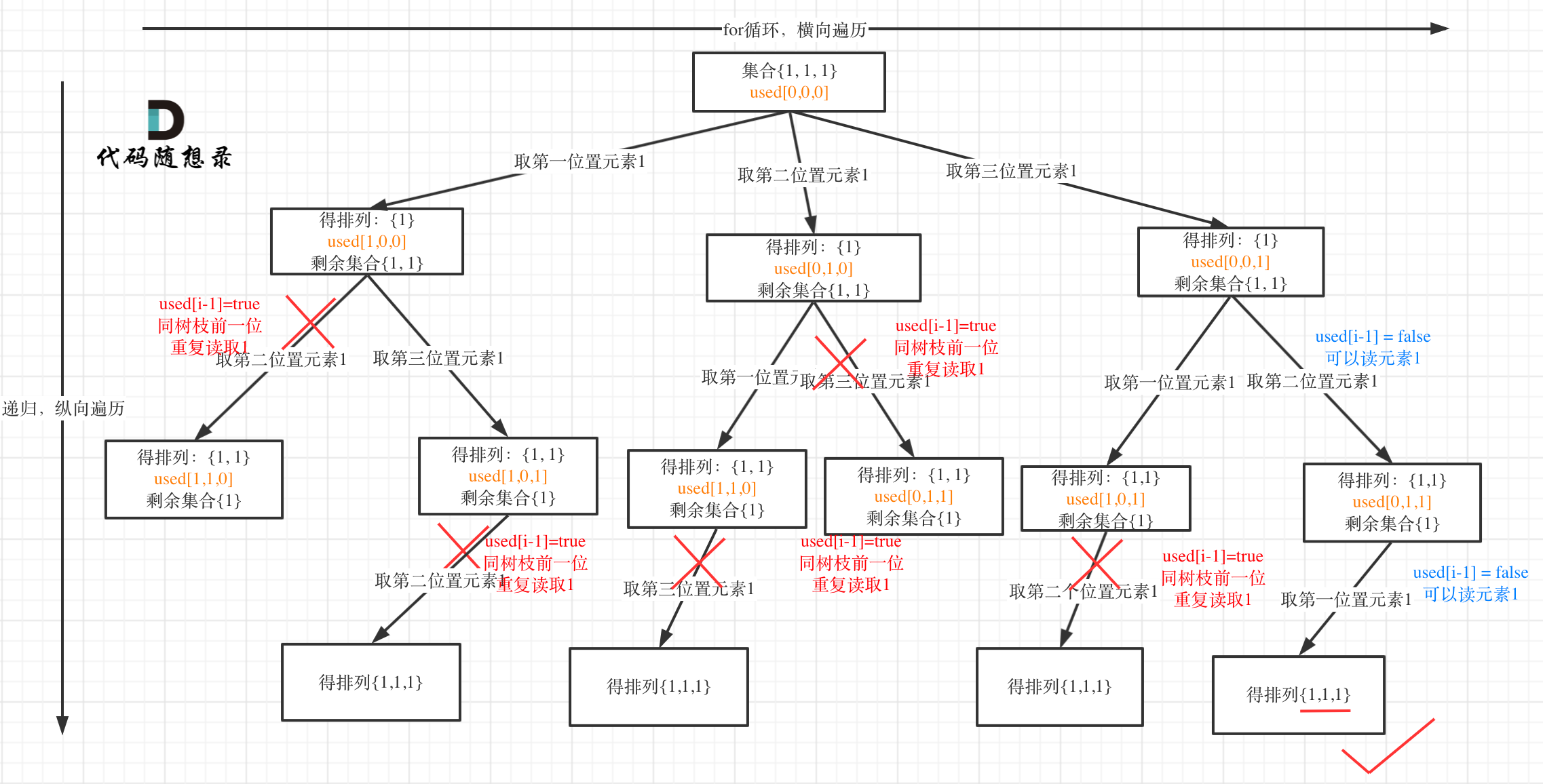
+
大家应该很清晰的看到,树层上对前一位去重非常彻底,效率很高,树枝上对前一位去重虽然最后可以得到答案,但是做了很多无用搜索。
## 总结
这道题其实还是用了我们之前讲过的去重思路,但有意思的是,去重的代码中,这么写:
+
```cpp
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
```
+
和这么写:
+
```cpp
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == true) {
continue;
@@ -150,11 +160,24 @@ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == true) {
所以我通过举[1,1,1]的例子,把这两个去重的逻辑分别抽象成树形结构,大家可以一目了然:为什么两种写法都可以以及哪一种效率更高!
+这里可能大家又有疑惑,既然 `used[i - 1] == false`也行而`used[i - 1] == true`也行,那为什么还要写这个条件呢?
+
+直接这样写 不就完事了?
+
+```cpp
+if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
+ continue;
+}
+```
+
+其实并不行,一定要加上 `used[i - 1] == false`或者`used[i - 1] == true`,因为 used[i - 1] 要一直是 true 或者一直是false 才可以,而不是 一会是true 一会又是false。 所以这个条件要写上。
+
+
是不是豁然开朗了!!
## 其他语言版本
-### java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -196,35 +219,32 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-### python
+Python
```python
class Solution:
- def permuteUnique(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
- # res用来存放结果
- if not nums: return []
- res = []
- used = [0] * len(nums)
- def backtracking(nums, used, path):
- # 终止条件
- if len(path) == len(nums):
- res.append(path.copy())
- return
- for i in range(len(nums)):
- if not used[i]:
- if i>0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and not used[i-1]:
- continue
- used[i] = 1
- path.append(nums[i])
- backtracking(nums, used, path)
- path.pop()
- used[i] = 0
- # 记得给nums排序
- backtracking(sorted(nums),used,[])
- return res
+ def permuteUnique(self, nums):
+ nums.sort() # 排序
+ result = []
+ self.backtracking(nums, [], [False] * len(nums), result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, nums, path, used, result):
+ if len(path) == len(nums):
+ result.append(path[:])
+ return
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ if (i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1] and not used[i - 1]) or used[i]:
+ continue
+ used[i] = True
+ path.append(nums[i])
+ self.backtracking(nums, path, used, result)
+ path.pop()
+ used[i] = False
+
```
-### Go
+### Go
```go
var (
@@ -261,10 +281,9 @@ func dfs(nums []int, cur int) {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
-
var permuteUnique = function (nums) {
nums.sort((a, b) => {
return a - b
@@ -392,6 +411,7 @@ impl Solution {
```
### C
+
```c
//临时数组
int *path;
@@ -483,7 +503,7 @@ object Solution {
// 当前索引为0,不存在和前一个数字相等可以进入回溯
// 当前索引值和上一个索引不相等,可以回溯
// 前一个索引对应的值没有被选,可以回溯
- // 因为Scala没有continue,只能将逻辑反过来写
+ // 因为Scala没有continue,只能将逻辑反过来写
if (i == 0 || (i > 0 && num(i) != num(i - 1)) || used(i-1) == false) {
used(i) = true
path.append(num(i))
@@ -499,8 +519,37 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public List> res = new List>();
+ public List path = new List();
+ public IList> PermuteUnique(int[] nums)
+ {
+ Array.Sort(nums);
+ BackTracking(nums, new bool[nums.Length]);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int[] nums, bool[] used)
+ {
+ if (nums.Length == path.Count)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
+ {
+ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) continue;
+ if (used[i]) continue;
+ path.Add(nums[i]);
+ used[i] = true;
+ BackTracking(nums, used);
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ used[i] = false;
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 624452fd2c..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 624452fd2c..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 51. N皇后
@@ -17,7 +15,7 @@ n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,
示例 1:
-
+
* 输入:n = 4
* 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
@@ -28,9 +26,9 @@ n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,
* 输入:n = 1
* 输出:[["Q"]]
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[这就是传说中的N皇后? 回溯算法安排!| LeetCode:51.N皇后](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Rd4y1c7Bq/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[这就是传说中的N皇后? 回溯算法安排!| LeetCode:51.N皇后](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Rd4y1c7Bq/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -47,7 +45,7 @@ n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,
下面我用一个 3 * 3 的棋盘,将搜索过程抽象为一棵树,如图:
-
+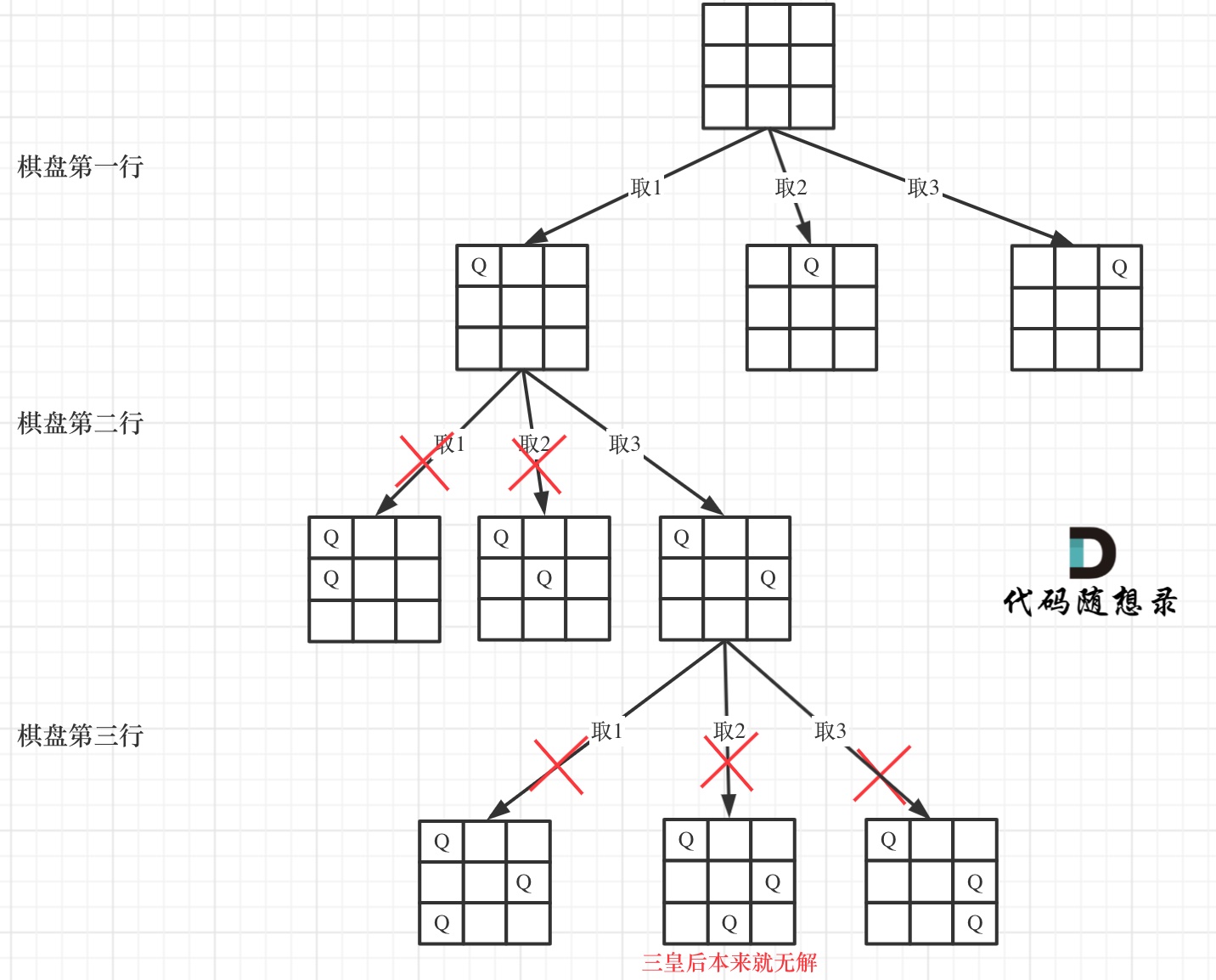
从图中,可以看出,二维矩阵中矩阵的高就是这棵树的高度,矩阵的宽就是树形结构中每一个节点的宽度。
@@ -87,7 +85,7 @@ void backtracking(int n, int row, vector& chessboard) {
* 递归终止条件
在如下树形结构中:
-
+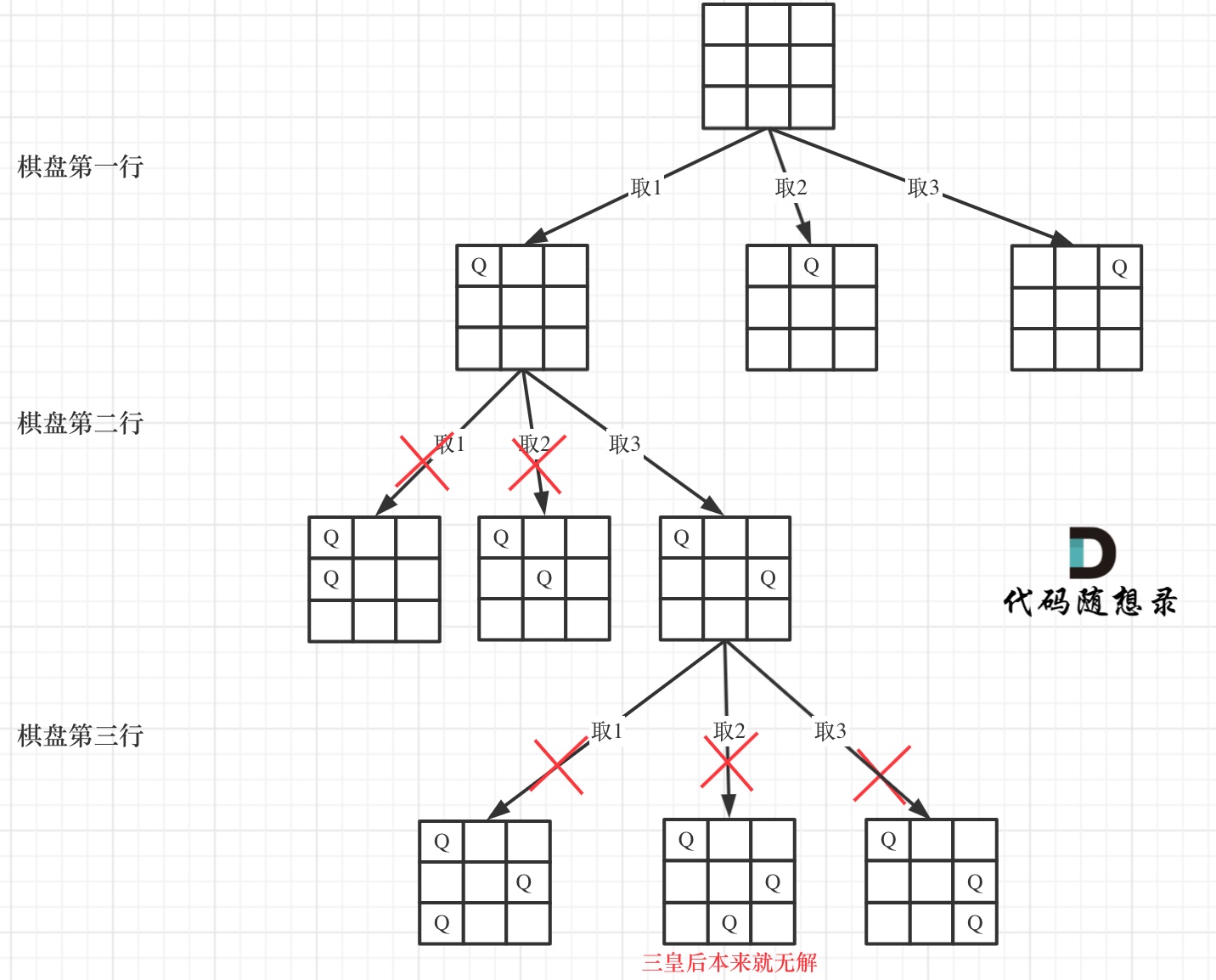
可以看出,当递归到棋盘最底层(也就是叶子节点)的时候,就可以收集结果并返回了。
@@ -208,6 +206,9 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n!)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
+
可以看出,除了验证棋盘合法性的代码,省下来部分就是按照回溯法模板来的。
@@ -348,48 +349,47 @@ class Solution {
```python
class Solution:
def solveNQueens(self, n: int) -> List[List[str]]:
- if not n: return []
- board = [['.'] * n for _ in range(n)]
- res = []
- def isVaild(board,row, col):
- #判断同一列是否冲突
- for i in range(len(board)):
- if board[i][col] == 'Q':
- return False
- # 判断左上角是否冲突
- i = row -1
- j = col -1
- while i>=0 and j>=0:
- if board[i][j] == 'Q':
- return False
- i -= 1
- j -= 1
- # 判断右上角是否冲突
- i = row - 1
- j = col + 1
- while i>=0 and j < len(board):
- if board[i][j] == 'Q':
- return False
- i -= 1
- j += 1
- return True
-
- def backtracking(board, row, n):
- # 如果走到最后一行,说明已经找到一个解
- if row == n:
- temp_res = []
- for temp in board:
- temp_str = "".join(temp)
- temp_res.append(temp_str)
- res.append(temp_res)
- for col in range(n):
- if not isVaild(board, row, col):
- continue
- board[row][col] = 'Q'
- backtracking(board, row+1, n)
- board[row][col] = '.'
- backtracking(board, 0, n)
- return res
+ result = [] # 存储最终结果的二维字符串数组
+
+ chessboard = ['.' * n for _ in range(n)] # 初始化棋盘
+ self.backtracking(n, 0, chessboard, result) # 回溯求解
+ return [[''.join(row) for row in solution] for solution in result] # 返回结果集
+
+ def backtracking(self, n: int, row: int, chessboard: List[str], result: List[List[str]]) -> None:
+ if row == n:
+ result.append(chessboard[:]) # 棋盘填满,将当前解加入结果集
+ return
+
+ for col in range(n):
+ if self.isValid(row, col, chessboard):
+ chessboard[row] = chessboard[row][:col] + 'Q' + chessboard[row][col+1:] # 放置皇后
+ self.backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard, result) # 递归到下一行
+ chessboard[row] = chessboard[row][:col] + '.' + chessboard[row][col+1:] # 回溯,撤销当前位置的皇后
+
+ def isValid(self, row: int, col: int, chessboard: List[str]) -> bool:
+ # 检查列
+ for i in range(row):
+ if chessboard[i][col] == 'Q':
+ return False # 当前列已经存在皇后,不合法
+
+ # 检查 45 度角是否有皇后
+ i, j = row - 1, col - 1
+ while i >= 0 and j >= 0:
+ if chessboard[i][j] == 'Q':
+ return False # 左上方向已经存在皇后,不合法
+ i -= 1
+ j -= 1
+
+ # 检查 135 度角是否有皇后
+ i, j = row - 1, col + 1
+ while i >= 0 and j < len(chessboard):
+ if chessboard[i][j] == 'Q':
+ return False # 右上方向已经存在皇后,不合法
+ i -= 1
+ j += 1
+
+ return True # 当前位置合法
+
```
@@ -449,62 +449,68 @@ func isValid(n, row, col int, chessboard [][]string) bool {
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
-var solveNQueens = function(n) {
- function isValid(row, col, chessBoard, n) {
-
- for(let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
- if(chessBoard[i][col] === 'Q') {
- return false
- }
- }
-
- for(let i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
- if(chessBoard[i][j] === 'Q') {
- return false
- }
- }
-
- for(let i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
- if(chessBoard[i][j] === 'Q') {
- return false
- }
- }
- return true
- }
-
- function transformChessBoard(chessBoard) {
- let chessBoardBack = []
- chessBoard.forEach(row => {
- let rowStr = ''
- row.forEach(value => {
- rowStr += value
- })
- chessBoardBack.push(rowStr)
- })
-
- return chessBoardBack
- }
-
- let result = []
- function backtracing(row,chessBoard) {
- if(row === n) {
- result.push(transformChessBoard(chessBoard))
- return
- }
- for(let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
- if(isValid(row, col, chessBoard, n)) {
- chessBoard[row][col] = 'Q'
- backtracing(row + 1,chessBoard)
- chessBoard[row][col] = '.'
- }
- }
- }
- let chessBoard = new Array(n).fill([]).map(() => new Array(n).fill('.'))
- backtracing(0,chessBoard)
- return result
-
+/**
+ * @param {number} n
+ * @return {string[][]}
+ */
+var solveNQueens = function (n) {
+ const ans = [];
+ const path = [];
+ const matrix = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill("."));
+ // 判断是否能相互攻击
+ const canAttack = (matrix, row, col) => {
+ let i;
+ let j;
+ // 判断正上方和正下方是否有皇后
+ for (i = 0, j = col; i < n; i++) {
+ if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ // 判断正左边和正右边是否有皇后
+ for (i = row, j = 0; j < n; j++) {
+ if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ // 判断左上方是否有皇后
+ for (i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
+ if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ // 判断右上方是否有皇后
+ for (i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
+ if (matrix[i][j] === "Q") {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ };
+ const backtrack = (matrix, row, col) => {
+ if (path.length === matrix.length) {
+ ans.push(path.slice());
+ return;
+ }
+ for (let i = row; i < matrix.length; i++) {
+ for (let j = col; j < matrix.length; j++) {
+ // 当前位置会导致互相攻击 继续下一轮搜索
+ if (canAttack(matrix, i, j)) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ matrix[i][j] = "Q";
+ path.push(matrix[i].join(""));
+ // 另起一行搜索 同一行只能有一个皇后
+ backtrack(matrix, i + 1, 0);
+ matrix[i][j] = ".";
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ }
+ };
+ backtrack(matrix, 0, 0);
+ return ans;
};
```
@@ -857,8 +863,59 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public List> res = new();
+ public IList> SolveNQueens(int n)
+ {
+ char[][] chessBoard = new char[n][];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
+ {
+ chessBoard[i] = new char[n];
+ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
+ {
+ chessBoard[i][j] = '.';
+ }
+ }
+ BackTracking(n, 0, chessBoard);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int n, int row, char[][] chessBoard)
+ {
+ if (row == n)
+ {
+ res.Add(chessBoard.Select(x => new string(x)).ToList());
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
+ {
+ if (IsValid(row, col, chessBoard, n))
+ {
+ chessBoard[row][col] = 'Q';
+ BackTracking(n, row + 1, chessBoard);
+ chessBoard[row][col] = '.';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ public bool IsValid(int row, int col, char[][] chessBoard, int n)
+ {
+ for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
+ {
+ if (chessBoard[i][col] == 'Q') return false;
+ }
+ for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
+ {
+ if (chessBoard[i][j] == 'Q') return false;
+ }
+ for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++)
+ {
+ if (chessBoard[i][j] == 'Q') return false;
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c88fb3c7b..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c88fb3c7b..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -13,7 +11,9 @@
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
上图为 8 皇后问题的一种解法。
-
+
+
+
给定一个整数 n,返回 n 皇后不同的解决方案的数量。
@@ -41,13 +41,11 @@ n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并
".Q.."]
]
-# 思路
+## 思路
详看:[51.N皇后](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lU_QwCMj6g60nh8m98GAWg) ,基本没有区别
-# C++代码
-
```CPP
class Solution {
private:
@@ -98,8 +96,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言补充
-JavaScript
+## 其他语言补充
+### JavaScript
+
```javascript
var totalNQueens = function(n) {
let count = 0;
@@ -144,7 +143,7 @@ var totalNQueens = function(n) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript
```typescript
// 0-该格为空,1-该格有皇后
@@ -197,7 +196,7 @@ function checkValid(chess: GridStatus[][], i: number, j: number, n: number): boo
}
```
-C
+### C
```c
//path[i]为在i行,path[i]列上存在皇后
@@ -256,7 +255,8 @@ int totalNQueens(int n){
return answer;
}
```
-Java
+### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
int count = 0;
@@ -304,8 +304,4 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14017f9899..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14017f9899..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 53. 最大子序和
@@ -12,17 +9,21 @@
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
示例:
-* 输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
-* 输出: 6
-* 解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
+- 输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
+- 输出: 6
+- 解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
-## 暴力解法
+## 算法公开课
-暴力解法的思路,第一层for 就是设置起始位置,第二层for循环遍历数组寻找最大值
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[贪心算法的巧妙需要慢慢体会!LeetCode:53. 最大子序和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1aY4y1Z7ya),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+## 思路
+
+### 暴力解法
+
+暴力解法的思路,第一层 for 就是设置起始位置,第二层 for 循环遍历数组寻找最大值
-* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
-* 空间复杂度:O(1)
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -41,14 +42,17 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
+* 空间复杂度:O(1)
-以上暴力的解法C++勉强可以过,其他语言就不确定了。
-## 贪心解法
+以上暴力的解法 C++勉强可以过,其他语言就不确定了。
+
+### 贪心解法
**贪心贪的是哪里呢?**
-如果 -2 1 在一起,计算起点的时候,一定是从1开始计算,因为负数只会拉低总和,这就是贪心贪的地方!
+如果 -2 1 在一起,计算起点的时候,一定是从 1 开始计算,因为负数只会拉低总和,这就是贪心贪的地方!
局部最优:当前“连续和”为负数的时候立刻放弃,从下一个元素重新计算“连续和”,因为负数加上下一个元素 “连续和”只会越来越小。
@@ -56,29 +60,27 @@ public:
**局部最优的情况下,并记录最大的“连续和”,可以推出全局最优**。
-
-从代码角度上来讲:遍历nums,从头开始用count累积,如果count一旦加上nums[i]变为负数,那么就应该从nums[i+1]开始从0累积count了,因为已经变为负数的count,只会拖累总和。
+从代码角度上来讲:遍历 nums,从头开始用 count 累积,如果 count 一旦加上 nums[i]变为负数,那么就应该从 nums[i+1]开始从 0 累积 count 了,因为已经变为负数的 count,只会拖累总和。
**这相当于是暴力解法中的不断调整最大子序和区间的起始位置**。
-
**那有同学问了,区间终止位置不用调整么? 如何才能得到最大“连续和”呢?**
-区间的终止位置,其实就是如果count取到最大值了,及时记录下来了。例如如下代码:
+区间的终止位置,其实就是如果 count 取到最大值了,及时记录下来了。例如如下代码:
```
if (count > result) result = count;
```
-**这样相当于是用result记录最大子序和区间和(变相的算是调整了终止位置)**。
+**这样相当于是用 result 记录最大子序和区间和(变相的算是调整了终止位置)**。
如动画所示:
-
+
-红色的起始位置就是贪心每次取count为正数的时候,开始一个区间的统计。
+红色的起始位置就是贪心每次取 count 为正数的时候,开始一个区间的统计。
-那么不难写出如下C++代码(关键地方已经注释)
+那么不难写出如下 C++代码(关键地方已经注释)
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -97,39 +99,34 @@ public:
}
};
```
-
-* 时间复杂度:O(n)
-* 空间复杂度:O(1)
+- 时间复杂度:O(n)
+- 空间复杂度:O(1)
当然题目没有说如果数组为空,应该返回什么,所以数组为空的话返回啥都可以了。
+### 常见误区
-## 常见误区
-
-误区一:
-
-不少同学认为 如果输入用例都是-1,或者 都是负数,这个贪心算法跑出来的结果是0, 这是**又一次证明脑洞模拟不靠谱的经典案例**,建议大家把代码运行一下试一试,就知道了,也会理解 为什么 result 要初始化为最小负数了。
+误区一:
+不少同学认为 如果输入用例都是-1,或者 都是负数,这个贪心算法跑出来的结果是 0, 这是**又一次证明脑洞模拟不靠谱的经典案例**,建议大家把代码运行一下试一试,就知道了,也会理解 为什么 result 要初始化为最小负数了。
误区二:
-大家在使用贪心算法求解本题,经常陷入的误区,就是分不清,是遇到 负数就选择起始位置,还是连续和为负选择起始位置。
+大家在使用贪心算法求解本题,经常陷入的误区,就是分不清,是遇到 负数就选择起始位置,还是连续和为负选择起始位置。
-在动画演示用,大家可以发现, 4,遇到 -1 的时候,我们依然累加了,为什么呢?
+在动画演示用,大家可以发现, 4,遇到 -1 的时候,我们依然累加了,为什么呢?
-因为和为3,只要连续和还是正数就会 对后面的元素 起到增大总和的作用。 所以只要连续和为正数我们就保留。
+因为和为 3,只要连续和还是正数就会 对后面的元素 起到增大总和的作用。 所以只要连续和为正数我们就保留。
-这里也会有录友疑惑,那 4 + -1 之后 不就变小了吗? 会不会错过 4 成为最大连续和的可能性?
+这里也会有录友疑惑,那 4 + -1 之后 不就变小了吗? 会不会错过 4 成为最大连续和的可能性?
-其实并不会,因为还有一个变量result 一直在更新 最大的连续和,只要有更大的连续和出现,result就更新了,那么result已经把4更新了,后面 连续和变成3,也不会对最后结果有影响。
+其实并不会,因为还有一个变量 result 一直在更新 最大的连续和,只要有更大的连续和出现,result 就更新了,那么 result 已经把 4 更新了,后面 连续和变成 3,也不会对最后结果有影响。
+### 动态规划
+当然本题还可以用动态规划来做,在代码随想录动态规划章节我会详细介绍,如果大家想在想看,可以直接跳转:[动态规划版本详解](https://programmercarl.com/0053.%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%A7%E5%AD%90%E5%BA%8F%E5%92%8C%EF%BC%88%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E8%A7%84%E5%88%92%EF%BC%89.html#%E6%80%9D%E8%B7%AF)
-## 动态规划
-
-当然本题还可以用动态规划来做,当前[「代码随想录」](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20201124161234338.png)主要讲解贪心系列,后续到动态规划系列的时候会详细讲解本题的dp方法。
-
-那么先给出我的dp代码如下,有时间的录友可以提前做一做:
+那么先给出我的 dp 代码如下,有时间的录友可以提前做一做:
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -148,8 +145,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:O(n)
-* 空间复杂度:O(n)
+- 时间复杂度:O(n)
+- 空间复杂度:O(n)
## 总结
@@ -159,8 +156,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-
### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
@@ -201,22 +198,102 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python
+暴力法
```python
class Solution:
- def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- result = -float('inf')
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums):
+ result = float('-inf') # 初始化结果为负无穷大
+ count = 0
+ for i in range(len(nums)): # 设置起始位置
+ count = 0
+ for j in range(i, len(nums)): # 从起始位置i开始遍历寻找最大值
+ count += nums[j]
+ result = max(count, result) # 更新最大值
+ return result
+
+```
+贪心法
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums):
+ result = float('-inf') # 初始化结果为负无穷大
count = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
count += nums[i]
- if count > result:
+ if count > result: # 取区间累计的最大值(相当于不断确定最大子序终止位置)
result = count
- if count <= 0:
+ if count <= 0: # 相当于重置最大子序起始位置,因为遇到负数一定是拉低总和
count = 0
return result
```
+动态规划
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ dp = [0] * len(nums)
+ dp[0] = nums[0]
+ res = nums[0]
+ for i in range(1, len(nums)):
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i])
+ res = max(res, dp[i])
+ return res
+```
+
+动态规划
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums):
+ if not nums:
+ return 0
+ dp = [0] * len(nums) # dp[i]表示包括i之前的最大连续子序列和
+ dp[0] = nums[0]
+ result = dp[0]
+ for i in range(1, len(nums)):
+ dp[i] = max(dp[i-1]+nums[i], nums[i]) # 状态转移公式
+ if dp[i] > result:
+ result = dp[i] # result 保存dp[i]的最大值
+ return result
+```
+
+动态规划优化
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
+ max_sum = float("-inf") # 初始化结果为负无穷大,方便比较取最大值
+ current_sum = 0 # 初始化当前连续和
+
+ for num in nums:
+
+ # 更新当前连续和
+ # 如果原本的连续和加上当前数字之后没有当前数字大,说明原本的连续和是负数,那么就直接从当前数字开始重新计算连续和
+ current_sum = max(current_sum+num, num)
+ max_sum = max(max_sum, current_sum) # 更新结果
+
+ return max_sum
+```
### Go
+贪心法
+```go
+func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
+ max := nums[0]
+ count := 0
+ for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++{
+ count += nums[i]
+ if count > max{
+ max = count
+ }
+ if count < 0 {
+ count = 0
+ }
+ }
+ return max
+}
+```
+动态规划
```go
func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
maxSum := nums[0]
@@ -233,6 +310,7 @@ func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
```
### Rust
+
```rust
pub fn max_sub_array(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
let mut max_sum = i32::MIN;
@@ -246,7 +324,8 @@ pub fn max_sub_array(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
+
```Javascript
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
let result = -Infinity
@@ -264,14 +343,15 @@ var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
};
```
-
### C:
+
贪心:
+
```c
int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize){
int maxVal = INT_MIN;
int subArrSum = 0;
-
+
int i;
for(i = 0; i < numsSize; ++i) {
subArrSum += nums[i];
@@ -286,6 +366,7 @@ int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize){
```
动态规划:
+
```c
/**
* 解题思路:动态规划:
@@ -324,15 +405,15 @@ int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize){
```typescript
function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
- let curSum: number = 0;
- let resMax: number = -Infinity;
- for (let i = 0, length = nums.length; i < length; i++) {
- curSum += nums[i];
- resMax = Math.max(curSum, resMax);
- if (curSum < 0) curSum = 0;
- }
- return resMax;
-};
+ let curSum: number = 0;
+ let resMax: number = -Infinity;
+ for (let i = 0, length = nums.length; i < length; i++) {
+ curSum += nums[i];
+ resMax = Math.max(curSum, resMax);
+ if (curSum < 0) curSum = 0;
+ }
+ return resMax;
+}
```
**动态规划**
@@ -340,17 +421,17 @@ function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
```typescript
// 动态规划
function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
- const length = nums.length;
- if (length === 0) return 0;
- const dp: number[] = [];
- dp[0] = nums[0];
- let resMax: number = nums[0];
- for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
- dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
- resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
- }
- return resMax;
-};
+ const length = nums.length;
+ if (length === 0) return 0;
+ const dp: number[] = [];
+ dp[0] = nums[0];
+ let resMax: number = nums[0];
+ for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
+ resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
+ }
+ return resMax;
+}
```
### Scala
@@ -388,8 +469,24 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+**贪心**
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public int MaxSubArray(int[] nums)
+ {
+ int res = Int32.MinValue;
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
+ {
+ count += nums[i];
+ res = Math.Max(res, count);
+ if (count < 0) count = 0;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 506c000fd2..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 506c000fd2..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 53. 最大子序和
@@ -11,9 +9,14 @@
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
示例:
-输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
-输出: 6
-解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
+* 输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
+* 输出: 6
+* 解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
+
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[看起来复杂,其实是简单动态规划 | LeetCode:53.最大子序和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19V4y1F7b5),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
## 思路
@@ -51,7 +54,7 @@ dp[0]应该是多少呢?
5. 举例推导dp数组
以示例一为例,输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],对应的dp状态如下:
-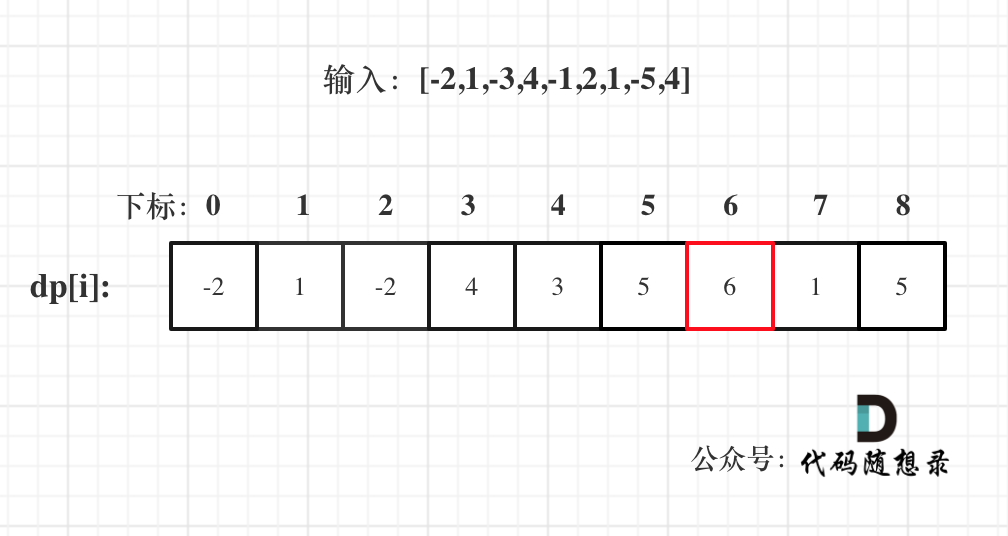
+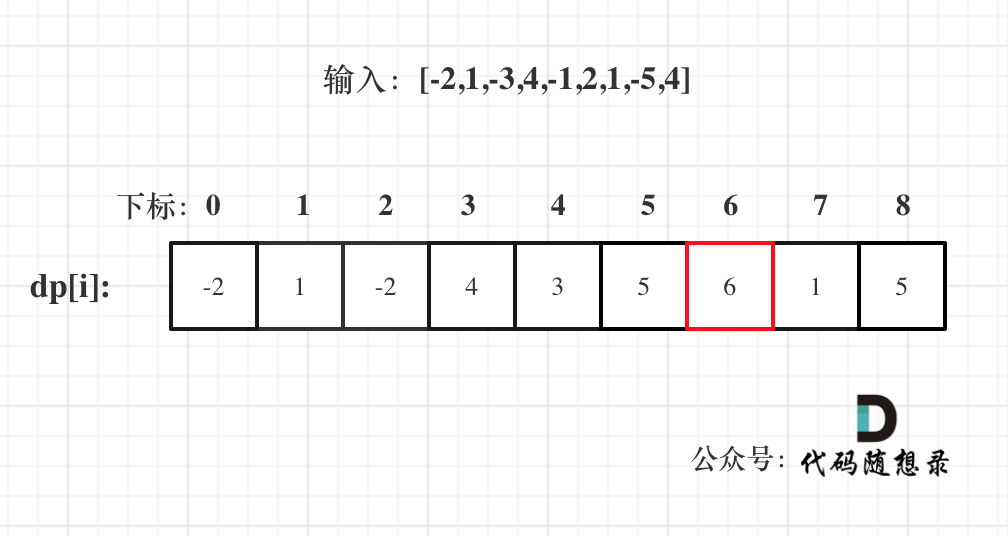
**注意最后的结果可不是dp[nums.size() - 1]!** ,而是dp[6]。
@@ -92,8 +95,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
+### Java:
-Java:
```java
/**
* 1.dp[i]代表当前下标对应的最大值
@@ -135,12 +138,11 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
class Solution:
def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- if len(nums) == 0:
- return 0
dp = [0] * len(nums)
dp[0] = nums[0]
result = dp[0]
@@ -150,7 +152,8 @@ class Solution:
return result
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```Go
// solution
// 1, dp
@@ -181,7 +184,7 @@ func max(a,b int) int{
}
```
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
const maxSubArray = nums => {
@@ -200,8 +203,7 @@ const maxSubArray = nums => {
};
```
-
-Scala:
+### Scala:
```scala
object Solution {
@@ -218,26 +220,25 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function maxSubArray(nums: number[]): number {
- /**
- dp[i]:以nums[i]结尾的最大和
- */
- const dp: number[] = []
- dp[0] = nums[0];
- let resMax: number = 0;
- for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
- dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]);
- resMax = Math.max(resMax, dp[i]);
+ const len = nums.length
+ if (len === 1) return nums[0]
+
+ const dp: number[] = new Array(len)
+ let resMax: number = dp[0] = nums[0]
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
+ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i])
+ // 注意值为负数的情况
+ if (dp[i] > resMax) resMax = dp[i]
}
- return resMax;
-};
+
+ return resMax
+}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 858741d0b0..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 858741d0b0..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-## 54.螺旋矩阵
+# 54.螺旋矩阵
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix/)
@@ -37,7 +35,8 @@
由外向内一圈一圈这么画下去,如下所示:
-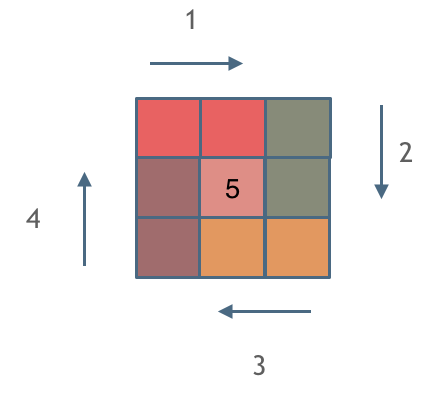
+
+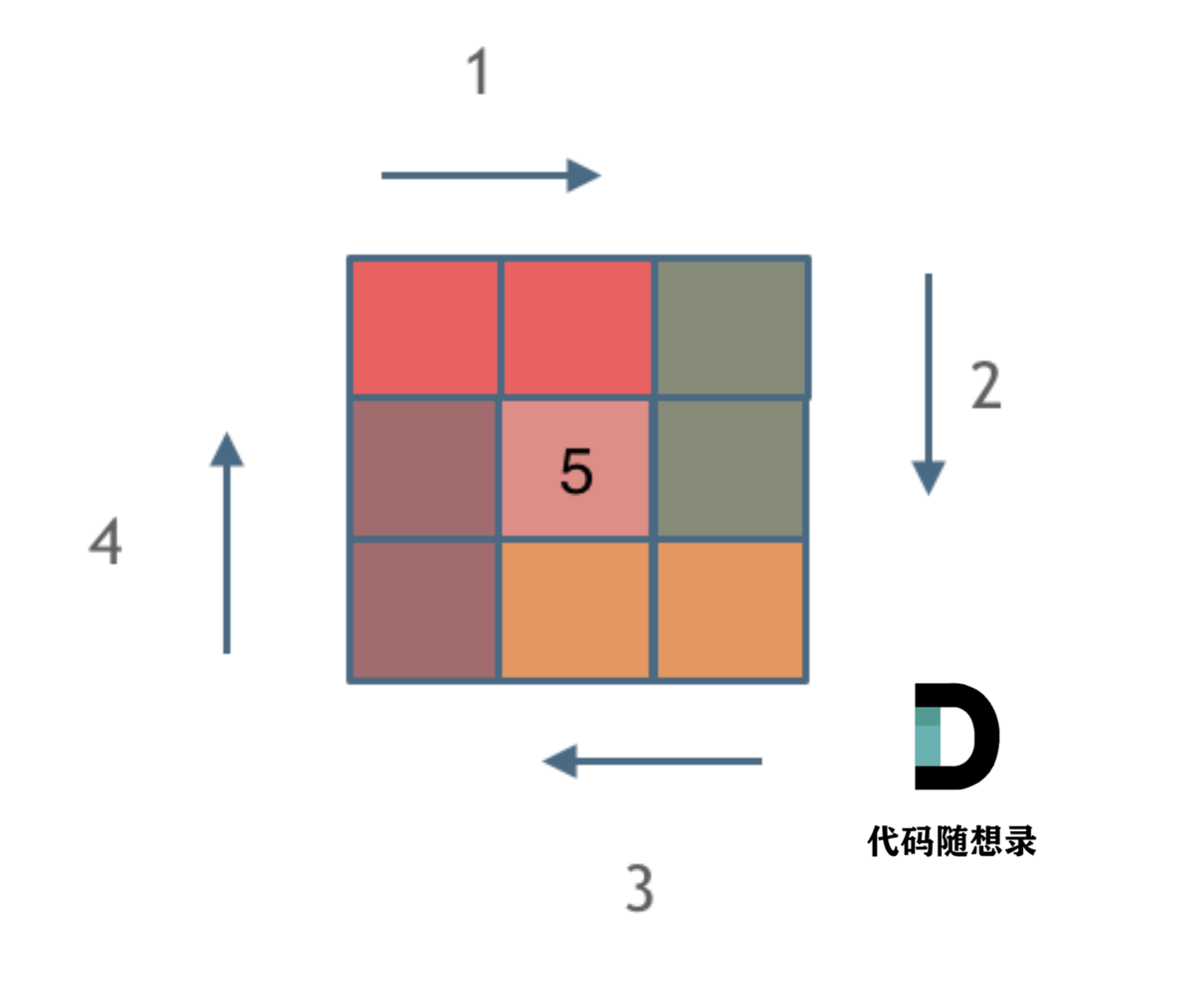
这里每一种颜色,代表一条边,我们遍历的长度,可以看出每一个拐角处的处理规则,拐角处让给新的一条边来继续画。
@@ -199,9 +198,288 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public List spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
+ List res = new ArrayList<>(); // 存放结果
+ if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
+ return res;
+ int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
+ int startx = 0, starty = 0; // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
+ int loop = 0; // 循环次数
+ int offset = 1; // 每一圈循环,需要控制每一条边遍历的长度
+ while (loop < Math.min(rows, columns) / 2) {
+ int i = startx;
+ int j = starty;
+ // 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
+ for (; j < columns - offset; j++) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+ // 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
+ for (; i < rows - offset; i++) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+ // 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
+ for (; j > starty; j--) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+ // 模拟填充左列从下到上(左闭右开)
+ for (; i > startx; i--) {
+ res.add(matrix[i][j]);
+ }
+
+ // 起始位置加1 循环次数加1 并控制每条边遍历的长度
+ startx++;
+ starty++;
+ offset++;
+ loop++;
+ }
+
+ // 如果列或行中的最小值为奇数 则一定有未遍历的部分
+ // 可以自行画图理解
+ if (Math.min(rows, columns) % 2 == 1) {
+ // 当行大于列时 未遍历的部分是列
+ // (startx, starty)即下一个要遍历位置 从该位置出发 遍历完未遍历的列
+ // 遍历次数为rows - columns + 1
+ if (rows > columns) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < rows - columns + 1; i++) {
+ res.add(matrix[startx++][starty]);
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 此处与上面同理 遍历完未遍历的行
+ for (int i = 0; i < columns - rows + 1; i++) {
+ res.add(matrix[startx][starty++]);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript
+```
+/**
+ * @param {number[][]} matrix
+ * @return {number[]}
+ */
+var spiralOrder = function(matrix) {
+ let m = matrix.length
+ let n = matrix[0].length
+
+ let startX = startY = 0
+ let i = 0
+ let arr = new Array(m*n).fill(0)
+ let offset = 1
+ let loop = mid = Math.floor(Math.min(m,n) / 2)
+ while (loop--) {
+ let row = startX
+ let col = startY
+ // -->
+ for (; col < n + startY - offset; col++) {
+ arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
+ }
+ // down
+ for (; row < m + startX - offset; row++) {
+ arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
+ }
+ // <--
+ for (; col > startY; col--) {
+ arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
+ }
+ for (; row > startX; row--) {
+ arr[i++] = matrix[row][col]
+ }
+ startX++
+ startY++
+ offset += 2
+ }
+ if (Math.min(m, n) % 2 === 1) {
+ if (n > m) {
+ for (let j = mid; j < mid + n - m + 1; j++) {
+ arr[i++] = matrix[mid][j]
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (let j = mid; j < mid + m - n + 1; j++) {
+ arr[i++] = matrix[j][mid]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return arr
+};
+```
+### Python
+
+```python
+class Solution(object):
+ def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
+ """
+ :type matrix: List[List[int]]
+ :rtype: List[int]
+ """
+ if len(matrix) == 0 or len(matrix[0]) == 0 : # 判定List是否为空
+ return []
+ row, col = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) # 行数,列数
+ loop = min(row, col) // 2 # 循环轮数
+ stx, sty = 0, 0 # 起始x,y坐标
+ i, j =0, 0
+ count = 0 # 计数
+ offset = 1 # 每轮减少的格子数
+ result = [0] * (row * col)
+ while loop>0 :# 左闭右开
+ i, j = stx, sty
+ while j < col - offset : # 从左到右
+ result[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count += 1
+ j += 1
+ while i < row - offset : # 从上到下
+ result[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count += 1
+ i += 1
+ while j>sty : # 从右到左
+ result[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count += 1
+ j -= 1
+ while i>stx : # 从下到上
+ result[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count += 1
+ i -= 1
+ stx += 1
+ sty += 1
+ offset += 1
+ loop -= 1
+ if min(row, col) % 2 == 1 : # 判定是否需要填充多出来的一行
+ i = stx
+ if row < col :
+ while i < stx + col - row + 1 :
+ result[count] = matrix[stx][i]
+ count += 1
+ i += 1
+ else :
+ while i < stx + row - col + 1 :
+ result[count] = matrix[i][stx]
+ count += 1
+ i += 1
+ return result
+```
+
+版本二:定义四个边界
+```python
+class Solution(object):
+ def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
+ """
+ :type matrix: List[List[int]]
+ :rtype: List[int]
+ """
+ if not matrix:
+ return []
+
+ rows = len(matrix)
+ cols = len(matrix[0])
+ top, bottom, left, right = 0, rows - 1, 0, cols - 1
+ print_list = []
+
+ while top <= bottom and left <= right:
+ # 从左到右
+ for i in range(left, right + 1):
+ print_list.append(matrix[top][i])
+ top += 1
+
+ # 从上到下
+ for i in range(top, bottom + 1):
+ print_list.append(matrix[i][right])
+ right -= 1
+
+ # 从右到左
+ if top <= bottom:
+ for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
+ print_list.append(matrix[bottom][i])
+ bottom -= 1
+
+ # 从下到上
+ if left <= right:
+ for i in range(bottom, top - 1, -1):
+ print_list.append(matrix[i][left])
+ left += 1
+
+ return print_list
+```
+
+### Go
+
+```go
+func spiralOrder(matrix [][]int) []int {
+ rows := len(matrix)
+ if rows == 0 {
+ return []int{}
+ }
+ columns := len(matrix[0])
+ if columns == 0 {
+ return []int{}
+ }
+ res := make([]int, rows * columns)
+ startx, starty := 0, 0 // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
+ loop := min(rows, columns) / 2
+ mid := min(rows, columns) / 2
+ count := 0 // 用来给矩阵中每一个空格赋值
+ offset := 1 // 每一圈循环,需要控制每一条边遍历的长度
+ for loop > 0 {
+ i, j := startx, starty
+
+ // 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
+ for ; j < starty + columns - offset; j++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[startx][j]
+ count++
+ }
+ // 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
+ for ; i < startx + rows - offset; i++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count++
+ }
+ // 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
+ for ; j > starty; j-- {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][j]
+ count++
+ }
+ // 模拟填充左列从下到上(左闭右开)
+ for ; i > startx; i-- {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][starty]
+ count++
+ }
+
+ // 第二圈开始的时候,起始位置要各自加1, 例如:第一圈起始位置是(0, 0),第二圈起始位置是(1, 1)
+ startx++
+ starty++
+
+ // offset 控制每一圈里每一条边遍历的长度
+ offset += 2
+ loop--
+ }
+
+ // 如果min(rows, columns)为奇数的话,需要单独给矩阵最中间的位置赋值
+ if min(rows, columns) % 2 == 1 {
+ if rows > columns {
+ for i := mid; i < mid + rows - columns + 1; i++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[i][mid]
+ count++
+ }
+ } else {
+ for i := mid; i < mid + columns - rows + 1; i++ {
+ res[count] = matrix[mid][i]
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func min(x, y int) int {
+ if x < y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7b02075bdb..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7b02075bdb..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 55. 跳跃游戏
@@ -15,20 +12,25 @@
判断你是否能够到达最后一个位置。
-示例 1:
-* 输入: [2,3,1,1,4]
-* 输出: true
-* 解释: 我们可以先跳 1 步,从位置 0 到达 位置 1, 然后再从位置 1 跳 3 步到达最后一个位置。
+示例 1:
+
+- 输入: [2,3,1,1,4]
+- 输出: true
+- 解释: 我们可以先跳 1 步,从位置 0 到达 位置 1, 然后再从位置 1 跳 3 步到达最后一个位置。
+
+示例 2:
-示例 2:
-* 输入: [3,2,1,0,4]
-* 输出: false
-* 解释: 无论怎样,你总会到达索引为 3 的位置。但该位置的最大跳跃长度是 0 , 所以你永远不可能到达最后一个位置。
+- 输入: [3,2,1,0,4]
+- 输出: false
+- 解释: 无论怎样,你总会到达索引为 3 的位置。但该位置的最大跳跃长度是 0 , 所以你永远不可能到达最后一个位置。
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[贪心算法,怎么跳跃不重要,关键在覆盖范围 | LeetCode:55.跳跃游戏](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1VG4y1X7kB),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
-刚看到本题一开始可能想:当前位置元素如果是3,我究竟是跳一步呢,还是两步呢,还是三步呢,究竟跳几步才是最优呢?
+刚看到本题一开始可能想:当前位置元素如果是 3,我究竟是跳一步呢,还是两步呢,还是三步呢,究竟跳几步才是最优呢?
其实跳几步无所谓,关键在于可跳的覆盖范围!
@@ -46,13 +48,14 @@
如图:
-
+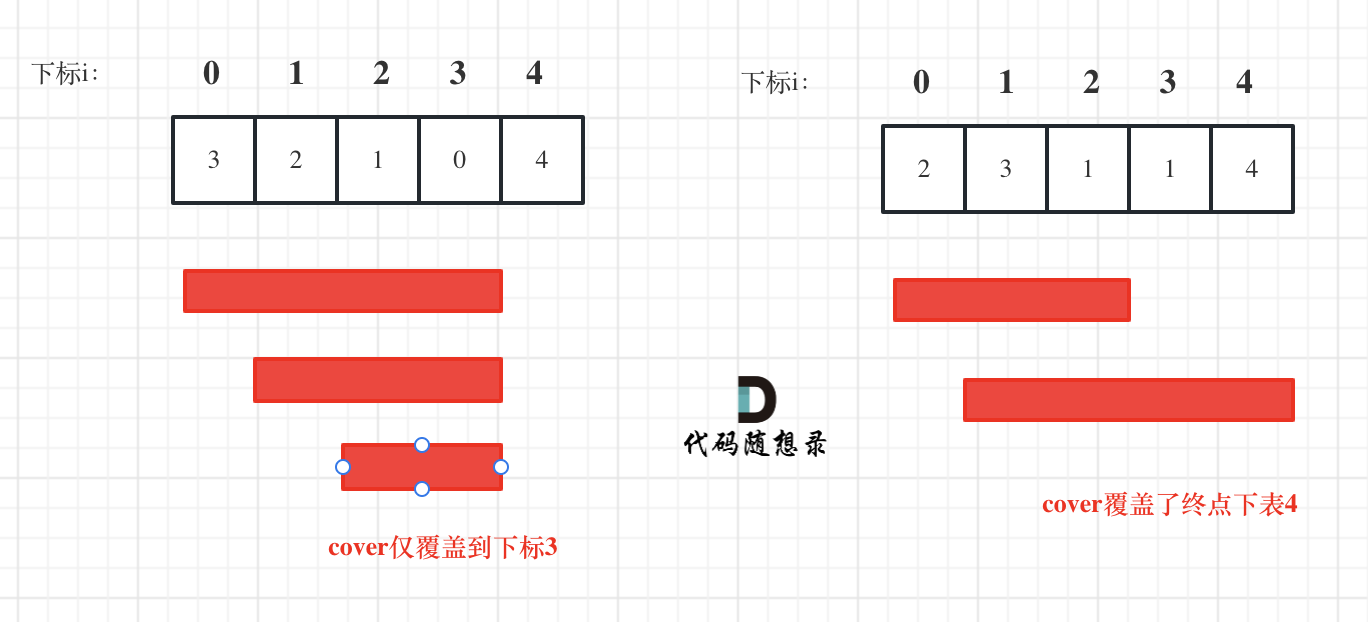
+
-i每次移动只能在cover的范围内移动,每移动一个元素,cover得到该元素数值(新的覆盖范围)的补充,让i继续移动下去。
+i 每次移动只能在 cover 的范围内移动,每移动一个元素,cover 得到该元素数值(新的覆盖范围)的补充,让 i 继续移动下去。
-而cover每次只取 max(该元素数值补充后的范围, cover本身范围)。
+而 cover 每次只取 max(该元素数值补充后的范围, cover 本身范围)。
-如果cover大于等于了终点下标,直接return true就可以了。
+如果 cover 大于等于了终点下标,直接 return true 就可以了。
C++代码如下:
@@ -70,6 +73,11 @@ public:
}
};
```
+
+* 时间复杂度: O(n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(1)
+
+
## 总结
这道题目关键点在于:不用拘泥于每次究竟跳几步,而是看覆盖范围,覆盖范围内一定是可以跳过来的,不用管是怎么跳的。
@@ -82,8 +90,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
+### Java
-### Java
```Java
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
@@ -105,6 +113,7 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python
+
```python
class Solution:
def canJump(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
@@ -132,6 +141,23 @@ class Solution:
return False
```
+```python
+## 基于当前最远可到达位置判断
+class Solution:
+ def canJump(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
+ far = nums[0]
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ # 要考虑两个情况
+ # 1. i <= far - 表示 当前位置i 可以到达
+ # 2. i > far - 表示 当前位置i 无法到达
+ if i > far:
+ return False
+ far = max(far, nums[i]+i)
+ # 如果循环正常结束,表示最后一个位置也可以到达,否则会在中途直接退出
+ # 关键点在于,要想明白其实列表中的每个位置都是需要验证能否到达的
+ return True
+```
+
### Go
```go
@@ -155,9 +181,7 @@ func max(a, b int ) int {
}
```
-
-
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var canJump = function(nums) {
@@ -177,16 +201,16 @@ var canJump = function(nums) {
```Rust
impl Solution {
- fn max(a: usize, b: usize) -> usize {
- if a > b { a } else { b }
- }
pub fn can_jump(nums: Vec) -> bool {
- let mut cover = 0;
- if (nums.len() == 1) { return true; }
- let mut i = 0;
+ if nums.len() == 1 {
+ return true;
+ }
+ let (mut i, mut cover) = (0, 0);
while i <= cover {
- cover = Self::max(i + nums[i] as usize, cover);
- if cover >= nums.len() - 1 { return true; }
+ cover = (i + nums[i] as usize).max(cover);
+ if cover >= nums.len() - 1 {
+ return true;
+ }
i += 1;
}
false
@@ -195,6 +219,7 @@ impl Solution {
```
### C
+
```c
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
@@ -216,23 +241,23 @@ bool canJump(int* nums, int numsSize){
}
```
-
### TypeScript
```typescript
function canJump(nums: number[]): boolean {
- let farthestIndex: number = 0;
- let cur: number = 0;
- while (cur <= farthestIndex) {
- farthestIndex = Math.max(farthestIndex, cur + nums[cur]);
- if (farthestIndex >= nums.length - 1) return true;
- cur++;
- }
- return false;
-};
+ let farthestIndex: number = 0;
+ let cur: number = 0;
+ while (cur <= farthestIndex) {
+ farthestIndex = Math.max(farthestIndex, cur + nums[cur]);
+ if (farthestIndex >= nums.length - 1) return true;
+ cur++;
+ }
+ return false;
+}
```
### Scala
+
```scala
object Solution {
def canJump(nums: Array[Int]): Boolean = {
@@ -248,9 +273,21 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public bool CanJump(int[] nums)
+ {
+ int cover = 0;
+ if (nums.Length == 1) return true;
+ for (int i = 0; i <= cover; i++)
+ {
+ cover = Math.Max(i + nums[i], cover);
+ if (cover >= nums.Length - 1) return true;
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3c980c2be3..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3c980c2be3..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 56. 合并区间
@@ -22,6 +20,9 @@
* 解释: 区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
* 注意:输入类型已于2019年4月15日更改。 请重置默认代码定义以获取新方法签名。
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[贪心算法,合并区间有细节!LeetCode:56.合并区间](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wx4y157nD),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -37,7 +38,7 @@
这么说有点抽象,看图:(**注意图中区间都是按照左边界排序之后了**)
-
+
知道如何判断重复之后,剩下的就是合并了,如何去模拟合并区间呢?
@@ -70,6 +71,10 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(nlogn)
+* 空间复杂度: O(logn),排序需要的空间开销
+
+
## 其他语言版本
@@ -106,7 +111,6 @@ class Solution {
}
}
-}
```
```java
// 版本2
@@ -134,18 +138,24 @@ class Solution {
### Python
```python
class Solution:
- def merge(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
- if len(intervals) == 0: return intervals
- intervals.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])
+ def merge(self, intervals):
result = []
- result.append(intervals[0])
+ if len(intervals) == 0:
+ return result # 区间集合为空直接返回
+
+ intervals.sort(key=lambda x: x[0]) # 按照区间的左边界进行排序
+
+ result.append(intervals[0]) # 第一个区间可以直接放入结果集中
+
for i in range(1, len(intervals)):
- last = result[-1]
- if last[1] >= intervals[i][0]:
- result[-1] = [last[0], max(last[1], intervals[i][1])]
+ if result[-1][1] >= intervals[i][0]: # 发现重叠区间
+ # 合并区间,只需要更新结果集最后一个区间的右边界,因为根据排序,左边界已经是最小的
+ result[-1][1] = max(result[-1][1], intervals[i][1])
else:
- result.append(intervals[i])
+ result.append(intervals[i]) # 区间不重叠
+
return result
+
```
### Go
@@ -174,8 +184,36 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
return b
}
```
+```go
+// 版本2
+func merge(intervals [][]int) [][]int {
+ if len(intervals) == 1 {
+ return intervals
+ }
+ sort.Slice(intervals, func(i, j int) bool {
+ return intervals[i][0] < intervals[j][0]
+ })
+ res := make([][]int, 0)
+ res = append(res, intervals[0])
+ for i := 1; i < len(intervals); i++ {
+ if intervals[i][0] <= res[len(res)-1][1]{
+ res[len(res)-1][1] = max56(res[len(res)-1][1],intervals[i][1])
+ } else {
+ res = append(res, intervals[i])
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+func max56(a, b int) int {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+```
+
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
var merge = function (intervals) {
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
@@ -277,29 +315,91 @@ object Solution {
```Rust
impl Solution {
- fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
- if a > b { a } else { b }
+ pub fn merge(mut intervals: Vec>) -> Vec> {
+ let mut res = vec![];
+ if intervals.is_empty() {
+ return res;
+ }
+ intervals.sort_by_key(|a| a[0]);
+ res.push(intervals[0].clone());
+ for interval in intervals.into_iter().skip(1) {
+ let res_last_ele = res.last_mut().unwrap();
+ if res_last_ele[1] >= interval[0] {
+ res_last_ele[1] = interval[1].max(res_last_ele[1]);
+ } else {
+ res.push(interval);
+ }
+ }
+ res
}
+}
+```
+### C
- pub fn merge(intervals: Vec>) -> Vec> {
- let mut intervals = intervals;
- let mut result = Vec::new();
- if intervals.len() == 0 { return result; }
- intervals.sort_by(|a, b| a[0].cmp(&b[0]));
- result.push(intervals[0].clone());
- for i in 1..intervals.len() {
- if result.last_mut().unwrap()[1] >= intervals[i][0] {
- result.last_mut().unwrap()[1] = Self::max(result.last_mut().unwrap()[1], intervals[i][1]);
- } else {
- result.push(intervals[i].clone());
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+// 根据左边界进行排序
+int cmp(const void * var1, const void * var2){
+ int *v1 = *(int **) var1;
+ int *v2 = *(int **) var2;
+ return v1[0] - v2[0];
+}
+
+int** merge(int** intervals, int intervalsSize, int* intervalsColSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
+ int ** result = malloc(sizeof (int *) * intervalsSize);
+ * returnColumnSizes = malloc(sizeof (int ) * intervalsSize);
+ for(int i = 0; i < intervalsSize; i++){
+ result[i] = malloc(sizeof (int ) * 2);
+ }
+ qsort(intervals, intervalsSize, sizeof (int *), cmp);
+ int count = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < intervalsSize; i++){
+ // 记录区间的左右边界
+ int L = intervals[i][0], R = intervals[i][1];
+ // 如果count为0或者前一区间的右区间小于此时的左边,加入结果中
+ if (count == 0 || result[count - 1][1] < L) {
+ returnColumnSizes[0][count] = 2;
+ result[count][0] = L;
+ result[count][1] = R;
+ count++;
+ }
+ else{ // 更新右边界的值
+ result[count - 1][1] = max(R, result[count - 1][1]);
+ }
+ }
+ *returnSize = count;
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+
+
+### C#
+
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public int[][] Merge(int[][] intervals)
+ {
+ if (intervals.Length == 0)
+ return intervals;
+ Array.Sort(intervals, (a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
+ List> res = new List>();
+ res.Add(intervals[0].ToList());
+ for (int i = 1; i < intervals.Length; i++)
+ {
+ if (res[res.Count - 1][1] >= intervals[i][0])
+ {
+ res[res.Count - 1][1] = Math.Max(res[res.Count - 1][1], intervals[i][1]);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ res.Add(intervals[i].ToList());
}
}
- result
+ return res.Select(x => x.ToArray()).ToArray();
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d9a656b9f6..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d9a656b9f6..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-## 59.螺旋矩阵II
+# 59.螺旋矩阵II
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/)
@@ -22,9 +20,12 @@
[ 7, 6, 5 ]
]
-## 思路
-为了利于录友们理解,我特意录制了视频,[拿下螺旋矩阵!LeetCode:59.螺旋矩阵II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1SL4y1N7mV),结合视频一起看,事半功倍!
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[拿下螺旋矩阵!LeetCode:59.螺旋矩阵II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1SL4y1N7mV),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+## 思路
这道题目可以说在面试中出现频率较高的题目,**本题并不涉及到什么算法,就是模拟过程,但却十分考察对代码的掌控能力。**
@@ -53,7 +54,7 @@
那么我按照左闭右开的原则,来画一圈,大家看一下:
-
+
这里每一种颜色,代表一条边,我们遍历的长度,可以看出每一个拐角处的处理规则,拐角处让给新的一条边来继续画。
@@ -84,11 +85,11 @@ public:
// 下面开始的四个for就是模拟转了一圈
// 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
- for (j = starty; j < n - offset; j++) {
- res[startx][j] = count++;
+ for (j; j < n - offset; j++) {
+ res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
- for (i = startx; i < n - offset; i++) {
+ for (i; i < n - offset; i++) {
res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
@@ -117,60 +118,72 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度 O(n^2): 模拟遍历二维矩阵的时间
+* 空间复杂度 O(1)
+
## 类似题目
-* 54.螺旋矩阵
-* 剑指Offer 29.顺时针打印矩阵
+* [54.螺旋矩阵](https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix/)
+* [剑指Offer 29.顺时针打印矩阵](https://leetcode.cn/problems/shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof/)
## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
```Java
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
- int loop = 0; // 控制循环次数
- int[][] res = new int[n][n];
- int start = 0; // 每次循环的开始点(start, start)
- int count = 1; // 定义填充数字
- int i, j;
-
- while (loop++ < n / 2) { // 判断边界后,loop从1开始
- // 模拟上侧从左到右
- for (j = start; j < n - loop; j++) {
- res[start][j] = count++;
+ int[][] nums = new int[n][n];
+ int startX = 0, startY = 0; // 每一圈的起始点
+ int offset = 1;
+ int count = 1; // 矩阵中需要填写的数字
+ int loop = 1; // 记录当前的圈数
+ int i, j; // j 代表列, i 代表行;
+
+ while (loop <= n / 2) {
+
+ // 顶部
+ // 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, j 不能等于 n - offset
+ for (j = startY; j < n - offset; j++) {
+ nums[startX][j] = count++;
}
- // 模拟右侧从上到下
- for (i = start; i < n - loop; i++) {
- res[i][j] = count++;
+ // 右列
+ // 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, i 不能等于 n - offset
+ for (i = startX; i < n - offset; i++) {
+ nums[i][j] = count++;
}
- // 模拟下侧从右到左
- for (; j >= loop; j--) {
- res[i][j] = count++;
+ // 底部
+ // 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, j != startY
+ for (; j > startY; j--) {
+ nums[i][j] = count++;
}
- // 模拟左侧从下到上
- for (; i >= loop; i--) {
- res[i][j] = count++;
+ // 左列
+ // 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, i != startX
+ for (; i > startX; i--) {
+ nums[i][j] = count++;
}
- start++;
+ startX++;
+ startY++;
+ offset++;
+ loop++;
}
-
- if (n % 2 == 1) {
- res[start][start] = count;
+ if (n % 2 == 1) { // n 为奇数时,单独处理矩阵中心的值
+ nums[startX][startY] = count;
}
-
- return res;
+ return nums;
}
}
+
+
```
-python3:
+### python3:
```python
class Solution:
@@ -201,14 +214,54 @@ class Solution:
return nums
```
-javaScript
+版本二:定义四个边界
+```python
+class Solution(object):
+ def generateMatrix(self, n):
+ if n <= 0:
+ return []
+
+ # 初始化 n x n 矩阵
+ matrix = [[0]*n for _ in range(n)]
+
+ # 初始化边界和起始值
+ top, bottom, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1
+ num = 1
+
+ while top <= bottom and left <= right:
+ # 从左到右填充上边界
+ for i in range(left, right + 1):
+ matrix[top][i] = num
+ num += 1
+ top += 1
+
+ # 从上到下填充右边界
+ for i in range(top, bottom + 1):
+ matrix[i][right] = num
+ num += 1
+ right -= 1
+
+ # 从右到左填充下边界
+
+ for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
+ matrix[bottom][i] = num
+ num += 1
+ bottom -= 1
+
+ # 从下到上填充左边界
+
+ for i in range(bottom, top - 1, -1):
+ matrix[i][left] = num
+ num += 1
+ left += 1
+
+ return matrix
+```
+
+### JavaScript:
```javascript
-/**
- * @param {number} n
- * @return {number[][]}
- */
var generateMatrix = function(n) {
let startX = startY = 0; // 起始位置
let loop = Math.floor(n/2); // 旋转圈数
@@ -220,11 +273,11 @@ var generateMatrix = function(n) {
while (loop--) {
let row = startX, col = startY;
// 上行从左到右(左闭右开)
- for (; col < startY + n - offset; col++) {
+ for (; col < n - offset; col++) {
res[row][col] = count++;
}
// 右列从上到下(左闭右开)
- for (; row < startX + n - offset; row++) {
+ for (; row < n - offset; row++) {
res[row][col] = count++;
}
// 下行从右到左(左闭右开)
@@ -241,7 +294,7 @@ var generateMatrix = function(n) {
startY++;
// 更新offset
- offset += 2;
+ offset += 1;
}
// 如果n为奇数的话,需要单独给矩阵最中间的位置赋值
if (n % 2 === 1) {
@@ -249,11 +302,12 @@ var generateMatrix = function(n) {
}
return res;
};
+
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function generateMatrix(n: number): number[][] {
@@ -298,7 +352,7 @@ function generateMatrix(n: number): number[][] {
};
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
package main
@@ -391,7 +445,7 @@ func generateMatrix(n int) [][]int {
}
```
-Swift:
+### Swift:
```swift
func generateMatrix(_ n: Int) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -447,7 +501,7 @@ func generateMatrix(_ n: Int) -> [[Int]] {
}
```
-Rust:
+### Rust:
```rust
impl Solution {
@@ -500,7 +554,8 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-PHP:
+### PHP:
+
```php
class Solution {
/**
@@ -542,7 +597,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-C:
+### C:
+
```c
int** generateMatrix(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
//初始化返回的结果数组的大小
@@ -601,7 +657,8 @@ int** generateMatrix(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
return ans;
}
```
-Scala:
+### Scala:
+
```scala
object Solution {
def generateMatrix(n: Int): Array[Array[Int]] = {
@@ -653,32 +710,120 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
-C#:
+### C#:
+
```csharp
-public class Solution {
- public int[][] GenerateMatrix(int n) {
- int[][] answer = new int[n][];
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- answer[i] = new int[n];
- int start = 0;
- int end = n - 1;
- int tmp = 1;
- while(tmp < n * n)
+public int[][] GenerateMatrix(int n)
+{
+ // 参考Carl的代码随想录里面C++的思路
+ // https://www.programmercarl.com/0059.%E8%9E%BA%E6%97%8B%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5II.html#%E6%80%9D%E8%B7%AF
+ int startX = 0, startY = 0; // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
+ int loop = n / 2; // 每个圈循环几次,例如n为奇数3,那么loop = 1 只是循环一圈,矩阵中间的值需要单独处理
+ int count = 1; // 用来给矩阵每个空格赋值
+ int mid = n / 2; // 矩阵中间的位置,例如:n为3, 中间的位置就是(1,1),n为5,中间位置为(2, 2)
+ int offset = 1;// 需要控制每一条边遍历的长度,每次循环右边界收缩一位
+
+ // 构建result二维数组
+ int[][] result = new int[n][];
+ for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
+ {
+ result[k] = new int[n];
+ }
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // [i,j]
+ while (loop > 0)
+ {
+ i = startX;
+ j = startY;
+ // 四个For循环模拟转一圈
+ // 第一排,从左往右遍历,不取最右侧的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; j < n - offset; j++)
+ {
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+ // 右侧的第一列,从上往下遍历,不取最下面的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; i < n - offset; i++)
+ {
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+
+ // 最下面的第一行,从右往左遍历,不取最左侧的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; j > startY; j--)
+ {
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+
+ // 左侧第一列,从下往上遍历,不取最左侧的值(左闭右开)
+ for (; i > startX; i--)
{
- for(int i = start; i < end; i++) answer[start][i] = tmp++;
- for(int i = start; i < end; i++) answer[i][end] = tmp++;
- for(int i = end; i > start; i--) answer[end][i] = tmp++;
- for(int i = end; i > start; i--) answer[i][start] = tmp++;
- start++;
- end--;
- }
- if(n % 2 == 1) answer[n / 2][n / 2] = tmp;
- return answer;
+ result[i][j] = count++;
+ }
+ // 第二圈开始的时候,起始位置要各自加1, 例如:第一圈起始位置是(0, 0),第二圈起始位置是(1, 1)
+ startX++;
+ startY++;
+
+ // offset 控制每一圈里每一条边遍历的长度
+ offset++;
+ loop--;
}
+ if (n % 2 == 1)
+ {
+ // n 为奇数
+ result[mid][mid] = count;
+ }
+ return result;
}
```
-
-
-  -
+### Ruby:
+```ruby
+def generate_matrix(n)
+ result = Array.new(n) { Array.new(n, 0) }
+ #循环次数
+ loop_times = 0
+ #步长
+ step = n - 1
+ val = 1
+
+
+ while loop_times < n / 2
+ #模拟从左向右
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[loop_times][i+loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从上到下
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[i+loop_times][n-loop_times-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从右到左
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[n-loop_times-1][n-loop_times-i-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从下到上
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[n-loop_times-i-1][loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ loop_times += 1
+ step -= 2
+ end
+
+ #如果是奇数,则填充最后一个元素
+ result[n/2][n/2] = n**2 if n % 2
+
+ return result
+
+end
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40655f0c28..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
-
-
+### Ruby:
+```ruby
+def generate_matrix(n)
+ result = Array.new(n) { Array.new(n, 0) }
+ #循环次数
+ loop_times = 0
+ #步长
+ step = n - 1
+ val = 1
+
+
+ while loop_times < n / 2
+ #模拟从左向右
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[loop_times][i+loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从上到下
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[i+loop_times][n-loop_times-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从右到左
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[n-loop_times-1][n-loop_times-i-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从下到上
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[n-loop_times-i-1][loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ loop_times += 1
+ step -= 2
+ end
+
+ #如果是奇数,则填充最后一个元素
+ result[n/2][n/2] = n**2 if n % 2
+
+ return result
+
+end
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40655f0c28..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
# 62.不同路径
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-paths/)
-一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
+一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为 “Finish” )。
@@ -16,36 +16,41 @@
示例 1:
-
+
* 输入:m = 3, n = 7
* 输出:28
示例 2:
+
* 输入:m = 2, n = 3
* 输出:3
解释: 从左上角开始,总共有 3 条路径可以到达右下角。
+
1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下
2. 向右 -> 向下 -> 向右
3. 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
示例 3:
+
* 输入:m = 7, n = 3
* 输出:28
示例 4:
+
* 输入:m = 3, n = 3
* 输出:6
提示:
+
* 1 <= m, n <= 100
* 题目数据保证答案小于等于 2 * 10^9
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[动态规划中如何初始化很重要!| LeetCode:62.不同路径](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ve4y1x7Eu/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划中如何初始化很重要!| LeetCode:62.不同路径](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ve4y1x7Eu/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -57,7 +62,7 @@
如图举例:
-
+
此时问题就可以转化为求二叉树叶子节点的个数,代码如下:
@@ -126,7 +131,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
如图所示:
-
+
以上动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
@@ -175,7 +180,7 @@ public:
在这个图中,可以看出一共m,n的话,无论怎么走,走到终点都需要 m + n - 2 步。
-
+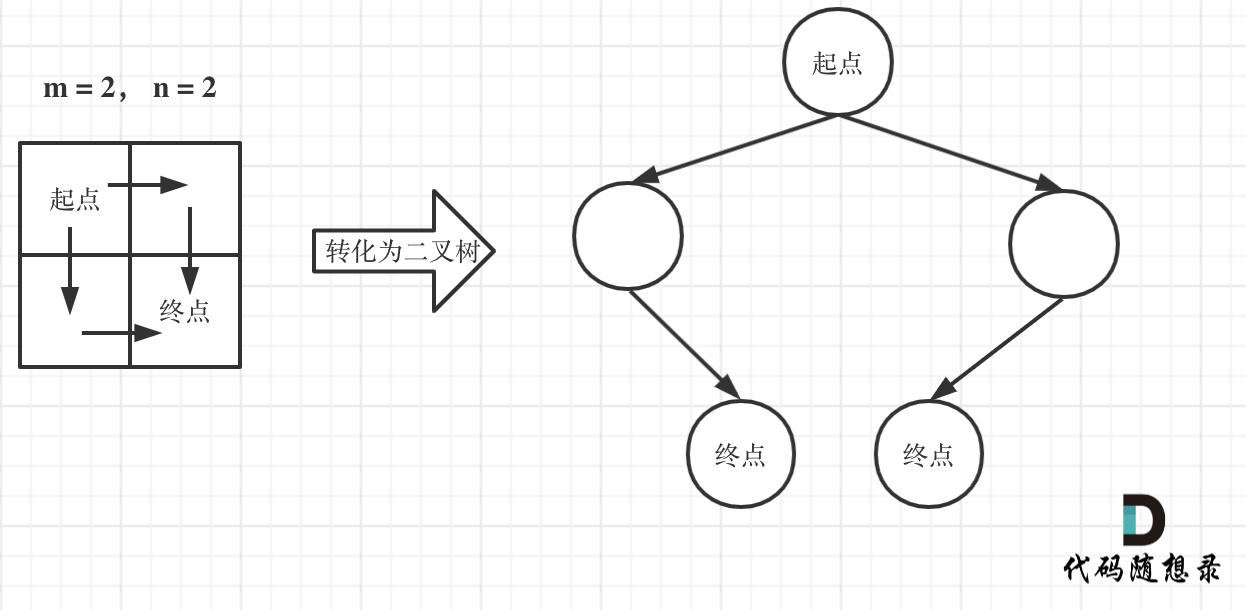
在这m + n - 2 步中,一定有 m - 1 步是要向下走的,不用管什么时候向下走。
@@ -185,7 +190,7 @@ public:
那么答案,如图所示:
-
+
**求组合的时候,要防止两个int相乘溢出!** 所以不能把算式的分子都算出来,分母都算出来再做除法。
@@ -245,7 +250,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-### Java
+### Java
+
```java
/**
* 1. 确定dp数组下标含义 dp[i][j] 到每一个坐标可能的路径种类
@@ -277,19 +283,93 @@ public:
}
```
+状态压缩
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
+ // 在二维dp数组中,当前值的计算只依赖正上方和正左方,因此可以压缩成一维数组。
+ int[] dp = new int[n];
+ // 初始化,第一行只能从正左方跳过来,所以只有一条路径。
+ Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
+ for (int i = 1; i < m; i ++) {
+ // 第一列也只有一条路,不用迭代,所以从第二列开始
+ for (int j = 1; j < n; j ++) {
+ dp[j] += dp[j - 1]; // dp[j] = dp[j] (正上方)+ dp[j - 1] (正左方)
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n - 1];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Python
+递归
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
+ if m == 1 or n == 1:
+ return 1
+ return self.uniquePaths(m - 1, n) + self.uniquePaths(m, n - 1)
-### Python
+```
+动态规划(版本一)
```python
-class Solution: # 动态规划
+class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
- dp = [[1 for i in range(n)] for j in range(m)]
+ # 创建一个二维列表用于存储唯一路径数
+ dp = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
+
+ # 设置第一行和第一列的基本情况
+ for i in range(m):
+ dp[i][0] = 1
+ for j in range(n):
+ dp[0][j] = 1
+
+ # 计算每个单元格的唯一路径数
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
- dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j]
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
+
+ # 返回右下角单元格的唯一路径数
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
+
```
+动态规划(版本二)
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
+ # 创建一个一维列表用于存储每列的唯一路径数
+ dp = [1] * n
+
+ # 计算每个单元格的唯一路径数
+ for j in range(1, m):
+ for i in range(1, n):
+ dp[i] += dp[i - 1]
+
+ # 返回右下角单元格的唯一路径数
+ return dp[n - 1]
+```
+数论
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
+ numerator = 1 # 分子
+ denominator = m - 1 # 分母
+ count = m - 1 # 计数器,表示剩余需要计算的乘积项个数
+ t = m + n - 2 # 初始乘积项
+ while count > 0:
+ numerator *= t # 计算乘积项的分子部分
+ t -= 1 # 递减乘积项
+ while denominator != 0 and numerator % denominator == 0:
+ numerator //= denominator # 约简分子
+ denominator -= 1 # 递减分母
+ count -= 1 # 计数器减1,继续下一项的计算
+ return numerator # 返回最终的唯一路径数
-### Go
+```
+### Go
+
+动态规划
```Go
func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
dp := make([][]int, m)
@@ -309,19 +389,40 @@ func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+数论方法
+```Go
+func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
+ numerator := 1
+ denominator := m - 1
+ count := m - 1
+ t := m + n - 2
+ for count > 0 {
+ numerator *= t
+ t--
+ for denominator != 0 && numerator % denominator == 0 {
+ numerator /= denominator
+ denominator--
+ }
+ count--
+ }
+ return numerator
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript
+
```Javascript
var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
const dp = Array(m).fill().map(item => Array(n))
-
+
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
dp[i][0] = 1
}
-
+
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
dp[0][i] = 1
}
-
+
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
@@ -330,7 +431,9 @@ var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
};
```
+
>版本二:直接将dp数值值初始化为1
+
```javascript
/**
* @param {number} m
@@ -382,21 +485,14 @@ function uniquePaths(m: number, n: number): number {
```Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn unique_paths(m: i32, n: i32) -> i32 {
- let m = m as usize;
- let n = n as usize;
- let mut dp = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
- for i in 0..m {
- dp[i][0] = 1;
- }
- for j in 0..n {
- dp[0][j] = 1;
- }
- for i in 1..m {
- for j in 1..n {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
- }
+ let (m, n) = (m as usize, n as usize);
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![1; n]; m];
+ for i in 1..m {
+ for j in 1..n {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
}
- dp[m-1][n-1]
+ }
+ dp[m - 1][n - 1]
}
}
```
@@ -414,9 +510,9 @@ int **initDP(int m, int n) {
}
//从0,0到i,0只有一种走法,所以dp[i][0]都是1,同理dp[0][j]也是1
- for(i = 0; i < m; ++i)
+ for(i = 0; i < m; ++i)
dp[i][0] = 1;
- for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
+ for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
dp[0][j] = 1;
return dp;
}
@@ -440,6 +536,7 @@ int uniquePaths(int m, int n){
```
滚动数组解法:
+
```c
int uniquePaths(int m, int n){
int i, j;
@@ -455,7 +552,7 @@ int uniquePaths(int m, int n){
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
}
}
- return dp[n - 1];
+ return dp[n - 1];
}
```
@@ -476,8 +573,29 @@ object Solution {
```
### c#
+```csharp
+// 二维数组
+public class Solution
+{
+ public int UniquePaths(int m, int n)
+ {
+ int[,] dp = new int[m, n];
+ for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) dp[i, 0] = 1;
+ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0, j] = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
+ {
+ for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
+ {
+ dp[i, j] = dp[i - 1, j] + dp[i, j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1, n - 1];
+ }
+}
+```
-```c#
+```csharp
+// 一维数组
public class Solution
{
public int UniquePaths(int m, int n)
@@ -495,7 +613,4 @@ public class Solution
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c4ce3f954f..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c4ce3f954f..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
# 63. 不同路径 II
@@ -14,38 +14,39 @@
现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
-
+
网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 1 和 0 来表示。
示例 1:
-
+
* 输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
* 输出:2
-解释:
+ 解释:
* 3x3 网格的正中间有一个障碍物。
* 从左上角到右下角一共有 2 条不同的路径:
- 1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下 -> 向下
- 2. 向下 -> 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
+ 1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下 -> 向下
+ 2. 向下 -> 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
示例 2:
-
+
* 输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,1],[0,0]]
* 输出:1
提示:
-* m == obstacleGrid.length
-* n == obstacleGrid[i].length
+
+* m == obstacleGrid.length
+* n == obstacleGrid[i].length
* 1 <= m, n <= 100
* obstacleGrid[i][j] 为 0 或 1
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[动态规划,这次遇到障碍了| LeetCode:63. 不同路径 II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ld4y1k7c6/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划,这次遇到障碍了| LeetCode:63. 不同路径 II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ld4y1k7c6/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -92,7 +93,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
如图:
-
+
下标(0, j)的初始化情况同理。
@@ -126,13 +127,13 @@ for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
拿示例1来举例如题:
-
+
对应的dp table 如图:
-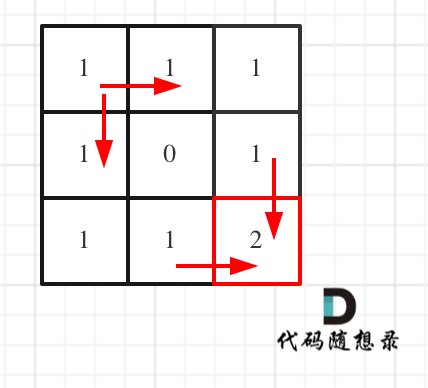
+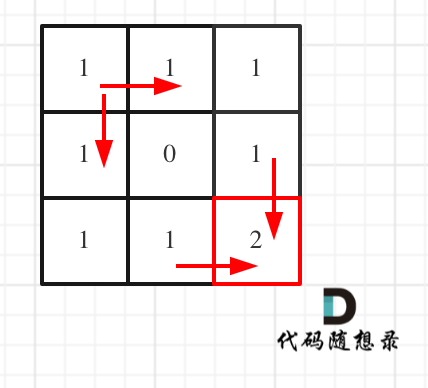
-如果这个图看不同,建议在理解一下递归公式,然后照着文章中说的遍历顺序,自己推导一下!
+如果这个图看不懂,建议再理解一下递归公式,然后照着文章中说的遍历顺序,自己推导一下!
动规五部分分析完毕,对应C++代码如下:
@@ -142,7 +143,7 @@ public:
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector>& obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
- if (obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1 || obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) //如果在起点或终点出现了障碍,直接返回0
+ if (obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1 || obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) //如果在起点或终点出现了障碍,直接返回0
return 0;
vector> dp(m, vector(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < m && obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0; i++) dp[i][0] = 1;
@@ -163,6 +164,7 @@ public:
同样我们给出空间优化版本:
+
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
@@ -208,7 +210,7 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-### Java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -246,11 +248,11 @@ class Solution {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
-
+
for (int j = 0; j < n && obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0; j++) {
dp[j] = 1;
}
-
+
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
@@ -267,72 +269,165 @@ class Solution {
### Python
-
+动态规划(版本一)
```python
class Solution:
- def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- # 构造一个DP table
- row = len(obstacleGrid)
- col = len(obstacleGrid[0])
- dp = [[0 for _ in range(col)] for _ in range(row)]
- dp[0][0] = 0 if obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1 else 1
- if dp[0][0] == 0:
- return 0 # 如果第一个格子就是障碍,return 0
- # 第一行
- for i in range(1, col):
- if obstacleGrid[0][i] == 1:
- # 遇到障碍物时,直接退出循环,后面默认都是0
+ def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid):
+ m = len(obstacleGrid)
+ n = len(obstacleGrid[0])
+ if obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1 or obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1:
+ return 0
+ dp = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
+ for i in range(m):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0: # 遇到障碍物时,直接退出循环,后面默认都是0
+ dp[i][0] = 1
+ else:
break
- dp[0][i] = 1
-
- # 第一列
- for i in range(1, row):
- if obstacleGrid[i][0] == 1:
- # 遇到障碍物时,直接退出循环,后面默认都是0
+ for j in range(n):
+ if obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0:
+ dp[0][j] = 1
+ else:
break
- dp[i][0] = 1
- # print(dp)
-
- for i in range(1, row):
- for j in range(1, col):
- if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0:
- dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
- return dp[-1][-1]
+ for i in range(1, m):
+ for j in range(1, n):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1:
+ continue
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
+
```
+动态规划(版本二)
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid):
+ m = len(obstacleGrid) # 网格的行数
+ n = len(obstacleGrid[0]) # 网格的列数
+
+ if obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1 or obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1:
+ # 如果起点或终点有障碍物,直接返回0
+ return 0
+
+ dp = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)] # 创建一个二维列表用于存储路径数
+
+ # 设置起点的路径数为1
+ dp[0][0] = 1 if obstacleGrid[0][0] == 0 else 0
+
+ # 计算第一列的路径数
+ for i in range(1, m):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0:
+ dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0]
+
+ # 计算第一行的路径数
+ for j in range(1, n):
+ if obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0:
+ dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1]
+
+ # 计算其他位置的路径数
+ for i in range(1, m):
+ for j in range(1, n):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1:
+ continue
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
+
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1] # 返回终点的路径数
+
+
+```
+动态规划(版本三)
```python
class Solution:
- """
- 使用一维dp数组
- """
+ def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid):
+ if obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1:
+ return 0
+
+ dp = [0] * len(obstacleGrid[0]) # 创建一个一维列表用于存储路径数
+
+ # 初始化第一行的路径数
+ for j in range(len(dp)):
+ if obstacleGrid[0][j] == 1:
+ dp[j] = 0
+ elif j == 0:
+ dp[j] = 1
+ else:
+ dp[j] = dp[j - 1]
+
+ # 计算其他行的路径数
+ for i in range(1, len(obstacleGrid)):
+ for j in range(len(dp)):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1:
+ dp[j] = 0
+ elif j != 0:
+ dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1]
+
+ return dp[-1] # 返回最后一个元素,即终点的路径数
- def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- m, n = len(obstacleGrid), len(obstacleGrid[0])
+```
+动态规划(版本四)
- # 初始化dp数组
- # 该数组缓存当前行
- curr = [0] * n
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid):
+ if obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1:
+ return 0
+
+ m, n = len(obstacleGrid), len(obstacleGrid[0])
+
+ dp = [0] * n # 创建一个一维列表用于存储路径数
+
+ # 初始化第一行的路径数
for j in range(n):
if obstacleGrid[0][j] == 1:
break
- curr[j] = 1
-
- for i in range(1, m): # 从第二行开始
- for j in range(n): # 从第一列开始,因为第一列可能有障碍物
- # 有障碍物处无法通行,状态就设成0
+ dp[j] = 1
+
+ # 计算其他行的路径数
+ for i in range(1, m):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][0] == 1:
+ dp[0] = 0
+ for j in range(1, n):
if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1:
- curr[j] = 0
- elif j > 0:
- # 等价于
- # dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
- curr[j] = curr[j] + curr[j - 1]
- # 隐含的状态更新
- # dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0]
+ dp[j] = 0
+ else:
+ dp[j] += dp[j - 1]
- return curr[n - 1]
+ return dp[-1] # 返回最后一个元素,即终点的路径数
+
```
+动态规划(版本五)
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid):
+ if obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1:
+ return 0
+
+ m, n = len(obstacleGrid), len(obstacleGrid[0])
+
+ dp = [0] * n # 创建一个一维列表用于存储路径数
+
+ # 初始化第一行的路径数
+ for j in range(n):
+ if obstacleGrid[0][j] == 1:
+ break
+ dp[j] = 1
+
+ # 计算其他行的路径数
+ for i in range(1, m):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][0] == 1:
+ dp[0] = 0
+ for j in range(1, n):
+ if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1:
+ dp[j] = 0
+ continue
+
+ dp[j] += dp[j - 1]
+
+ return dp[-1] # 返回最后一个元素,即终点的路径数
+
+
+```
### Go
```go
@@ -368,27 +463,28 @@ func uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
+
```Javascript
var uniquePathsWithObstacles = function(obstacleGrid) {
const m = obstacleGrid.length
const n = obstacleGrid[0].length
const dp = Array(m).fill().map(item => Array(n).fill(0))
-
+
for (let i = 0; i < m && obstacleGrid[i][0] === 0; ++i) {
dp[i][0] = 1
}
-
+
for (let i = 0; i < n && obstacleGrid[0][i] === 0; ++i) {
dp[0][i] = 1
}
-
+
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
dp[i][j] = obstacleGrid[i][j] === 1 ? 0 : dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
}
}
-
+
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
};
@@ -452,6 +548,27 @@ function uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number {
};
```
+// 版本二: dp改為使用一維陣列,從終點開始遍歷
+```typescript
+function uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number {
+ const m = obstacleGrid.length;
+ const n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
+
+ const dp: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);
+ dp[n - 1] = 1;
+
+ // 由下而上,右而左進行遍歷
+ for (let i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ for (let j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
+ if (obstacleGrid[i][j] === 1) dp[j] = 0;
+ else dp[j] = dp[j] + (dp[j + 1] || 0);
+ }
+ }
+
+ return dp[0];
+};
+```
+
### Rust
```Rust
@@ -488,6 +605,33 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+空间优化:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn unique_paths_with_obstacles(obstacle_grid: Vec>) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![0; obstacle_grid[0].len()];
+ for (i, &v) in obstacle_grid[0].iter().enumerate() {
+ if v == 0 {
+ dp[i] = 1;
+ } else {
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+ for rows in obstacle_grid.iter().skip(1) {
+ for j in 0..rows.len() {
+ if rows[j] == 1 {
+ dp[j] = 0;
+ } else if j != 0 {
+ dp[j] += dp[j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ dp.pop().unwrap()
+ }
+}
+```
+
### C
```c
@@ -545,9 +689,10 @@ int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int** obstacleGrid, int obstacleGridSize, int* obst
```
空间优化版本:
+
```c
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int** obstacleGrid, int obstacleGridSize, int* obstacleGridColSize){
- int m = obstacleGridSize;
+ int m = obstacleGridSize;
int n = obstacleGridColSize[0];
int *dp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
int i, j;
@@ -608,8 +753,29 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public int UniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid)
+ {
+ int m = obstacleGrid.Length;
+ int n = obstacleGrid[0].Length;
+ int[,] dp = new int[m, n];
+ if (obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1 || obstacleGrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 1) return 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < m && obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0; i++) dp[i, 0] = 1;
+ for (int j = 0; j < n && obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0; j++) dp[0, j] = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
+ {
+ for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
+ {
+ if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) continue;
+ dp[i, j] = dp[i - 1, j] + dp[i, j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1, n - 1];
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14aeef0142..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14aeef0142..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 70. 爬楼梯
@@ -29,9 +27,9 @@
* 1 阶 + 2 阶
* 2 阶 + 1 阶
-# 视频讲解
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[带你学透动态规划-爬楼梯|LeetCode:70.爬楼梯)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17h411h7UH),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[带你学透动态规划-爬楼梯|LeetCode:70.爬楼梯)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17h411h7UH),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -72,7 +70,7 @@ dp[i]: 爬到第i层楼梯,有dp[i]种方法
3. dp数组如何初始化
-在回顾一下dp[i]的定义:爬到第i层楼梯,有dp[i]中方法。
+再回顾一下dp[i]的定义:爬到第i层楼梯,有dp[i]种方法。
那么i为0,dp[i]应该是多少呢,这个可以有很多解释,但基本都是直接奔着答案去解释的。
@@ -102,7 +100,8 @@ dp[i]: 爬到第i层楼梯,有dp[i]种方法
举例当n为5的时候,dp table(dp数组)应该是这样的
-
+
+
如果代码出问题了,就把dp table 打印出来,看看究竟是不是和自己推导的一样。
@@ -129,8 +128,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
-* 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(n)
当然依然也可以,优化一下空间复杂度,代码如下:
@@ -153,8 +152,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
-* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
+* 时间复杂度:O(n)
+* 空间复杂度:O(1)
后面将讲解的很多动规的题目其实都是当前状态依赖前两个,或者前三个状态,都可以做空间上的优化,**但我个人认为面试中能写出版本一就够了哈,清晰明了,如果面试官要求进一步优化空间的话,我们再去优化**。
@@ -164,9 +163,12 @@ public:
这道题目还可以继续深化,就是一步一个台阶,两个台阶,三个台阶,直到 m个台阶,有多少种方法爬到n阶楼顶。
-这又有难度了,这其实是一个完全背包问题,但力扣上没有这种题目,所以后续我在讲解背包问题的时候,今天这道题还会从背包问题的角度上来再讲一遍。 如果想提前看一下,可以看这篇:[70.爬楼梯完全背包版本](https://programmercarl.com/0070.%E7%88%AC%E6%A5%BC%E6%A2%AF%E5%AE%8C%E5%85%A8%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85%E7%89%88%E6%9C%AC.html)
+这又有难度了,这其实是一个完全背包问题,但力扣上没有这种题目,大家可以去卡码网去做一下 [57. 爬楼梯](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1067)
+
-这里我先给出我的实现代码:
+所以后续我在讲解背包问题的时候,今天这道题还会从背包问题的角度上来再讲一遍。 如果想提前看一下,可以看这篇:[70.爬楼梯完全背包版本](https://programmercarl.com/0070.%E7%88%AC%E6%A5%BC%E6%A2%AF%E5%AE%8C%E5%85%A8%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85%E7%89%88%E6%9C%AC.html)
+
+这里我先给出本题的代码:
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -211,8 +213,6 @@ public:
所以不要轻视简单题,那种凭感觉就刷过去了,其实和没掌握区别不大,只有掌握方法论并说清一二三,才能触类旁通,举一反三哈!
-就酱,循序渐进学算法,认准「代码随想录」!
-
## 其他语言版本
@@ -250,32 +250,66 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python
-
+动态规划(版本一)
```python
# 空间复杂度为O(n)版本
class Solution:
def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:
- # dp[i] 为第 i 阶楼梯有多少种方法爬到楼顶
- dp = [0]*(n+1)
- dp[0] = 1
+ if n <= 1:
+ return n
+
+ dp = [0] * (n + 1)
dp[1] = 1
- for i in range(2, n+1):
- dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2]
+ dp[2] = 2
+
+ for i in range(3, n + 1):
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
+
return dp[n]
-# 空间复杂度为O(1)版本
+```
+动态规划(版本二)
+```python
+
+# 空间复杂度为O(3)版本
class Solution:
def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:
- dp = [0]*(n+1)
- dp[0] = 1
+ if n <= 1:
+ return n
+
+ dp = [0] * 3
dp[1] = 1
- for i in range(2,n+1):
- tmp = dp[0] + dp[1]
- dp[0] = dp[1]
- dp[1] = tmp
- return dp[1]
+ dp[2] = 2
+
+ for i in range(3, n + 1):
+ total = dp[1] + dp[2]
+ dp[1] = dp[2]
+ dp[2] = total
+
+ return dp[2]
+
```
+动态规划(版本三)
+```python
+
+# 空间复杂度为O(1)版本
+class Solution:
+ def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:
+ if n <= 1:
+ return n
+
+ prev1 = 1
+ prev2 = 2
+
+ for i in range(3, n + 1):
+ total = prev1 + prev2
+ prev1 = prev2
+ prev2 = total
+
+ return prev2
+
+```
### Go
```Go
func climbStairs(n int) int {
@@ -291,7 +325,7 @@ func climbStairs(n int) int {
return dp[n]
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var climbStairs = function(n) {
// dp[i] 为第 i 阶楼梯有多少种方法爬到楼顶
@@ -432,7 +466,7 @@ object Solution {
### C#
-```c#
+```csharp
public class Solution {
public int ClimbStairs(int n) {
if(n<=2) return n;
@@ -453,23 +487,35 @@ public class Solution {
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn climb_stairs(n: i32) -> i32 {
- if n <= 2 {
+ if n <= 1 {
return n;
}
- let mut a = 1;
- let mut b = 2;
- let mut f = 0;
- for i in 2..n {
+ let (mut a, mut b, mut f) = (1, 1, 0);
+ for _ in 2..=n {
f = a + b;
a = b;
b = f;
}
- return f;
+ f
+}
+```
+
+dp 数组
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn climb_stairs(n: i32) -> i32 {
+ let n = n as usize;
+ let mut dp = vec![0; n + 1];
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ dp[1] = 1;
+ for i in 2..=n {
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
+ }
+ dp[n]
}
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3093c83325..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,33 +1,35 @@
-
-
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3093c83325..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,33 +1,35 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-# 70. 爬楼梯
+# 70. 爬楼梯(进阶版)
-[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/climbing-stairs/)
+[卡码网:57. 爬楼梯](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1067)
-假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
+假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
-每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
+每次你可以爬至多m (1 <= m < n)个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
-注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
+注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
-示例 1:
-输入: 2
-输出: 2
-解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
-1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
-2. 2 阶
+输入描述:输入共一行,包含两个正整数,分别表示n, m
+
+输出描述:输出一个整数,表示爬到楼顶的方法数。
+
+输入示例:3 2
+
+输出示例:3
+
+提示:
+
+当 m = 2,n = 3 时,n = 3 这表示一共有三个台阶,m = 2 代表你每次可以爬一个台阶或者两个台阶。
+
+此时你有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
+
+* 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶段
+* 1 阶 + 2 阶
+* 2 阶 + 1 阶
-示例 2:
-输入: 3
-输出: 3
-解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
-1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
-2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
-3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
## 思路
@@ -35,11 +37,13 @@
**这次终于讲到了背包问题,我选择带录友们再爬一次楼梯!**
-这道题目 我们在[动态规划:爬楼梯](https://programmercarl.com/0070.爬楼梯.html) 中已经讲过一次了,原题其实是一道简单动规的题目。
+这道题目 我们在[动态规划:爬楼梯](https://programmercarl.com/0070.爬楼梯.html) 中已经讲过一次了,这次我又给本题加点料,力扣上没有原题,所以可以在卡码网[57. 爬楼梯](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1067)上来刷这道题目。
-既然这么简单为什么还要讲呢,其实本题稍加改动就是一道面试好题。
+我们之前做的 爬楼梯 是只能至多爬两个台阶。
-**改为:一步一个台阶,两个台阶,三个台阶,.......,直到 m个台阶。问有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?**
+这次**改为:一步一个台阶,两个台阶,三个台阶,.......,直到 m个台阶。问有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?**
+
+这又有难度了,这其实是一个完全背包问题。
1阶,2阶,.... m阶就是物品,楼顶就是背包。
@@ -86,9 +90,12 @@
以上分析完毕,C++代码如下:
```CPP
-class Solution {
-public:
- int climbStairs(int n) {
+#include
+#include
+using namespace std;
+int main() {
+ int n, m;
+ while (cin >> n >> m) {
vector dp(n + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 遍历背包
@@ -96,12 +103,18 @@ public:
if (i - j >= 0) dp[i] += dp[i - j];
}
}
- return dp[n];
+ cout << dp[n] << endl;
}
-};
+}
```
-代码中m表示最多可以爬m个台阶,代码中把m改成2就是本题70.爬楼梯可以AC的代码了。
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * m)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
+
+代码中m表示最多可以爬m个台阶,代码中把m改成2就是 力扣:70.爬楼梯的解题思路。
+
+**当然注意 力扣是 核心代码模式,卡码网是ACM模式**
+
## 总结
@@ -122,108 +135,118 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-
-Java:
-```java
-class Solution {
- public int climbStairs(int n) {
- int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
- int[] weight = {1,2};
- dp[0] = 1;
-
- for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < weight.length; j++) {
- if (i >= weight[j]) dp[i] += dp[i - weight[j]];
+### Java:
+
+```Java
+import java.util.Scanner;
+class climbStairs{
+ public static void main(String [] args){
+ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
+ int m, n;
+ while (sc.hasNextInt()) {
+ // 从键盘输入参数,中间用空格隔开
+ n = sc.nextInt();
+ m = sc.nextInt();
+
+ // 求排列问题,先遍历背包再遍历物品
+ int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
+ for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
+ if (j - i >= 0) dp[j] += dp[j - i];
+ }
}
+ System.out.println(dp[n]);
}
-
- return dp[n];
}
}
```
-Python3:
-
-
-```python
-class Solution:
- def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:
- dp = [0]*(n + 1)
- dp[0] = 1
- m = 2
- # 遍历背包
- for j in range(n + 1):
- # 遍历物品
- for step in range(1, m + 1):
- if j >= step:
- dp[j] += dp[j - step]
- return dp[n]
+### Python3:
+```python3
+def climbing_stairs(n,m):
+ dp = [0]*(n+1) # 背包总容量
+ dp[0] = 1
+ # 排列题,注意循环顺序,背包在外物品在内
+ for j in range(1,n+1):
+ for i in range(1,m+1):
+ if j>=i:
+ dp[j] += dp[j-i] # 这里i就是重量而非index
+ return dp[n]
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ n,m = list(map(int,input().split(' ')))
+ print(climbing_stairs(n,m))
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
-func climbStairs(n int) int {
- //定义
- dp := make([]int, n+1)
- //初始化
- dp[0] = 1
- // 本题物品只有两个1,2
- m := 2
- // 遍历顺序
- for j := 1; j <= n; j++ { //先遍历背包
- for i := 1; i <= m; i++ { //再遍历物品
- if j >= i {
- dp[j] += dp[j-i]
- }
- //fmt.Println(dp)
- }
- }
- return dp[n]
+package main
+
+import (
+ "bufio"
+ "fmt"
+ "os"
+ "strconv"
+ "strings"
+)
+
+func climbStairs(n int, m int) int {
+ dp := make([]int, n+1)
+ dp[0] = 1
+ for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
+ for j := 1; j <= m; j++ {
+ if i-j >= 0 {
+ dp[i] += dp[i-j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n]
+}
+
+func main() {
+ // 读取输入n,m
+ reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
+ input, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')
+ input = strings.TrimSpace(input)
+ nv := strings.Split(input, " ")
+ n, _ := strconv.Atoi(nv[0])
+ m, _ := strconv.Atoi(nv[1])
+ result := climbStairs(n, m)
+ fmt.Println(result)
}
```
-JavaScript:
-```javascript
-var climbStairs = function(n) {
- const dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
- const m = 2;
- dp[0] = 1;
- for(let i = 1; i <= n; i++){
- for(let j = 1; j <= m; j++){
- if(i >= j) {
- dp[i] += dp[i - j];
- }
- }
+### JavaScript:
+```javaScript
+var climbStairs = function (n) {
+ let dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ // 排列题,注意循环顺序,背包在外物品在内
+ for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {//遍历背包
+ for (let i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {//遍历物品
+ if (j - i >= 0) dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - i];
}
- return dp[n];
-};
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+}
```
-TypeScript:
-
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
-function climbStairs(n: number): number {
- const m: number = 2; // 本题m为2
- const dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
+var climbStairs = function (n: number): number {
+ let dp: number[] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
- // 遍历背包
- for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
- // 遍历物品
- for (let j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
- if (j <= i) {
- dp[i] += dp[i - j];
- }
+ for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {//遍历背包
+ for (let i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {//遍历物品
+ if (j - i >= 0) dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - i];
}
}
return dp[n];
-};
+}
```
+### Rust:
-
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8a877d2088..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8a877d2088..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 72. 编辑距离
@@ -40,6 +38,9 @@ exection -> execution (插入 'u')
* 0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
* word1 和 word2 由小写英文字母组成
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划终极绝杀! LeetCode:72.编辑距离](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1qv4y1q78f/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -169,7 +170,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
可以看出dp[i][j]是依赖左方,上方和左上方元素的,如图:
-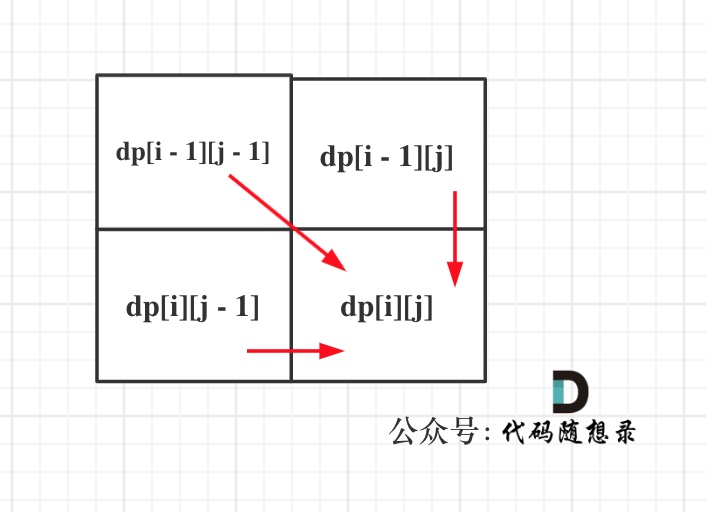
+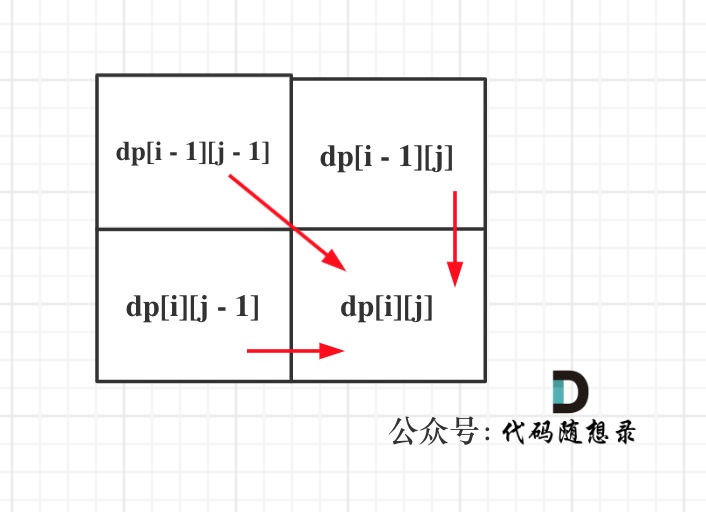
所以在dp矩阵中一定是从左到右从上到下去遍历。
@@ -193,7 +194,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= word1.size(); i++) {
以示例1为例,输入:`word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"`为例,dp矩阵状态图如下:
-
+
以上动规五部分析完毕,C++代码如下:
@@ -218,11 +219,15 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * m)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n * m)
+
+
## 其他语言版本
+### Java:
-Java:
```java
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int m = word1.length();
@@ -250,7 +255,8 @@ public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
class Solution:
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
@@ -268,7 +274,8 @@ class Solution:
return dp[-1][-1]
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```Go
func minDistance(word1 string, word2 string) int {
m, n := len(word1), len(word2)
@@ -304,8 +311,8 @@ func Min(args ...int) int {
}
```
+### JavaScript:
-Javascript:
```javascript
const minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
let dp = Array.from(Array(word1.length + 1), () => Array(word2.length+1).fill(0));
@@ -332,7 +339,7 @@ const minDistance = (word1, word2) => {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function minDistance(word1: string, word2: string): number {
@@ -367,7 +374,7 @@ function minDistance(word1: string, word2: string): number {
};
```
-C:
+### C:
```c
@@ -395,7 +402,61 @@ int minDistance(char * word1, char * word2){
}
```
-
-
-  -
+Rust:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; word2.len() + 1]; word1.len() + 1];
+ for i in 1..=word2.len() {
+ dp[0][i] = i;
+ }
+
+ for (j, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ v[0] = j;
+ }
+ for (i, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ for (j, char2) in word2.chars().enumerate() {
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j];
+ continue;
+ }
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].min(dp[i + 1][j]).min(dp[i][j]) + 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()][word2.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 一维 dp
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![0; word1.len() + 1];
+ for (i, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ *v = i;
+ }
+
+ for char2 in word2.chars() {
+ // 相当于 dp[i][0] 的初始化
+ let mut pre = dp[0];
+ dp[0] += 1; // j = 0, 将前 i 个字符变成空串的个数
+ for (j, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ let temp = dp[j + 1];
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[j + 1] = pre;
+ } else {
+ dp[j + 1] = dp[j + 1].min(dp[j]).min(pre) + 1;
+ }
+ pre = temp;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 77ea5e80eb..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,37 +1,32 @@
-
-
+Rust:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; word2.len() + 1]; word1.len() + 1];
+ for i in 1..=word2.len() {
+ dp[0][i] = i;
+ }
+
+ for (j, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ v[0] = j;
+ }
+ for (i, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ for (j, char2) in word2.chars().enumerate() {
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j];
+ continue;
+ }
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].min(dp[i + 1][j]).min(dp[i][j]) + 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()][word2.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 一维 dp
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![0; word1.len() + 1];
+ for (i, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ *v = i;
+ }
+
+ for char2 in word2.chars() {
+ // 相当于 dp[i][0] 的初始化
+ let mut pre = dp[0];
+ dp[0] += 1; // j = 0, 将前 i 个字符变成空串的个数
+ for (j, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ let temp = dp[j + 1];
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[j + 1] = pre;
+ } else {
+ dp[j + 1] = dp[j + 1].min(dp[j]).min(pre) + 1;
+ }
+ pre = temp;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 77ea5e80eb..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,37 +1,32 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-
-
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 第77题. 组合
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/ )
-给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
-
-示例:
-输入: n = 4, k = 2
-输出:
-[
- [2,4],
- [3,4],
- [2,3],
- [1,2],
- [1,3],
- [1,4],
-]
+给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
-# 算法公开课
+示例:
+输入: n = 4, k = 2
+输出:
+[
+ [2,4],
+ [3,4],
+ [2,3],
+ [1,2],
+ [1,3],
+ [1,4],
+]
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[带你学透回溯算法-组合问题(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv),[组合问题的剪枝操作](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[带你学透回溯算法-组合问题(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv),[组合问题的剪枝操作](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-# 思路
+## 思路
本题是回溯法的经典题目。
@@ -39,6 +34,7 @@
直接的解法当然是使用for循环,例如示例中k为2,很容易想到 用两个for循环,这样就可以输出 和示例中一样的结果。
代码如下:
+
```CPP
int n = 4;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
@@ -66,7 +62,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
**此时就会发现虽然想暴力搜索,但是用for循环嵌套连暴力都写不出来!**
-咋整?
+咋整?
回溯搜索法来了,虽然回溯法也是暴力,但至少能写出来,不像for循环嵌套k层让人绝望。
@@ -86,7 +82,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
那么我把组合问题抽象为如下树形结构:
-
+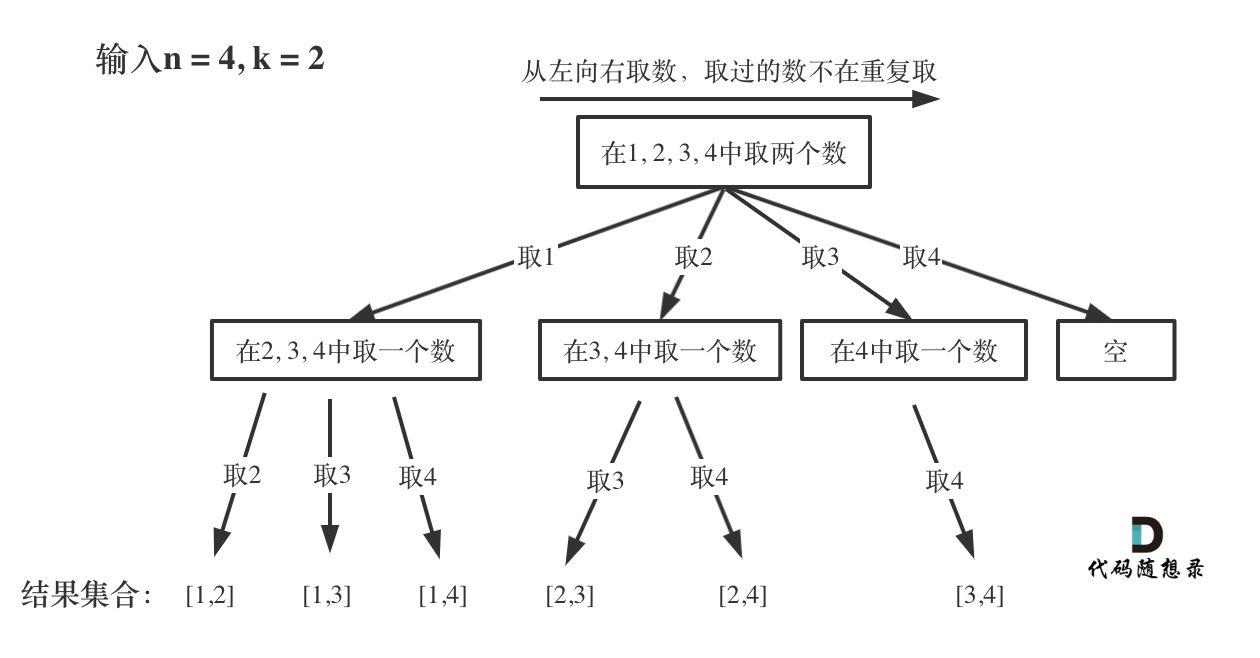
可以看出这棵树,一开始集合是 1,2,3,4, 从左向右取数,取过的数,不再重复取。
@@ -94,7 +90,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
**每次从集合中选取元素,可选择的范围随着选择的进行而收缩,调整可选择的范围**。
-**图中可以发现n相当于树的宽度,k相当于树的深度**。
+**图中可以发现n相当于树的宽度,k相当于树的深度**。
那么如何在这个树上遍历,然后收集到我们要的结果集呢?
@@ -105,9 +101,9 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
在[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/回溯算法理论基础.html)中我们提到了回溯法三部曲,那么我们按照回溯法三部曲开始正式讲解代码了。
-## 回溯法三部曲
+### 回溯法三部曲
-* 递归函数的返回值以及参数
+* 递归函数的返回值以及参数
在这里要定义两个全局变量,一个用来存放符合条件单一结果,一个用来存放符合条件结果的集合。
@@ -124,25 +120,25 @@ vector path; // 用来存放符合条件结果
然后还需要一个参数,为int型变量startIndex,这个参数用来记录本层递归的中,集合从哪里开始遍历(集合就是[1,...,n] )。
-为什么要有这个startIndex呢?
+为什么要有这个startIndex呢?
**建议在[77.组合视频讲解](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv)中,07:36的时候开始听,startIndex 就是防止出现重复的组合**。
从下图中红线部分可以看出,在集合[1,2,3,4]取1之后,下一层递归,就要在[2,3,4]中取数了,那么下一层递归如何知道从[2,3,4]中取数呢,靠的就是startIndex。
-
+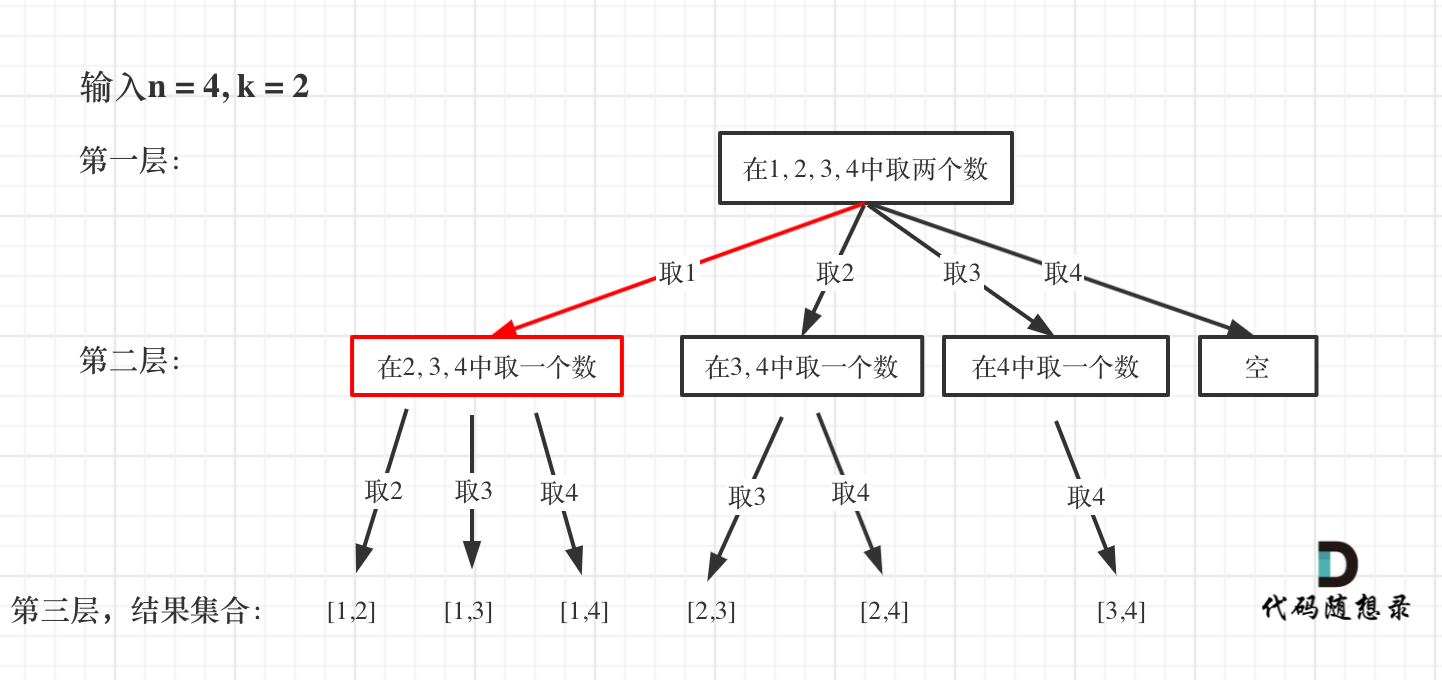
-所以需要startIndex来记录下一层递归,搜索的起始位置。
+所以需要startIndex来记录下一层递归,搜索的起始位置。
那么整体代码如下:
```cpp
vector> result; // 存放符合条件结果的集合
vector path; // 用来存放符合条件单一结果
-void backtracking(int n, int k, int startIndex)
+void backtracking(int n, int k, int startIndex)
```
-* 回溯函数终止条件
+* 回溯函数终止条件
什么时候到达所谓的叶子节点了呢?
@@ -150,7 +146,7 @@ path这个数组的大小如果达到k,说明我们找到了一个子集大小
如图红色部分:
-
+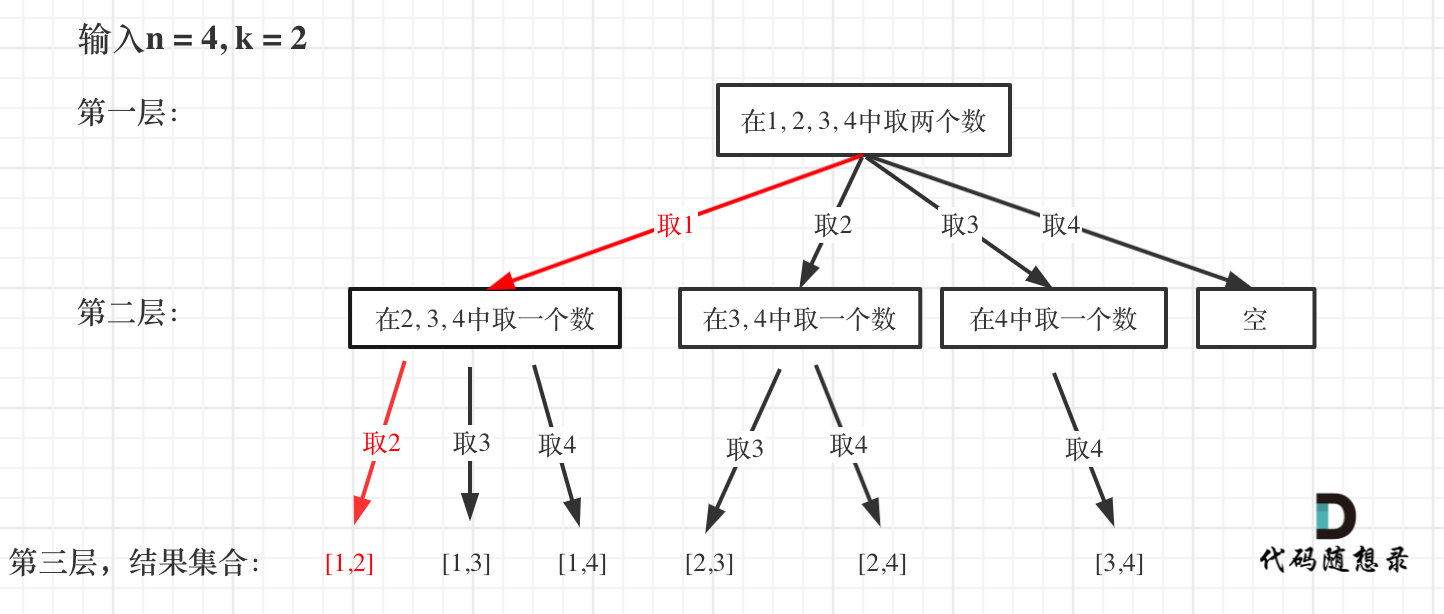
此时用result二维数组,把path保存起来,并终止本层递归。
@@ -163,21 +159,21 @@ if (path.size() == k) {
}
```
-* 单层搜索的过程
+* 单层搜索的过程
回溯法的搜索过程就是一个树型结构的遍历过程,在如下图中,可以看出for循环用来横向遍历,递归的过程是纵向遍历。
-
+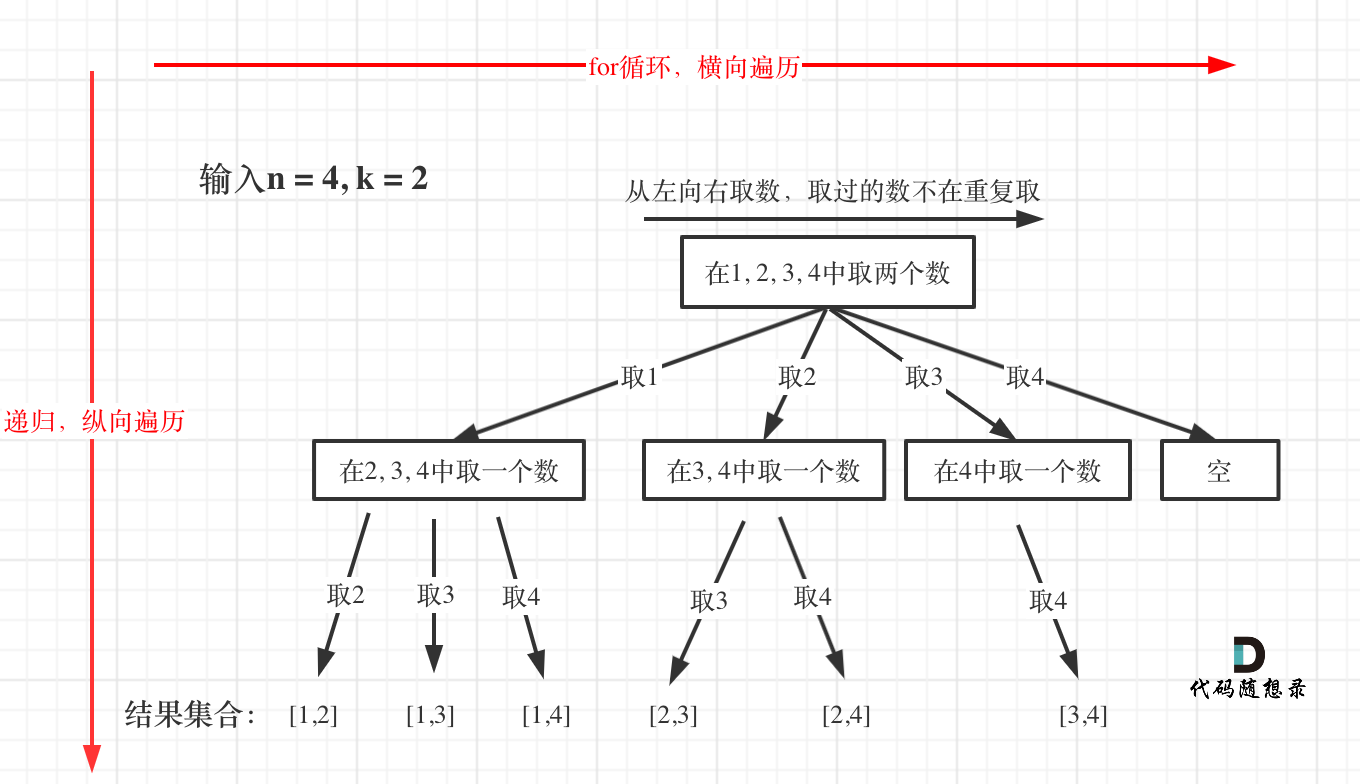
如此我们才遍历完图中的这棵树。
-for循环每次从startIndex开始遍历,然后用path保存取到的节点i。
+for循环每次从startIndex开始遍历,然后用path保存取到的节点i。
代码如下:
```CPP
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) { // 控制树的横向遍历
- path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
+ path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
backtracking(n, k, i + 1); // 递归:控制树的纵向遍历,注意下一层搜索要从i+1开始
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,撤销处理的节点
}
@@ -201,7 +197,7 @@ private:
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
- path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
+ path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
backtracking(n, k, i + 1); // 递归
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,撤销处理的节点
}
@@ -215,10 +211,15 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
+
-还记得我们在[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/回溯算法理论基础.html)中给出的回溯法模板么?
+
+还记得我们在[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/回溯算法理论基础.html)中给出的回溯法模板么?
如下:
+
```
void backtracking(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
@@ -234,15 +235,15 @@ void backtracking(参数) {
}
```
-**对比一下本题的代码,是不是发现有点像!** 所以有了这个模板,就有解题的大体方向,不至于毫无头绪。
+**对比一下本题的代码,是不是发现有点像!** 所以有了这个模板,就有解题的大体方向,不至于毫无头绪。
-## 总结
+## 总结
组合问题是回溯法解决的经典问题,我们开始的时候给大家列举一个很形象的例子,就是n为100,k为50的话,直接想法就需要50层for循环。
从而引出了回溯法就是解决这种k层for循环嵌套的问题。
-然后进一步把回溯法的搜索过程抽象为树形结构,可以直观的看出搜索的过程。
+然后进一步把回溯法的搜索过程抽象为树形结构,可以直观的看出搜索的过程。
接着用回溯法三部曲,逐步分析了函数参数、终止条件和单层搜索的过程。
@@ -266,7 +267,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
这么说有点抽象,如图所示:
-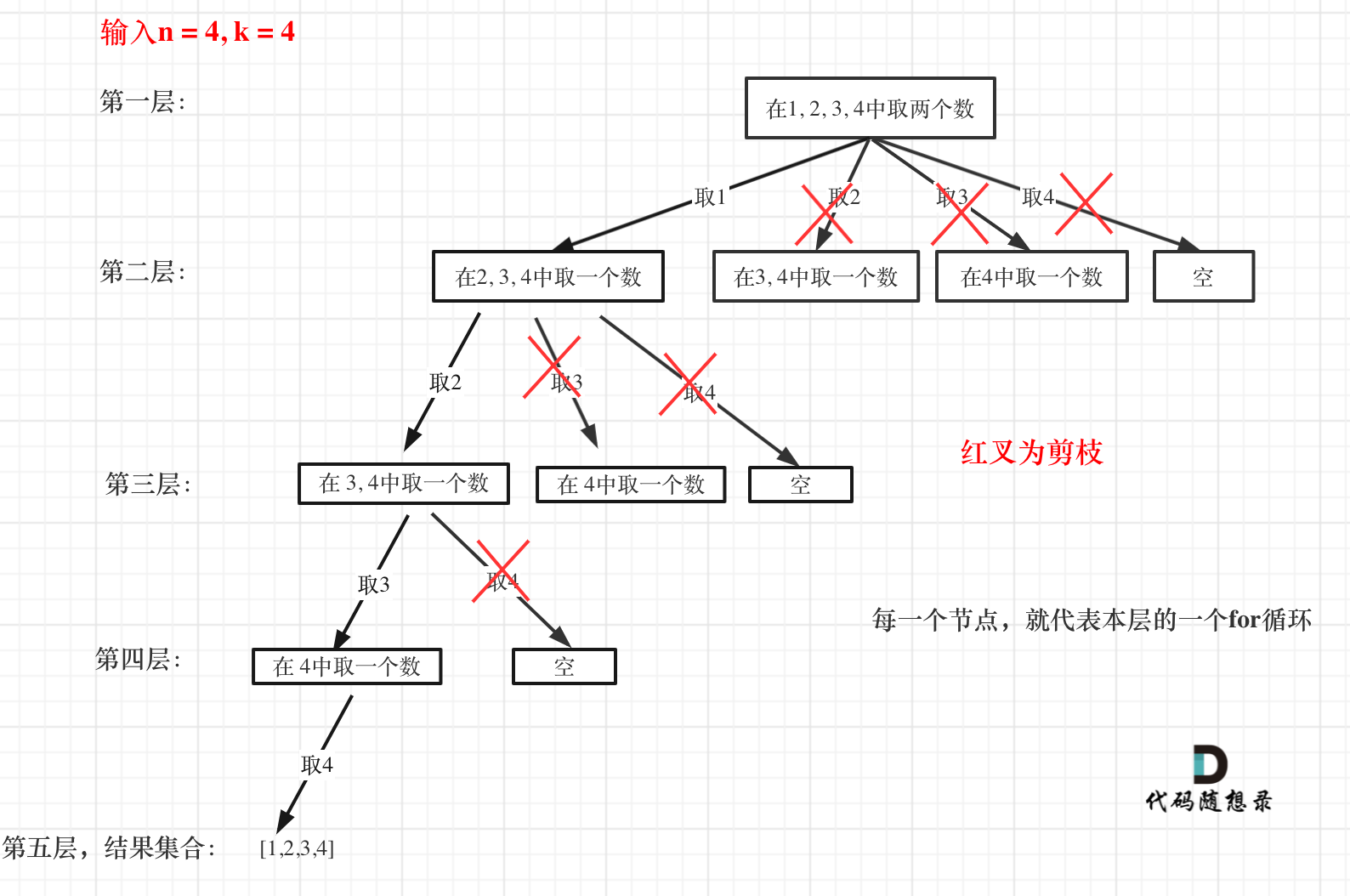
+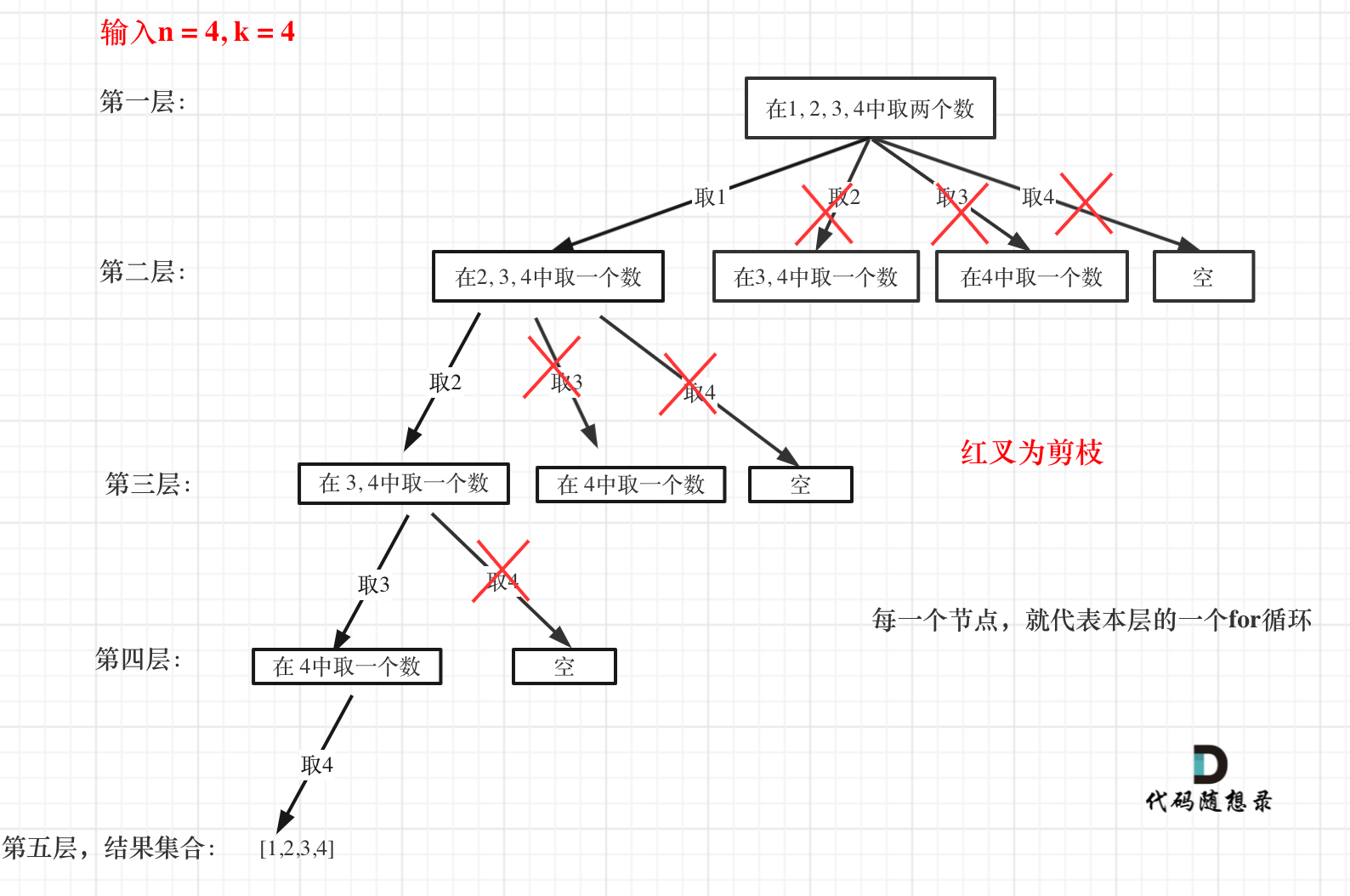
图中每一个节点(图中为矩形),就代表本层的一个for循环,那么每一层的for循环从第二个数开始遍历的话,都没有意义,都是无效遍历。
@@ -275,6 +276,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
**如果for循环选择的起始位置之后的元素个数 已经不足 我们需要的元素个数了,那么就没有必要搜索了**。
注意代码中i,就是for循环里选择的起始位置。
+
```
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
```
@@ -336,12 +338,35 @@ public:
-
-
## 其他语言版本
+
### Java:
+未剪枝优化
+```java
+class Solution {
+ List> result= new ArrayList<>();
+ LinkedList path = new LinkedList<>();
+ public List> combine(int n, int k) {
+ backtracking(n,k,1);
+ return result;
+ }
+
+ public void backtracking(int n,int k,int startIndex){
+ if (path.size() == k){
+ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i =startIndex;i<=n;i++){
+ path.add(i);
+ backtracking(n,k,i+1);
+ path.removeLast();
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+剪枝优化:
```java
class Solution {
List> result = new ArrayList<>();
@@ -370,71 +395,47 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-### Python
-
+### Python
+未剪枝优化
```python
-class Solution(object):
- def combine(self, n, k):
- """
- :type n: int
- :type k: int
- :rtype: List[List[int]]
- """
- result = []
- path = []
- def backtracking(n, k, startidx):
- if len(path) == k:
- result.append(path[:])
- return
-
- # 剪枝, 最后k - len(path)个节点直接构造结果,无需递归
- last_startidx = n - (k - len(path)) + 1
-
- for x in range(startidx, last_startidx + 1):
- path.append(x)
- backtracking(n, k, x + 1) # 递归
- path.pop() # 回溯
-
- backtracking(n, k, 1)
+class Solution:
+ def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+ result = [] # 存放结果集
+ self.backtracking(n, k, 1, [], result)
return result
+ def backtracking(self, n, k, startIndex, path, result):
+ if len(path) == k:
+ result.append(path[:])
+ return
+ for i in range(startIndex, n + 1): # 需要优化的地方
+ path.append(i) # 处理节点
+ self.backtracking(n, k, i + 1, path, result)
+ path.pop() # 回溯,撤销处理的节点
+
```
+
+剪枝优化:
+
```python
class Solution:
def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = []
- path = []
- def backtrack(n, k, StartIndex):
- if len(path) == k:
- res.append(path[:])
- return
- for i in range(StartIndex, n + 1):
- path.append(i)
- backtrack(n, k, i+1)
- path.pop()
- backtrack(n, k, 1)
- return res
+ result = [] # 存放结果集
+ self.backtracking(n, k, 1, [], result)
+ return result
+ def backtracking(self, n, k, startIndex, path, result):
+ if len(path) == k:
+ result.append(path[:])
+ return
+ for i in range(startIndex, n - (k - len(path)) + 2): # 优化的地方
+ path.append(i) # 处理节点
+ self.backtracking(n, k, i + 1, path, result)
+ path.pop() # 回溯,撤销处理的节点
+
```
-剪枝:
-```python
-class Solution:
- def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res=[] #存放符合条件结果的集合
- path=[] #用来存放符合条件结果
- def backtrack(n,k,startIndex):
- if len(path) == k:
- res.append(path[:])
- return
- for i in range(startIndex,n-(k-len(path))+2): #优化的地方
- path.append(i) #处理节点
- backtrack(n,k,i+1) #递归
- path.pop() #回溯,撤销处理的节点
- backtrack(n,k,1)
- return res
-```
-
-### Go
+### Go
+
```Go
var (
path []int
@@ -452,7 +453,7 @@ func dfs(n int, k int, start int) {
tmp := make([]int, k)
copy(tmp, path)
res = append(res, tmp)
- return
+ return
}
for i := start; i <= n; i++ { // 从start开始,不往回走,避免出现重复组合
if n - i + 1 < k - len(path) { // 剪枝
@@ -465,28 +466,59 @@ func dfs(n int, k int, start int) {
}
```
-### javascript
+### JavaScript
+未剪枝:
+
+```js
+var combine = function (n, k) {
+ // 回溯法
+ let result = [],
+ path = [];
+ let backtracking = (_n, _k, startIndex) => {
+ // 终止条件
+ if (path.length === _k) {
+ result.push(path.slice());
+ return;
+ }
+ // 循环本层集合元素
+ for (let i = startIndex; i <= _n; i++) {
+ path.push(i);
+ // 递归
+ backtracking(_n, _k, i + 1);
+ // 回溯操作
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ };
+ backtracking(n, k, 1);
+ return result;
+};
+```
剪枝:
+
```javascript
-let result = []
-let path = []
-var combine = function(n, k) {
- result = []
- combineHelper(n, k, 1)
- return result
+var combine = function (n, k) {
+ // 回溯法
+ let result = [],
+ path = [];
+ let backtracking = (_n, _k, startIndex) => {
+ // 终止条件
+ if (path.length === _k) {
+ result.push(path.slice());
+ return;
+ }
+ // 循环本层集合元素
+ for (let i = startIndex; i <= _n - (_k - path.length) + 1; i++) {
+ path.push(i);
+ // 递归
+ backtracking(_n, _k, i + 1);
+ // 回溯操作
+ path.pop();
+ }
+ };
+ backtracking(n, k, 1);
+ return result;
};
-const combineHelper = (n, k, startIndex) => {
- if (path.length === k) {
- result.push([...path])
- return
- }
- for (let i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.length) + 1; ++i) {
- path.push(i)
- combineHelper(n, k, i + 1)
- path.pop()
- }
-}
```
### TypeScript
@@ -536,6 +568,7 @@ impl Solution {
```
剪枝
+
```Rust
impl Solution {
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec>, path: &mut Vec, n: i32, k: i32, start_index: i32) {
@@ -561,6 +594,7 @@ impl Solution {
```
### C
+
```c
int* path;
int pathTop;
@@ -615,6 +649,7 @@ int** combine(int n, int k, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
```
剪枝:
+
```c
int* path;
int pathTop;
@@ -701,13 +736,14 @@ func combine(_ n: Int, _ k: Int) -> [[Int]] {
### Scala
暴力:
+
```scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable // 导包
def combine(n: Int, k: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]() // 存放结果集
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]() //存放符合条件的结果
-
+
def backtracking(n: Int, k: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
if (path.size == k) {
// 如果path的size == k就达到题目要求,添加到结果集,并返回
@@ -720,7 +756,7 @@ object Solution {
path = path.take(path.size - 1) // 回溯完再删除掉刚刚添加的数字
}
}
-
+
backtracking(n, k, 1) // 执行回溯
result.toList // 最终返回result的List形式,return关键字可以省略
}
@@ -743,7 +779,7 @@ object Solution {
return
}
// 剪枝优化
- for (i <- startIndex to (n - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
+ for (i <- startIndex to (n - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
path.append(i) // 先把数字添加进去
backtracking(n, k, i + 1) // 进行下一步回溯
path = path.take(path.size - 1) // 回溯完再删除掉刚刚添加的数字
@@ -756,7 +792,85 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+### Ruby
+
+```ruby
+
+def combine(n, k)
+ result = []
+ path = []
+ backtracking(result, path, n, 1, k)
+ return result
+end
+
+#剪枝优化
+def backtracking(result, path, n, j, k)
+ if path.size == k
+ result << path.map {|item| item}
+ return
+ end
+
+ for i in j..(n-(k - path.size)) + 1
+ #处理节点
+ path << i
+ backtracking(result, path, n, i + 1, k)
+ #回溯,撤销处理过的节点
+ path.pop
+ end
+end
+
+```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 暴力
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> Combine(int n, int k)
+ {
+ BackTracking(n, k, 1);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int n, int k, int start)
+ {
+ if (path.Count == k)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i <= n; i++)
+ {
+ path.Add(i);
+ BackTracking(n, k, i + 1);
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+// 剪枝
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> Combine(int n, int k)
+ {
+ BackTracking(n, k, 1);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int n, int k, int start)
+ {
+ if (path.Count == k)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i <= n - (k - path.Count) + 1; i++)
+ {
+ path.Add(i);
+ BackTracking(n, k, i + 1);
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 066e1b3329..8ddc4058cc
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,15 @@
-
-
+### Ruby
+
+```ruby
+
+def combine(n, k)
+ result = []
+ path = []
+ backtracking(result, path, n, 1, k)
+ return result
+end
+
+#剪枝优化
+def backtracking(result, path, n, j, k)
+ if path.size == k
+ result << path.map {|item| item}
+ return
+ end
+
+ for i in j..(n-(k - path.size)) + 1
+ #处理节点
+ path << i
+ backtracking(result, path, n, i + 1, k)
+ #回溯,撤销处理过的节点
+ path.pop
+ end
+end
+
+```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 暴力
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> Combine(int n, int k)
+ {
+ BackTracking(n, k, 1);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int n, int k, int start)
+ {
+ if (path.Count == k)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i <= n; i++)
+ {
+ path.Add(i);
+ BackTracking(n, k, i + 1);
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+// 剪枝
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> Combine(int n, int k)
+ {
+ BackTracking(n, k, 1);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int n, int k, int start)
+ {
+ if (path.Count == k)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i <= n - (k - path.Count) + 1; i++)
+ {
+ path.Add(i);
+ BackTracking(n, k, i + 1);
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 066e1b3329..8ddc4058cc
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210\344\274\230\345\214\226.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,15 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 77.组合优化
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[组合问题的剪枝操作](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[组合问题的剪枝操作](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。**
+
+## 思路
在[回溯算法:求组合问题!](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)中,我们通过回溯搜索法,解决了n个数中求k个数的组合问题。
@@ -46,7 +47,7 @@ public:
};
```
-# 剪枝优化
+## 剪枝优化
我们说过,回溯法虽然是暴力搜索,但也有时候可以有点剪枝优化一下的。
@@ -66,7 +67,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
这么说有点抽象,如图所示:
-
+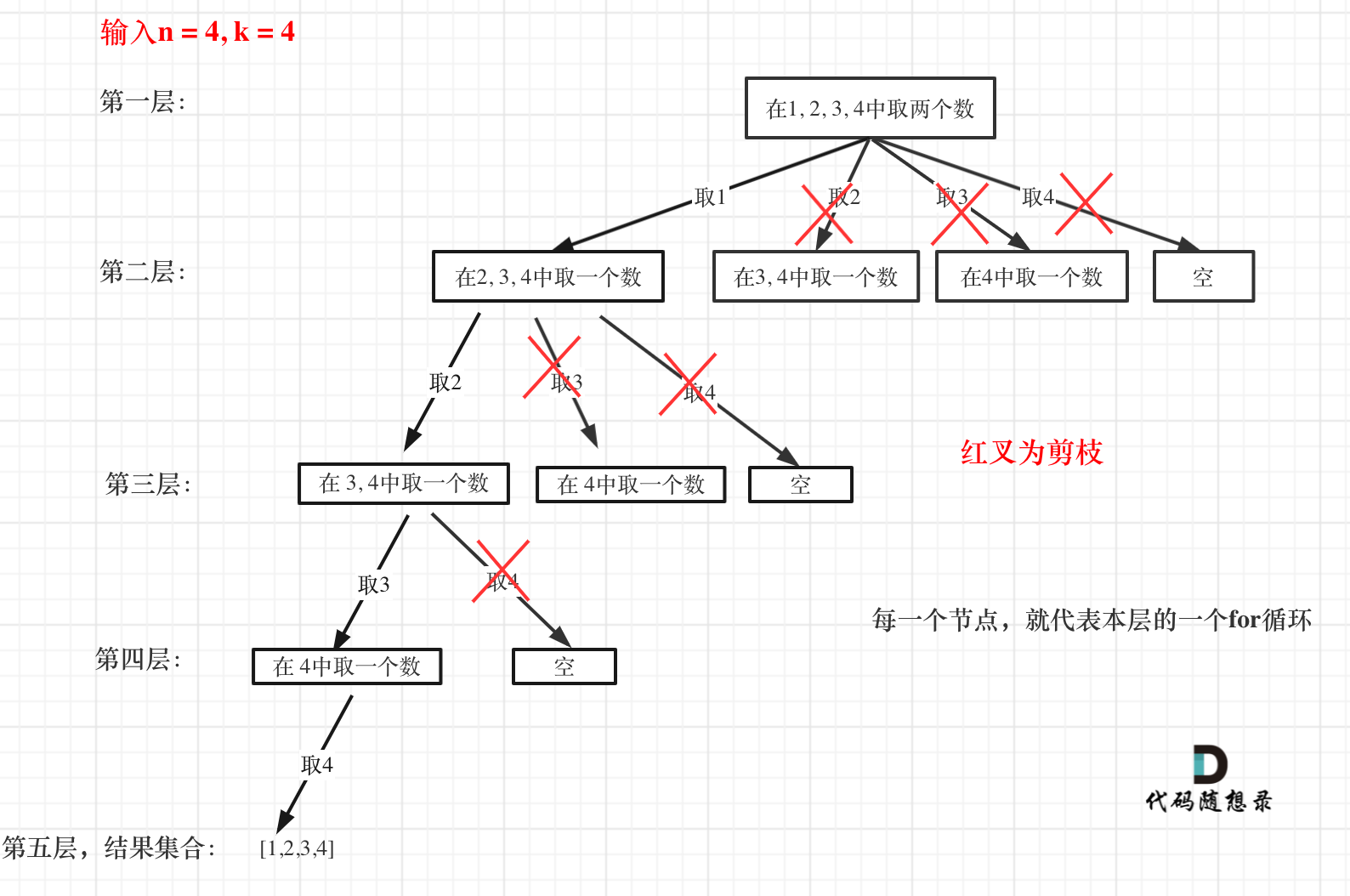
图中每一个节点(图中为矩形),就代表本层的一个for循环,那么每一层的for循环从第二个数开始遍历的话,都没有意义,都是无效遍历。
@@ -130,8 +131,12 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
+
-# 总结
+
+## 总结
本篇我们针对求组合问题的回溯法代码做了剪枝优化,这个优化如果不画图的话,其实不好理解,也不好讲清楚。
@@ -139,14 +144,10 @@ public:
**就酱,学到了就帮Carl转发一下吧,让更多的同学知道这里!**
-
-
-
-
## 其他语言版本
+### Java
-Java:
```java
class Solution {
List> result = new ArrayList<>();
@@ -175,24 +176,29 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python
+
```python
class Solution:
def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res=[] #存放符合条件结果的集合
- path=[] #用来存放符合条件结果
- def backtrack(n,k,startIndex):
- if len(path) == k:
- res.append(path[:])
- return
- for i in range(startIndex,n-(k-len(path))+2): #优化的地方
- path.append(i) #处理节点
- backtrack(n,k,i+1) #递归
- path.pop() #回溯,撤销处理的节点
- backtrack(n,k,1)
- return res
+ result = [] # 存放结果集
+ self.backtracking(n, k, 1, [], result)
+ return result
+ def backtracking(self, n, k, startIndex, path, result):
+ if len(path) == k:
+ result.append(path[:])
+ return
+ for i in range(startIndex, n - (k - len(path)) + 2): # 优化的地方
+ path.append(i) # 处理节点
+ self.backtracking(n, k, i + 1, path, result)
+ path.pop() # 回溯,撤销处理的节点
+
+
+
+
```
-Go:
+### Go
+
```Go
var (
path []int
@@ -220,7 +226,7 @@ func dfs(n int, k int, start int) {
}
```
-javaScript:
+### JavaScript
```js
var combine = function(n, k) {
@@ -242,7 +248,7 @@ var combine = function(n, k) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript
```typescript
function combine(n: number, k: number): number[][] {
@@ -263,7 +269,7 @@ function combine(n: number, k: number): number[][] {
};
```
-Rust:
+### Rust
```Rust
impl Solution {
@@ -289,7 +295,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-C:
+### C
```c
int* path;
@@ -344,7 +350,7 @@ int** combine(int n, int k, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
}
```
-Swift:
+### Swift
```swift
func combine(_ n: Int, _ k: Int) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -374,7 +380,7 @@ func combine(_ n: Int, _ k: Int) -> [[Int]] {
}
```
-Scala:
+### Scala
```scala
object Solution {
@@ -403,7 +409,4 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0c51d4496..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0c51d4496..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 78.子集
@@ -27,12 +25,12 @@
[]
]
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[回溯算法解决子集问题,树上节点都是目标集和! | LeetCode:78.子集](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1U84y1q7Ci),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[回溯算法解决子集问题,树上节点都是目标集和! | LeetCode:78.子集](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1U84y1q7Ci),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-# 思路
+## 思路
求子集问题和[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)和[131.分割回文串](https://programmercarl.com/0131.分割回文串.html)又不一样了。
@@ -48,11 +46,11 @@
以示例中nums = [1,2,3]为例把求子集抽象为树型结构,如下:
-
+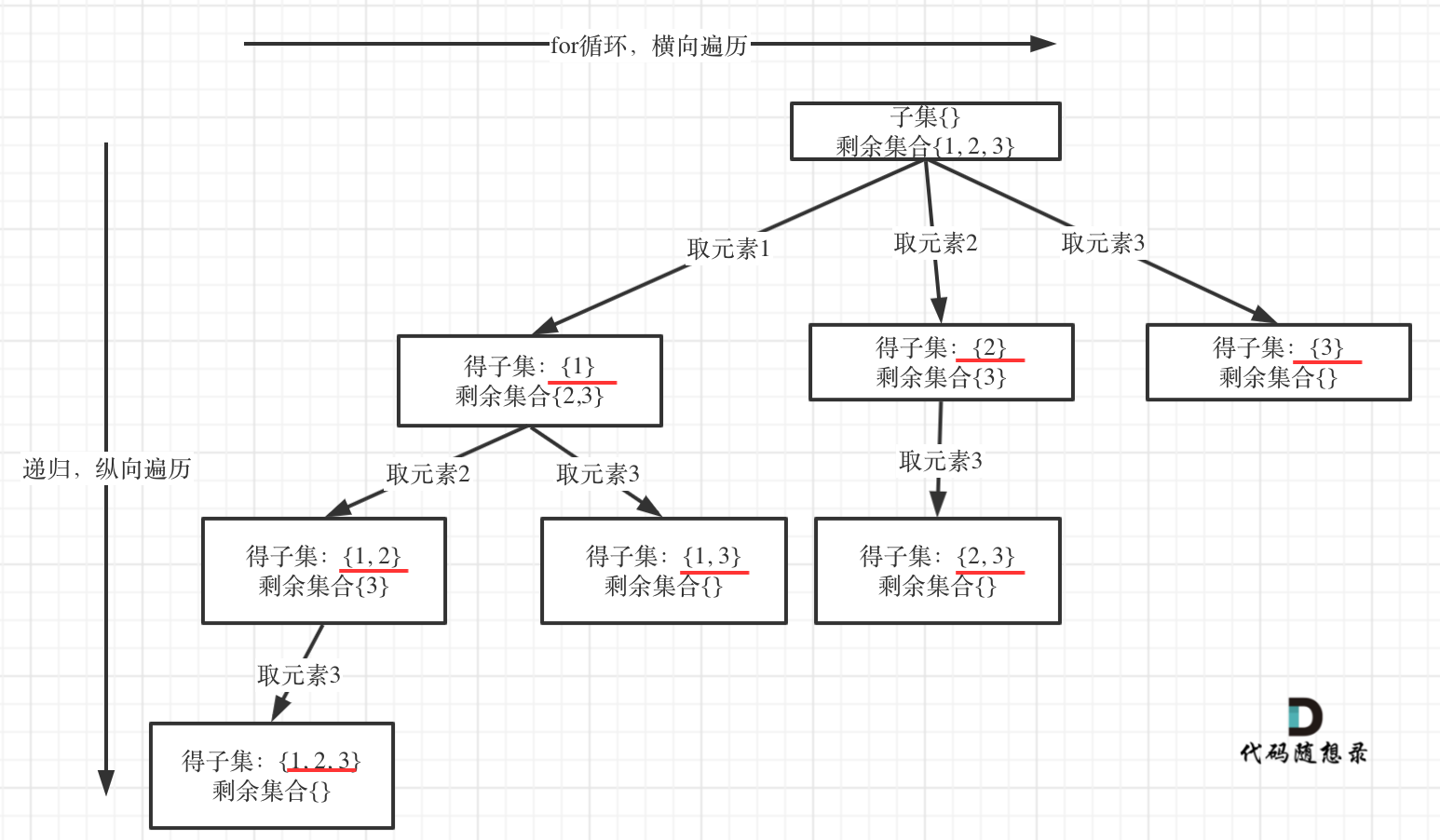
从图中红线部分,可以看出**遍历这个树的时候,把所有节点都记录下来,就是要求的子集集合**。
-## 回溯三部曲
+### 回溯三部曲
* 递归函数参数
@@ -72,7 +70,7 @@ void backtracking(vector& nums, int startIndex) {
从图中可以看出:
-
+
剩余集合为空的时候,就是叶子节点。
@@ -102,8 +100,6 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.size(); i++) {
}
```
-## C++代码
-
根据[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/回溯算法理论基础.html)给出的回溯算法模板:
```
@@ -149,6 +145,8 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
在注释中,可以发现可以不写终止条件,因为本来我们就要遍历整棵树。
@@ -156,7 +154,7 @@ public:
并不会,因为每次递归的下一层就是从i+1开始的。
-# 总结
+## 总结
相信大家经过了
* 组合问题:
@@ -176,10 +174,10 @@ public:
**而组合问题、分割问题是收集树形结构中叶子节点的结果**。
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
List> result = new ArrayList<>();// 存放符合条件结果的集合
@@ -203,34 +201,26 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+### Python
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.path: List[int] = []
- self.paths: List[List[int]] = []
-
- def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
- self.paths.clear()
- self.path.clear()
- self.backtracking(nums, 0)
- return self.paths
-
- def backtracking(self, nums: List[int], start_index: int) -> None:
- # 收集子集,要先于终止判断
- self.paths.append(self.path[:])
- # Base Case
- if start_index == len(nums):
- return
-
- # 单层递归逻辑
- for i in range(start_index, len(nums)):
- self.path.append(nums[i])
- self.backtracking(nums, i+1)
- self.path.pop() # 回溯
+ def subsets(self, nums):
+ result = []
+ path = []
+ self.backtracking(nums, 0, path, result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, path, result):
+ result.append(path[:]) # 收集子集,要放在终止添加的上面,否则会漏掉自己
+ # if startIndex >= len(nums): # 终止条件可以不加
+ # return
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
+ path.append(nums[i])
+ self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, path, result)
+ path.pop()
```
-## Go
+### Go
```Go
var (
path []int
@@ -254,7 +244,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, start int) {
}
```
-## Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
var subsets = function(nums) {
@@ -273,7 +263,7 @@ var subsets = function(nums) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
```typescript
function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
@@ -293,8 +283,9 @@ function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
};
```
-## Rust
+### Rust
+思路一:使用本题的标准解法,递归回溯。
```Rust
impl Solution {
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec>, path: &mut Vec, nums: &Vec, start_index: usize) {
@@ -316,8 +307,32 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+思路二:使用二进制枚举,n个元素的子集问题一共是$2^n$种情况。如果我们使用一个二进制数字,每一位根据0和1来决定是选取该元素与否,那么一共也是$2^n$的情况,正好可以一一对应,所以我们可以不使用递归,直接利用循环枚举完成子集问题。
+这种方法的优点在于效率高,不需要递归调用,并且代码容易编写。缺点则是过滤某些非法情况时会比递归方法难写一点,不过在子集问题中不存在这个问题。
+```Rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn subsets(nums: Vec) -> Vec> {
+ let n = nums.len();
+ // 预分配2^n空间
+ let mut result = Vec::with_capacity(1 << n);
+ // 二进制枚举,2^n种情况
+ for i in 0..(1 << n) {
+ let mut subset = Vec::new();
+ for j in 0..n {
+ // 枚举该二进制数字的每一位
+ // 如果该位是1,对应位置上的元素加入子集,否则跳过
+ if i & (1 << j) != 0 {
+ subset.push(nums[j]);
+ }
+ }
+ result.push(subset);
+ }
+ result
+ }
+}
+```
-## C
+### C
```c
int* path;
@@ -375,7 +390,7 @@ int** subsets(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes)
}
```
-## Swift
+### Swift
```swift
func subsets(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -398,7 +413,7 @@ func subsets(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
}
```
-## Scala
+### Scala
思路一: 使用本题解思路
@@ -451,9 +466,27 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution {
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> Subsets(int[] nums) {
+ BackTracking(nums, 0);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int[] nums, int start){
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ if(start > nums.Length) return;
+ for (int i = start; i < nums.Length; i++)
+ {
+ path.Add(nums[i]);
+ BackTracking(nums, i + 1);
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb06414334..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb06414334..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 84.柱状图中最大的矩形
@@ -13,14 +11,18 @@
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
-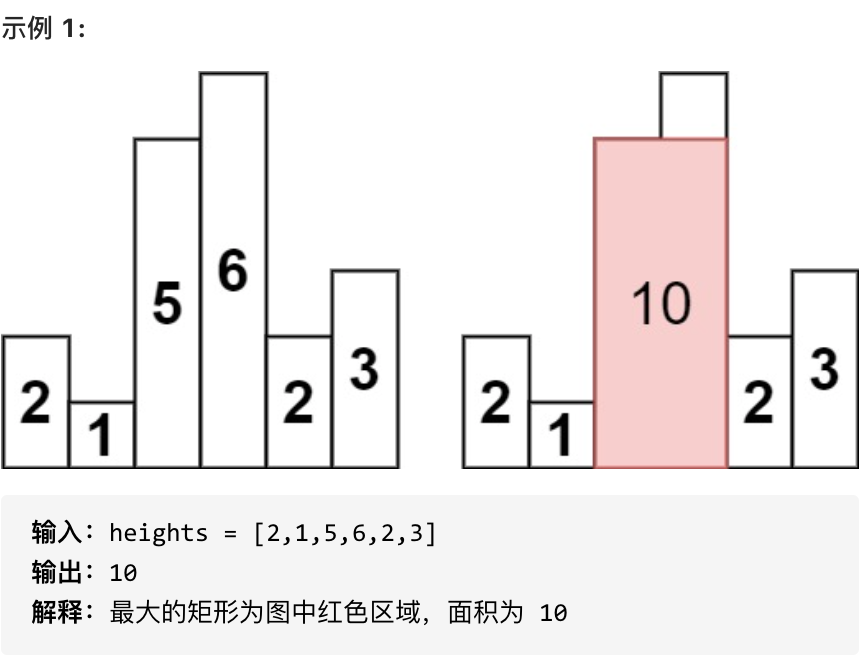
+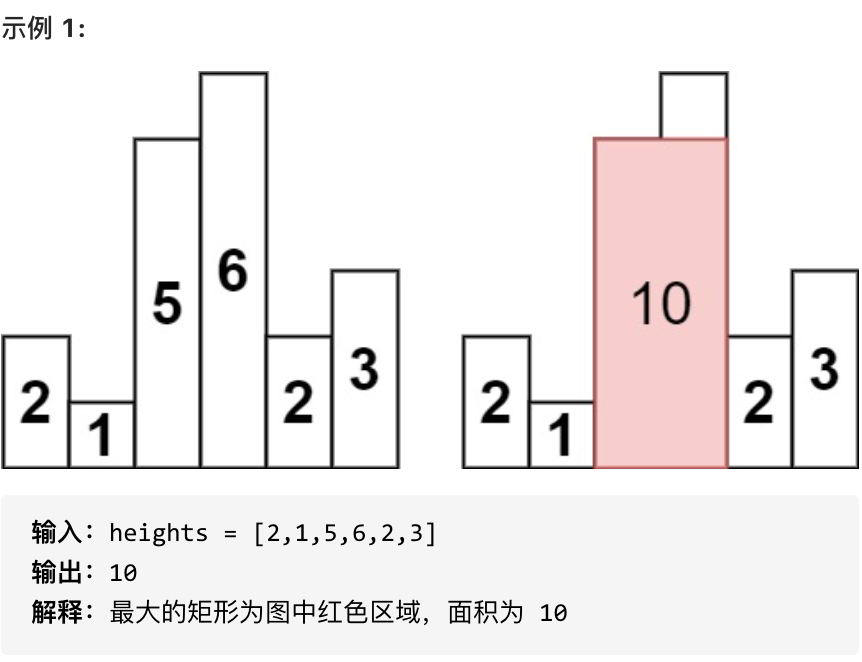
-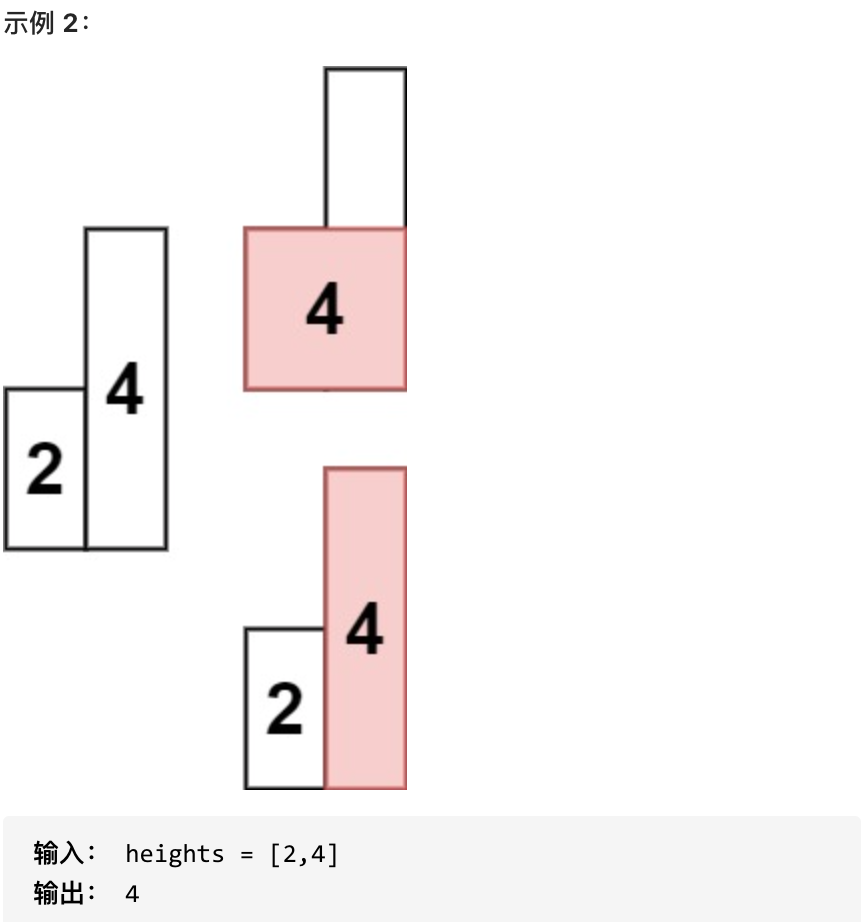
+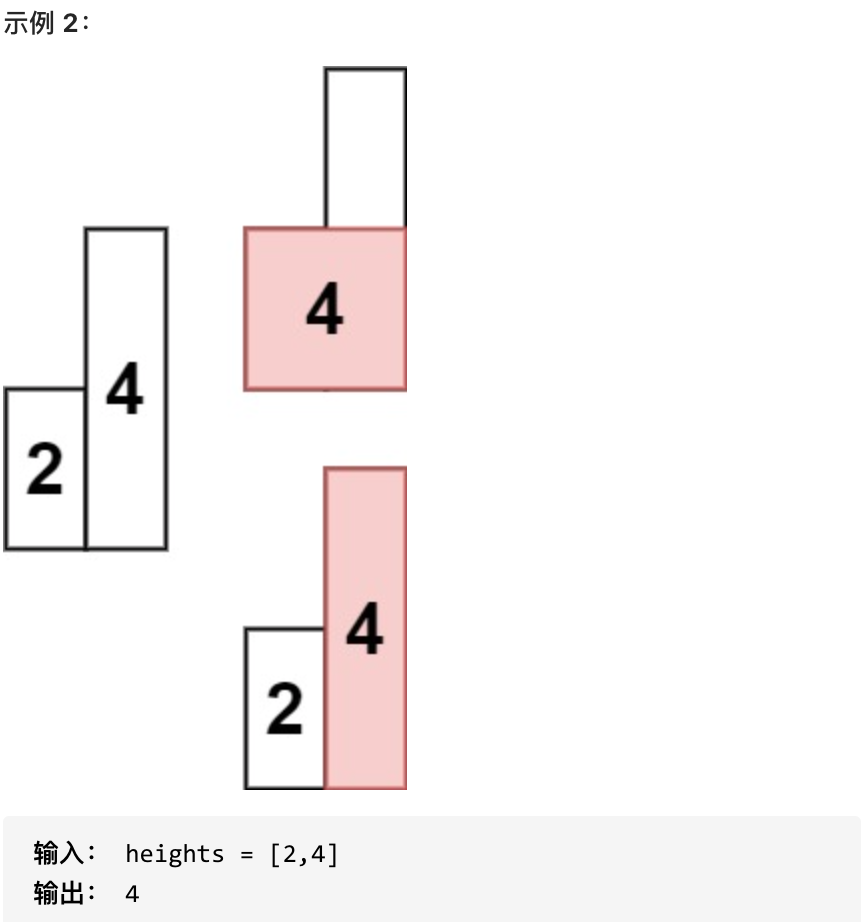
* 1 <= heights.length <=10^5
* 0 <= heights[i] <= 10^4
-# 思路
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[单调栈,又一次经典来袭! LeetCode:84.柱状图中最大的矩形](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ns4y1o7uB/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+## 思路
本题和[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html),是遥相呼应的两道题目,建议都要仔细做一做,原理上有很多相同的地方,但细节上又有差异,更可以加深对单调栈的理解!
@@ -28,7 +30,7 @@
我们先来看一下暴力解法的解法:
-## 暴力解法
+### 暴力解法
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -55,7 +57,7 @@ public:
如上代码并不能通过leetcode,超时了,因为时间复杂度是$O(n^2)$。
-## 双指针解法
+### 双指针解法
本题双指针的写法整体思路和[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)是一致的,但要比[42. 接雨水](https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html)难一些。
@@ -98,7 +100,7 @@ public:
};
```
-## 单调栈
+### 单调栈
本地单调栈的解法和接雨水的题目是遥相呼应的。
@@ -112,7 +114,7 @@ public:
我来举一个例子,如图:
-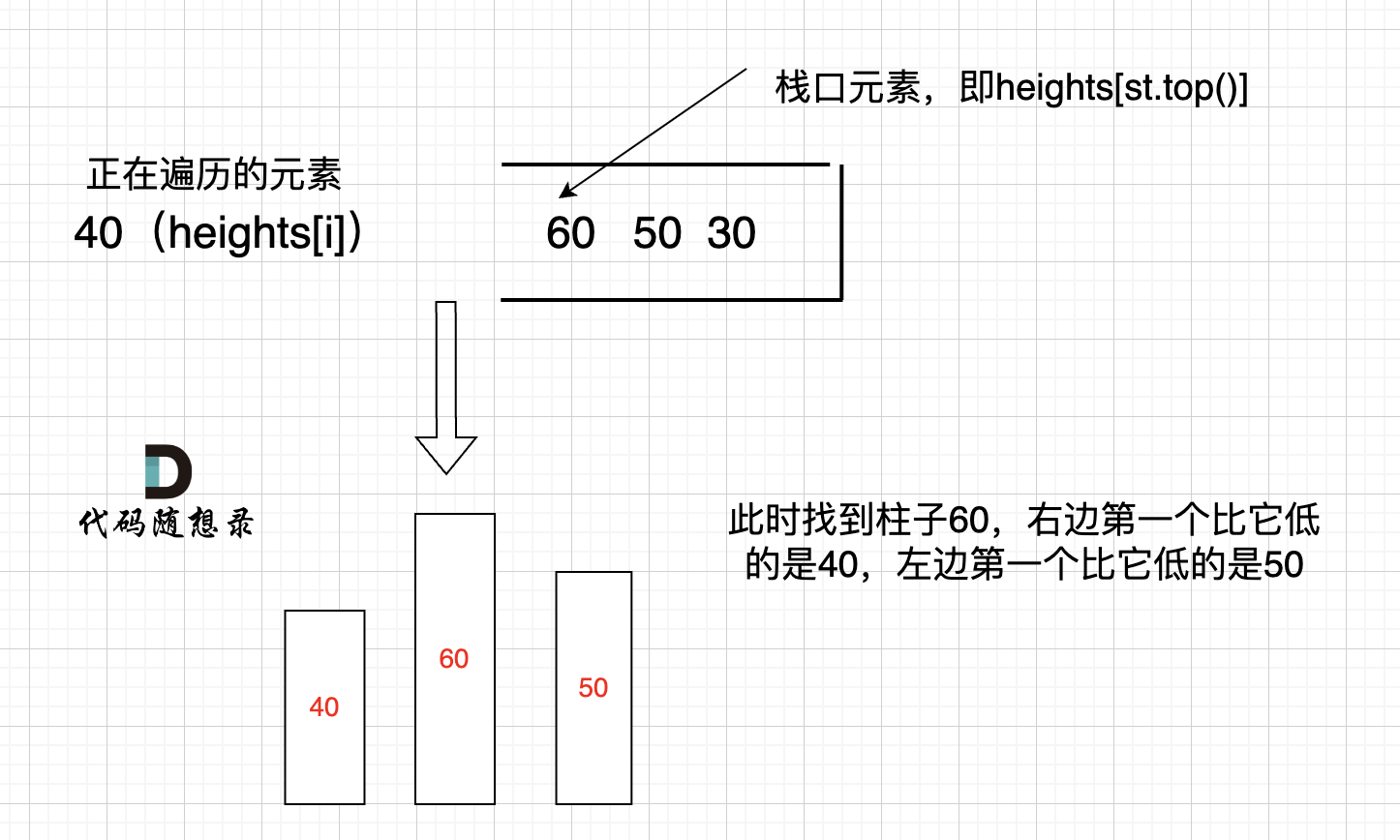
+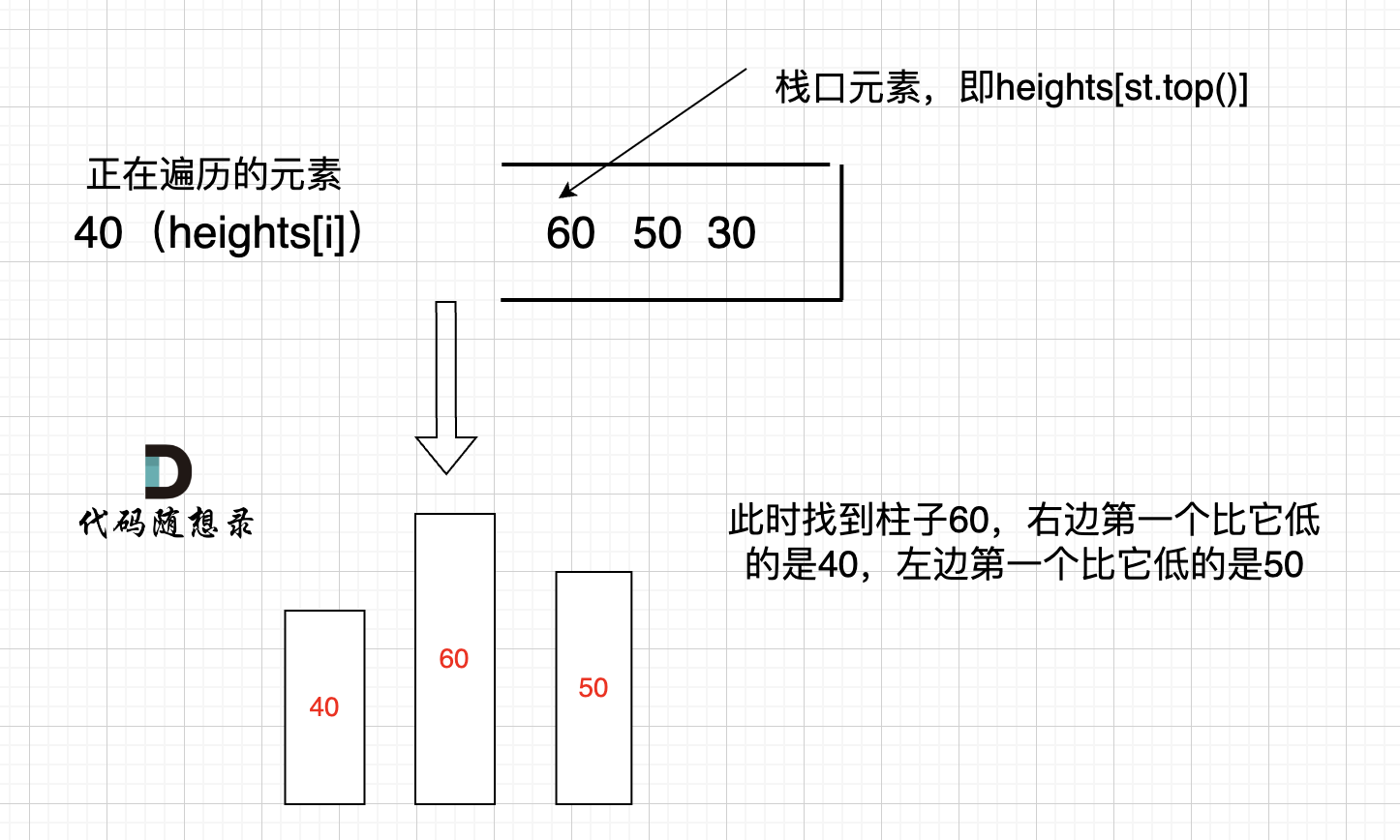
只有栈里从大到小的顺序,才能保证栈顶元素找到左右两边第一个小于栈顶元素的柱子。
@@ -169,7 +171,7 @@ public:
}
};
-```
+```
细心的录友会发现,我在 height数组上后,都加了一个元素0, 为什么这么做呢?
@@ -177,22 +179,22 @@ public:
如果数组本身就是升序的,例如[2,4,6,8],那么入栈之后 都是单调递减,一直都没有走 情况三 计算结果的哪一步,所以最后输出的就是0了。 如图:
-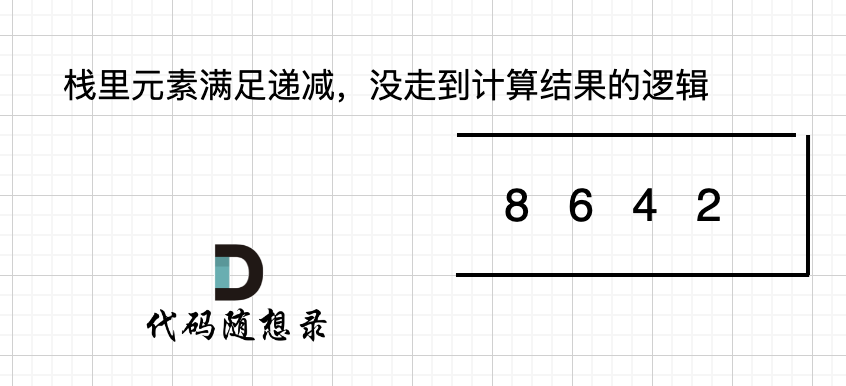
+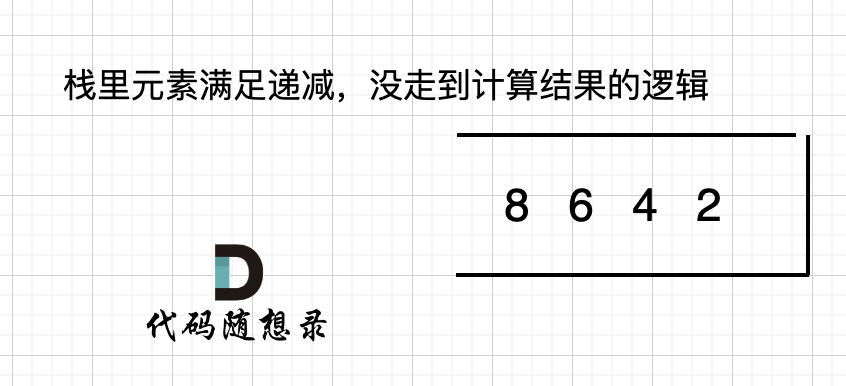
那么结尾加一个0,就会让栈里的所有元素,走到情况三的逻辑。
开头为什么要加元素0?
-如果数组本身是降序的,例如 [8,6,4,2],在 8 入栈后,6 开始与8 进行比较,此时我们得到 mid(8),rigt(6),但是得不到 left。
+如果数组本身是降序的,例如 [8,6,4,2],在 8 入栈后,6 开始与8 进行比较,此时我们得到 mid(8),right(6),但是得不到 left。
(mid、left,right 都是对应版本一里的逻辑)
因为 将 8 弹出之后,栈里没有元素了,那么为了避免空栈取值,直接跳过了计算结果的逻辑。
-之后又将6 加入栈(此时8已经弹出了),然后 就是 4 与 栈口元素 8 进行比较,周而复始,那么计算的最后结果resutl就是0。 如图所示:
+之后又将6 加入栈(此时8已经弹出了),然后 就是 4 与 栈口元素 6 进行比较,周而复始,那么计算的最后结果result就是0。 如图所示:
-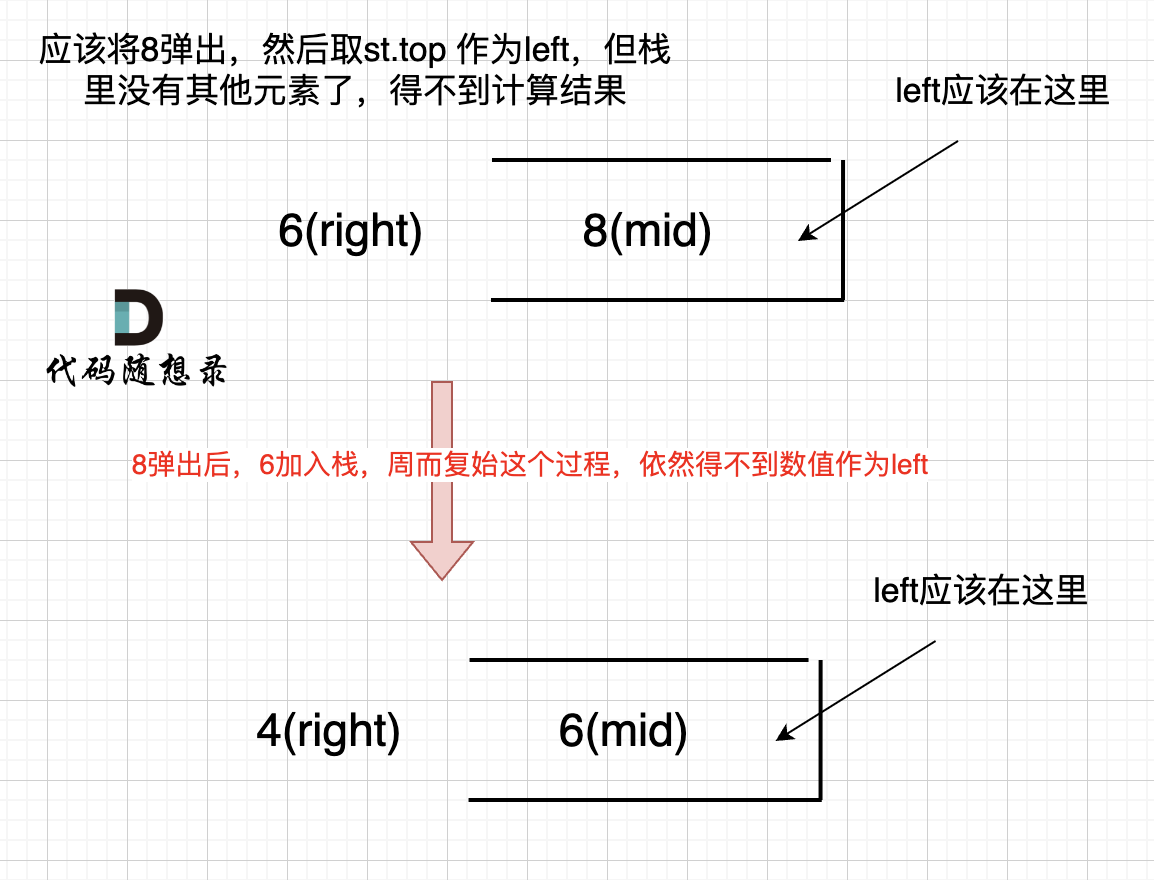
+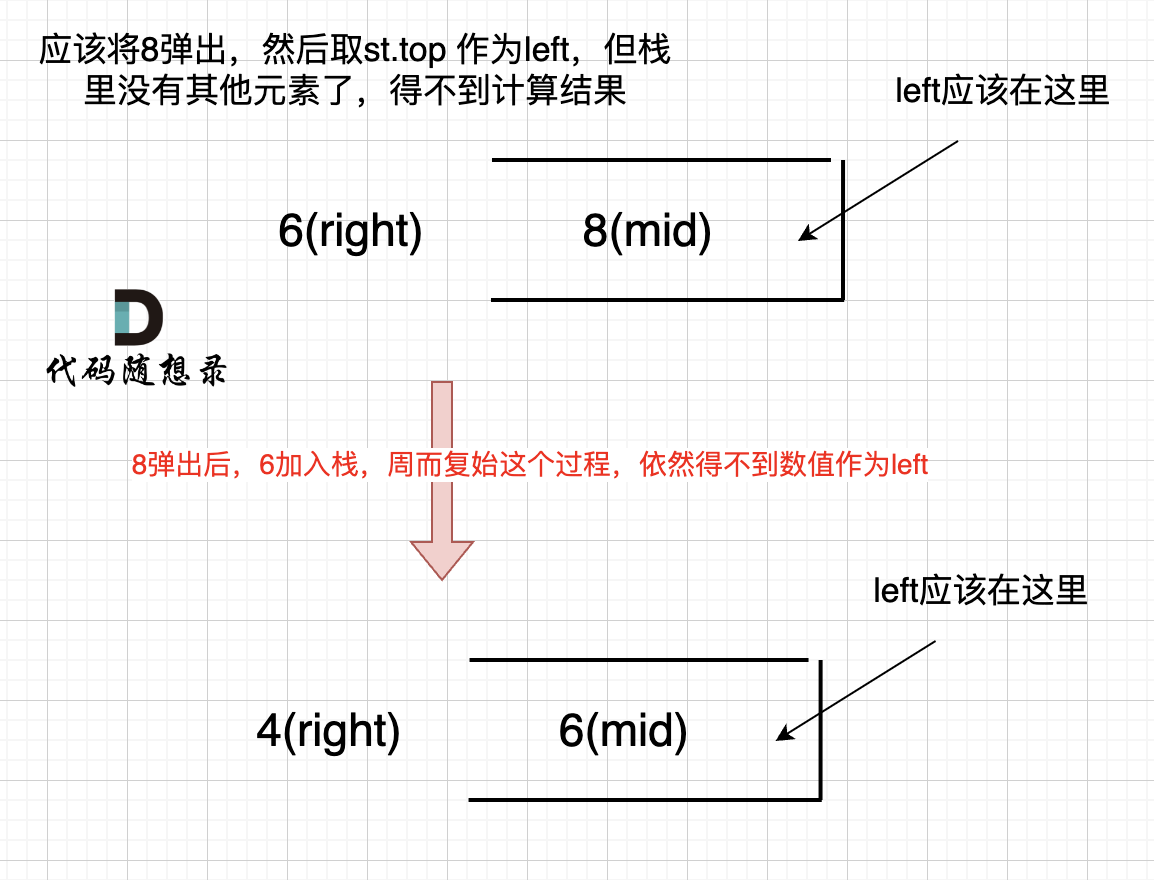
所以我们需要在 height数组前后各加一个元素0。
@@ -229,7 +231,7 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
暴力解法:
```java
@@ -307,8 +309,35 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+单调栈精简
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
+ int[] newHeight = new int[heights.length + 2];
+ System.arraycopy(heights, 0, newHeight, 1, heights.length);
+ newHeight[heights.length+1] = 0;
+ newHeight[0] = 0;
+
+ Stack stack = new Stack<>();
+ stack.push(0);
+
+ int res = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < newHeight.length; i++) {
+ while (newHeight[i] < newHeight[stack.peek()]) {
+ int mid = stack.pop();
+ int w = i - stack.peek() - 1;
+ int h = newHeight[mid];
+ res = Math.max(res, w * h);
+ }
+ stack.push(i);
+
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
-Python3:
+### Python3:
```python
@@ -441,71 +470,195 @@ class Solution:
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
+暴力解法
+
+```go
+func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
+ sum := 0
+ for i := 0; i < len(heights); i++ {
+ left, right := i, i
+ for left >= 0 {
+ if heights[left] < heights[i] {
+ break
+ }
+ left--
+ }
+ for right < len(heights) {
+ if heights[right] < heights[i] {
+ break
+ }
+ right++
+ }
+ w := right - left - 1
+ h := heights[i]
+ sum = max(sum, w * h)
+ }
+ return sum
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
-> 单调栈
+双指针解法
```go
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
- // 声明max并初始化为0
- max := 0
- // 使用切片实现栈
- stack := make([]int, 0)
- // 数组头部加入0
- heights = append([]int{0}, heights...)
- // 数组尾部加入0
- heights = append(heights, 0)
- // 初始化栈,序号从0开始
- stack = append(stack, 0)
- for i := 1; i < len(heights); i++ {
- // 结束循环条件为:当即将入栈元素>top元素,也就是形成非单调递增的趋势
- for heights[stack[len(stack)-1]] > heights[i] {
- // mid 是top
- mid := stack[len(stack)-1]
- // 出栈
- stack = stack[0 : len(stack)-1]
- // left是top的下一位元素,i是将要入栈的元素
- left := stack[len(stack)-1]
- // 高度x宽度
- tmp := heights[mid] * (i - left - 1)
- if tmp > max {
- max = tmp
- }
- }
- stack = append(stack, i)
- }
- return max
+ size := len(heights)
+ minLeftIndex := make([]int, size)
+ minRightIndex := make([]int, size)
+
+ // 记录每个柱子 左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
+ minLeftIndex[0] = -1 // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
+ for i := 1; i < size; i++ {
+ t := i - 1
+ // 这里不是用if,而是不断向左寻找的过程
+ for t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i] {
+ t = minLeftIndex[t]
+ }
+ minLeftIndex[i] = t
+ }
+ // 记录每个柱子 右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
+ minRightIndex[size - 1] = size; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
+ for i := size - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
+ t := i + 1
+ // 这里不是用if,而是不断向右寻找的过程
+ for t < size && heights[t] >= heights[i] {
+ t = minRightIndex[t]
+ }
+ minRightIndex[i] = t
+ }
+ // 求和
+ result := 0
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ sum := heights[i] * (minRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1)
+ result = max(sum, result)
+ }
+ return result
}
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
```
-JavaScript:
+单调栈
+
+```go
+func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
+ result := 0
+ heights = append([]int{0}, heights...) // 数组头部加入元素0
+ heights = append(heights, 0) // 数组尾部加入元素0
+ st := []int{0}
+
+ // 第一个元素已经入栈,从下标1开始
+ for i := 1; i < len(heights); i++ {
+ if heights[i] > heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ st = append(st, i)
+ } else if heights[i] == heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ st = append(st, i)
+ } else {
+ for len(st) > 0 && heights[i] < heights[st[len(st)-1]] {
+ mid := st[len(st)-1]
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ if len(st) > 0 {
+ left := st[len(st)-1]
+ right := i
+ w := right - left - 1
+ h := heights[mid]
+ result = max(result, w * h)
+ }
+ }
+ st = append(st, i)
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+单调栈精简
+
+```go
+func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
+ max := 0
+ // 使用切片实现栈
+ stack := make([]int, 0)
+ // 数组头部加入0
+ heights = append([]int{0}, heights...)
+ // 数组尾部加入0
+ heights = append(heights, 0)
+ // 初始化栈,序号从0开始
+ stack = append(stack, 0)
+ for i := 1; i < len(heights); i ++ {
+ // 结束循环条件为:当即将入栈元素>top元素,也就是形成非单调递增的趋势
+ for heights[stack[len(stack) - 1]] > heights[i] {
+ // mid 是top
+ mid := stack[len(stack) - 1]
+ // 出栈
+ stack = stack[0 : len(stack) - 1]
+ // left是top的下一位元素,i是将要入栈的元素
+ left := stack[len(stack) - 1]
+ // 高度x宽度
+ tmp := heights[mid] * (i - left - 1)
+ if tmp > max {
+ max = tmp
+ }
+ }
+ stack = append(stack, i)
+ }
+ return max
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
//双指针 js中运行速度最快
var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
const len = heights.length;
const minLeftIndex = new Array(len);
- const maxRigthIndex = new Array(len);
+ const maxRightIndex = new Array(len);
// 记录每个柱子 左边第一个小于该柱子的下标
minLeftIndex[0] = -1; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
for(let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
let t = i - 1;
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向左寻找的过程
- while(t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i]) t = minLeftIndex[t];
+ while (t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i]) {
+ t = minLeftIndex[t];
+ }
minLeftIndex[i] = t;
}
// 记录每个柱子 右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
- maxRigthIndex[len - 1] = len; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
+ maxRightIndex[len - 1] = len; // 注意这里初始化,防止下面while死循环
for(let i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--){
let t = i + 1;
// 这里不是用if,而是不断向右寻找的过程
- while(t < len && heights[t] >= heights[i]) t = maxRigthIndex[t];
- maxRigthIndex[i] = t;
+ while (t <= n && heights[t] > heights[i]) {
+ t = maxRightIndex[t];
+ }
+ maxRightIndex[i] = t;
}
// 求和
let maxArea = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < len; i++){
- let sum = heights[i] * (maxRigthIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1);
+ let sum = heights[i] * (maxRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1);
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea , sum);
}
return maxArea;
@@ -513,27 +666,37 @@ var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
//单调栈
var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
- let maxArea = 0;
- const stack = [];
- heights = [0,...heights,0]; // 数组头部加入元素0 数组尾部加入元素0
- for(let i = 0; i < heights.length; i++){
- if(heights[i] > heights[stack[stack.length-1]]){ // 情况三
- stack.push(i);
- } else if(heights[i] === heights[stack[stack.length-1]]){ // 情况二
- stack.pop(); // 这个可以加,可以不加,效果一样,思路不同
- stack.push(i);
- } else { // 情况一
- while(heights[i] < heights[stack[stack.length-1]]){// 当前bar比栈顶bar矮
- const stackTopIndex = stack.pop();// 栈顶元素出栈,并保存栈顶bar的索引
- let w = i - stack[stack.length -1] - 1;
- let h = heights[stackTopIndex]
+ let maxArea = 0;
+ const stack = [0];
+ heights.push(0);
+ const n = heights.length;
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
+ let top = stack.at(-1);
+ // 情况三
+ if (heights[top] < heights[i]) {
+ stack.push(i);
+ }
+ // 情况二
+ if (heights[top] === heights[i]) {
+ stack.pop(); // 这个可以加,可以不加,效果一样,思路不同
+ stack.push(i);
+ }
+ // 情况一
+ if (heights[top] > heights[i]) {
+ while (stack.length > 0 && heights[top] > heights[i]) {
+ // 栈顶元素出栈,并保存栈顶bar的索引
+ const h = heights[stack.pop()];
+ const left = stack.at(-1) ?? -1;
+ const w = i - left - 1;
// 计算面积,并取最大面积
- maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, w * h);
- }
- stack.push(i);// 当前bar比栈顶bar高了,入栈
- }
- }
- return maxArea;
+ maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, w * h);
+ top = stack.at(-1);
+ }
+ stack.push(i);
+ }
+ }
+ return maxArea;
};
//单调栈 简洁
@@ -554,7 +717,7 @@ var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
return maxArea;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
> 暴力法(会超时):
@@ -642,9 +805,59 @@ function largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {
};
```
+### Rust:
+
+双指针预处理
+```rust
+
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn largest_rectangle_area(v: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let n = v.len();
+ let mut left_smaller_idx = vec![-1; n];
+ let mut right_smaller_idx = vec![n as i32; n];
+ for i in 1..n {
+ let mut mid = i as i32 - 1;
+ while mid >= 0 && v[mid as usize] >= v[i] {
+ mid = left_smaller_idx[mid as usize];
+ }
+ left_smaller_idx[i] = mid;
+ }
+ for i in (0..n-1).rev() {
+ let mut mid = i + 1;
+ while mid < n && v[mid] >= v[i] {
+ mid = right_smaller_idx[mid] as usize;
+ }
+ right_smaller_idx[i] = mid as i32;
+ }
+ let mut res = 0;
+ for (idx, &e) in v.iter().enumerate() {
+ res = res.max((right_smaller_idx[idx] - left_smaller_idx[idx] - 1) * e);
+ }
+ dbg!(res)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+单调栈
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn largest_rectangle_area1(mut v: Vec) -> i32 {
+ v.insert(0, 0); // 便于使第一个元素能够有左侧<=它的值
+ v.push(0); // 便于在结束处理最后一个元素后清空残留在栈中的值
+ let mut res = 0;
+ let mut stack = vec![]; // 递增的栈
+ for (idx, &e) in v.iter().enumerate() {
+ while !stack.is_empty() && v[*stack.last().unwrap()] > e {
+ let pos = stack.pop().unwrap();
+ let prev_pos = *stack.last().unwrap();
+ let s = (idx - prev_pos - 1) as i32 * v[pos];
+ res = res.max(s);
+ }
+ stack.push(idx);
+ }
+ res
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a02161aa92..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a02161aa92..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 90.子集II
@@ -25,9 +22,9 @@
[]
]
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[回溯算法解决子集问题,如何去重?| LeetCode:90.子集II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vm4y1F71J/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[回溯算法解决子集问题,如何去重?| LeetCode:90.子集II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vm4y1F71J/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -42,7 +39,7 @@
用示例中的[1, 2, 2] 来举例,如图所示: (**注意去重需要先对集合排序**)
-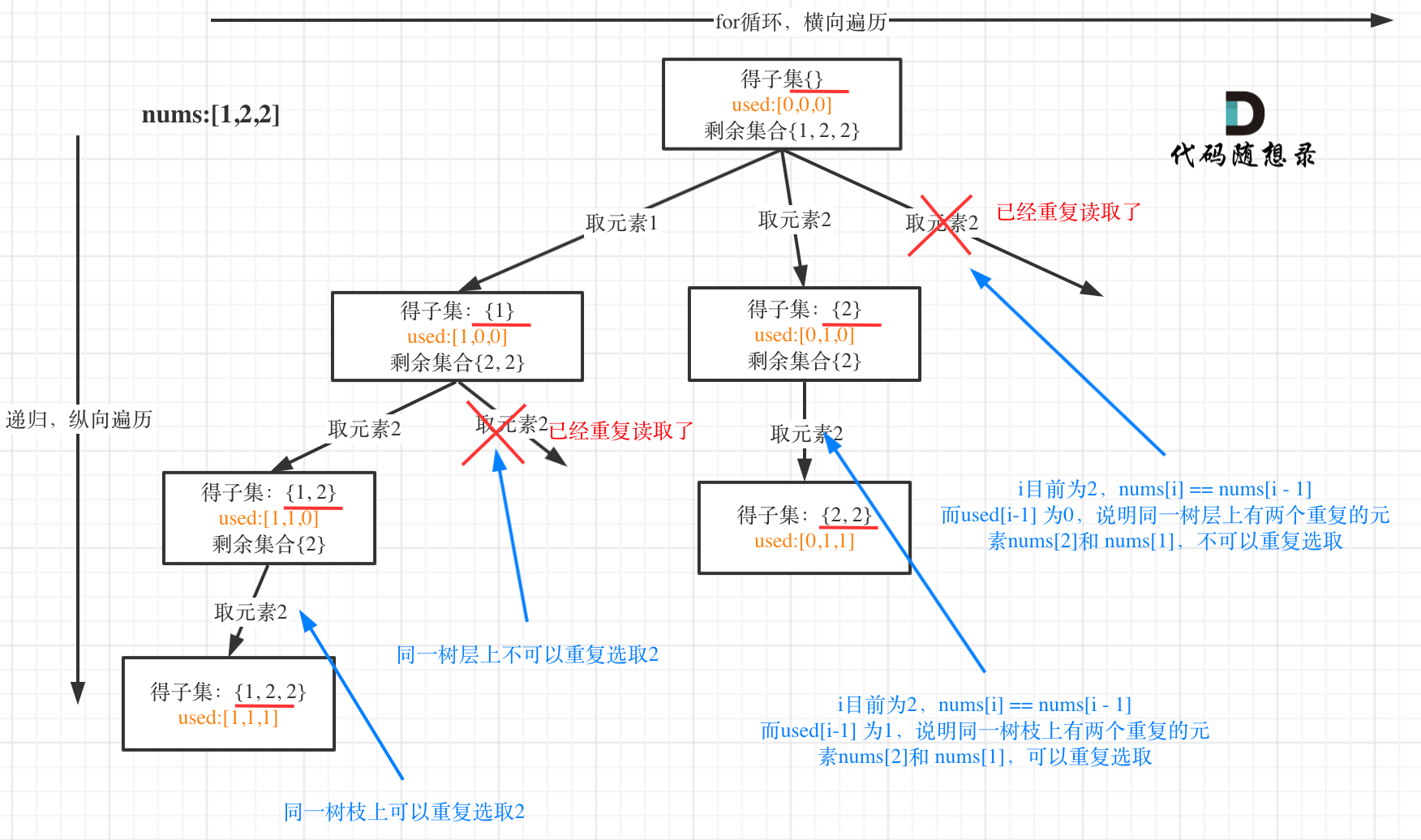
+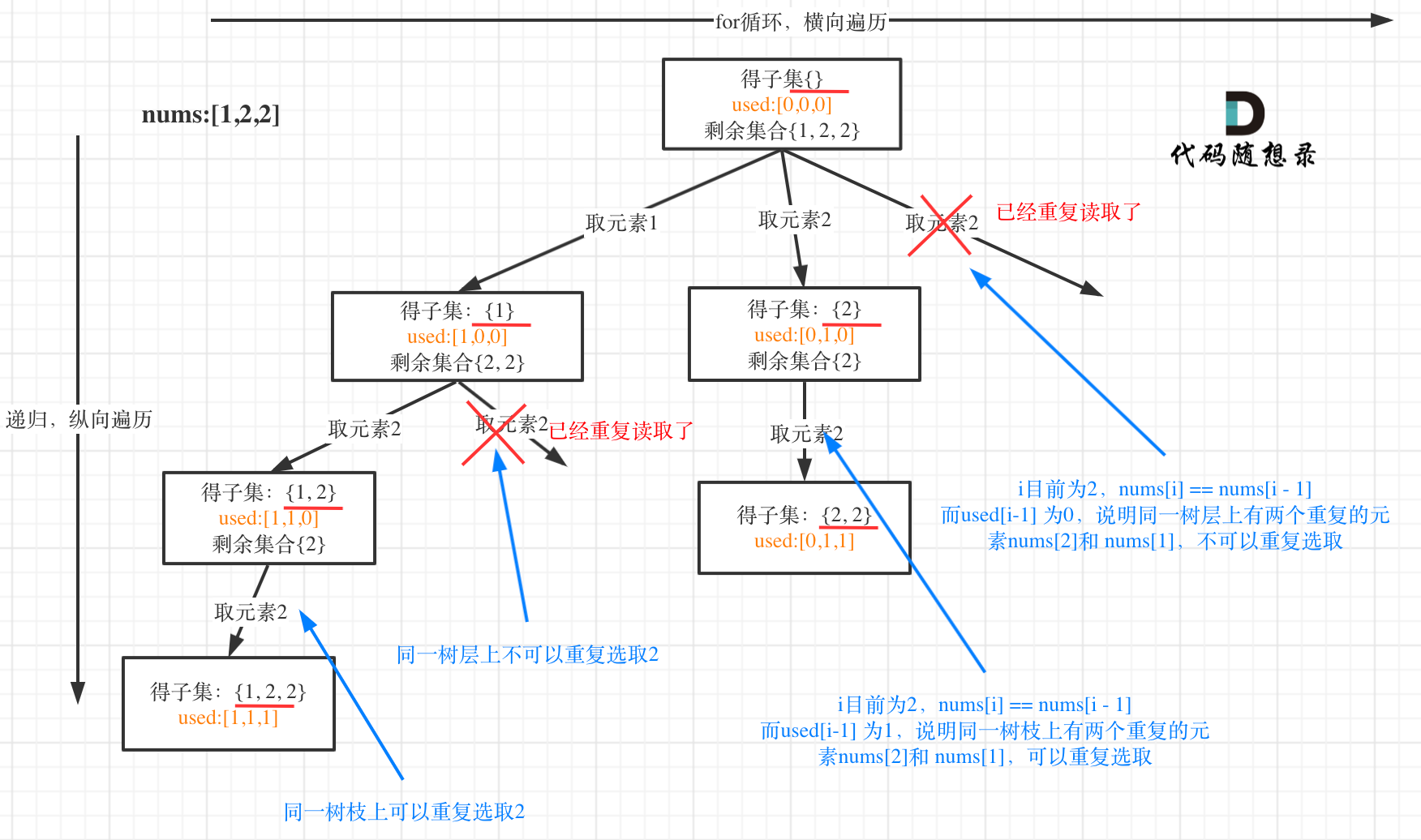
从图中可以看出,同一树层上重复取2 就要过滤掉,同一树枝上就可以重复取2,因为同一树枝上元素的集合才是唯一子集!
@@ -83,6 +80,9 @@ public:
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * 2^n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
+
使用set去重的版本。
```CPP
@@ -156,13 +156,6 @@ public:
其实这道题目的知识点,我们之前都讲过了,如果之前讲过的子集问题和去重问题都掌握的好,这道题目应该分分钟AC。
-当然本题去重的逻辑,也可以这么写
-
-```cpp
-if (i > startIndex && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] ) {
- continue;
-}
-```
## 其他语言版本
@@ -235,88 +228,123 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-### Python
+
+
+### Python3
+
+回溯 利用used数组去重
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.paths = []
- self.path = []
-
- def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
- nums.sort()
- self.backtracking(nums, 0)
- return self.paths
-
- def backtracking(self, nums: List[int], start_index: int) -> None:
- # ps.空集合仍符合要求
- self.paths.append(self.path[:])
- # Base Case
- if start_index == len(nums):
- return
-
- # 单层递归逻辑
- for i in range(start_index, len(nums)):
- if i > start_index and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
- # 当前后元素值相同时,跳入下一个循环,去重
+ def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
+ result = []
+ path = []
+ used = [False] * len(nums)
+ nums.sort() # 去重需要排序
+ self.backtracking(nums, 0, used, path, result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, used, path, result):
+ result.append(path[:]) # 收集子集
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
+ # used[i - 1] == True,说明同一树枝 nums[i - 1] 使用过
+ # used[i - 1] == False,说明同一树层 nums[i - 1] 使用过
+ # 而我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过
+ if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1] and not used[i - 1]:
continue
- self.path.append(nums[i])
- self.backtracking(nums, i+1)
- self.path.pop()
+ path.append(nums[i])
+ used[i] = True
+ self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, used, path, result)
+ used[i] = False
+ path.pop()
+
```
-#### Python3
+回溯 利用集合去重
-不使用used数组
```python
class Solution:
- def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = []
+ def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
+ result = []
path = []
- nums.sort() # 去重需要先对数组进行排序
-
- def backtracking(nums, startIndex):
- # 终止条件
- res.append(path[:])
- if startIndex == len(nums):
- return
-
- # for循环
- for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
- # 数层去重
- if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i-1]: # 去重
- continue
- path.append(nums[i])
- backtracking(nums, i+1)
- path.pop()
-
- backtracking(nums, 0)
- return res
+ nums.sort() # 去重需要排序
+ self.backtracking(nums, 0, path, result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, path, result):
+ result.append(path[:]) # 收集子集
+ uset = set()
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
+ if nums[i] in uset:
+ continue
+ uset.add(nums[i])
+ path.append(nums[i])
+ self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, path, result)
+ path.pop()
+
```
-使用used数组
+回溯 利用递归的时候下一个startIndex是i+1而不是0去重
+
```python
class Solution:
- def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
+ def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
result = []
path = []
- nums.sort()
- used = [0] * len(nums)
- def backtrack(nums, startIdx):
- result.append(path[:])
- for i in range(startIdx, len(nums)):
- if i > startIdx and nums[i] == nums[i-1] and used[i-1] == 0:
- continue
- used[i] = 1
- path.append(nums[i])
- backtrack(nums, i+1)
- path.pop()
- used[i] = 0
- backtrack(nums, 0)
+ nums.sort() # 去重需要排序
+ self.backtracking(nums, 0, path, result)
return result
-```
+ def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, path, result):
+ result.append(path[:]) # 收集子集
+ for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
+ # 而我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过
+ if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
+ continue
+ path.append(nums[i])
+ self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, path, result)
+ path.pop()
+
+
+```
### Go
+使用used数组
+```Go
+var (
+ result [][]int
+ path []int
+)
+
+func subsetsWithDup(nums []int) [][]int {
+ result = make([][]int, 0)
+ path = make([]int, 0)
+ used := make([]bool, len(nums))
+ sort.Ints(nums) // 去重需要排序
+ backtracing(nums, 0, used)
+ return result
+}
+
+func backtracing(nums []int, startIndex int, used []bool) {
+ tmp := make([]int, len(path))
+ copy(tmp, path)
+ result = append(result, tmp)
+ for i := startIndex; i < len(nums); i++ {
+ // used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
+ // used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
+ // 而我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过
+ if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && used[i-1] == false {
+ continue
+ }
+ path = append(path, nums[i])
+ used[i] = true
+ backtracing(nums, i + 1, used)
+ path = path[:len(path)-1]
+ used[i] = false
+ }
+}
+```
+
+不使用used数组
```Go
var (
path []int
@@ -346,7 +374,7 @@ func dfs(nums []int, start int) {
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
```Javascript
@@ -640,8 +668,30 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList> res = new List>();
+ public IList path = new List();
+ public IList> SubsetsWithDup(int[] nums)
+ {
+ Array.Sort(nums);
+ BackTracking(nums, 0);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(int[] nums, int start)
+ {
+ res.Add(new List(path));
+ for (int i = start; i < nums.Length; i++)
+ {
+ if (i > start && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
+ path.Add(nums[i]);
+ BackTracking(nums, i + 1);
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f99a7a5d0..b9a3e08f63
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f99a7a5d0..b9a3e08f63
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -40,16 +38,12 @@
* 0 <= s.length <= 3000
* s 仅由数字组成
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[93.复原IP地址](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XP4y1U73i/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[回溯算法如何分割字符串并判断是合法IP?| LeetCode:93.复原IP地址](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XP4y1U73i/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-# 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[回溯算法如何分割字符串并判断是合法IP?| LeetCode:93.复原IP地址](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XP4y1U73i/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-
-
-# 思路
+## 思路
做这道题目之前,最好先把[131.分割回文串](https://programmercarl.com/0131.分割回文串.html)这个做了。
@@ -59,10 +53,11 @@
切割问题可以抽象为树型结构,如图:
-
+
+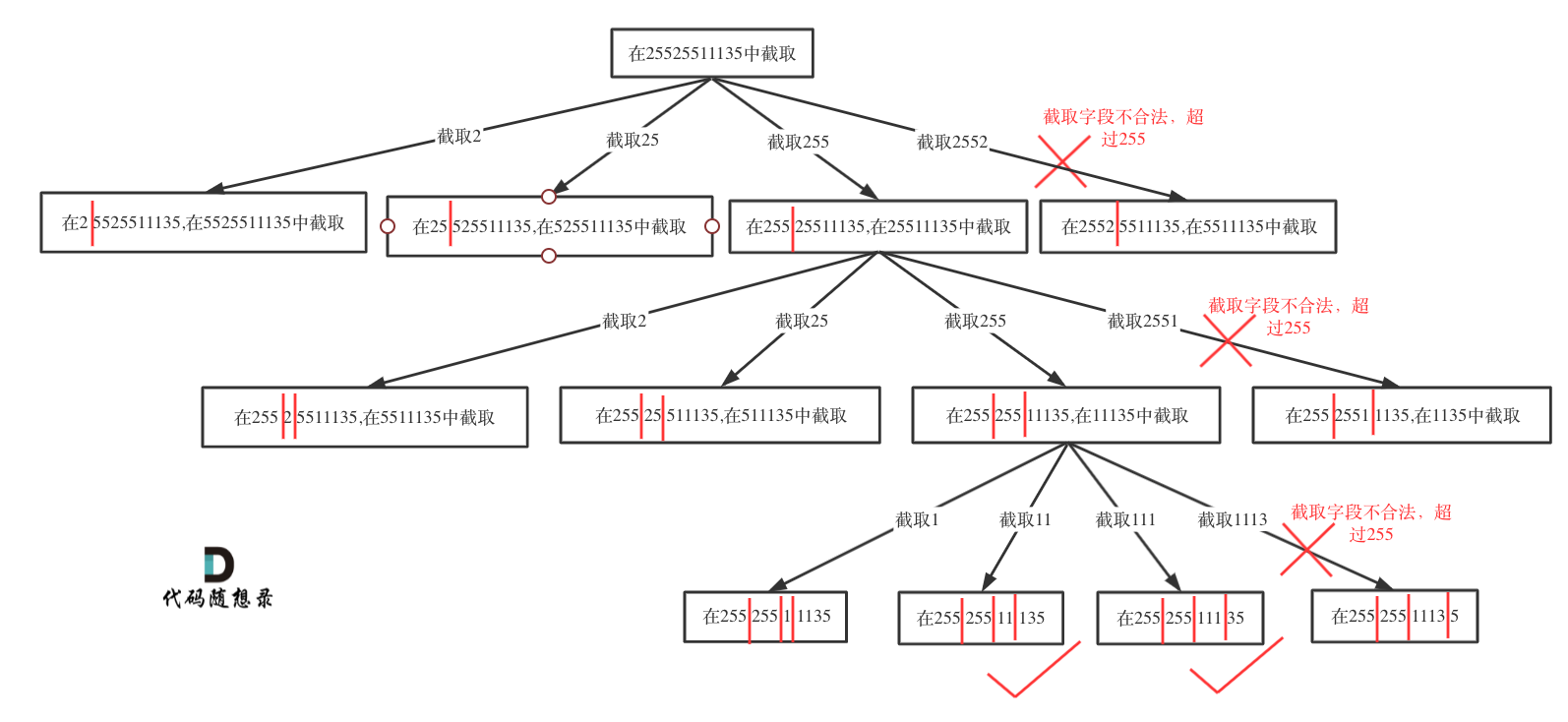
-## 回溯三部曲
+### 回溯三部曲
* 递归参数
@@ -110,7 +105,8 @@ if (pointNum == 3) { // 逗点数量为3时,分隔结束
如果不合法就结束本层循环,如图中剪掉的分支:
-
+
+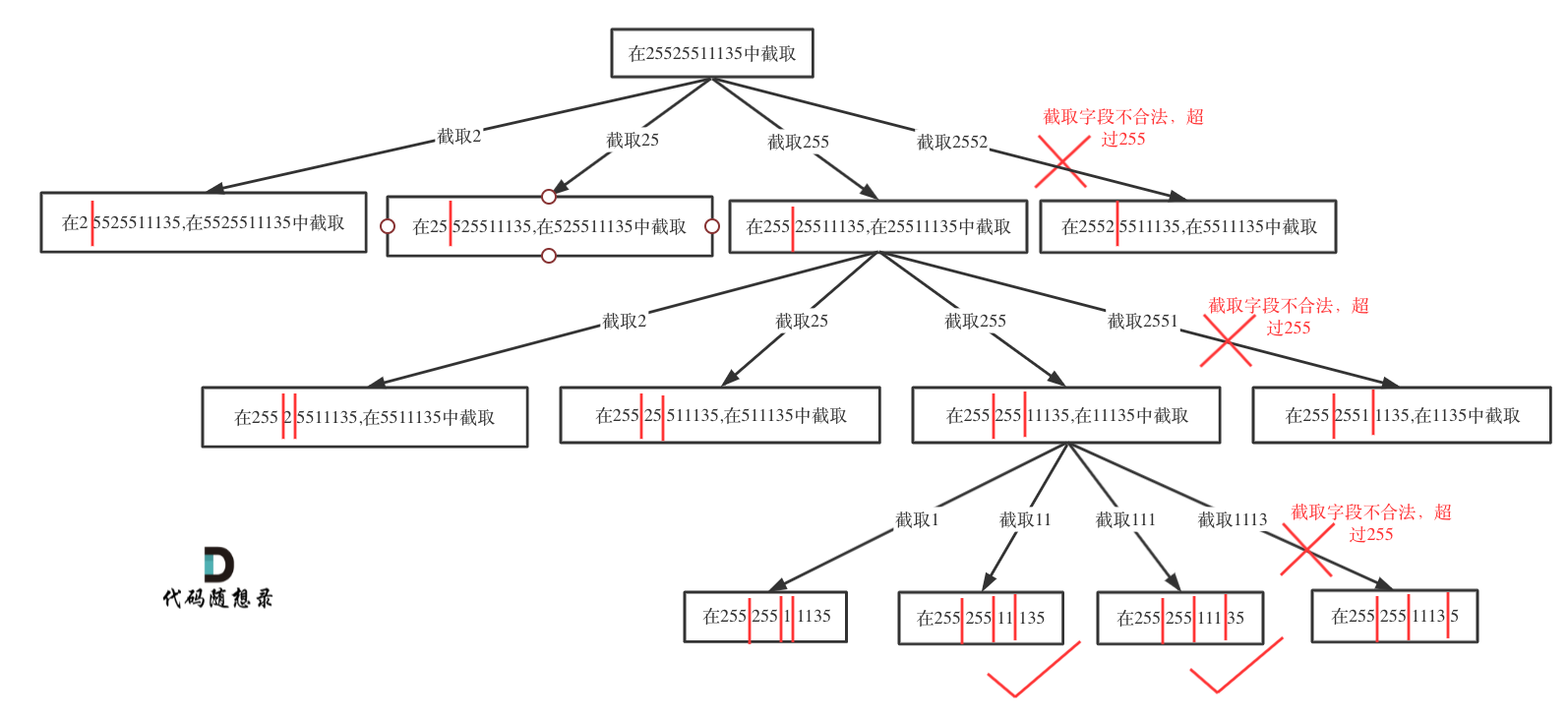
然后就是递归和回溯的过程:
@@ -132,7 +128,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
}
```
-## 判断子串是否合法
+### 判断子串是否合法
最后就是在写一个判断段位是否是有效段位了。
@@ -145,7 +141,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
代码如下:
```CPP
-// 判断字符串s在左闭又闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
+// 判断字符串s在左闭右闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
bool isValid(const string& s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
@@ -167,8 +163,6 @@ bool isValid(const string& s, int start, int end) {
}
```
-## C++代码
-
根据[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/回溯算法理论基础.html)给出的回溯算法模板:
@@ -212,7 +206,7 @@ private:
} else break; // 不合法,直接结束本层循环
}
}
- // 判断字符串s在左闭又闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
+ // 判断字符串s在左闭右闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
bool isValid(const string& s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
@@ -242,8 +236,10 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(3^4),IP地址最多包含4个数字,每个数字最多有3种可能的分割方式,则搜索树的最大深度为4,每个节点最多有3个子节点。
+* 空间复杂度: O(n)
-# 总结
+## 总结
在[131.分割回文串](https://programmercarl.com/0131.分割回文串.html)中我列举的分割字符串的难点,本题都覆盖了。
@@ -255,9 +251,9 @@ public:
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -312,6 +308,47 @@ class Solution {
return true;
}
}
+//方法一:但使用stringBuilder,故优化时间、空间复杂度,因为向字符串插入字符时无需复制整个字符串,从而减少了操作的时间复杂度,也不用开新空间存subString,从而减少了空间复杂度。
+class Solution {
+ List result = new ArrayList<>();
+ public List restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
+ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
+ backTracking(sb, 0, 0);
+ return result;
+ }
+ private void backTracking(StringBuilder s, int startIndex, int dotCount){
+ if(dotCount == 3){
+ if(isValid(s, startIndex, s.length() - 1)){
+ result.add(s.toString());
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+ for(int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){
+ if(isValid(s, startIndex, i)){
+ s.insert(i + 1, '.');
+ backTracking(s, i + 2, dotCount + 1);
+ s.deleteCharAt(i + 1);
+ }else{
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ //[start, end]
+ private boolean isValid(StringBuilder s, int start, int end){
+ if(start > end)
+ return false;
+ if(s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end)
+ return false;
+ int num = 0;
+ for(int i = start; i <= end; i++){
+ int digit = s.charAt(i) - '0';
+ num = num * 10 + digit;
+ if(num > 255)
+ return false;
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
//方法二:比上面的方法时间复杂度低,更好地剪枝,优化时间复杂度
class Solution {
@@ -337,9 +374,8 @@ class Solution {
// 剪枝:ip段的长度最大是3,并且ip段处于[0,255]
for (int i = start; i < s.length() && i - start < 3 && Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, i + 1)) >= 0
&& Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, i + 1)) <= 255; i++) {
- // 如果ip段的长度大于1,并且第一位为0的话,continue
if (i + 1 - start > 1 && s.charAt(start) - '0' == 0) {
- continue;
+ break;
}
stringBuilder.append(s.substring(start, i + 1));
// 当stringBuilder里的网段数量小于3时,才会加点;如果等于3,说明已经有3段了,最后一段不需要再加点
@@ -356,107 +392,112 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## python
-python2:
-```python
-class Solution(object):
- def restoreIpAddresses(self, s):
- """
- :type s: str
- :rtype: List[str]
- """
- ans = []
- path = []
- def backtrack(path, startIndex):
- if len(s) > 12: return []
- if len(path) == 4:
- if startIndex == len(s):
- ans.append(".".join(path[:]))
- return
- for i in range(startIndex+1, min(startIndex+4, len(s)+1)): # 剪枝
- string = s[startIndex:i]
- if not 0 <= int(string) <= 255:
- continue
- if not string == "0" and not string.lstrip('0') == string:
- continue
- path.append(string)
- backtrack(path, i)
- path.pop()
-
- backtrack([], 0)
- return ans
-```
+### Python
-python3:
+回溯(版本一)
```python
class Solution:
- def __init__(self):
- self.result = []
-
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
- '''
- 本质切割问题使用回溯搜索法,本题只能切割三次,所以纵向递归总共四层
- 因为不能重复分割,所以需要start_index来记录下一层递归分割的起始位置
- 添加变量point_num来记录逗号的数量[0,3]
- '''
- self.result.clear()
- if len(s) > 12: return []
- self.backtracking(s, 0, 0)
- return self.result
-
- def backtracking(self, s: str, start_index: int, point_num: int) -> None:
- # Base Case
- if point_num == 3:
- if self.is_valid(s, start_index, len(s)-1):
- self.result.append(s[:])
+ result = []
+ self.backtracking(s, 0, 0, "", result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, s, start_index, point_num, current, result):
+ if point_num == 3: # 逗点数量为3时,分隔结束
+ if self.is_valid(s, start_index, len(s) - 1): # 判断第四段子字符串是否合法
+ current += s[start_index:] # 添加最后一段子字符串
+ result.append(current)
return
- # 单层递归逻辑
+
for i in range(start_index, len(s)):
- # [start_index, i]就是被截取的子串
- if self.is_valid(s, start_index, i):
- s = s[:i+1] + '.' + s[i+1:]
- self.backtracking(s, i+2, point_num+1) # 在填入.后,下一子串起始后移2位
- s = s[:i+1] + s[i+2:] # 回溯
+ if self.is_valid(s, start_index, i): # 判断 [start_index, i] 这个区间的子串是否合法
+ sub = s[start_index:i + 1]
+ self.backtracking(s, i + 1, point_num + 1, current + sub + '.', result)
else:
- # 若当前被截取的子串大于255或者大于三位数,直接结束本层循环
break
-
- def is_valid(self, s: str, start: int, end: int) -> bool:
- if start > end: return False
- # 若数字是0开头,不合法
- if s[start] == '0' and start != end:
+
+ def is_valid(self, s, start, end):
+ if start > end:
return False
- if not 0 <= int(s[start:end+1]) <= 255:
+ if s[start] == '0' and start != end: # 0开头的数字不合法
return False
+ num = 0
+ for i in range(start, end + 1):
+ if not s[i].isdigit(): # 遇到非数字字符不合法
+ return False
+ num = num * 10 + int(s[i])
+ if num > 255: # 如果大于255了不合法
+ return False
return True
+
```
+回溯(版本二)
-python3; 简单拼接版本(类似Leetcode131写法):
```python
-class Solution:
+class Solution:
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
- global results, path
results = []
- path = []
- self.backtracking(s,0)
+ self.backtracking(s, 0, [], results)
return results
- def backtracking(self,s,index):
- global results,path
- if index == len(s) and len(path)==4:
- results.append('.'.join(path)) # 在连接时需要中间间隔符号的话就在''中间写上对应的间隔符
+ def backtracking(self, s, index, path, results):
+ if index == len(s) and len(path) == 4:
+ results.append('.'.join(path))
return
- for i in range(index,len(s)):
- if len(path)>3: break # 剪枝
- temp = s[index:i+1]
- if (int(temp)<256 and int(temp)>0 and temp[0]!='0') or (temp=='0'):
- path.append(temp)
- self.backtracking(s,i+1)
- path.pop()
+
+ if len(path) > 4: # 剪枝
+ return
+
+ for i in range(index, min(index + 3, len(s))):
+ if self.is_valid(s, index, i):
+ sub = s[index:i+1]
+ path.append(sub)
+ self.backtracking(s, i+1, path, results)
+ path.pop()
+
+ def is_valid(self, s, start, end):
+ if start > end:
+ return False
+ if s[start] == '0' and start != end: # 0开头的数字不合法
+ return False
+ num = int(s[start:end+1])
+ return 0 <= num <= 255
```
+回溯(版本三)
-## Go
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def restoreIpAddresses(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
+ result = []
+ self.backtracking(s, 0, [], result)
+ return result
+
+ def backtracking(self, s, startIndex, path, result):
+ if startIndex == len(s):
+ result.append('.'.join(path[:]))
+ return
+
+ for i in range(startIndex, min(startIndex+3, len(s))):
+ # 如果 i 往后遍历了,并且当前地址的第一个元素是 0 ,就直接退出
+ if i > startIndex and s[startIndex] == '0':
+ break
+ # 比如 s 长度为 5,当前遍历到 i = 3 这个元素
+ # 因为还没有执行任何操作,所以此时剩下的元素数量就是 5 - 3 = 2 ,即包括当前的 i 本身
+ # path 里面是当前包含的子串,所以有几个元素就表示储存了几个地址
+ # 所以 (4 - len(path)) * 3 表示当前路径至多能存放的元素个数
+ # 4 - len(path) 表示至少要存放的元素个数
+ if (4 - len(path)) * 3 < len(s) - i or 4 - len(path) > len(s) - i:
+ break
+ if i - startIndex == 2:
+ if not int(s[startIndex:i+1]) <= 255:
+ break
+ path.append(s[startIndex:i+1])
+ self.backtracking(s, i+1, path, result)
+ path.pop()
+```
+
+### Go
```go
var (
@@ -493,7 +534,7 @@ func dfs(s string, start int) {
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
/**
@@ -523,7 +564,7 @@ var restoreIpAddresses = function(s) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
```typescript
function isValidIpSegment(str: string): boolean {
@@ -562,7 +603,7 @@ function restoreIpAddresses(s: string): string[] {
};
```
-## Rust
+### Rust
```Rust
impl Solution {
@@ -619,7 +660,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-## C
+### C
```c
//记录结果
char** result;
@@ -695,7 +736,7 @@ char ** restoreIpAddresses(char * s, int* returnSize){
}
```
-## Swift
+### Swift
```swift
// 判断区间段是否合法
@@ -742,7 +783,7 @@ func restoreIpAddresses(_ s: String) -> [String] {
}
```
-## Scala
+### Scala
```scala
object Solution {
@@ -783,9 +824,53 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList res = new List();
+ public IList RestoreIpAddresses(string s)
+ {
+ if (s.Length < 4 || s.Length > 12) return res;
+ BackTracking(s, 0, 0);
+ return res;
+ }
+ public void BackTracking(string s, int start, int pointSum)
+ {
+ if (pointSum == 3)
+ {
+ if (IsValid(s, start, s.Length - 1))
+ {
+ res.Add(s);
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = start; i < s.Length; i++)
+ {
+ if (IsValid(s, start, i))
+ {
+ s = s.Insert(i + 1, ".");
+ BackTracking(s, i + 2, pointSum + 1);
+ s = s.Remove(i + 1, 1);
+ }
+ else break;
+ }
+ }
+ public bool IsValid(string s, int start, int end)
+ {
+ if (start > end) return false;
+ if (s[start] == '0' && start != end) return false;
+ int num = 0;
+ for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
+ {
+ if (s[i] > '9' || s[i] < '0') return false;
+ num = num * 10 + s[i] - '0';
+ if (num > 255) return false;
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 99a4b8dda3..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 99a4b8dda3..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
# 96.不同的二叉搜索树
@@ -12,11 +12,11 @@
示例:
-
+
-# 算法公开课
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[动态规划找到子状态之间的关系很重要!| LeetCode:96.不同的二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1eK411o7QA/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划找到子状态之间的关系很重要!| LeetCode:96.不同的二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1eK411o7QA/),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -27,11 +27,11 @@
了解了二叉搜索树之后,我们应该先举几个例子,画画图,看看有没有什么规律,如图:
-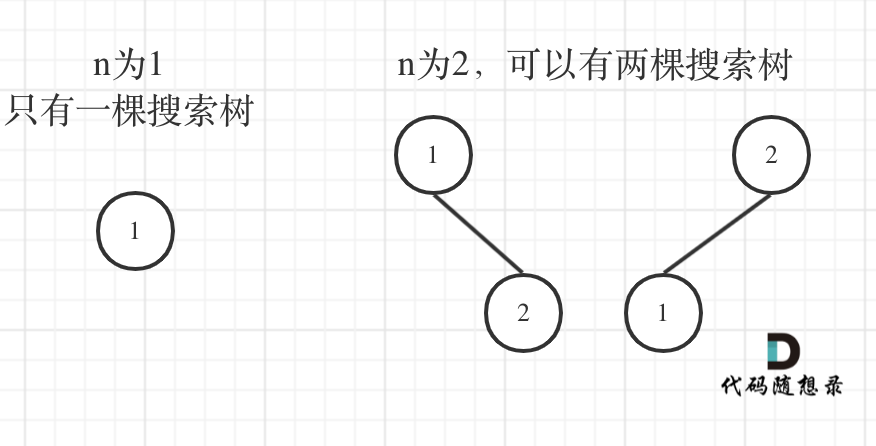
+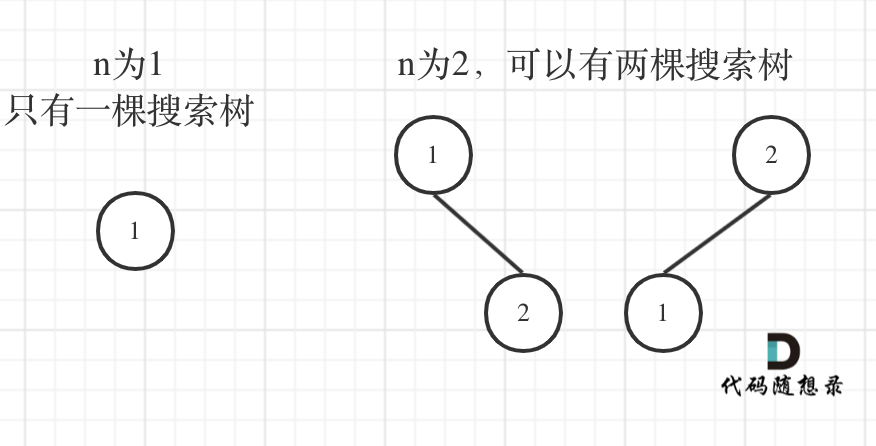
n为1的时候有一棵树,n为2有两棵树,这个是很直观的。
-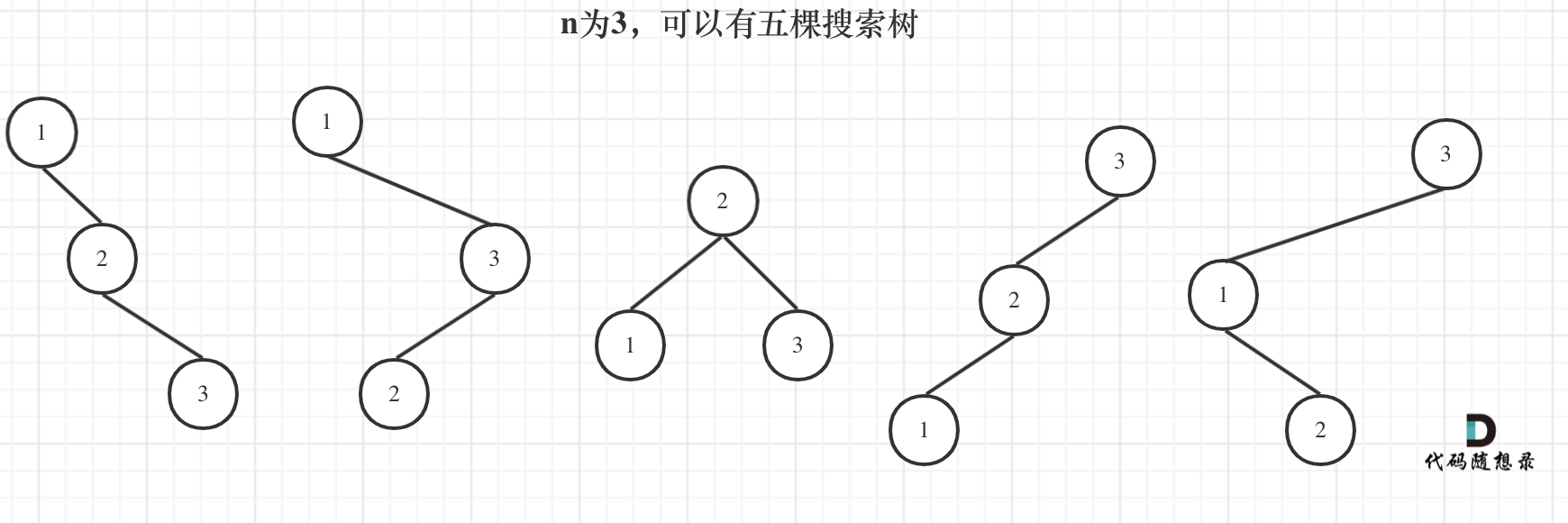
+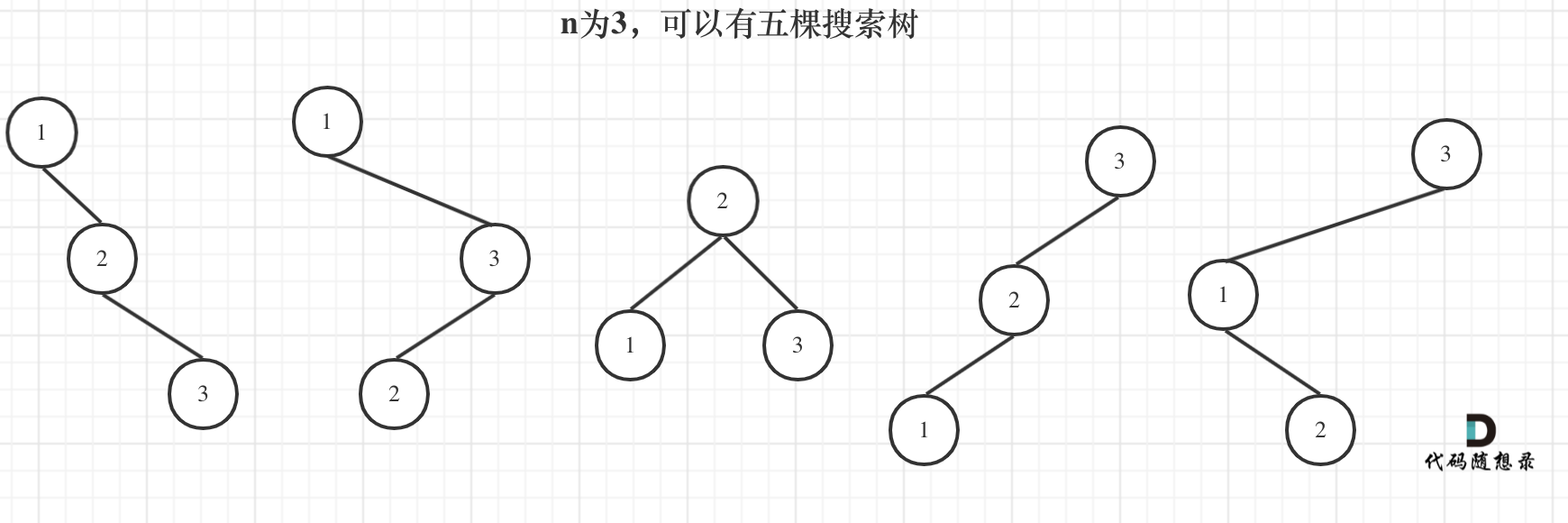
来看看n为3的时候,有哪几种情况。
@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ dp[3],就是 元素1为头结点搜索树的数量 + 元素2为头结点搜索
如图所示:
-
+
此时我们已经找到递推关系了,那么可以用动规五部曲再系统分析一遍。
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
n为5时候的dp数组状态如图:
-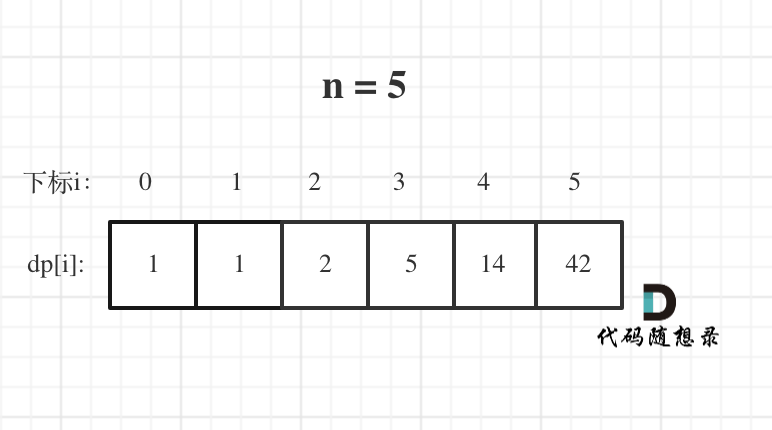
+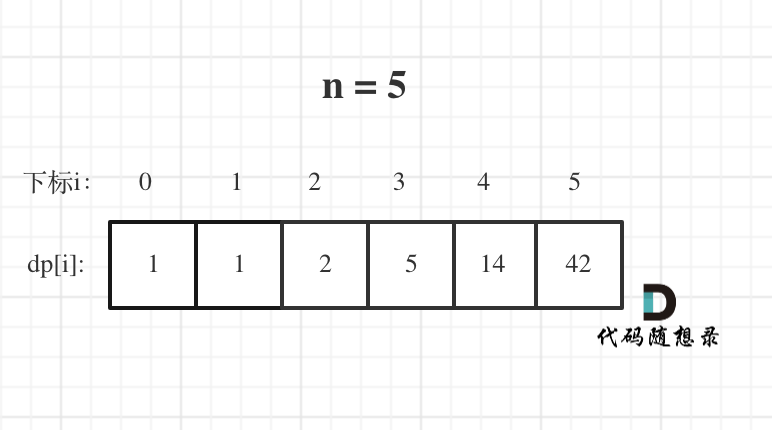
当然如果自己画图举例的话,基本举例到n为3就可以了,n为4的时候,画图已经比较麻烦了。
@@ -157,7 +157,7 @@ public:
可以看出我依然还是用动规五部曲来进行分析,会把题目的方方面面都覆盖到!
-**而且具体这五部分析是我自己平时总结的经验,找不出来第二个的,可能过一阵子 其他题解也会有动规五部曲了,哈哈**。
+**而且具体这五部分析是我自己平时总结的经验,找不出来第二个的,可能过一阵子 其他题解也会有动规五部曲了**。
当时我在用动规五部曲讲解斐波那契的时候,一些录友和我反应,感觉讲复杂了。
@@ -168,7 +168,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-### Java
+### Java
+
```Java
class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
@@ -190,18 +191,21 @@ class Solution {
```
### Python
+
```python
class Solution:
def numTrees(self, n: int) -> int:
- dp = [0] * (n + 1)
- dp[0], dp[1] = 1, 1
- for i in range(2, n + 1):
- for j in range(1, i + 1):
- dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j]
- return dp[-1]
+ dp = [0] * (n + 1) # 创建一个长度为n+1的数组,初始化为0
+ dp[0] = 1 # 当n为0时,只有一种情况,即空树,所以dp[0] = 1
+ for i in range(1, n + 1): # 遍历从1到n的每个数字
+ for j in range(1, i + 1): # 对于每个数字i,计算以i为根节点的二叉搜索树的数量
+ dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j] # 利用动态规划的思想,累加左子树和右子树的组合数量
+ return dp[n] # 返回以1到n为节点的二叉搜索树的总数量
+
```
### Go
+
```Go
func numTrees(n int)int{
dp := make([]int, n+1)
@@ -215,7 +219,8 @@ func numTrees(n int)int{
}
```
-### Javascript
+### JavaScript
+
```Javascript
const numTrees =(n) => {
let dp = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
@@ -241,7 +246,7 @@ function numTrees(n: number): number {
dp[0]: -1; 无意义;
dp[1]: 1;
...
- dp[i]: 2 * dp[i - 1] +
+ dp[i]: 2 * dp[i - 1] +
(dp[1] * dp[i - 2] + dp[2] * dp[i - 3] + ... + dp[i - 2] * dp[1]); 从1加到i-2
*/
const dp: number[] = [];
@@ -282,7 +287,7 @@ impl Solution {
int *initDP(int n) {
int *dp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 1));
int i;
- for(i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
+ for(i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
dp[i] = 0;
return dp;
}
@@ -321,8 +326,23 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public int NumTrees(int n)
+ {
+ int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
+ dp[0] = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
+ {
+ for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
+ {
+ dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93c2272cf6..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93c2272cf6..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 98.验证二叉搜索树
@@ -18,20 +16,20 @@
* 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
* 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
-
+
-# 视频讲解
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[你对二叉搜索树了解的还不够! | LeetCode:98.验证二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18P411n7Q4),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[你对二叉搜索树了解的还不够! | LeetCode:98.验证二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18P411n7Q4),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-# 思路
+## 思路
要知道中序遍历下,输出的二叉搜索树节点的数值是有序序列。
有了这个特性,**验证二叉搜索树,就相当于变成了判断一个序列是不是递增的了。**
-## 递归法
+### 递归法
可以递归中序遍历将二叉搜索树转变成一个数组,代码如下:
@@ -104,7 +102,7 @@ if (root->val > root->left->val && root->val < root->right->val) {
例如: [10,5,15,null,null,6,20] 这个case:
-
+
节点10大于左节点5,小于右节点15,但右子树里出现了一个6 这就不符合了!
@@ -211,7 +209,7 @@ public:
最后这份代码看上去整洁一些,思路也清晰。
-## 迭代法
+### 迭代法
可以用迭代法模拟二叉树中序遍历,对前中后序迭代法生疏的同学可以看这两篇[二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的迭代遍历.html),[二叉树:前中后序迭代方式统一写法](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的统一迭代法.html)
@@ -245,20 +243,50 @@ public:
在[二叉树:二叉搜索树登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.html)中我们分明写出了痛哭流涕的简洁迭代法,怎么在这里不行了呢,因为本题是要验证二叉搜索树啊。
-# 总结
+## 总结
这道题目是一个简单题,但对于没接触过的同学还是有难度的。
-所以初学者刚开始学习算法的时候,看到简单题目没有思路很正常,千万别怀疑自己智商,学习过程都是这样的,大家智商都差不多,哈哈。
+所以初学者刚开始学习算法的时候,看到简单题目没有思路很正常,千万别怀疑自己智商,学习过程都是这样的,大家智商都差不多。
-只要把基本类型的题目都做过,总结过之后,思路自然就开阔了。
+只要把基本类型的题目都做过,总结过之后,思路自然就开阔了,加油💪
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
+```Java
+//使用統一迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
+ Stack stack = new Stack<>();
+ TreeNode pre = null;
+ if(root != null)
+ stack.add(root);
+ while(!stack.isEmpty()){
+ TreeNode curr = stack.peek();
+ if(curr != null){
+ stack.pop();
+ if(curr.right != null)
+ stack.add(curr.right);
+ stack.add(curr);
+ stack.add(null);
+ if(curr.left != null)
+ stack.add(curr.left);
+ }else{
+ stack.pop();
+ TreeNode temp = stack.pop();
+ if(pre != null && pre.val >= temp.val)
+ return false;
+ pre = temp;
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+ }
+}
+```
```Java
class Solution {
// 递归
@@ -339,121 +367,117 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+### Python
-**递归** - 利用BST中序遍历特性,把树"压缩"成数组
+递归法(版本一)利用中序递增性质,转换成数组
```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
- # 思路: 利用BST中序遍历的特性.
- # 中序遍历输出的二叉搜索树节点的数值是有序序列
- candidate_list = []
-
- def __traverse(root: TreeNode) -> None:
- nonlocal candidate_list
- if not root:
- return
- __traverse(root.left)
- candidate_list.append(root.val)
- __traverse(root.right)
-
- def __is_sorted(nums: list) -> bool:
- for i in range(1, len(nums)):
- if nums[i] <= nums[i - 1]: # ⚠️ 注意: Leetcode定义二叉搜索树中不能有重复元素
- return False
- return True
-
- __traverse(root)
- res = __is_sorted(candidate_list)
-
- return res
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.vec = []
+
+ def traversal(self, root):
+ if root is None:
+ return
+ self.traversal(root.left)
+ self.vec.append(root.val) # 将二叉搜索树转换为有序数组
+ self.traversal(root.right)
+
+ def isValidBST(self, root):
+ self.vec = [] # 清空数组
+ self.traversal(root)
+ for i in range(1, len(self.vec)):
+ # 注意要小于等于,搜索树里不能有相同元素
+ if self.vec[i] <= self.vec[i - 1]:
+ return False
+ return True
+
```
-**递归** - 标准做法
+递归法(版本二)设定极小值,进行比较
```python
class Solution:
- def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
- # 规律: BST的中序遍历节点数值是从小到大.
- cur_max = -float("INF")
- def __isValidBST(root: TreeNode) -> bool:
- nonlocal cur_max
-
- if not root:
- return True
-
- is_left_valid = __isValidBST(root.left)
- if cur_max < root.val:
- cur_max = root.val
- else:
- return False
- is_right_valid = __isValidBST(root.right)
-
- return is_left_valid and is_right_valid
- return __isValidBST(root)
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.maxVal = float('-inf') # 因为后台测试数据中有int最小值
+
+ def isValidBST(self, root):
+ if root is None:
+ return True
+
+ left = self.isValidBST(root.left)
+ # 中序遍历,验证遍历的元素是不是从小到大
+ if self.maxVal < root.val:
+ self.maxVal = root.val
+ else:
+ return False
+ right = self.isValidBST(root.right)
+
+ return left and right
+
```
-**递归** - 避免初始化最小值做法:
+递归法(版本三)直接取该树的最小值
```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
- # 规律: BST的中序遍历节点数值是从小到大.
- pre = None
- def __isValidBST(root: TreeNode) -> bool:
- nonlocal pre
-
- if not root:
- return True
-
- is_left_valid = __isValidBST(root.left)
- if pre and pre.val>=root.val: return False
- pre = root
- is_right_valid = __isValidBST(root.right)
-
- return is_left_valid and is_right_valid
- return __isValidBST(root)
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.pre = None # 用来记录前一个节点
+
+ def isValidBST(self, root):
+ if root is None:
+ return True
+
+ left = self.isValidBST(root.left)
+
+ if self.pre is not None and self.pre.val >= root.val:
+ return False
+ self.pre = root # 记录前一个节点
+
+ right = self.isValidBST(root.right)
+ return left and right
+
+
+
```
+迭代法
```python
-迭代-中序遍历
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
+ def isValidBST(self, root):
stack = []
cur = root
- pre = None
- while cur or stack:
- if cur: # 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
+ pre = None # 记录前一个节点
+ while cur is not None or len(stack) > 0:
+ if cur is not None:
stack.append(cur)
- cur = cur.left
- else: # 逐一处理节点
- cur = stack.pop()
- if pre and cur.val <= pre.val: # 比较当前节点和前节点的值的大小
+ cur = cur.left # 左
+ else:
+ cur = stack.pop() # 中
+ if pre is not None and cur.val <= pre.val:
return False
- pre = cur
- cur = cur.right
+ pre = cur # 保存前一个访问的结点
+ cur = cur.right # 右
return True
```
-```python
-# 遵循Carl的写法,只添加了节点判断的部分
-class Solution:
- def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
- # method 2
- que, pre = [], None
- while root or que:
- while root:
- que.append(root)
- root = root.left
- root = que.pop()
- # 对第一个节点只做记录,对后面的节点进行比较
- if pre is None:
- pre = root.val
- else:
- if pre >= root.val: return False
- pre = root.val
- root = root.right
- return True
-```
-## Go
+
+### Go
```Go
func isValidBST(root *TreeNode) bool {
@@ -500,7 +524,7 @@ func isValidBST(root *TreeNode) bool {
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
辅助数组解决
@@ -569,7 +593,44 @@ var isValidBST = function (root) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+> 迭代法:
+
+```JavaScript
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
+ * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
+ * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
+ * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
+ * }
+ */
+/**
+ * @param {TreeNode} root
+ * @return {boolean}
+ */
+let pre = null;
+var isValidBST = function (root) {
+ const queue = [];
+ let cur = root;
+ let pre = null;
+ while (cur !== null || queue.length !== 0) {
+ if (cur !== null) {
+ queue.push(cur);
+ cur = cur.left;
+ } else {
+ cur = queue.pop();
+ if (pre !== null && cur.val <= pre.val) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ pre = cur;
+ cur = cur.right;
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+};
+```
+
+### TypeScript
> 辅助数组解决:
@@ -611,7 +672,31 @@ function isValidBST(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
};
```
-## Scala
+> 迭代法:
+
+```TypeScript
+function isValidBST(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
+ const queue: TreeNode[] = [];
+ let cur: TreeNode | null = root;
+ let pre: TreeNode | null = null;
+ while (cur !== null || queue.length !== 0) {
+ if (cur !== null) {
+ queue.push(cur);
+ cur = cur.left;
+ } else {
+ cur = queue.pop()!;
+ if (pre !== null && cur!.val <= pre.val) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ pre = cur;
+ cur = cur!.right;
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+```
+
+### Scala
辅助数组解决:
```scala
@@ -656,7 +741,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-## rust
+### Rust
递归:
@@ -704,8 +789,19 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 递归
+public long val = Int64.MinValue;
+public bool IsValidBST(TreeNode root)
+{
+ if (root == null) return true;
+ bool left = IsValidBST(root.left);
+ if (root.val > val) val = root.val;
+ else return false;
+ bool right = IsValidBST(root.right);
+ return left && right;
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96acacf61c..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96acacf61c..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -14,12 +12,12 @@
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
-
+
-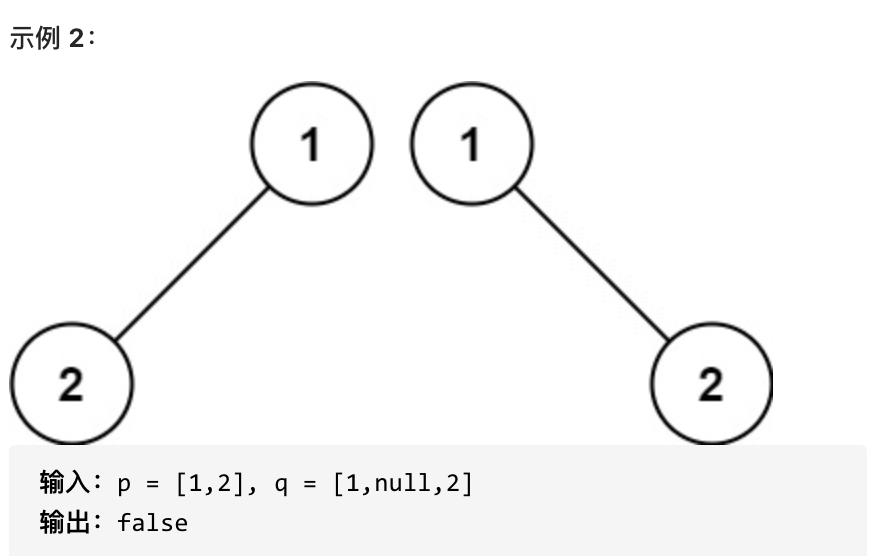
+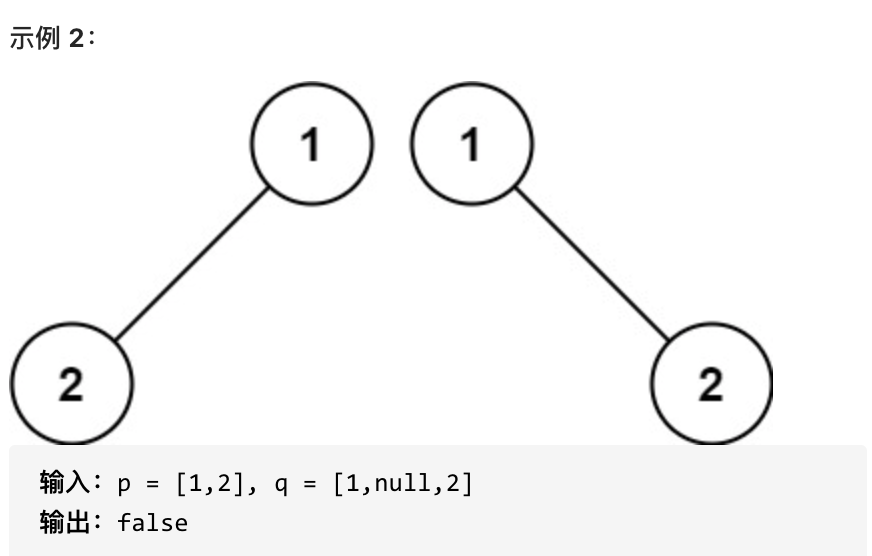
-# 思路
+## 思路
在[101.对称二叉树](https://programmercarl.com/0101.对称二叉树.html)中,我们讲到对于二叉树是否对称,要比较的是根节点的左子树与右子树是不是相互翻转的,理解这一点就知道了**其实我们要比较的是两个树(这两个树是根节点的左右子树)**,所以在递归遍历的过程中,也是要同时遍历两棵树。
@@ -115,7 +113,7 @@ public:
当然我可以把如上代码整理如下:
-## 递归
+### 递归
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -134,7 +132,7 @@ public:
};
```
-## 迭代法
+### 迭代法
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -166,9 +164,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
```java
// 递归法
@@ -205,7 +203,8 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
# 递归法
class Solution:
@@ -236,7 +235,8 @@ class Solution:
que.append(rightNode.right)
return True
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
> 递归法
```go
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
@@ -258,7 +258,7 @@ func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
}
```
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
> 递归法
@@ -296,7 +296,7 @@ var isSameTree = (p, q) => {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
> 递归法-先序遍历
@@ -337,7 +337,4 @@ function isSameTree(p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null): boolean {
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c2812fa64..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c2812fa64..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 101. 对称二叉树
@@ -11,11 +9,13 @@
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
-
+
-# 思路
+## 算法公开课
-《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[同时操作两个二叉树 | LeetCode:101. 对称二叉树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ue4y1Y7Mf),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[同时操作两个二叉树 | LeetCode:101. 对称二叉树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ue4y1Y7Mf), 相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+## 思路
**首先想清楚,判断对称二叉树要比较的是哪两个节点,要比较的可不是左右节点!**
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@
比较的是两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等。如图所示:
-
+
那么遍历的顺序应该是什么样的呢?
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@
那么我们先来看看递归法的代码应该怎么写。
-## 递归法
+### 递归法
递归三部曲
@@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ else if (left->val != right->val) return false; // 注意这里我没有
* 比较二叉树外侧是否对称:传入的是左节点的左孩子,右节点的右孩子。
-* 比较内测是否对称,传入左节点的右孩子,右节点的左孩子。
+* 比较内侧是否对称,传入左节点的右孩子,右节点的左孩子。
* 如果左右都对称就返回true ,有一侧不对称就返回false 。
代码如下:
@@ -157,19 +157,19 @@ public:
**这个代码就很简洁了,但隐藏了很多逻辑,条理不清晰,而且递归三部曲,在这里完全体现不出来。**
-**所以建议大家做题的时候,一定要想清楚逻辑,每一步做什么。把道题目所有情况想到位,相应的代码写出来之后,再去追求简洁代码的效果。**
+**所以建议大家做题的时候,一定要想清楚逻辑,每一步做什么。把题目所有情况想到位,相应的代码写出来之后,再去追求简洁代码的效果。**
-## 迭代法
+### 迭代法
这道题目我们也可以使用迭代法,但要注意,这里的迭代法可不是前中后序的迭代写法,因为本题的本质是判断两个树是否是相互翻转的,其实已经不是所谓二叉树遍历的前中后序的关系了。
这里我们可以使用队列来比较两个树(根节点的左右子树)是否相互翻转,(**注意这不是层序遍历**)
-### 使用队列
+#### 使用队列
通过队列来判断根节点的左子树和右子树的内侧和外侧是否相等,如动画所示:
-
+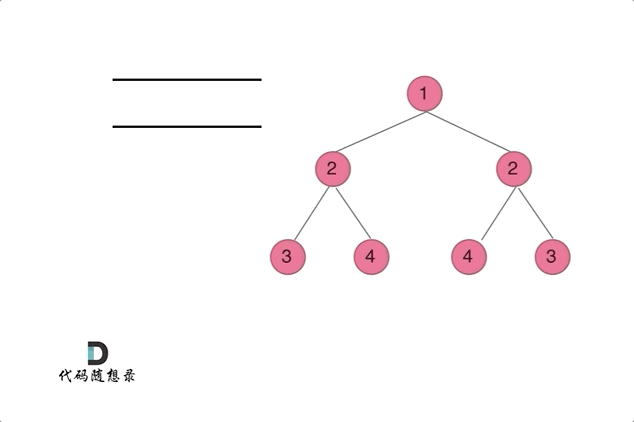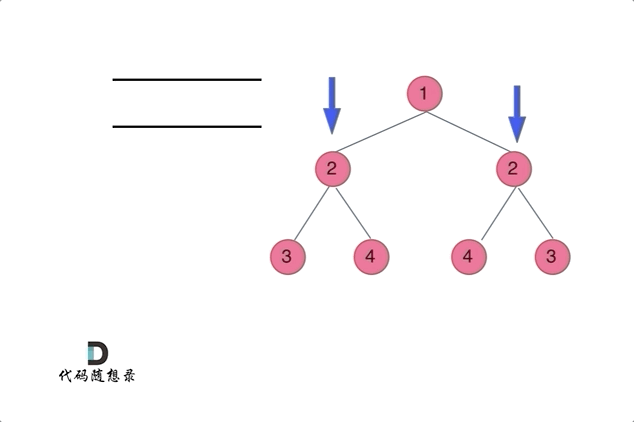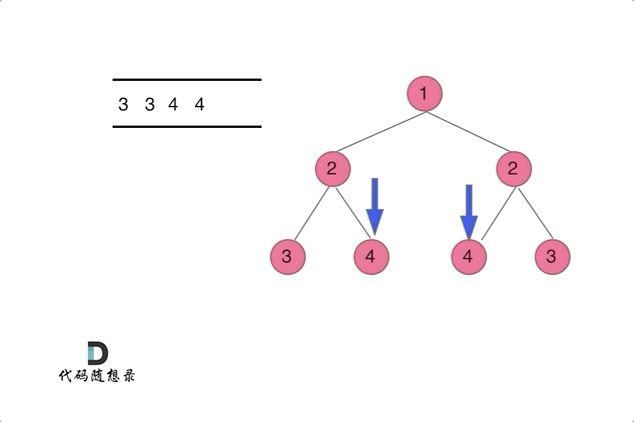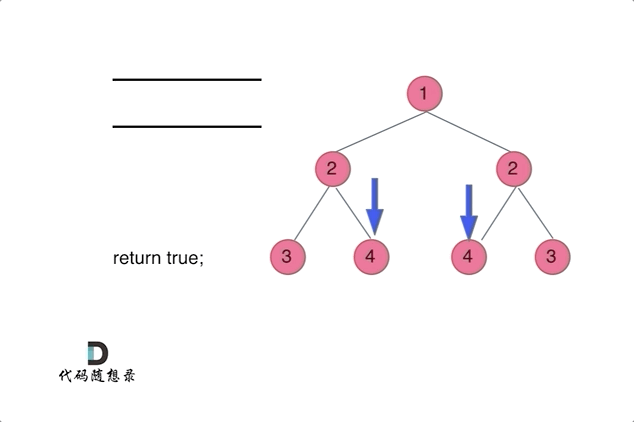
@@ -207,7 +207,7 @@ public:
};
```
-### 使用栈
+#### 使用栈
细心的话,其实可以发现,这个迭代法,其实是把左右两个子树要比较的元素顺序放进一个容器,然后成对成对的取出来进行比较,那么其实使用栈也是可以的。
@@ -222,8 +222,8 @@ public:
st.push(root->left);
st.push(root->right);
while (!st.empty()) {
- TreeNode* leftNode = st.top(); st.pop();
TreeNode* rightNode = st.top(); st.pop();
+ TreeNode* leftNode = st.top(); st.pop();
if (!leftNode && !rightNode) {
continue;
}
@@ -254,12 +254,12 @@ public:
这两道题目基本和本题是一样的,只要稍加修改就可以AC。
-* 100.相同的树
-* 572.另一个树的子树
+* [100.相同的树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/)
+* [572.另一个树的子树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/)
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-Java
+### Java:
```Java
/**
@@ -364,7 +364,7 @@ Java
```
-Python
+### Python:
递归法:
```python
@@ -442,29 +442,36 @@ class Solution:
层次遍历
```python
class Solution:
- def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
+ def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not root:
return True
-
- que = [root]
- while que:
- this_level_length = len(que)
- for i in range(this_level_length // 2):
- # 要么其中一个是None但另外一个不是
- if (not que[i] and que[this_level_length - 1 - i]) or (que[i] and not que[this_level_length - 1 - i]):
- return False
- # 要么两个都不是None
- if que[i] and que[i].val != que[this_level_length - 1 - i].val:
- return False
- for i in range(this_level_length):
- if not que[i]: continue
- que.append(que[i].left)
- que.append(que[i].right)
- que = que[this_level_length:]
+
+ queue = collections.deque([root.left, root.right])
+
+ while queue:
+ level_size = len(queue)
+
+ if level_size % 2 != 0:
+ return False
+
+ level_vals = []
+ for i in range(level_size):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+ if node:
+ level_vals.append(node.val)
+ queue.append(node.left)
+ queue.append(node.right)
+ else:
+ level_vals.append(None)
+
+ if level_vals != level_vals[::-1]:
+ return False
+
return True
```
-Go
+### Go:
+
```go
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -515,8 +522,7 @@ func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
}
```
-
-JavaScript
+### JavaScript:
递归判断是否为对称二叉树:
```javascript
@@ -604,7 +610,7 @@ var isSymmetric = function(root) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
> 递归法
@@ -673,7 +679,7 @@ function isSymmetric(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
};
```
-Swift:
+### Swift:
> 递归
```swift
@@ -755,7 +761,7 @@ func isSymmetric3(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Bool {
}
```
-Scala
+### Scala:
> 递归:
```scala
@@ -829,7 +835,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-## Rust
+### Rust:
递归:
```rust
@@ -889,8 +895,53 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 递归
+public bool IsSymmetric(TreeNode root)
+{
+ if (root == null) return true;
+ return Compare(root.left, root.right);
+}
+public bool Compare(TreeNode left, TreeNode right)
+{
+ if(left == null && right != null) return false;
+ else if(left != null && right == null ) return false;
+ else if(left == null && right == null) return true;
+ else if(left.val != right.val) return false;
+
+ var outside = Compare(left.left, right.right);
+ var inside = Compare(left.right, right.left);
+
+ return outside&&inside;
+}
+```
+``` C#
+// 迭代法
+public bool IsSymmetric(TreeNode root)
+{
+ if (root == null) return true;
+ var st = new Stack();
+ st.Push(root.left);
+ st.Push(root.right);
+ while (st.Count != 0)
+ {
+ var left = st.Pop();
+ var right = st.Pop();
+ if (left == null && right == null)
+ continue;
+
+ if ((left == null || right == null || (left.val != right.val)))
+ return false;
+
+ st.Push(left.left);
+ st.Push(right.right);
+ st.Push(left.right);
+ st.Push(right.left);
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+```
+
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c6ce488cb..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,43 +1,45 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c6ce488cb..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,43 +1,45 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
# 二叉树层序遍历登场!
-《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[讲透二叉树的层序遍历 | 广度优先搜索 | LeetCode:102.二叉树的层序遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1GY4y1u7b2),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[讲透二叉树的层序遍历 | 广度优先搜索 | LeetCode:102.二叉树的层序遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1GY4y1u7b2),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
学会二叉树的层序遍历,可以一口气打完以下十题:
-* 102.二叉树的层序遍历
-* 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
-* 199.二叉树的右视图
-* 637.二叉树的层平均值
-* 429.N叉树的层序遍历
-* 515.在每个树行中找最大值
-* 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
-* 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
-* 104.二叉树的最大深度
-* 111.二叉树的最小深度
+* [102.二叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
+* [107.二叉树的层次遍历II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/)
+* [199.二叉树的右视图](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
+* [637.二叉树的层平均值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/)
+* [429.N叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
+* [515.在每个树行中找最大值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/)
+* [116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
+* [117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/)
+* [104.二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
+* [111.二叉树的最小深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
-
+
-# 102.二叉树的层序遍历
+## 102.二叉树的层序遍历
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
-
+
-思路:
+### 思路
我们之前讲过了三篇关于二叉树的深度优先遍历的文章:
@@ -55,13 +57,13 @@
使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历,动画如下:
-
+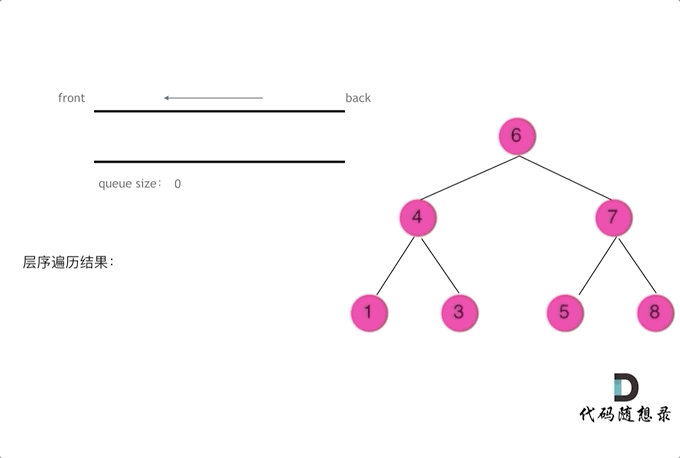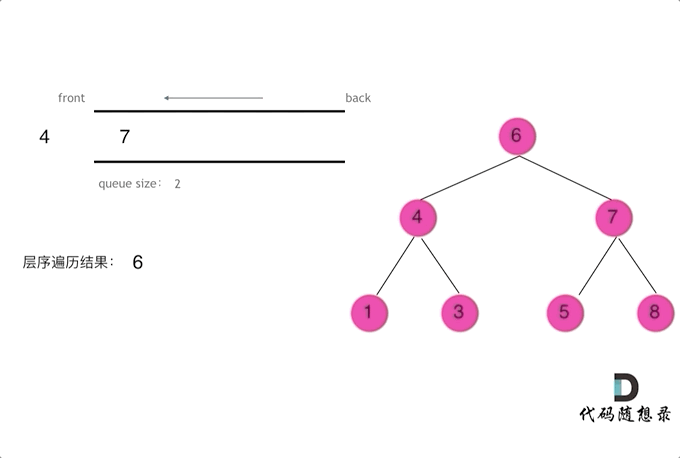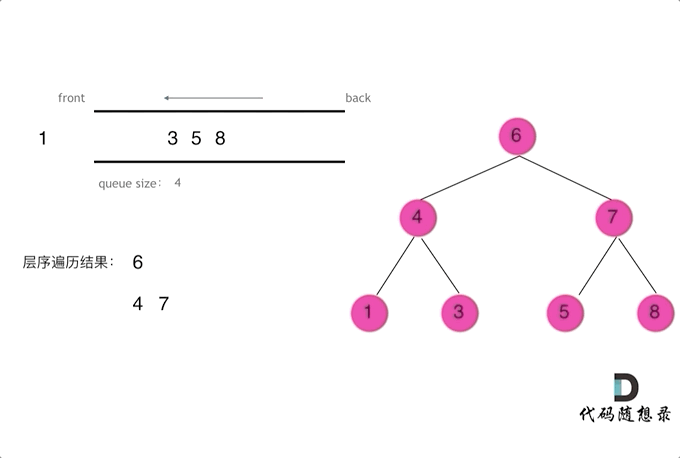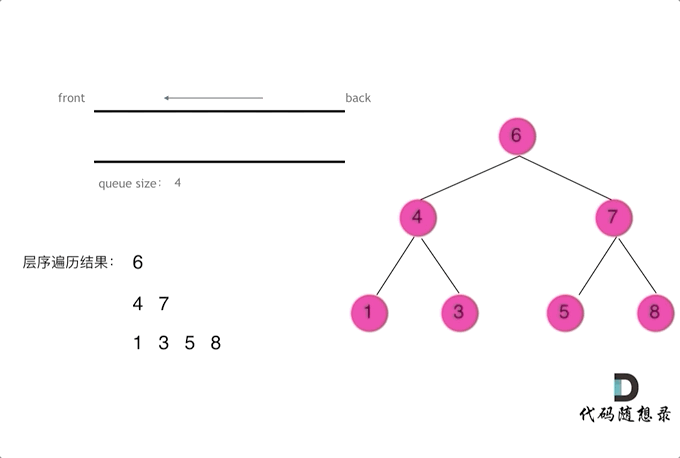
这样就实现了层序从左到右遍历二叉树。
代码如下:**这份代码也可以作为二叉树层序遍历的模板,打十个就靠它了**。
-C++代码:
+c++代码如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -87,6 +89,7 @@ public:
}
};
```
+
```CPP
# 递归法
class Solution {
@@ -108,7 +111,9 @@ public:
};
```
-java:
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Java:
```Java
// 102.二叉树的层序遍历
@@ -122,7 +127,7 @@ class Solution {
return resList;
}
- //DFS--递归方式
+ //BFS--递归方式
public void checkFun01(TreeNode node, Integer deep) {
if (node == null) return;
deep++;
@@ -164,52 +169,67 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-python3代码:
+#### Python:
```python
-
+# 利用长度法
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
- """二叉树层序遍历迭代解法"""
-
- def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
- results = []
+ def levelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
- return results
-
- from collections import deque
- que = deque([root])
-
- while que:
- size = len(que)
- result = []
- for _ in range(size):
- cur = que.popleft()
- result.append(cur.val)
+ return []
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+ result = []
+ while queue:
+ level = []
+ for _ in range(len(queue)):
+ cur = queue.popleft()
+ level.append(cur.val)
if cur.left:
- que.append(cur.left)
+ queue.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
- que.append(cur.right)
- results.append(result)
-
- return results
+ queue.append(cur.right)
+ result.append(level)
+ return result
```
```python
-# 递归法
+#递归法
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = []
- def helper(root, depth):
- if not root: return []
- if len(res) == depth: res.append([]) # start the current depth
- res[depth].append(root.val) # fulfil the current depth
- if root.left: helper(root.left, depth + 1) # process child nodes for the next depth
- if root.right: helper(root.right, depth + 1)
- helper(root, 0)
- return res
+ def levelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
+ if not root:
+ return []
+
+ levels = []
+
+ def traverse(node, level):
+ if not node:
+ return
+
+ if len(levels) == level:
+ levels.append([])
+
+ levels[level].append(node.val)
+ traverse(node.left, level + 1)
+ traverse(node.right, level + 1)
+
+ traverse(root, 0)
+ return levels
+
```
-go:
+#### Go:
```go
/**
@@ -243,7 +263,7 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
```go
/**
-102. 二叉树的层序遍历
+102. 二叉树的层序遍历 使用container包
*/
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
res := [][]int{}
@@ -252,9 +272,9 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
}
queue := list.New()
queue.PushBack(root)
-
+
var tmpArr []int
-
+
for queue.Len() > 0 {
length := queue.Len() //保存当前层的长度,然后处理当前层(十分重要,防止添加下层元素影响判断层中元素的个数)
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
@@ -270,16 +290,45 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
res = append(res, tmpArr) //放入结果集
tmpArr = []int{} //清空层的数据
}
-
+
return res
}
+/**
+ 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 使用切片
+*/
+func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
+ res := make([][]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ level := make([]int, 0)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ level = append(level, node.Val)
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ res = append(res, level)
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
/**
102. 二叉树的层序遍历:使用切片模拟队列,易理解
*/
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) (res [][]int) {
if root == nil {
- return
+ return
}
curLevel := []*TreeNode{root} // 存放当前层节点
@@ -305,7 +354,7 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) (res [][]int) {
}
```
-javascript代码:
+#### JavaScript:
```javascript
var levelOrder = function(root) {
@@ -318,7 +367,7 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
while(queue.length !== 0) {
// 记录当前层级节点数
let length = queue.length;
- //存放每一层的节点
+ //存放每一层的节点
let curLevel = [];
for(let i = 0;i < length; i++) {
let node = queue.shift();
@@ -335,7 +384,7 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
```
-TypeScript:
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function levelOrder(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] {
@@ -362,7 +411,7 @@ function levelOrder(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func levelOrder(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -387,7 +436,9 @@ func levelOrder(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
return result
}
```
-Scala:
+
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 102.二叉树的层序遍历
object Solution {
@@ -413,7 +464,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-Rust:
+#### Rust:
```rust
use std::cell::RefCell;
@@ -444,20 +495,46 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public IList> LevelOrder(TreeNode root)
+{
+ var res = new List>();
+ var que = new Queue();
+ if (root == null) return res;
+ que.Enqueue(root);
+ while (que.Count != 0)
+ {
+ var size = que.Count;
+ var vec = new List();
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
+ {
+ var cur = que.Dequeue();
+ vec.Add(cur.val);
+ if (cur.left != null) que.Enqueue(cur.left);
+ if (cur.right != null) que.Enqueue(cur.right);
+ }
+ res.Add(vec);
+
+
+ }
+ return res;
+}
+```
**此时我们就掌握了二叉树的层序遍历了,那么如下九道力扣上的题目,只需要修改模板的两三行代码(不能再多了),便可打倒!**
-# 107.二叉树的层次遍历 II
+## 107.二叉树的层次遍历 II
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/)
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
-
+
-思路:
+### 思路
相对于102.二叉树的层序遍历,就是最后把result数组反转一下就可以了。
@@ -488,36 +565,41 @@ public:
}
};
```
-python代码:
+
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Python:
```python
class Solution:
"""二叉树层序遍历II迭代解法"""
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
def levelOrderBottom(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
- results = []
if not root:
- return results
-
- from collections import deque
- que = deque([root])
-
- while que:
- result = []
- for _ in range(len(que)):
- cur = que.popleft()
- result.append(cur.val)
+ return []
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+ result = []
+ while queue:
+ level = []
+ for _ in range(len(queue)):
+ cur = queue.popleft()
+ level.append(cur.val)
if cur.left:
- que.append(cur.left)
+ queue.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
- que.append(cur.right)
- results.append(result)
-
- results.reverse()
- return results
+ queue.append(cur.right)
+ result.append(level)
+ return result[::-1]
```
-Java:
+#### Java:
```java
// 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
@@ -572,7 +654,7 @@ class Solution {
public List> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
// 利用链表可以进行 O(1) 头部插入, 这样最后答案不需要再反转
LinkedList> ans = new LinkedList<>();
-
+
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) q.offer(root);
@@ -584,9 +666,9 @@ class Solution {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
-
+
temp.add(node.val);
-
+
if (node.left != null) q.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) q.offer(node.right);
@@ -598,12 +680,10 @@ class Solution {
return ans;
}
-}
-```
-
+```
-go:
+#### Go:
```GO
/**
@@ -616,7 +696,7 @@ func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
return res
}
queue.PushBack(root)
-
+
for queue.Len() > 0 {
length := queue.Len()
tmp := []int{}
@@ -632,43 +712,80 @@ func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
}
res=append(res, tmp)
}
-
+
//反转结果集
for i:=0; i 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ level := make([]int, 0)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ level = append(level, node.Val)
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
}
- // 从数组前头插入值,避免最后反转数组,减少运算时间
- res.unshift(curLevel);
+ res = append(res, level)
}
- return res;
+ l, r := 0, len(res)-1
+ for l < r {
+ res[l], res[r] = res[r], res[l]
+ l++
+ r--
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
+
+```javascript
+var levelOrderBottom = function (root) {
+ let res = [],
+ queue = [];
+ queue.push(root);
+ while (queue.length && root !== null) {
+ // 存放当前层级节点数组
+ let curLevel = [];
+ // 计算当前层级节点数量
+ let length = queue.length;
+ while (length--) {
+ let node = queue.shift();
+ // 把当前层节点存入curLevel数组
+ curLevel.push(node.val);
+ // 把下一层级的左右节点存入queue队列
+ node.left && queue.push(node.left);
+ node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+ }
+ // 从数组前头插入值,避免最后反转数组,减少运算时间
+ res.unshift(curLevel);
+ }
+ return res;
};
+
```
-TypeScript:
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function levelOrderBottom(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] {
@@ -691,7 +808,7 @@ function levelOrderBottom(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func levelOrderBottom(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -717,8 +834,8 @@ func levelOrderBottom(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
}
```
+#### Scala:
-Scala:
```scala
// 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
object Solution {
@@ -743,7 +860,10 @@ object Solution {
res.reverse.toList
}
-Rust:
+
+```
+
+#### Rust:
```rust
use std::cell::RefCell;
@@ -774,16 +894,41 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public IList> LevelOrderBottom(TreeNode root)
+{
+ var res = new List>();
+ var que = new Queue();
+ if (root == null) return res;
+ que.Enqueue(root);
+ while (que.Count != 0)
+ {
+ var size = que.Count;
+ var vec = new List();
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
+ {
+ var cur = que.Dequeue();
+ vec.Add(cur.val);
+ if (cur.left != null) que.Enqueue(cur.left);
+ if (cur.right != null) que.Enqueue(cur.right);
+ }
+ res.Add(vec);
+ }
+ res.Reverse();
+ return res;
+}
+```
-# 199.二叉树的右视图
+## 199.二叉树的右视图
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
-
+
-思路:
+### 思路
层序遍历的时候,判断是否遍历到单层的最后面的元素,如果是,就放进result数组中,随后返回result就可以了。
@@ -810,42 +955,44 @@ public:
}
};
```
-python代码:
+
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Python:
```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
- # deque来自collections模块,不在力扣平台时,需要手动写入
- # 'from collections import deque' 导入
- # deque相比list的好处是,list的pop(0)是O(n)复杂度,deque的popleft()是O(1)复杂度
-
- quene = deque([root])
- out_list = []
-
- while quene:
- # 每次都取最后一个node就可以了
- node = quene[-1]
- out_list.append(node.val)
-
- # 执行这个遍历的目的是获取下一层所有的node
- for _ in range(len(quene)):
- node = quene.popleft()
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+ right_view = []
+
+ while queue:
+ level_size = len(queue)
+
+ for i in range(level_size):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+
+ if i == level_size - 1:
+ right_view.append(node.val)
+
if node.left:
- quene.append(node.left)
+ queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
- quene.append(node.right)
+ queue.append(node.right)
- return out_list
-
-# 执行用时:36 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了89.47%的用户
-# 内存消耗:14.6 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了96.65%的用户
+ return right_view
```
-
-Java:
+#### Java:
```java
// 199.二叉树的右视图
@@ -889,10 +1036,9 @@ public class N0199 {
}
```
-go:
+#### Go:
```GO
-
/**
199. 二叉树的右视图
*/
@@ -924,15 +1070,43 @@ func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
}
```
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
+ res := make([]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ if i == size-1 {
+ res = append(res, node.Val)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
-javascript代码:
+#### JavaScript:
```javascript
var rightSideView = function(root) {
//二叉树右视图 只需要把每一层最后一个节点存储到res数组
let res = [], queue = [];
queue.push(root);
-
+
while(queue.length && root!==null) {
// 记录当前层级节点个数
let length = queue.length;
@@ -946,12 +1120,12 @@ var rightSideView = function(root) {
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
-
+
return res;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function rightSideView(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
@@ -971,7 +1145,7 @@ function rightSideView(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func rightSideView(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
@@ -996,7 +1170,8 @@ func rightSideView(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
}
```
-Scala:
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 199.二叉树的右视图
object Solution {
@@ -1021,7 +1196,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-rust:
+#### Rust:
```rust
use std::cell::RefCell;
@@ -1054,17 +1229,58 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-# 637.二叉树的层平均值
+#### C#:
+
+```C# 199.二叉树的右视图
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList RightSideView(TreeNode root)
+ {
+ var result = new List();
+ Queue queue = new();
+
+ if (root != null)
+ {
+ queue.Enqueue(root);
+ }
+ while (queue.Count > 0)
+ {
+ int count = queue.Count;
+ int lastValue = count - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
+ {
+ var currentNode = queue.Dequeue();
+ if (i == lastValue)
+ {
+ result.Add(currentNode.val);
+ }
+
+ // lastValue == i == count -1 : left 先于 right 进入Queue
+ if (currentNode.left != null) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.left);
+ if (currentNode.right != null) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.right);
+
+ //// lastValue == i == 0: right 先于 left 进入Queue
+ // if(currentNode.right !=null ) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.right);
+ // if(currentNode.left !=null ) queue.Enqueue(currentNode.left);
+ }
+ }
+
+ return result;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## 637.二叉树的层平均值
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/)
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组。
-
+
-思路:
+### 思路
-本题就是层序遍历的时候把一层求个总和在取一个均值。
+本题就是层序遍历的时候把一层求个总和再取一个均值。
C++代码:
@@ -1093,39 +1309,51 @@ public:
```
-python代码:
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Python:
```python
class Solution:
"""二叉树层平均值迭代解法"""
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
def averageOfLevels(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[float]:
- results = []
if not root:
- return results
+ return []
+
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+ averages = []
- from collections import deque
- que = deque([root])
+ while queue:
+ size = len(queue)
+ level_sum = 0
+
+ for i in range(size):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+
+
+ level_sum += node.val
+
+ if node.left:
+ queue.append(node.left)
+ if node.right:
+ queue.append(node.right)
+
+ averages.append(level_sum / size)
- while que:
- size = len(que)
- sum_ = 0
- for _ in range(size):
- cur = que.popleft()
- sum_ += cur.val
- if cur.left:
- que.append(cur.left)
- if cur.right:
- que.append(cur.right)
- results.append(sum_ / size)
-
- return results
+ return averages
```
-java:
-
-```java
+#### Java:
+```java
// 637. 二叉树的层平均值
public class N0637 {
@@ -1165,7 +1393,7 @@ public class N0637 {
}
```
-go:
+#### Go:
```GO
/**
@@ -1203,34 +1431,63 @@ func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
}
```
-javascript代码:
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
+ res := make([]float64, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ sum := 0
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ sum += node.Val
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ res = append(res, float64(sum)/float64(size))
+ }
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
```javascript
var averageOfLevels = function(root) {
- //层级平均值
- let res = [], queue = [];
- queue.push(root);
-
- while(queue.length && root!==null) {
- //每一层节点个数
- let length = queue.length;
- //sum记录每一层的和
- let sum = 0;
- for(let i=0; i < length; i++) {
- let node = queue.shift();
- sum += node.val;
- node.left && queue.push(node.left);
- node.right && queue.push(node.right);
- }
- //每一层的平均值存入数组res
- res.push(sum/length);
- }
-
- return res;
+ let res = [],
+ queue = [];
+ queue.push(root);
+ while (queue.length) {
+ // 每一层节点个数;
+ let lengthLevel = queue.length,
+ len = queue.length,
+ // sum记录每一层的和;
+ sum = 0;
+ while (lengthLevel--) {
+ const node = queue.shift();
+ sum += node.val;
+ // 队列存放下一层节点
+ node.left && queue.push(node.left);
+ node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+ }
+ // 求平均值
+ res.push(sum / len);
+ }
+ return res;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function averageOfLevels(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
@@ -1254,7 +1511,7 @@ function averageOfLevels(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func averageOfLevels(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Double] {
@@ -1280,7 +1537,9 @@ func averageOfLevels(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Double] {
return result
}
```
-Scala:
+
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 637.二叉树的层平均值
object Solution {
@@ -1305,7 +1564,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-rust:
+#### Rust:
```rust
use std::cell::RefCell;
@@ -1338,7 +1597,36 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-# 429.N叉树的层序遍历
+#### C#:
+
+```C# 二叉树的层平均值
+public class Solution {
+ public IList AverageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
+ var result= new List();
+ Queue queue = new();
+ if(root !=null) queue.Enqueue(root);
+
+ while (queue.Count > 0)
+ {
+ int count = queue.Count;
+ double value=0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
+ {
+ var curentNode=queue.Dequeue();
+ value += curentNode.val;
+ if (curentNode.left!=null) queue.Enqueue(curentNode.left);
+ if (curentNode.right!=null) queue.Enqueue(curentNode.right);
+ }
+ result.Add(value/count);
+ }
+
+ return result;
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+## 429.N叉树的层序遍历
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
@@ -1346,7 +1634,7 @@ impl Solution {
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
-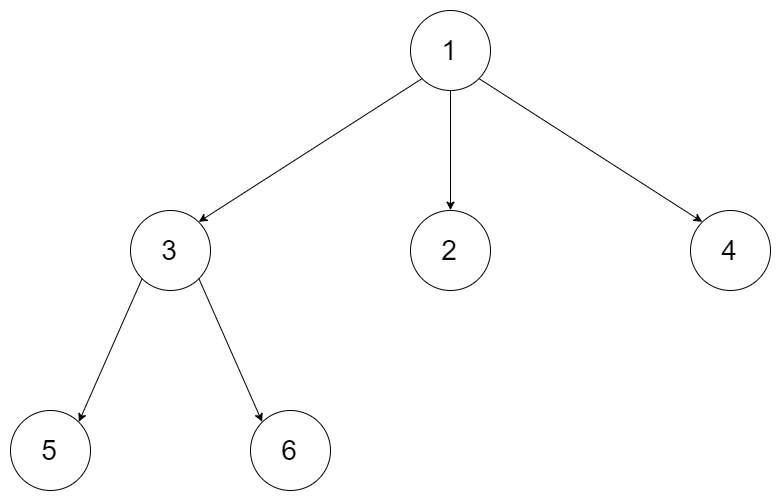
+
返回其层序遍历:
@@ -1356,8 +1644,7 @@ impl Solution {
[5,6]
]
-
-思路:
+### 思路
这道题依旧是模板题,只不过一个节点有多个孩子了
@@ -1389,31 +1676,41 @@ public:
};
```
-python代码:
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Python:
```python
-class Solution:
- """N叉树的层序遍历迭代法"""
+"""
+# Definition for a Node.
+class Node:
+ def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
+ self.val = val
+ self.children = children
+"""
+class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]:
- results = []
if not root:
- return results
-
- from collections import deque
- que = deque([root])
-
- while que:
- result = []
- for _ in range(len(que)):
- cur = que.popleft()
- result.append(cur.val)
- # cur.children 是 Node 对象组成的列表,也可能为 None
- if cur.children:
- que.extend(cur.children)
- results.append(result)
+ return []
+
+ result = []
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
+ while queue:
+ level_size = len(queue)
+ level = []
- return results
+ for _ in range(level_size):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+ level.append(node.val)
+
+ for child in node.children:
+ queue.append(child)
+
+ result.append(level)
+
+ return result
```
```python
@@ -1426,16 +1723,16 @@ class Solution:
def traversal(root,depth):
if len(result)==depth:result.append([])
result[depth].append(root.val)
- if root.children:
+ if root.children:
for i in range(len(root.children)):traversal(root.children[i],depth+1)
-
+
traversal(root,0)
- return result
+ return result
```
-java:
-```java
+#### Java:
+```java
// 429. N 叉树的层序遍历
public class N0429 {
/**
@@ -1493,8 +1790,7 @@ public class N0429 {
}
```
-
-go:
+#### Go:
```GO
/**
@@ -1520,19 +1816,45 @@ func levelOrder(root *Node) [][]int {
}
res = append(res, tmp)
}
-
+
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func levelOrder(root *Node) [][]int {
+ res := make([][]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*Node, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ level := make([]int, 0)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ level = append(level, node.Val)
+ if len(node.Children) > 0 {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Children...)
+ }
+ }
+ res = append(res, level)
+ }
return res
}
```
-JavaScript代码:
+#### JavaScript:
```JavaScript
var levelOrder = function(root) {
//每一层可能有2个以上,所以不再使用node.left node.right
let res = [], queue = [];
queue.push(root);
-
+
while(queue.length && root!==null) {
//记录每一层节点个数还是和二叉树一致
let length = queue.length;
@@ -1541,7 +1863,7 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
while(length--) {
let node = queue.shift();
curLevel.push(node.val);
-
+
//这里不再是 ndoe.left node.right 而是循坏node.children
for(let item of node.children){
item && queue.push(item);
@@ -1549,12 +1871,12 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
}
res.push(curLevel);
}
-
+
return res;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function levelOrder(root: Node | null): number[][] {
@@ -1576,7 +1898,7 @@ function levelOrder(root: Node | null): number[][] {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func levelOrder(_ root: Node?) -> [[Int]] {
@@ -1601,7 +1923,8 @@ func levelOrder(_ root: Node?) -> [[Int]] {
}
```
-Scala:
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 429.N叉树的层序遍历
object Solution {
@@ -1629,7 +1952,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-rust:
+#### Rust:
```rust
pub struct Solution;
@@ -1677,15 +2000,15 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-# 515.在每个树行中找最大值
+## 515.在每个树行中找最大值
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/)
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
-
+
-思路:
+### 思路
层序遍历,取每一层的最大值
@@ -1714,27 +2037,46 @@ public:
}
};
```
-python代码:
+
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Python:
```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
def largestValues(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
- if root is None:
+ if not root:
return []
- queue = [root]
- out_list = []
+
+ result = []
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
while queue:
- length = len(queue)
- in_list = []
- for _ in range(length):
- curnode = queue.pop(0)
- in_list.append(curnode.val)
- if curnode.left: queue.append(curnode.left)
- if curnode.right: queue.append(curnode.right)
- out_list.append(max(in_list))
- return out_list
-```
-java代码:
+ level_size = len(queue)
+ max_val = float('-inf')
+
+ for _ in range(level_size):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+ max_val = max(max_val, node.val)
+
+ if node.left:
+ queue.append(node.left)
+
+ if node.right:
+ queue.append(node.right)
+
+ result.append(max_val)
+
+ return result
+```
+
+#### Java:
```java
class Solution {
@@ -1754,13 +2096,13 @@ class Solution {
if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
result.add(max);
- }
+ }
return result;
}
}
```
-go:
+#### Go:
```GO
/**
@@ -1804,33 +2146,66 @@ func max(x, y int) int {
}
```
-javascript代码:
-
-```javascript
-var largestValues = function(root) {
- //使用层序遍历
- let res = [], queue = [];
- queue.push(root);
-
- while(root !== null && queue.length) {
- //设置max初始值就是队列的第一个元素
- let max = queue[0].val;
- let length = queue.length;
- while(length--) {
- let node = queue.shift();
- max = max > node.val ? max : node.val;
- node.left && queue.push(node.left);
- node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func largestValues(root *TreeNode) []int {
+ res := make([]int, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return res
+ }
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ maxValue := math.MinInt64
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Val > maxValue {
+ maxValue = node.Val
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
}
- //把每一层的最大值放到res数组
- res.push(max);
+ res = append(res, maxValue)
}
-
+ return res
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
+
+```javascript
+var largestValues = function (root) {
+ let res = [],
+ queue = [];
+ queue.push(root);
+ if (root === null) {
return res;
+ }
+ while (queue.length) {
+ let lengthLevel = queue.length,
+ // 初始值设为负无穷大
+ max = -Infinity;
+ while (lengthLevel--) {
+ const node = queue.shift();
+ // 在当前层中找到最大值
+ max = Math.max(max, node.val);
+ // 找到下一层的节点
+ node.left && queue.push(node.left);
+ node.right && queue.push(node.right);
+ }
+ res.push(max);
+ }
+ return res;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function largestValues(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
@@ -1856,7 +2231,7 @@ function largestValues(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func largestValues(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
@@ -1883,7 +2258,8 @@ func largestValues(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
}
```
-Scala:
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 515.在每个树行中找最大值
object Solution {
@@ -1909,7 +2285,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-rust:
+#### Rust:
```rust
use std::cell::RefCell;
@@ -1941,7 +2317,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-# 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
+## 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
@@ -1959,11 +2335,11 @@ struct Node {
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
-初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
+初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
-
+
-思路:
+### 思路
本题依然是层序遍历,只不过在单层遍历的时候记录一下本层的头部节点,然后在遍历的时候让前一个节点指向本节点就可以了
@@ -2002,72 +2378,79 @@ public:
};
```
-java代码:
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Java:
```java
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
Queue tmpQueue = new LinkedList();
if (root != null) tmpQueue.add(root);
-
+
while (tmpQueue.size() != 0){
int size = tmpQueue.size();
-
+
Node cur = tmpQueue.poll();
if (cur.left != null) tmpQueue.add(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) tmpQueue.add(cur.right);
-
+
for (int index = 1; index < size; index++){
Node next = tmpQueue.poll();
if (next.left != null) tmpQueue.add(next.left);
if (next.right != null) tmpQueue.add(next.right);
-
+
cur.next = next;
cur = next;
}
}
-
+
return root;
}
}
```
-python代码:
+#### Python:
```python
-# 层序遍历解法
+"""
+# Definition for a Node.
+class Node:
+ def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
+ self.val = val
+ self.left = left
+ self.right = right
+ self.next = next
+"""
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root:
- return None
- queue = [root]
+ return root
+
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
while queue:
- n = len(queue)
- for i in range(n):
- node = queue.pop(0)
+ level_size = len(queue)
+ prev = None
+
+ for i in range(level_size):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+
+ if prev:
+ prev.next = node
+
+ prev = node
+
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
+
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
- if i == n - 1:
- break
- node.next = queue[0]
- return root
-
-# 链表解法
-class Solution:
- def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
- first = root
- while first:
- cur = first
- while cur: # 遍历每一层的节点
- if cur.left: cur.left.next = cur.right # 找左节点的next
- if cur.right and cur.next: cur.right.next = cur.next.left # 找右节点的next
- cur = cur.next # cur同层移动到下一节点
- first = first.left # 从本层扩展到下一层
+
return root
```
-go:
+
+#### Go:
```GO
/**
@@ -2107,9 +2490,37 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
```
-JavaScript:
-```javascript
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func connect(root *Node) *Node {
+ if root == nil {
+ return root
+ }
+ queue := make([]*Node, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[i]
+ if i != size - 1 {
+ queue[i].Next = queue[i+1]
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ queue = queue[size:]
+ }
+ return root
+}
+```
+#### JavaScript:
+
+```javascript
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, left, right, next) {
@@ -2142,7 +2553,8 @@ var connect = function(root) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function connect(root: Node | null): Node | null {
@@ -2167,7 +2579,7 @@ function connect(root: Node | null): Node | null {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
@@ -2199,7 +2611,8 @@ func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
}
```
-Scala:
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
object Solution {
@@ -2228,11 +2641,12 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
-# 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
+
+## 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/)
-思路:
+### 思路
这道题目说是二叉树,但116题目说是完整二叉树,其实没有任何差别,一样的代码一样的逻辑一样的味道
@@ -2270,7 +2684,9 @@ public:
};
```
-Java 代码:
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Java:
```java
// 二叉树之层次遍历
@@ -2284,7 +2700,7 @@ class Solution {
int size = queue.size();
Node node = null;
Node nodePre = null;
-
+
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
nodePre = queue.poll(); // 取出本层头一个节点
@@ -2307,29 +2723,51 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
-python代码:
+
+#### Python:
```python
# 层序遍历解法
+"""
+# Definition for a Node.
+class Node:
+ def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
+ self.val = val
+ self.left = left
+ self.right = right
+ self.next = next
+"""
+
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root:
- return None
- queue = [root]
- while queue: # 遍历每一层
- length = len(queue)
- tail = None # 每一层维护一个尾节点
- for i in range(length): # 遍历当前层
- curnode = queue.pop(0)
- if tail:
- tail.next = curnode # 让尾节点指向当前节点
- tail = curnode # 让当前节点成为尾节点
- if curnode.left : queue.append(curnode.left)
- if curnode.right: queue.append(curnode.right)
+ return root
+
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
+ while queue:
+ level_size = len(queue)
+ prev = None
+
+ for i in range(level_size):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+
+ if prev:
+ prev.next = node
+
+ prev = node
+
+ if node.left:
+ queue.append(node.left)
+
+ if node.right:
+ queue.append(node.right)
+
return root
```
-go:
+
+#### Go:
```GO
/**
@@ -2368,7 +2806,36 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
}
```
-JavaScript:
+```GO
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func connect(root *Node) *Node {
+ if root == nil {
+ return root
+ }
+ queue := make([]*Node, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[i]
+ if i != size - 1 {
+ queue[i].Next = queue[i+1]
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ queue = queue[size:]
+ }
+ return root
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
@@ -2401,7 +2868,8 @@ var connect = function(root) {
return root;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function connect(root: Node | null): Node | null {
@@ -2426,7 +2894,7 @@ function connect(root: Node | null): Node | null {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
@@ -2458,7 +2926,8 @@ func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
}
```
-Scala:
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
object Solution {
@@ -2487,7 +2956,8 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
-# 104.二叉树的最大深度
+
+## 104.二叉树的最大深度
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
@@ -2501,17 +2971,17 @@ object Solution {
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
-
+
返回它的最大深度 3 。
-思路:
+### 思路
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
-
+
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
@@ -2540,7 +3010,10 @@ public:
};
```
-Java:
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Java:
+
```Java
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
@@ -2565,29 +3038,37 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+#### Python:
+
```python 3
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
- if root == None:
+ if not root:
return 0
- queue_ = [root]
depth = 0
- while queue_:
- length = len(queue_)
- for i in range(length):
- cur = queue_.pop(0)
- sub.append(cur.val)
- #子节点入队列
- if cur.left: queue_.append(cur.left)
- if cur.right: queue_.append(cur.right)
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
+ while queue:
depth += 1
-
+ for _ in range(len(queue)):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+ if node.left:
+ queue.append(node.left)
+ if node.right:
+ queue.append(node.right)
+
return depth
+
```
-Go:
+#### Go:
```go
/**
@@ -2622,7 +3103,35 @@ func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
}
```
-JavaScript:
+```go
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
+ if root == nil {
+ return 0
+ }
+ depth := 0
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ }
+ depth++
+ }
+ return depth
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -2636,25 +3145,27 @@ JavaScript:
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
-var maxDepth = function(root) {
- // 最大的深度就是二叉树的层数
- if (root === null) return 0;
- let queue = [root];
- let height = 0;
- while (queue.length) {
- let n = queue.length;
- height++;
- for (let i=0; i Int {
@@ -2699,7 +3210,8 @@ func maxDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
}
```
-Scala:
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 104.二叉树的最大深度
object Solution {
@@ -2723,7 +3235,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-rust:
+#### Rust:
```rust
use std::cell::RefCell;
@@ -2753,10 +3265,12 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-# 111.二叉树的最小深度
+## 111.二叉树的最小深度
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
+### 思路
+
相对于 104.二叉树的最大深度 ,本题还也可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
**需要注意的是,只有当左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了。如果其中一个孩子为空则不是最低点**
@@ -2789,7 +3303,10 @@ public:
};
```
-Java:
+### 其他语言版本
+
+#### Java:
+
```java
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root){
@@ -2818,9 +3335,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-
-
-Python 3:
+#### Python:
```python 3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -2831,26 +3346,29 @@ Python 3:
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
- if root == None:
+ if not root:
return 0
-
- #根节点的深度为1
- queue_ = [(root,1)]
- while queue_:
- cur, depth = queue_.pop(0)
+ depth = 0
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
+ while queue:
+ depth += 1
+ for _ in range(len(queue)):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+
+ if not node.left and not node.right:
+ return depth
- if cur.left == None and cur.right == None:
- return depth
- #先左子节点,由于左子节点没有孩子,则就是这一层了
- if cur.left:
- queue_.append((cur.left,depth + 1))
- if cur.right:
- queue_.append((cur.right,depth + 1))
+ if node.left:
+ queue.append(node.left)
+
+ if node.right:
+ queue.append(node.right)
- return 0
+ return depth
```
-Go:
+#### Go:
```go
/**
@@ -2884,12 +3402,43 @@ func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
}
ans++//记录层数
}
-
- return ans+1
+
+ return ans
}
```
-JavaScript:
+```go
+// 使用切片作为队列
+func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
+ if root == nil {
+ return 0
+ }
+ depth := 0
+ queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ queue = append(queue, root)
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ size := len(queue)
+ depth++
+ for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
+ node := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Left)
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ queue = append(queue, node.Right)
+ }
+ if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil {
+ return depth
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return depth
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -2924,7 +3473,7 @@ var minDepth = function(root) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+#### TypeScript:
```typescript
function minDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
@@ -2945,7 +3494,7 @@ function minDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
};
```
-Swift:
+#### Swift:
```swift
func minDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
@@ -2971,7 +3520,8 @@ func minDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
}
```
-Scala:
+#### Scala:
+
```scala
// 111.二叉树的最小深度
object Solution {
@@ -2996,7 +3546,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-rust:
+#### Rust:
```rust
use std::cell::RefCell;
@@ -3029,28 +3579,23 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-# 总结
+## 总结
二叉树的层序遍历,**就是图论中的广度优先搜索在二叉树中的应用**,需要借助队列来实现(此时又发现队列的一个应用了)。
来吧,一口气打十个:
-* 102.二叉树的层序遍历
-* 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
-* 199.二叉树的右视图
-* 637.二叉树的层平均值
-* 429.N叉树的层序遍历
-* 515.在每个树行中找最大值
-* 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
-* 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
-* 104.二叉树的最大深度
-* 111.二叉树的最小深度
+* [102.二叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
+* [107.二叉树的层次遍历II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/)
+* [199.二叉树的右视图](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
+* [637.二叉树的层平均值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
+* [429.N叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
+* [515.在每个树行中找最大值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/)
+* [116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/)
+* [117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/)
+* [104.二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
+* [111.二叉树的最小深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
**致敬叶师傅!**
-
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e54221db8c..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e54221db8c..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
# 104.二叉树的最大深度
@@ -18,26 +17,29 @@
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
-
+
+
返回它的最大深度 3 。
-# 思路
+## 算法公开课
-看完本篇可以一起做了如下两道题目:
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[二叉树的高度和深度有啥区别?究竟用什么遍历顺序?很多录友搞不懂 | 104.二叉树的最大深度](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Gd4y1V75u),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+## 思路
-* 104.二叉树的最大深度
-* 559.n叉树的最大深度
+看完本篇可以一起做了如下两道题目:
-《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[二叉树的高度和深度有啥区别?究竟用什么遍历顺序?很多录友搞不懂 | 104.二叉树的最大深度](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Gd4y1V75u),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
+* [104.二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
+* [559.n叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/)
-## 递归法
+### 递归法
本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
* 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
-* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数后者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
+* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
**而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度**,所以本题中我们通过后序求的根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
@@ -49,7 +51,7 @@
代码如下:
```CPP
-int getdepth(treenode* node)
+int getdepth(TreeNode* node)
```
2. 确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
@@ -73,16 +75,16 @@ return depth;
所以整体c++代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
- int getdepth(treenode* node) {
+ int getdepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
}
- int maxdepth(treenode* root) {
+ int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};
@@ -90,11 +92,11 @@ public:
代码精简之后c++代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
- int maxdepth(treenode* root) {
+ int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
- return 1 + max(maxdepth(root->left), maxdepth(root->right));
+ return 1 + max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right));
}
};
@@ -106,10 +108,10 @@ public:
本题当然也可以使用前序,代码如下:(**充分表现出求深度回溯的过程**)
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int result;
- void getdepth(treenode* node, int depth) {
+ void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
@@ -126,7 +128,7 @@ public:
}
return ;
}
- int maxdepth(treenode* root) {
+ int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == NULL) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
@@ -140,10 +142,10 @@ public:
注意以上代码是为了把细节体现出来,简化一下代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
int result;
- void getdepth(treenode* node, int depth) {
+ void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
@@ -154,7 +156,7 @@ public:
}
return ;
}
- int maxdepth(treenode* root) {
+ int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == 0) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
@@ -163,13 +165,14 @@ public:
};
```
-## 迭代法
+### 迭代法
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
-
+
+
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
@@ -178,18 +181,18 @@ public:
c++代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
- int maxdepth(treenode* root) {
+ int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
- queue que;
+ queue que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
- treenode* node = que.front();
+ TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
@@ -200,10 +203,11 @@ public:
};
```
-
那么我们可以顺便解决一下n叉树的最大深度问题
-# 559.n叉树的最大深度
+## 相关题目推荐
+
+### 559.n叉树的最大深度
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/)
@@ -213,47 +217,47 @@ public:
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
-
+
我们应返回其最大深度,3。
-思路:
+### 思路
依然可以提供递归法和迭代法,来解决这个问题,思路是和二叉树思路一样的,直接给出代码如下:
-## 递归法
+#### 递归法
c++代码:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
- int maxdepth(node* root) {
+ int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == 0) return 0;
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
- depth = max (depth, maxdepth(root->children[i]));
+ depth = max (depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return depth + 1;
}
};
```
-## 迭代法
+#### 迭代法
依然是层序遍历,代码如下:
```CPP
-class solution {
+class Solution {
public:
- int maxdepth(node* root) {
- queue que;
+ int maxDepth(Node* root) {
+ queue que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
- node* node = que.front();
+ Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < node->children.size(); j++) {
if (node->children[j]) que.push(node->children[j]);
@@ -265,14 +269,14 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## java
+### Java:
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
+104.二叉树的最大深度
```java
-class solution {
+class Solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
@@ -313,7 +317,7 @@ class Solution {
```
```java
-class solution {
+class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
*/
@@ -342,7 +346,8 @@ class solution {
}
```
-### 559.n叉树的最大深度
+559.n叉树的最大深度
+
```java
class Solution {
/*递归法,后序遍历求root节点的高度*/
@@ -362,7 +367,7 @@ class Solution {
```
```java
-class solution {
+class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
*/
@@ -389,13 +394,13 @@ class solution {
}
```
-## python
+### Python :
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
+104.二叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```python
-class solution:
+class Solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
return self.getdepth(root)
@@ -410,98 +415,120 @@ class solution:
递归法:精简代码
```python
-class solution:
+class Solution:
def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
return 1 + max(self.maxdepth(root.left), self.maxdepth(root.right))
```
-迭代法:
+层序遍历迭代法:
```python
-import collections
-class solution:
- def maxdepth(self, root: treenode) -> int:
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
+ def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
- depth = 0 #记录深度
- queue = collections.deque()
- queue.append(root)
+
+ depth = 0
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
while queue:
- size = len(queue)
depth += 1
- for i in range(size):
+ for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
+
return depth
+
```
-### 559.n叉树的最大深度
+559.n叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```python
-class solution:
- def maxdepth(self, root: 'node') -> int:
+class Solution:
+ def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
- depth = 0
- for i in range(len(root.children)):
- depth = max(depth, self.maxdepth(root.children[i]))
- return depth + 1
+
+ max_depth = 1
+
+ for child in root.children:
+ max_depth = max(max_depth, self.maxDepth(child) + 1)
+
+ return max_depth
```
迭代法:
```python
-import collections
-class solution:
- def maxdepth(self, root: 'node') -> int:
- queue = collections.deque()
- if root:
- queue.append(root)
- depth = 0 #记录深度
+"""
+# Definition for a Node.
+class Node:
+ def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
+ self.val = val
+ self.children = children
+"""
+
+class Solution:
+ def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
+ if not root:
+ return 0
+
+ depth = 0
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
while queue:
- size = len(queue)
depth += 1
- for i in range(size):
+ for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
- for j in range(len(node.children)):
- if node.children[j]:
- queue.append(node.children[j])
+ for child in node.children:
+ queue.append(child)
+
return depth
+
```
-使用栈来模拟后序遍历依然可以
+使用栈
```python
-class solution:
- def maxdepth(self, root: 'node') -> int:
- st = []
- if root:
- st.append(root)
- depth = 0
- result = 0
- while st:
- node = st.pop()
- if node != none:
- st.append(node) #中
- st.append(none)
- depth += 1
- for i in range(len(node.children)): #处理孩子
- if node.children[i]:
- st.append(node.children[i])
-
- else:
- node = st.pop()
- depth -= 1
- result = max(result, depth)
- return result
-```
-
-
-## go
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
+"""
+# Definition for a Node.
+class Node:
+ def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
+ self.val = val
+ self.children = children
+"""
+
+class Solution:
+ def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
+ if not root:
+ return 0
+
+ max_depth = 0
+
+ stack = [(root, 1)]
+
+ while stack:
+ node, depth = stack.pop()
+ max_depth = max(max_depth, depth)
+ for child in node.children:
+ stack.append((child, depth + 1))
+
+ return max_depth
+```
+
+### Go:
+
+104.二叉树的最大深度
+
```go
/**
* definition for a binary tree node.
@@ -551,7 +578,7 @@ func maxdepth(root *treenode) int {
```
-### 559. n叉树的最大深度
+559. n叉树的最大深度
```go
func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
@@ -575,9 +602,9 @@ func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
}
```
-## javascript
+### JavaScript :
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
+104.二叉树的最大深度
```javascript
var maxdepth = function(root) {
@@ -626,7 +653,7 @@ var maxDepth = function(root) {
};
```
-### 559.n叉树的最大深度
+559.n叉树的最大深度
N叉树的最大深度 递归写法
```js
@@ -660,9 +687,9 @@ var maxDepth = function(root) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript:
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
+104.二叉树的最大深度
```typescript
// 后续遍历(自下而上)
@@ -705,37 +732,47 @@ function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
};
```
-### 559.n叉树的最大深度
+559.n叉树的最大深度
```typescript
// 后续遍历(自下而上)
-function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
- if (root === null) return 0;
- return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
-};
+function maxDepth(root: Node | null): number {
+ if (root === null) return 0
+ let depth = 0
+ for (let i = 0; i < root.children.length; i++) {
+ depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(root.children[i]))
+ }
+ return depth + 1
+}
// 前序遍历(自上而下)
-function maxDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
- function recur(node: TreeNode | null, count: number) {
- if (node === null) {
- resMax = resMax > count ? resMax : count;
- return;
+function maxDepth(root: Node | null): number {
+ if (root === null) return 0
+
+ let depth: number = 0
+ const queue: Array = []
+ queue.push(root)
+
+ while (queue.length > 0) {
+ let len = queue.length
+ depth++
+ for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
+ // 当前层遍历
+ let curNode: Node | null = queue.shift()!
+ for (let j = 0; j < curNode.children.length; j++) {
+ if (curNode.children[j]) queue.push(curNode.children[j])
+ }
}
- recur(node.left, count + 1);
- recur(node.right, count + 1);
}
- let resMax: number = 0;
- let count: number = 0;
- recur(root, count);
- return resMax;
-};
+ return depth
+}
```
-## C
+### C:
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
+104.二叉树的最大深度
二叉树最大深度递归
```c
@@ -790,10 +827,45 @@ int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
return depth;
}
```
+二叉树最大深度迭代——后序遍历实现
+```c
+int maxDepth(struct TreeNode *root)
+{
+ if(root == NULL)
+ return 0;
+ struct TreeNode *stack[10000] = {};
+ int top = -1;
+ struct TreeNode *p = root, *r = NULL; // r指向上一个被访问的结点
+ int depth = 0, maxDepth = -1;
+ while(p != NULL || top >= 0)
+ {
+ if(p != NULL)
+ {
+ stack[++top] = p;
+ depth++;
+ p = p->left;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ p = stack[top];
+ if(p->right != NULL && p->right != r) // 右子树未被访问
+ p = p->right;
+ else
+ {
+ if(depth >= maxDepth) maxDepth = depth;
+ p = stack[top--];
+ depth--;
+ r = p;
+ p = NULL;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return maxDepth;
+}
+```
+### Swift:
-## Swift
-
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
+104.二叉树的最大深度
```swift
// 递归 - 后序
@@ -833,7 +905,7 @@ func maxDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
}
```
-### 559.n叉树的最大深度
+559.n叉树的最大深度
```swift
// 递归
@@ -870,9 +942,10 @@ func maxDepth1(_ root: Node?) -> Int {
}
```
-## Scala
+### Scala:
+
+104.二叉树的最大深度
-### 104.二叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```scala
object Solution {
@@ -911,7 +984,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-### 559.n叉树的最大深度
+559.n叉树的最大深度
递归法:
```scala
@@ -949,8 +1022,8 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-## rust
-### 0104.二叉树的最大深度
+### Rust:
+0104.二叉树的最大深度
递归:
```rust
@@ -992,8 +1065,131 @@ impl Solution {
max_depth
}
```
+### C#
+
+0104.二叉树的最大深度
+
+```csharp
+// 递归法
+public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root) {
+ if(root == null) return 0;
+
+ int leftDepth = MaxDepth(root.left);
+ int rightDepth = MaxDepth(root.right);
+
+ return 1 + Math.Max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
+}
+```
+```csharp
+// 前序遍历
+int result = 0;
+public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root)
+{
+ if (root == null) return result;
+ GetDepth(root, 1);
+ return result;
+}
+public void GetDepth(TreeNode root, int depth)
+{
+ result = depth > result ? depth : result;
+ if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return;
+
+ if (root.left != null)
+ GetDepth(root.left, depth + 1);
+ if (root.right != null)
+ GetDepth(root.right, depth + 1);
+ return;
+}
+```
+```csharp
+// 迭代法
+public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root)
+{
+ int depth = 0;
+ Queue que = new();
+ if (root == null) return depth;
+ que.Enqueue(root);
+ while (que.Count != 0)
+ {
+ int size = que.Count;
+ depth++;
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
+ {
+ var node = que.Dequeue();
+ if (node.left != null) que.Enqueue(node.left);
+ if (node.right != null) que.Enqueue(node.right);
+ }
+ }
+ return depth;
+}
+```
+
+559.n叉树的最大深度
+递归法
+```csharp
+ /*
+ 递归法
+ */
+ public class Solution {
+ public int MaxDepth(Node root) {
+ int res = 0;
+ /* 终止条件 */
+ if(root == null){
+ return 0;
+ }
+
+ /* logic */
+ // 遍历当前节点的子节点
+ for (int i = 0; i < root.children.Count; i++)
+ {
+ res = Math.Max(res, MaxDepth(root.children[i]));
+ }
+ return res + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ // @lc code=end
+```
+ 迭代法(层序遍历)
+```csharp
+ /*
+ 迭代法
+ */
+ public class Solution
+ {
+ public int MaxDepth(Node root)
+ {
+ Queue que = new Queue(); // 使用泛型队列存储节点
+
+ int res = 0;
+
+ if(root != null){
+ que.Enqueue(root); // 将根节点加入队列
+ }
+ while (que.Count > 0)
+ {
+ int size = que.Count; // 获取当前层的节点数
+ res++; // 深度加一
+
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
+ {
+ // 每一层的遍历
+
+ var curNode = que.Dequeue(); // 取出队列中的节点
+ for (int j = 0; j < curNode.children.Count; j++)
+ {
+ if (curNode.children[j] != null)
+ {
+ que.Enqueue(curNode.children[j]); // 将子节点加入队列
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return res; // 返回树的最大深度
+
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9c563619da..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9c563619da..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
看完本文,可以一起解决如下两道题目
@@ -21,15 +21,15 @@
例如,给出
-* 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
+* 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
* 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
-返回如下的二叉树:
+ 返回如下的二叉树:
-
+
-# 视频讲解
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[坑很多!来看看你掉过几次坑 | LeetCode:106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vW4y1i7dn),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[坑很多!来看看你掉过几次坑 | LeetCode:106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vW4y1i7dn),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@
流程如图:
-
+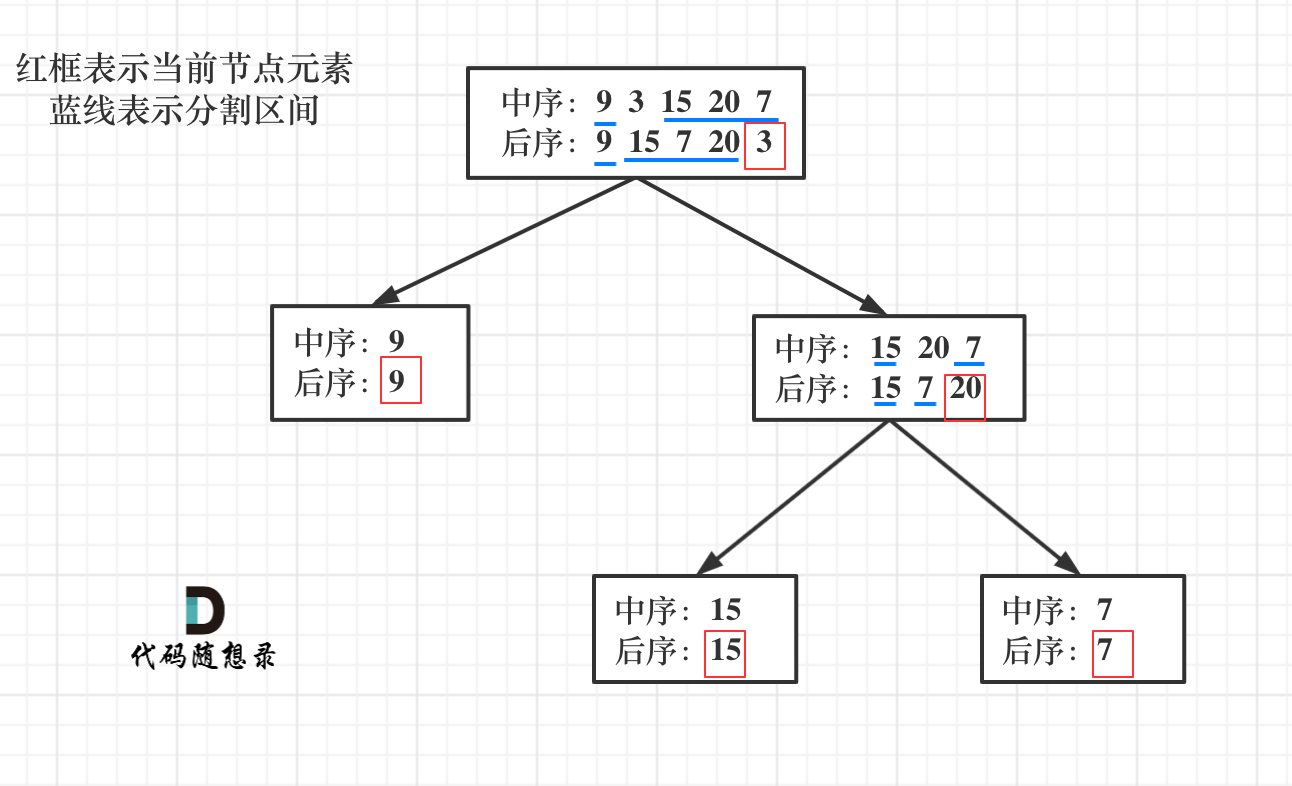
那么代码应该怎么写呢?
@@ -156,8 +156,6 @@ root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);
完整代码如下:
-### C++完整代码
-
```CPP
class Solution {
private:
@@ -279,7 +277,6 @@ public:
下面给出用下标索引写出的代码版本:(思路是一样的,只不过不用重复定义vector了,每次用下标索引来分割)
-### C++优化版本
```CPP
class Solution {
private:
@@ -397,10 +394,9 @@ public:
};
```
-## Python
+## 相关题目推荐
-
-# 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
+### 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/)
@@ -411,13 +407,13 @@ public:
例如,给出
-前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
+前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
返回如下的二叉树:
-
+
-## 思路
+### 思路
本题和106是一样的道理。
@@ -546,7 +542,7 @@ public:
};
```
-# 思考题
+## 思考题
前序和中序可以唯一确定一棵二叉树。
@@ -558,7 +554,7 @@ public:
举一个例子:
-
+
tree1 的前序遍历是[1 2 3], 后序遍历是[3 2 1]。
@@ -568,7 +564,7 @@ tree2 的前序遍历是[1 2 3], 后序遍历是[3 2 1]。
所以前序和后序不能唯一确定一棵二叉树!
-# 总结
+## 总结
之前我们讲的二叉树题目都是各种遍历二叉树,这次开始构造二叉树了,思路其实比较简单,但是真正代码实现出来并不容易。
@@ -584,9 +580,9 @@ tree2 的前序遍历是[1 2 3], 后序遍历是[3 2 1]。
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -601,7 +597,7 @@ class Solution {
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder,0, postorder.length); // 前闭后开
}
-
+
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
@@ -619,7 +615,42 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
+ if(postorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0)
+ return null;
+ return buildHelper(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
+
+ }
+ private TreeNode buildHelper(int[] inorder, int inorderStart, int inorderEnd, int[] postorder, int postorderStart, int postorderEnd){
+ if(postorderStart == postorderEnd)
+ return null;
+ int rootVal = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];
+ TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
+ int middleIndex;
+ for (middleIndex = inorderStart; middleIndex < inorderEnd; middleIndex++){
+ if(inorder[middleIndex] == rootVal)
+ break;
+ }
+ int leftInorderStart = inorderStart;
+ int leftInorderEnd = middleIndex;
+ int rightInorderStart = middleIndex + 1;
+ int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;
+
+
+ int leftPostorderStart = postorderStart;
+ int leftPostorderEnd = postorderStart + (middleIndex - inorderStart);
+ int rightPostorderStart = leftPostorderEnd;
+ int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1;
+ root.left = buildHelper(inorder, leftInorderStart, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderStart, leftPostorderEnd);
+ root.right = buildHelper(inorder, rightInorderStart, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderStart, rightPostorderEnd);
+
+ return root;
+ }
+}
+```
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
```java
@@ -642,7 +673,7 @@ class Solution {
int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]); // 找到前序遍历的第一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定前序数列的个数
- root.left = findNode(preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1,
+ root.left = findNode(preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1,
inorder, inBegin, rootIndex);
root.right = findNode(preorder, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1, preEnd,
inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);
@@ -652,38 +683,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
-```python
-class Solution:
- def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
- # 第一步: 特殊情况讨论: 树为空. 或者说是递归终止条件
- if not postorder:
- return
-
- # 第二步: 后序遍历的最后一个就是当前的中间节点
- root_val = postorder[-1]
- root = TreeNode(root_val)
-
- # 第三步: 找切割点.
- root_index = inorder.index(root_val)
-
- # 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
- left_inorder = inorder[:root_index]
- right_inorder = inorder[root_index + 1:]
-
- # 第五步: 切割postorder数组. 得到postorder数组的左,右半边.
- # ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟后序数组大小是相同的.
- left_postorder = postorder[:len(left_inorder)]
- right_postorder = postorder[len(left_inorder): len(postorder) - 1]
-
-
- # 第六步: 递归
- root.left = self.buildTree(left_inorder, left_postorder)
- root.right = self.buildTree(right_inorder, right_postorder)
-
- # 第七步: 返回答案
- return root
-```
+### Python
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -691,29 +691,29 @@ class Solution:
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
# 第一步: 特殊情况讨论: 树为空. 或者说是递归终止条件
- if not preorder:
+ if not preorder:
return None
- # 第二步: 前序遍历的第一个就是当前的中间节点.
+ # 第二步: 前序遍历的第一个就是当前的中间节点.
root_val = preorder[0]
root = TreeNode(root_val)
- # 第三步: 找切割点.
+ # 第三步: 找切割点.
separator_idx = inorder.index(root_val)
- # 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
+ # 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
inorder_left = inorder[:separator_idx]
inorder_right = inorder[separator_idx + 1:]
# 第五步: 切割preorder数组. 得到preorder数组的左,右半边.
- # ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟前序数组大小是相同的.
+ # ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟前序数组大小是相同的.
preorder_left = preorder[1:1 + len(inorder_left)]
preorder_right = preorder[1 + len(inorder_left):]
# 第六步: 递归
root.left = self.buildTree(preorder_left, inorder_left)
root.right = self.buildTree(preorder_right, inorder_right)
-
+ # 第七步: 返回答案
return root
```
@@ -723,33 +723,33 @@ class Solution:
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
# 第一步: 特殊情况讨论: 树为空. (递归终止条件)
- if not postorder:
+ if not postorder:
return None
- # 第二步: 后序遍历的最后一个就是当前的中间节点.
+ # 第二步: 后序遍历的最后一个就是当前的中间节点.
root_val = postorder[-1]
root = TreeNode(root_val)
- # 第三步: 找切割点.
+ # 第三步: 找切割点.
separator_idx = inorder.index(root_val)
- # 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
+ # 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
inorder_left = inorder[:separator_idx]
inorder_right = inorder[separator_idx + 1:]
# 第五步: 切割postorder数组. 得到postorder数组的左,右半边.
- # ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟后序数组大小是相同的.
+ # ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟后序数组大小是相同的.
postorder_left = postorder[:len(inorder_left)]
postorder_right = postorder[len(inorder_left): len(postorder) - 1]
# 第六步: 递归
root.left = self.buildTree(inorder_left, postorder_left)
root.right = self.buildTree(inorder_right, postorder_right)
-
- return root
+ # 第七步: 返回答案
+ return root
```
-## Go
+### Go
106 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -786,12 +786,66 @@ func rebuild(inorder []int, postorder []int, rootIdx int, l, r int) *TreeNode {
rootIn := hash[rootV] // 找到根节点在对应的中序数组中的位置
root := &TreeNode{Val : rootV} // 构造根节点
// 重建左节点和右节点
- root.Left = rebuild(inorder, postorder, rootIdx-(r-rootIn)-1, l, rootIn-1)
+ root.Left = rebuild(inorder, postorder, rootIdx-(r-rootIn)-1, l, rootIn-1)
root.Right = rebuild(inorder, postorder, rootIdx-1, rootIn+1, r)
return root
}
```
+```go
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
+func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
+ if len(postorder) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // 后序遍历数组最后一个元素,就是当前的中间节点
+ rootValue := postorder[len(postorder)-1]
+ root := &TreeNode{Val:rootValue}
+
+ // 叶子结点
+ if len(postorder) == 1 {
+ return root
+ }
+
+ // 找到中序遍历的切割点
+ var delimiterIndex int
+ for delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < len(inorder); delimiterIndex++ {
+ if inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue {
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 切割中序数组
+ // 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)
+ leftInorder := inorder[:delimiterIndex]
+ // [delimiterIndex + 1, end)
+ rightInorder := inorder[delimiterIndex+1:]
+
+ // postorder 舍弃末尾元素
+ postorder = postorder[:len(postorder)-1]
+
+ // 切割后序数组
+ // 依然左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点
+ // [0, len(leftInorder))
+ leftPostorder := postorder[:len(leftInorder)]
+ // [len(leftInorder), end)
+ rightPostorder := postorder[len(leftInorder):]
+
+ root.Left = buildTree(leftInorder, leftPostorder)
+ root.Right = buildTree(rightInorder, rightPostorder)
+
+ return root
+}
+```
+
105 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
```go
@@ -827,10 +881,62 @@ func build(pre []int, in []int, root int, l, r int) *TreeNode {
}
```
+```go
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
+func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
+ if len(preorder) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // 前序遍历数组第一个元素,就是当前的中间节点
+ rootValue := preorder[0]
+ root := &TreeNode{Val:rootValue}
+
+ // 叶子结点
+ if len(preorder) == 1 {
+ return root
+ }
+
+ // 找到中序遍历的切割点
+ var delimiterIndex int
+ for delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < len(inorder); delimiterIndex++ {
+ if inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ // 切割中序数组
+ // 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)
+ leftInorder := inorder[:delimiterIndex]
+ // [delimiterIndex + 1, end)
+ rightInorder := inorder[delimiterIndex+1:]
+
+ // preorder 舍弃首位元素
+ preorder = preorder[1:]
+
+ // 切割前序数组
+ // 依然左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点
+ // [0, len(leftInorder))
+ leftPreorder := preorder[:len(leftInorder)]
+ // [len(leftInorder), end)
+ rightPreorder := preorder[len(leftInorder):]
+
+ root.Left = buildTree(leftPreorder, leftInorder)
+ root.Right = buildTree(rightPreorder, rightInorder)
+
+ return root
+}
+```
-
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
@@ -858,7 +964,7 @@ var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
> 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -964,7 +1070,7 @@ function buildTree(preorder: number[], inorder: number[]): TreeNode | null {
};
```
-## C
+### C
106 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -1031,7 +1137,7 @@ struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* preorder, int preorderSize, int* inorder, int in
// 4.根据中序遍历数组左右数组的各子大小切割前序遍历数组。也分为左右数组
int* leftPreorder = preorder+1;
- int* rightPreorder = preorder + 1 + leftNum;
+ int* rightPreorder = preorder + 1 + leftNum;
// 5.递归进入左右数组,将返回的结果作为根结点的左右孩子
root->left = buildTree(leftPreorder, leftNum, leftInorder, leftNum);
@@ -1042,7 +1148,7 @@ struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* preorder, int preorderSize, int* inorder, int in
}
```
-## Swift
+### Swift
105 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -1056,26 +1162,26 @@ class Solution {
inorderBegin: 0,
inorderEnd: inorder.count)
}
-
+
func helper(preorder: [Int], preorderBegin: Int, preorderEnd: Int, inorder: [Int], inorderBegin: Int, inorderEnd: Int) -> TreeNode? {
if preorderBegin == preorderEnd {
return nil
}
-
+
// 前序遍历数组的第一个元素作为分割点
let rootValue = preorder[preorderBegin]
let root = TreeNode(rootValue)
-
-
+
+
if preorderEnd - preorderBegin == 1 {
return root
}
-
+
var index = 0 // 从中序遍历数组中找到根节点的下标
if let ind = inorder.firstIndex(of: rootValue) {
index = ind
}
-
+
// 递归
root.left = helper(preorder: preorder,
preorderBegin: preorderBegin + 1,
@@ -1102,28 +1208,28 @@ class Solution_0106 {
if postorderEnd - postorderBegin < 1 {
return nil
}
-
+
// 后序遍历数组的最后一个元素作为分割点
let rootValue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1]
let root = TreeNode(rootValue)
-
+
if postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1 {
return root
}
-
+
// 从中序遍历数组中找到根节点的下标
var delimiterIndex = 0
if let index = inorder.firstIndex(of: rootValue) {
delimiterIndex = index
}
-
+
root.left = buildTree(inorder: inorder,
inorderBegin: inorderBegin,
inorderEnd: delimiterIndex,
postorder: postorder,
postorderBegin: postorderBegin,
postorderEnd: postorderBegin + (delimiterIndex - inorderBegin))
-
+
root.right = buildTree(inorder: inorder,
inorderBegin: delimiterIndex + 1,
inorderEnd: inorderEnd,
@@ -1135,7 +1241,7 @@ class Solution_0106 {
}
```
-## Scala
+### Scala
106 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -1183,7 +1289,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-## rust
+### Rust
106 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
@@ -1228,8 +1334,18 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public TreeNode BuildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder)
+{
+ if (inorder.Length == 0 || postorder.Length == null) return null;
+ int rootValue = postorder.Last();
+ TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
+ int delimiterIndex = Array.IndexOf(inorder, rootValue);
+ root.left = BuildTree(inorder.Take(delimiterIndex).ToArray(), postorder.Take(delimiterIndex).ToArray());
+ root.right = BuildTree(inorder.Skip(delimiterIndex + 1).ToArray(), postorder.Skip(delimiterIndex).Take(inorder.Length - delimiterIndex - 1).ToArray());
+ return root;
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f0455a834f..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f0455a834f..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 构造二叉搜索树,一不小心就平衡了
@@ -17,13 +15,14 @@
示例:
-
-# 算法公开课
+
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[构造平衡二叉搜索树!| LeetCode:108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1uR4y1X7qL?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+## 算法公开课
-# 思路
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[构造平衡二叉搜索树!| LeetCode:108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1uR4y1X7qL?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+## 思路
做这道题目之前大家可以了解一下这几道:
@@ -37,11 +36,11 @@
题目中说要转换为一棵高度平衡二叉搜索树。为什么强调要平衡呢?
-因为只要给我们一个有序数组,如果强调平衡,都可以以线性结构来构造二叉搜索树。
+因为只要给我们一个有序数组,如果不强调平衡,都可以以线性结构来构造二叉搜索树。
例如 有序数组[-10,-3,0,5,9] 就可以构造成这样的二叉搜索树,如图。
-
+
上图中,是符合二叉搜索树的特性吧,如果要这么做的话,是不是本题意义就不大了,所以才强调是平衡二叉搜索树。
@@ -64,13 +63,13 @@
如下两棵树,都是这个数组的平衡二叉搜索树:
-
+
如果要分割的数组长度为偶数的时候,中间元素为两个,是取左边元素 就是树1,取右边元素就是树2。
**这也是题目中强调答案不是唯一的原因。 理解这一点,这道题目算是理解到位了**。
-## 递归
+### 递归
递归三部曲:
@@ -154,7 +153,7 @@ public:
**注意:在调用traversal的时候传入的left和right为什么是0和nums.size() - 1,因为定义的区间为左闭右闭**。
-## 迭代法
+### 迭代法
迭代法可以通过三个队列来模拟,一个队列放遍历的节点,一个队列放左区间下标,一个队列放右区间下标。
@@ -202,7 +201,7 @@ public:
};
```
-# 总结
+## 总结
**在[二叉树:构造二叉树登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.html) 和 [二叉树:构造一棵最大的二叉树](https://programmercarl.com/0654.最大二叉树.html)之后,我们顺理成章的应该构造一下二叉搜索树了,一不小心还是一棵平衡二叉搜索树**。
@@ -215,10 +214,10 @@ public:
最后依然给出迭代的方法,其实就是模拟取中间元素,然后不断分割去构造二叉树的过程。
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
递归: 左闭右开 [left,right)
```Java
@@ -314,77 +313,81 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
-**递归**
-
+### Python
+递归法
```python
-# Definition for a binary tree node.
-# class TreeNode:
-# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
-# self.val = val
-# self.left = left
-# self.right = right
class Solution:
- def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
- '''
- 构造二叉树:重点是选取数组最中间元素为分割点,左侧是递归左区间;右侧是递归右区间
- 必然是平衡树
- 左闭右闭区间
- '''
- # 返回根节点
- root = self.traversal(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
- return root
-
def traversal(self, nums: List[int], left: int, right: int) -> TreeNode:
- # Base Case
if left > right:
return None
- # 确定左右界的中心,防越界
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
- # 构建根节点
- mid_root = TreeNode(nums[mid])
- # 构建以左右界的中心为分割点的左右子树
- mid_root.left = self.traversal(nums, left, mid-1)
- mid_root.right = self.traversal(nums, mid+1, right)
-
- # 返回由被传入的左右界定义的某子树的根节点
- return mid_root
-```
+ root = TreeNode(nums[mid])
+ root.left = self.traversal(nums, left, mid - 1)
+ root.right = self.traversal(nums, mid + 1, right)
+ return root
+
+ def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
+ root = self.traversal(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
+ return root
-**迭代**(左闭右开)
+```
+递归 精简(自身调用)
```python
class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
- if len(nums) == 0: return None
- root = TreeNode() # 初始化
- nodeSt = [root]
- leftSt = [0]
- rightSt = [len(nums)]
-
- while nodeSt:
- node = nodeSt.pop() # 处理根节点
- left = leftSt.pop()
- right = rightSt.pop()
- mid = left + (right - left) // 2
- node.val = nums[mid]
-
- if left < mid: # 处理左区间
- node.left = TreeNode()
- nodeSt.append(node.left)
- leftSt.append(left)
- rightSt.append(mid)
-
- if right > mid + 1: # 处理右区间
- node.right = TreeNode()
- nodeSt.append(node.right)
- leftSt.append(mid + 1)
- rightSt.append(right)
+ if not nums:
+ return
+ mid = len(nums) // 2
+ root = TreeNode(nums[mid])
+ root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:mid])
+ root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[mid + 1 :])
+ return root
+```
+
+迭代法
+```python
+from collections import deque
+
+class Solution:
+ def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
+ if len(nums) == 0:
+ return None
+ root = TreeNode(0) # 初始根节点
+ nodeQue = deque() # 放遍历的节点
+ leftQue = deque() # 保存左区间下标
+ rightQue = deque() # 保存右区间下标
+
+ nodeQue.append(root) # 根节点入队列
+ leftQue.append(0) # 0为左区间下标初始位置
+ rightQue.append(len(nums) - 1) # len(nums) - 1为右区间下标初始位置
+
+ while nodeQue:
+ curNode = nodeQue.popleft()
+ left = leftQue.popleft()
+ right = rightQue.popleft()
+ mid = left + (right - left) // 2
+
+ curNode.val = nums[mid] # 将mid对应的元素给中间节点
+
+ if left <= mid - 1: # 处理左区间
+ curNode.left = TreeNode(0)
+ nodeQue.append(curNode.left)
+ leftQue.append(left)
+ rightQue.append(mid - 1)
+
+ if right >= mid + 1: # 处理右区间
+ curNode.right = TreeNode(0)
+ nodeQue.append(curNode.right)
+ leftQue.append(mid + 1)
+ rightQue.append(right)
+
return root
+
```
-## Go
+### Go
递归(隐含回溯)
@@ -403,7 +406,7 @@ func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
递归
```javascript
@@ -460,7 +463,7 @@ var sortedArrayToBST = function(nums) {
return root;
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
```typescript
function sortedArrayToBST(nums: number[]): TreeNode | null {
@@ -476,7 +479,7 @@ function sortedArrayToBST(nums: number[]): TreeNode | null {
};
```
-## C
+### C
递归
```c
@@ -497,7 +500,7 @@ struct TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(int* nums, int numsSize) {
}
```
-## Scala
+### Scala
递归:
@@ -518,7 +521,7 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-## rust
+### Rust
递归:
@@ -537,9 +540,23 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 递归
+public TreeNode SortedArrayToBST(int[] nums)
+{
+ return Traversal(nums, 0, nums.Length - 1);
+}
+public TreeNode Traversal(int[] nums, int left, int right)
+{
+ if (left > right) return null;
+ int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
+ TreeNode node = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
+ node.left = Traversal(nums, left, mid - 1);
+ node.right = Traversal(nums, mid + 1, right);
+ return node;
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 492e25d9a5..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 492e25d9a5..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
> 求高度还是求深度,你搞懂了不?
@@ -13,13 +13,13 @@
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
-本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
+本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-
+
返回 true 。
@@ -27,12 +27,13 @@
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
-
+
返回 false 。
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[后序遍历求高度,高度判断是否平衡 | LeetCode:110.平衡二叉树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ug411S7my),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[后序遍历求高度,高度判断是否平衡 | LeetCode:110.平衡二叉树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ug411S7my),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 题外话
@@ -45,7 +46,7 @@
但leetcode中强调的深度和高度很明显是按照节点来计算的,如图:
-
+
关于根节点的深度究竟是1 还是 0,不同的地方有不一样的标准,leetcode的题目中都是以节点为一度,即根节点深度是1。但维基百科上定义用边为一度,即根节点的深度是0,我们暂时以leetcode为准(毕竟要在这上面刷题)。
@@ -125,7 +126,7 @@ public:
1. 明确递归函数的参数和返回值
-参数:当前传入节点。
+参数:当前传入节点。
返回值:以当前传入节点为根节点的树的高度。
那么如何标记左右子树是否差值大于1呢?
@@ -355,7 +356,7 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-### Java
+### Java:
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -496,9 +497,10 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-### Python
+### Python:
递归法:
+
```python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
@@ -512,7 +514,7 @@ class Solution:
return True
else:
return False
-
+
def get_height(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# Base Case
if not root:
@@ -529,8 +531,71 @@ class Solution:
else:
return 1 + max(left_height, right_height)
```
+递归法精简版:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
+ return self.get_hight(root) != -1
+ def get_hight(self, node):
+ if not node:
+ return 0
+ left = self.get_hight(node.left)
+ right = self.get_hight(node.right)
+ if left == -1 or right == -1 or abs(left - right) > 1:
+ return -1
+ return max(left, right) + 1
+```
+
迭代法:
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def getDepth(self, cur):
+ st = []
+ if cur is not None:
+ st.append(cur)
+ depth = 0
+ result = 0
+ while st:
+ node = st[-1]
+ if node is not None:
+ st.pop()
+ st.append(node) # 中
+ st.append(None)
+ depth += 1
+ if node.right:
+ st.append(node.right) # 右
+ if node.left:
+ st.append(node.left) # 左
+
+ else:
+ node = st.pop()
+ st.pop()
+ depth -= 1
+ result = max(result, depth)
+ return result
+
+ def isBalanced(self, root):
+ st = []
+ if root is None:
+ return True
+ st.append(root)
+ while st:
+ node = st.pop() # 中
+ if abs(self.getDepth(node.left) - self.getDepth(node.right)) > 1:
+ return False
+ if node.right:
+ st.append(node.right) # 右(空节点不入栈)
+ if node.left:
+ st.append(node.left) # 左(空节点不入栈)
+ return True
+
+```
+
+迭代法精简版:
+
```python
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
@@ -542,10 +607,13 @@ class Solution:
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node:
- stack.append(node)
+ stack.append(node) # 中
stack.append(None)
- if node.left: stack.append(node.left)
- if node.right: stack.append(node.right)
+ # 采用数组进行迭代,先将右节点加入,保证左节点能够先出栈
+ if node.right: # 右
+ stack.append(node.right)
+ if node.left: # 左
+ stack.append(node.left)
else:
real_node = stack.pop()
left, right = height_map.get(real_node.left, 0), height_map.get(real_node.right, 0)
@@ -554,12 +622,13 @@ class Solution:
height_map[real_node] = 1 + max(left, right)
return True
```
+### Go:
+递归法
-### Go
```Go
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
- h := getHeight(root)
+ h := getHeight(root)
if h == -1 {
return false
}
@@ -587,8 +656,68 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### JavaScript
-递归法:
+迭代法
+
+```Go
+func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
+ st := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ if root == nil {
+ return true
+ }
+ st = append(st, root)
+ for len(st) > 0 {
+ node := st[len(st)-1]
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ if math.Abs(float64(getDepth(node.Left)) - float64(getDepth(node.Right))) > 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Right)
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Left)
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+}
+
+func getDepth(cur *TreeNode) int {
+ st := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
+ if cur != nil {
+ st = append(st, cur)
+ }
+ depth := 0
+ result := 0
+ for len(st) > 0 {
+ node := st[len(st)-1]
+ if node != nil {
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ st = append(st, node, nil)
+ depth++
+ if node.Right != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Right)
+ }
+ if node.Left != nil {
+ st = append(st, node.Left)
+ }
+ } else {
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ node = st[len(st)-1]
+ st = st[:len(st)-1]
+ depth--
+ }
+ if result < depth {
+ result = depth
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript:
+
+递归法:
+
```javascript
var isBalanced = function(root) {
//还是用递归三部曲 + 后序遍历 左右中 当前左子树右子树高度相差大于1就返回-1
@@ -614,6 +743,7 @@ var isBalanced = function(root) {
```
迭代法:
+
```javascript
// 获取当前节点的高度
var getHeight = function (curNode) {
@@ -644,7 +774,7 @@ var isBalanced = function (root) {
let queue = [root];
while (queue.length) {
let node = queue[queue.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶
- queue.pop();
+ queue.pop();
if (Math.abs(getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right)) > 1) {
return false;
}
@@ -655,7 +785,7 @@ var isBalanced = function (root) {
};
```
-### TypeScript
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
// 递归法
@@ -673,9 +803,10 @@ function isBalanced(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
};
```
-### C
+### C:
递归法:
+
```c
int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
//如果结点不存在,返回0
@@ -706,6 +837,7 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
```
迭代法:
+
```c
//计算结点深度
int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
@@ -717,7 +849,7 @@ int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
stack[stackTop++] = node;
int result = 0;
int depth = 0;
-
+
//当栈中有元素时,进行迭代遍历
while(stackTop) {
//取出栈顶元素
@@ -741,7 +873,7 @@ int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
tempNode = stack[--stackTop];
depth--;
}
- }
+ }
return result;
}
@@ -750,11 +882,11 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
//开辟栈空间
struct TreeNode** stack = (struct TreeNode**)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*) * 10000);
int stackTop = 0;
-
+
//若根节点不存在,返回True
if(!root)
return 1;
-
+
//将根节点入栈
stack[stackTop++] = root;
//当栈中有元素时,进行遍历
@@ -764,7 +896,7 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
//计算左右子树的深度
int diff = getDepth(node->right) - getDepth(node->left);
//若深度的绝对值大于1,返回False
- if(diff > 1 || diff < -1)
+ if(diff > 1 || diff < -1)
return 0;
//如果栈顶结点有左右结点,将左右结点入栈
if(node->left)
@@ -780,6 +912,7 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
### Swift:
>递归
+
```swift
func isBalanced(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Bool {
// -1 已经不是平衡二叉树
@@ -805,7 +938,7 @@ func getHeight(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
}
```
-### rust
+### Rust:
递归
@@ -836,8 +969,30 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public bool IsBalanced(TreeNode root)
+{
+ return GetHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;
+}
+public int GetHeight(TreeNode root)
+{
+ if (root == null) return 0;
+ int left = GetHeight(root.left);
+ if (left == -1) return -1;
+ int right = GetHeight(root.right);
+ if (right == -1) return -1;
+ int res;
+ if (Math.Abs(left - right) > 1)
+ {
+ res = -1;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ res = 1 + Math.Max(left, right);
+ }
+ return res;
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbe7b7ecad..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbe7b7ecad..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
> 和求最大深度一个套路?
@@ -21,13 +19,16 @@
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
-
+
+
返回它的最小深度 2.
-# 思路
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[看起来好像做过,一写就错! | LeetCode:111.二叉树的最小深度](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1QD4y1B7e2),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[看起来好像做过,一写就错! | LeetCode:111.二叉树的最小深度](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1QD4y1B7e2),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
+## 思路
看完了这篇[104.二叉树的最大深度](https://programmercarl.com/0104.二叉树的最大深度.html),再来看看如何求最小深度。
@@ -37,7 +38,7 @@
本题依然是前序遍历和后序遍历都可以,前序求的是深度,后序求的是高度。
* 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
-* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数后者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
+* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
那么使用后序遍历,其实求的是根节点到叶子节点的最小距离,就是求高度的过程,不过这个最小距离 也同样是最小深度。
@@ -45,13 +46,13 @@
本题还有一个误区,在处理节点的过程中,最大深度很容易理解,最小深度就不那么好理解,如图:
-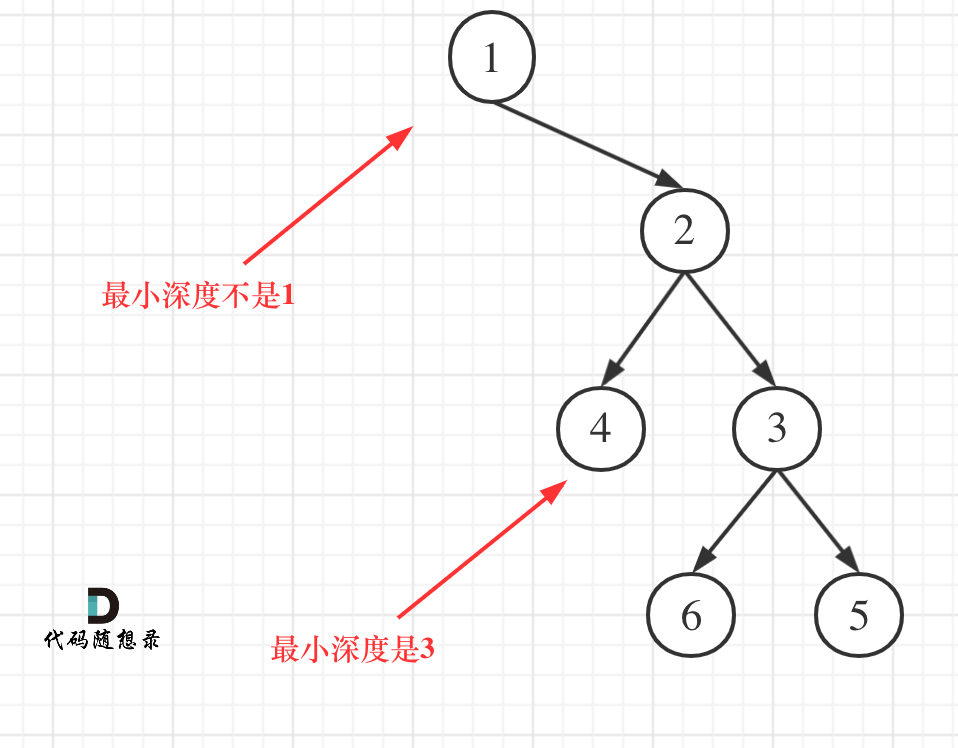
+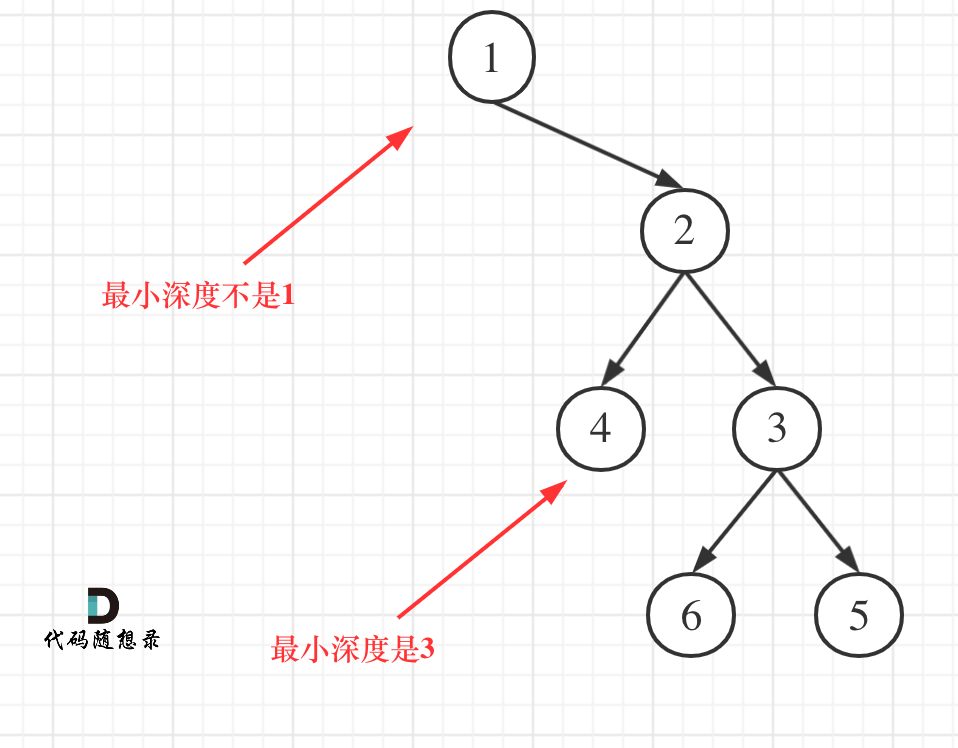
-这就重新审题了,题目中说的是:**最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。**,注意是**叶子节点**。
+这就重新审题了,题目中说的是:**最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。**注意是**叶子节点**。
什么是叶子节点,左右孩子都为空的节点才是叶子节点!
-## 递归法
+### 递归法
来来来,一起递归三部曲:
@@ -61,7 +62,7 @@
代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
```
@@ -71,14 +72,14 @@ int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
代码如下:
-```
+```CPP
if (node == NULL) return 0;
```
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
这块和求最大深度可就不一样了,一些同学可能会写如下代码:
-```
+```CPP
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right);
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
@@ -87,7 +88,7 @@ return result;
这个代码就犯了此图中的误区:
-
+
如果这么求的话,没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度。
@@ -169,11 +170,14 @@ class Solution {
private:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
- if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) {
- result = min(depth, result);
+ // 函数递归终止条件
+ if (node == nullptr) {
return;
}
- // 中 只不过中没有处理的逻辑
+ // 中,处理逻辑:判断是不是叶子结点
+ if (node -> left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) {
+ result = min(result, depth);
+ }
if (node->left) { // 左
getdepth(node->left, depth + 1);
}
@@ -185,7 +189,9 @@ private:
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
- if (root == NULL) return 0;
+ if (root == nullptr) {
+ return 0;
+ }
result = INT_MAX;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
@@ -193,7 +199,7 @@ public:
};
```
-## 迭代法
+### 迭代法
相对于[104.二叉树的最大深度](https://programmercarl.com/0104.二叉树的最大深度.html),本题还可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
@@ -231,10 +237,10 @@ public:
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java:
```Java
class Solution {
@@ -260,6 +266,34 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+```java
+class Solution {
+ /**
+ * 递归法(思路来自二叉树最大深度的递归法)
+ * 该题求最小深度,最小深度为根节点到叶子节点的深度,所以在迭代到每个叶子节点时更新最小值。
+ */
+ int depth = 0;
+ // 定义最小深度,初始化最大值
+ int minDepth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
+ dep(root);
+ return minDepth == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : minDepth;
+ }
+ void dep(TreeNode root){
+ if(root == null) return ;
+ // 递归开始,深度增加
+ depth++;
+ dep(root.left);
+ dep(root.right);
+ // 该位置表示递归到叶子节点了,需要更新最小深度minDepth
+ if(root.left == null && root.right == null)
+ minDepth = Math.min(minDepth , depth);
+ // 递归结束,深度减小
+ depth--;
+ }
+}
+```
+
```Java
class Solution {
/**
@@ -294,53 +328,107 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+### Python :
-递归法:
+递归法(版本一)
```python
class Solution:
- def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
- if not root:
+ def getDepth(self, node):
+ if node is None:
return 0
- if not root.left and not root.right:
- return 1
-
- min_depth = 10**9
- if root.left:
- min_depth = min(self.minDepth(root.left), min_depth) # 获得左子树的最小高度
- if root.right:
- min_depth = min(self.minDepth(root.right), min_depth) # 获得右子树的最小高度
- return min_depth + 1
+ leftDepth = self.getDepth(node.left) # 左
+ rightDepth = self.getDepth(node.right) # 右
+
+ # 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
+ if node.left is None and node.right is not None:
+ return 1 + rightDepth
+
+ # 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
+ if node.left is not None and node.right is None:
+ return 1 + leftDepth
+
+ result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth)
+ return result
+
+ def minDepth(self, root):
+ return self.getDepth(root)
+
```
+递归法(版本二)
-迭代法:
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def minDepth(self, root):
+ if root is None:
+ return 0
+ if root.left is None and root.right is not None:
+ return 1 + self.minDepth(root.right)
+ if root.left is not None and root.right is None:
+ return 1 + self.minDepth(root.left)
+ return 1 + min(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right))
+
+
+```
+递归法(版本三)前序
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.result = float('inf')
+
+ def getDepth(self, node, depth):
+ if node is None:
+ return
+ if node.left is None and node.right is None:
+ self.result = min(self.result, depth)
+ if node.left:
+ self.getDepth(node.left, depth + 1)
+ if node.right:
+ self.getDepth(node.right, depth + 1)
+
+ def minDepth(self, root):
+ if root is None:
+ return 0
+ self.getDepth(root, 1)
+ return self.result
+
+
+```
+迭代法
```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
- que = deque()
- que.append(root)
- res = 1
-
- while que:
- for _ in range(len(que)):
- node = que.popleft()
- # 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出
+ depth = 0
+ queue = collections.deque([root])
+
+ while queue:
+ depth += 1
+ for _ in range(len(queue)):
+ node = queue.popleft()
+
if not node.left and not node.right:
- return res
- if node.left is not None:
- que.append(node.left)
- if node.right is not None:
- que.append(node.right)
- res += 1
- return res
+ return depth
+
+ if node.left:
+ queue.append(node.left)
+
+ if node.right:
+ queue.append(node.right)
+
+ return depth
```
-
-## Go
+### Go:
```go
/**
@@ -401,7 +489,7 @@ func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript:
递归法:
@@ -447,7 +535,7 @@ var minDepth = function(root) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript:
> 递归法
@@ -485,7 +573,7 @@ function minDepth(root: TreeNode | null): number {
};
```
-## Swift
+### Swift:
> 递归
```Swift
@@ -532,7 +620,7 @@ func minDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
```
-## Scala
+### Scala:
递归法:
```scala
@@ -571,7 +659,8 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-rust:
+### Rust:
+
```rust
impl Solution {
// 递归
@@ -617,8 +706,47 @@ impl Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 递归
+public int MinDepth(TreeNode root)
+{
+ if (root == null) return 0;
+ int left = MinDepth(root.left);
+ int right = MinDepth(root.right);
+ if (root.left == null && root.right != null)
+ return 1+right;
+ else if(root.left!=null && root.right == null)
+ return 1+left;
+
+ int res = 1 + Math.Min(left, right);
+ return res;
+}
+```
+```csharp
+// 迭代
+public int MinDepth(TreeNode root)
+{
+ if (root == null) return 0;
+ int depth = 0;
+ var que = new Queue();
+ que.Enqueue(root);
+ while (que.Count > 0)
+ {
+ int size = que.Count;
+ depth++;
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
+ {
+ var node = que.Dequeue();
+ if (node.left != null)
+ que.Enqueue(node.left);
+ if (node.right != null)
+ que.Enqueue(node.right);
+ if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
+ return depth;
+ }
+ }
+ return depth;
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f0133663..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f0133663..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
+
+
# 112. 路径总和
@@ -10,18 +10,18 @@
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
-说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
+说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
-示例:
+示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
-
+
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
-## 视频讲解
+## 算法公开课
-**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[拿不准的遍历顺序,搞不清的回溯过程,我太难了! | LeetCode:112. 路径总和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19t4y1L7CR),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[拿不准的遍历顺序,搞不清的回溯过程,我太难了! | LeetCode:112. 路径总和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19t4y1L7CR),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -30,8 +30,8 @@
那么接下来我通过详细讲解如下两道题,来回答这个问题:
-* 112.路径总和
-* 113.路径总和ii
+* [112.路径总和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/)
+* [113.路径总和ii](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/)
这道题我们要遍历从根节点到叶子节点的路径看看总和是不是目标和。
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@
如图所示:
-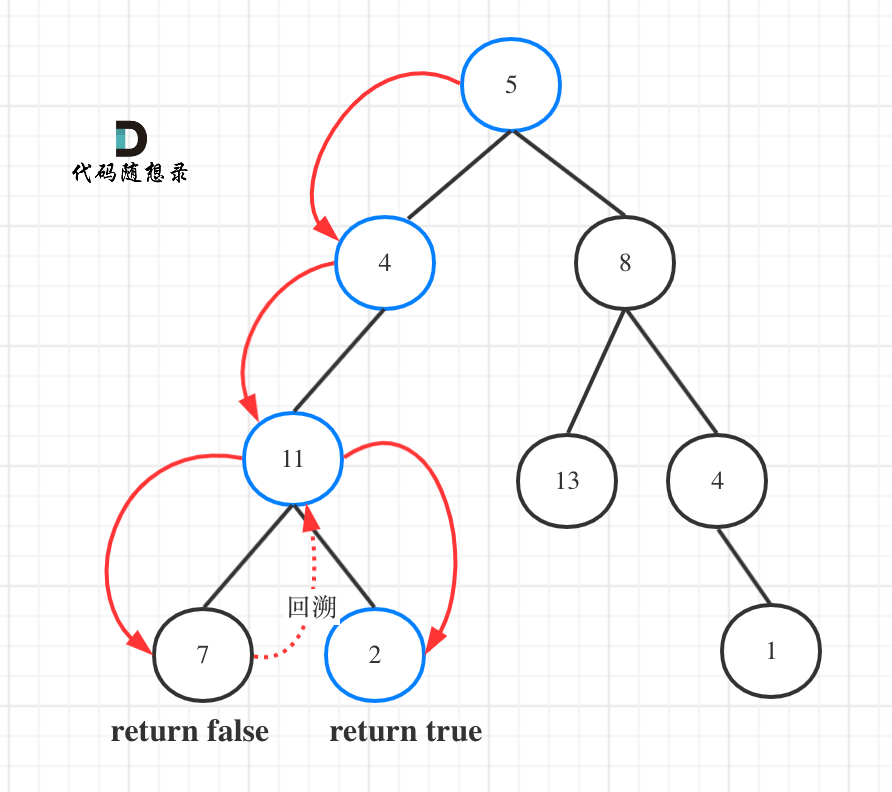
+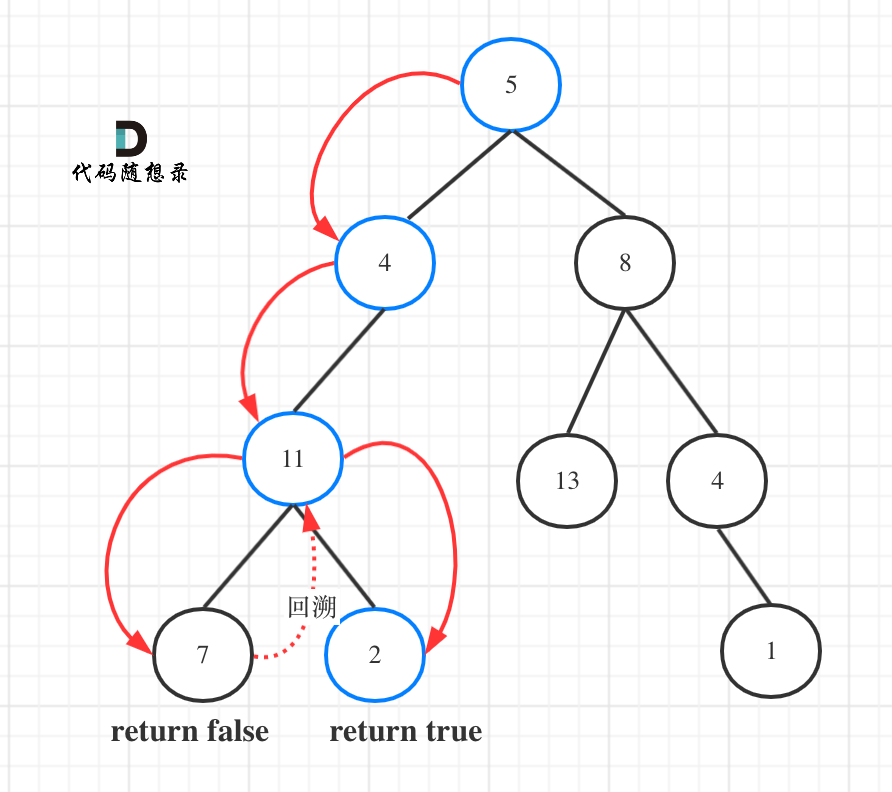
图中可以看出,遍历的路线,并不要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,可以用bool类型表示。
@@ -216,28 +216,30 @@ public:
如果大家完全理解了本题的递归方法之后,就可以顺便把leetcode上113. 路径总和ii做了。
-# 113. 路径总和ii
+## 相关题目推荐
+
+### 113. 路径总和ii
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/)
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
-说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
+说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
-给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
+给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
-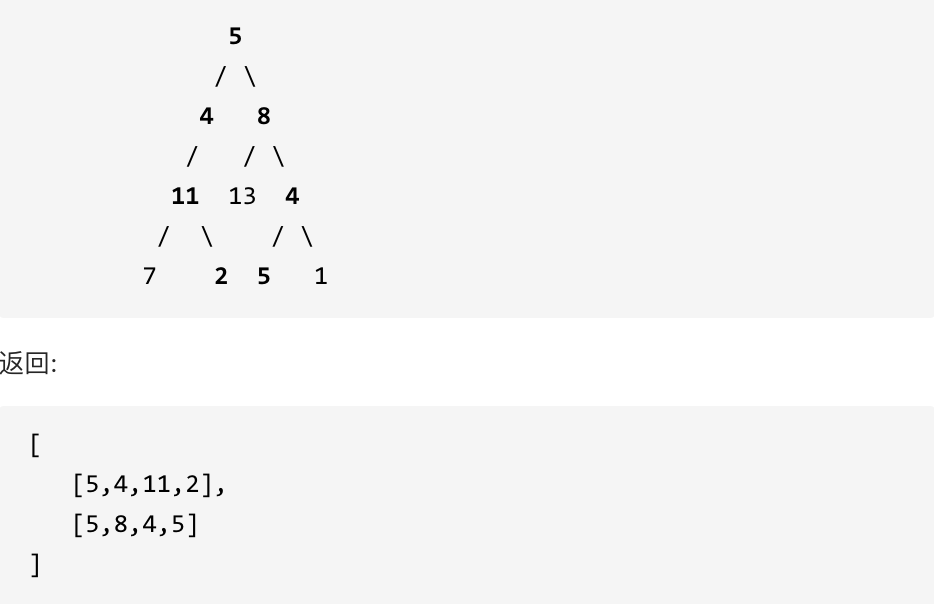
+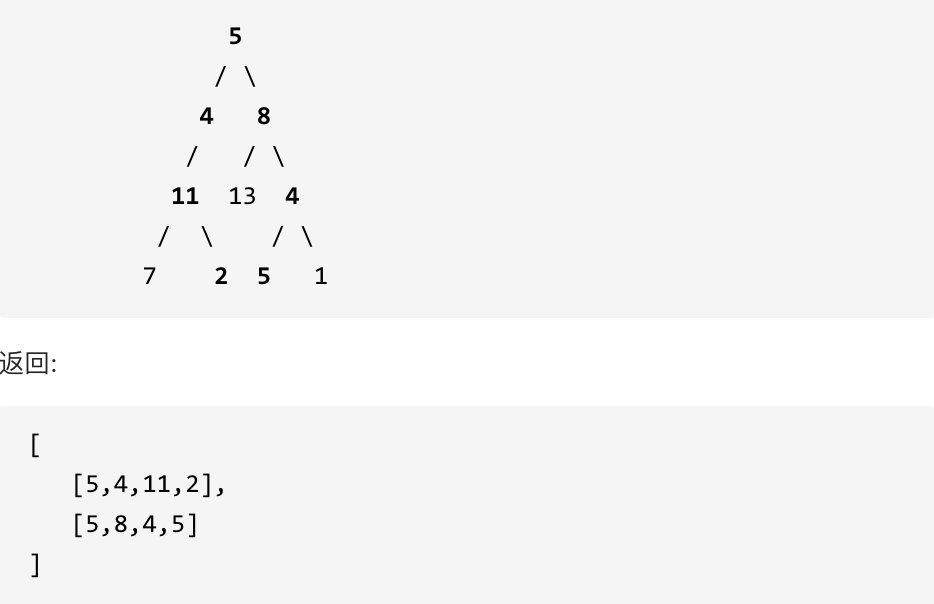
-## 思路
+### 思路
113.路径总和ii要遍历整个树,找到所有路径,**所以递归函数不要返回值!**
如图:
-
+
为了尽可能的把细节体现出来,我写出如下代码(**这份代码并不简洁,但是逻辑非常清晰**)
@@ -248,7 +250,7 @@ private:
vector> result;
vector path;
// 递归函数不需要返回值,因为我们要遍历整个树
- void traversal(treenode* cur, int count) {
+ void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) {
if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) { // 遇到了叶子节点且找到了和为sum的路径
result.push_back(path);
return;
@@ -274,10 +276,10 @@ private:
}
public:
- vector> pathsum(treenode* root, int sum) {
+ vector> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
- if (root == null) return result;
+ if (root == NULL) return result;
path.push_back(root->val); // 把根节点放进路径
traversal(root, sum - root->val);
return result;
@@ -287,7 +289,7 @@ public:
至于113. 路径总和ii 的迭代法我并没有写,用迭代方式记录所有路径比较麻烦,也没有必要,如果大家感兴趣的话,可以再深入研究研究。
-## 总结
+### 总结
本篇通过leetcode上112. 路径总和 和 113. 路径总和ii 详细的讲解了 递归函数什么时候需要返回值,什么不需要返回值。
@@ -298,31 +300,32 @@ public:
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## java
+### Java
+
+0112.路径总和
-### 0112.路径总和
```java
-class solution {
- public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
- targetsum -= root.val;
+ targetSum -= root.val;
// 叶子结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
- return targetsum == 0;
+ return targetSum == 0;
}
if (root.left != null) {
- boolean left = haspathsum(root.left, targetsum);
- if (left) { // 已经找到
+ boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum);
+ if (left) { // 已经找到,提前返回
return true;
}
}
if (root.right != null) {
- boolean right = haspathsum(root.right, targetsum);
- if (right) { // 已经找到
+ boolean right = hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum);
+ if (right) { // 已经找到,提前返回
return true;
}
}
@@ -331,39 +334,41 @@ class solution {
}
// lc112 简洁方法
-class solution {
- public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
-
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
+
if (root == null) return false; // 为空退出
-
+
// 叶子节点判断是否符合
- if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetsum;
+ if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetSum;
// 求两侧分支的路径和
- return haspathsum(root.left, targetsum - root.val) || haspathsum(root.right, targetsum - root.val);
+ return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
}
}
```
+
迭代
+
```java
-class solution {
- public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return false;
- stack stack1 = new stack<>();
- stack stack2 = new stack<>();
+ Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
+ Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(root);
stack2.push(root.val);
- while(!stack1.isempty()) {
+ while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
int size = stack1.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
- treenode node = stack1.pop();
+ TreeNode node = stack1.pop();
int sum = stack2.pop();
// 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
- if(node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetsum) {
+ if(node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetSum) {
return true;
- }
+ }
// 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
if(node.right != null){
stack1.push(node.right);
@@ -377,40 +382,78 @@ class solution {
}
}
return false;
- }
+ }
}
```
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
+ Stack treeNodeStack = new Stack<>();
+ Stack sumStack = new Stack<>();
-### 0113.路径总和-ii
+ if(root == null)
+ return false;
+ treeNodeStack.add(root);
+ sumStack.add(root.val);
+
+ while(!treeNodeStack.isEmpty()){
+ TreeNode curr = treeNodeStack.peek();
+ int tempsum = sumStack.pop();
+ if(curr != null){
+ treeNodeStack.pop();
+ treeNodeStack.add(curr);
+ treeNodeStack.add(null);
+ sumStack.add(tempsum);
+ if(curr.right != null){
+ treeNodeStack.add(curr.right);
+ sumStack.add(tempsum + curr.right.val);
+ }
+ if(curr.left != null){
+ treeNodeStack.add(curr.left);
+ sumStack.add(tempsum + curr.left.val);
+ }
+ }else{
+ treeNodeStack.pop();
+ TreeNode temp = treeNodeStack.pop();
+ if(temp.left == null && temp.right == null && tempsum == targetSum)
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+0113.路径总和-ii
```java
-class solution {
- public List> pathsum(TreeNode root, int targetsum) {
+class Solution {
+ public List> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res; // 非空判断
List path = new LinkedList<>();
- preorderdfs(root, targetsum, res, path);
+ preOrderDfs(root, targetSum, res, path);
return res;
}
- public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetsum, List> res, List path) {
+ public void preOrderDfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum, List> res, List path) {
path.add(root.val);
// 遇到了叶子节点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// 找到了和为 targetsum 的路径
- if (targetsum - root.val == 0) {
+ if (targetSum - root.val == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return; // 如果和不为 targetsum,返回
}
if (root.left != null) {
- preorderdfs(root.left, targetsum - root.val, res, path);
+ preOrderDfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
if (root.right != null) {
- preorderdfs(root.right, targetsum - root.val, res, path);
+ preOrderDfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
@@ -441,119 +484,246 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+```java
+// 解法3 DFS统一迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public List> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
+ List> result = new ArrayList<>();
+ Stack nodeStack = new Stack<>();
+ Stack sumStack = new Stack<>();
+ Stack> pathStack = new Stack<>();
+ if(root == null)
+ return result;
+ nodeStack.add(root);
+ sumStack.add(root.val);
+ pathStack.add(new ArrayList<>());
+
+ while(!nodeStack.isEmpty()){
+ TreeNode currNode = nodeStack.peek();
+ int currSum = sumStack.pop();
+ ArrayList currPath = pathStack.pop();
+ if(currNode != null){
+ nodeStack.pop();
+ nodeStack.add(currNode);
+ nodeStack.add(null);
+ sumStack.add(currSum);
+ currPath.add(currNode.val);
+ pathStack.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
+ if(currNode.right != null){
+ nodeStack.add(currNode.right);
+ sumStack.add(currSum + currNode.right.val);
+ pathStack.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
+ }
+ if(currNode.left != null){
+ nodeStack.add(currNode.left);
+ sumStack.add(currSum + currNode.left.val);
+ pathStack.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
+ }
+ }else{
+ nodeStack.pop();
+ TreeNode temp = nodeStack.pop();
+ if(temp.left == null && temp.right == null && currSum == targetSum)
+ result.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+}
+```
-## python
+### Python
-### 0112.路径总和
+0112.路径总和
-**递归**
+(版本一) 递归
```python
-class solution:
- def haspathsum(self, root: treenode, targetsum: int) -> bool:
- def isornot(root, targetsum) -> bool:
- if (not root.left) and (not root.right) and targetsum == 0:
- return true # 遇到叶子节点,并且计数为0
- if (not root.left) and (not root.right):
- return false # 遇到叶子节点,计数不为0
- if root.left:
- targetsum -= root.left.val # 左节点
- if isornot(root.left, targetsum): return true # 递归,处理左节点
- targetsum += root.left.val # 回溯
- if root.right:
- targetsum -= root.right.val # 右节点
- if isornot(root.right, targetsum): return true # 递归,处理右节点
- targetsum += root.right.val # 回溯
- return false
-
- if root == none:
- return false # 别忘记处理空treenode
- else:
- return isornot(root, targetsum - root.val)
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
+ def traversal(self, cur: TreeNode, count: int) -> bool:
+ if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0: # 遇到叶子节点,并且计数为0
+ return True
+ if not cur.left and not cur.right: # 遇到叶子节点直接返回
+ return False
+
+ if cur.left: # 左
+ count -= cur.left.val
+ if self.traversal(cur.left, count): # 递归,处理节点
+ return True
+ count += cur.left.val # 回溯,撤销处理结果
+
+ if cur.right: # 右
+ count -= cur.right.val
+ if self.traversal(cur.right, count): # 递归,处理节点
+ return True
+ count += cur.right.val # 回溯,撤销处理结果
+
+ return False
+
+ def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
+ if root is None:
+ return False
+ return self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
```
-**迭代 - 层序遍历**
+(版本二) 递归 + 精简
+```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
+ def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
+ if not root:
+ return False
+ if not root.left and not root.right and targetSum == root.val:
+ return True
+ return self.hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
+
+```
+(版本三) 迭代
```python
-class solution:
- def haspathsum(self, root: treenode, targetsum: int) -> bool:
- if not root:
- return false
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
+ def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
+ if not root:
+ return False
+ # 此时栈里要放的是pair<节点指针,路径数值>
+ st = [(root, root.val)]
+ while st:
+ node, path_sum = st.pop()
+ # 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
+ if not node.left and not node.right and path_sum == sum:
+ return True
+ # 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
+ if node.right:
+ st.append((node.right, path_sum + node.right.val))
+ # 左节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
+ if node.left:
+ st.append((node.left, path_sum + node.left.val))
+ return False
+
+
+
+```
- stack = [] # [(当前节点,路径数值), ...]
- stack.append((root, root.val))
- while stack:
- cur_node, path_sum = stack.pop()
- if not cur_node.left and not cur_node.right and path_sum == targetsum:
- return true
+0113.路径总和-ii
- if cur_node.right:
- stack.append((cur_node.right, path_sum + cur_node.right.val))
+(版本一) 递归
+```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.result = []
+ self.path = []
+
+ def traversal(self, cur, count):
+ if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0: # 遇到了叶子节点且找到了和为sum的路径
+ self.result.append(self.path[:])
+ return
+
+ if not cur.left and not cur.right: # 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
+ return
+
+ if cur.left: # 左 (空节点不遍历)
+ self.path.append(cur.left.val)
+ count -= cur.left.val
+ self.traversal(cur.left, count) # 递归
+ count += cur.left.val # 回溯
+ self.path.pop() # 回溯
+
+ if cur.right: # 右 (空节点不遍历)
+ self.path.append(cur.right.val)
+ count -= cur.right.val
+ self.traversal(cur.right, count) # 递归
+ count += cur.right.val # 回溯
+ self.path.pop() # 回溯
- if cur_node.left:
- stack.append((cur_node.left, path_sum + cur_node.left.val))
+ return
- return false
+ def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+ self.result.clear()
+ self.path.clear()
+ if not root:
+ return self.result
+ self.path.append(root.val) # 把根节点放进路径
+ self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
+ return self.result
```
-### 0113.路径总和-ii
-
-**递归**
+(版本二) 递归 + 精简
```python
-class solution:
- def pathsum(self, root: treenode, targetsum: int) -> list[list[int]]:
-
- def traversal(cur_node, remain):
- if not cur_node.left and not cur_node.right:
- if remain == 0:
- result.append(path[:])
- return
-
- if cur_node.left:
- path.append(cur_node.left.val)
- traversal(cur_node.left, remain-cur_node.left.val)
- path.pop()
-
- if cur_node.right:
- path.append(cur_node.right.val)
- traversal(cur_node.right, remain-cur_node.right.val)
- path.pop()
-
- result, path = [], []
- if not root:
- return []
- path.append(root.val)
- traversal(root, targetsum - root.val)
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
+class Solution:
+ def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
+
+ result = []
+ self.traversal(root, targetSum, [], result)
return result
+ def traversal(self,node, count, path, result):
+ if not node:
+ return
+ path.append(node.val)
+ count -= node.val
+ if not node.left and not node.right and count == 0:
+ result.append(list(path))
+ self.traversal(node.left, count, path, result)
+ self.traversal(node.right, count, path, result)
+ path.pop()
```
-
-**迭代法,用第二个队列保存目前的总和与路径**
+(版本三) 迭代
```python
+# Definition for a binary tree node.
+# class TreeNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.left = left
+# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
- que, temp = deque([root]), deque([(root.val, [root.val])])
- result = []
- while que:
- for _ in range(len(que)):
- node = que.popleft()
- value, path = temp.popleft()
- if (not node.left) and (not node.right):
- if value == targetSum:
- result.append(path)
- if node.left:
- que.append(node.left)
- temp.append((node.left.val+value, path+[node.left.val]))
- if node.right:
- que.append(node.right)
- temp.append((node.right.val+value, path+[node.right.val]))
- return result
+ stack = [(root, [root.val])]
+ res = []
+ while stack:
+ node, path = stack.pop()
+ if not node.left and not node.right and sum(path) == targetSum:
+ res.append(path)
+ if node.right:
+ stack.append((node.right, path + [node.right.val]))
+ if node.left:
+ stack.append((node.left, path + [node.left.val]))
+ return res
+
+
+
```
+### Go
-## go
-
-### 112. 路径总和
+112. 路径总和
```go
//递归法
@@ -569,7 +739,49 @@ func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
if root == nil {
return false
}
-
+ return traversal(root, targetSum - root.Val)
+}
+
+func traversal(cur *TreeNode, count int) bool {
+ if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil && count == 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+ if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil {
+ return false
+ }
+ if cur.Left != nil {
+ count -= cur.Left.Val
+ if traversal(cur.Left, count) {
+ return true
+ }
+ count += cur.Left.Val
+ }
+ if cur.Right != nil {
+ count -= cur.Right.Val
+ if traversal(cur.Right, count) {
+ return true
+ }
+ count += cur.Right.Val
+ }
+ return false
+}
+```
+
+```go
+//递归法精简
+/**
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * type TreeNode struct {
+ * Val int
+ * Left *TreeNode
+ * Right *TreeNode
+ * }
+ */
+func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
+ if root == nil {
+ return false
+ }
+
targetSum -= root.Val // 将targetSum在遍历每层的时候都减去本层节点的值
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil && targetSum == 0 { // 如果剩余的targetSum为0, 则正好就是符合的结果
return true
@@ -578,7 +790,7 @@ func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
}
```
-### 113. 路径总和 II
+113. 路径总和 II
```go
/**
@@ -602,10 +814,10 @@ func traverse(node *TreeNode, result *[][]int, currPath *[]int, targetSum int) {
targetSum -= node.Val // 将targetSum在遍历每层的时候都减去本层节点的值
*currPath = append(*currPath, node.Val) // 把当前节点放到路径记录里
-
+
if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil && targetSum == 0 { // 如果剩余的targetSum为0, 则正好就是符合的结果
// 不能直接将currPath放到result里面, 因为currPath是共享的, 每次遍历子树时都会被修改
- pathCopy := make([]int, len(*currPath))
+ pathCopy := make([]int, len(*currPath))
for i, element := range *currPath {
pathCopy[i] = element
}
@@ -618,11 +830,12 @@ func traverse(node *TreeNode, result *[][]int, currPath *[]int, targetSum int) {
}
```
-## javascript
+### JavaScript
-### 0112.路径总和
+0112.路径总和
**递归**
+
```javascript
/**
* @param {treenode} root
@@ -639,7 +852,7 @@ let haspathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
// 左(空节点不遍历).遇到叶子节点返回true,则直接返回true
if (node.left && traversal(node.left, cnt - node.left.val)) return true;
- // 右(空节点不遍历)
+ // 右(空节点不遍历)
if (node.right && traversal(node.right, cnt - node.right.val)) return true;
return false;
};
@@ -652,7 +865,9 @@ let haspathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
// return haspathsum(root.left, targetsum - root.val) || haspathsum(root.right, targetsum - root.val);
};
```
+
**迭代**
+
```javascript
let hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root === null) return false;
@@ -681,9 +896,10 @@ let hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
};
```
-### 0113.路径总和-ii
+0113.路径总和-ii
**递归**
+
```javascript
let pathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
// 递归法
@@ -715,7 +931,9 @@ let pathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
return res;
};
```
+
**递归 精简版**
+
```javascript
var pathsum = function(root, targetsum) {
//递归方法
@@ -739,7 +957,9 @@ var pathsum = function(root, targetsum) {
return resPath;
};
```
+
**迭代**
+
```javascript
let pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root === null) return [];
@@ -774,9 +994,9 @@ let pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
-### 0112.路径总和
+0112.路径总和
**递归法:**
@@ -858,7 +1078,7 @@ function hasPathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): boolean {
};
```
-### 0112.路径总和 ii
+0112.路径总和 ii
**递归法:**
@@ -894,9 +1114,9 @@ function pathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): number[][] {
};
```
-## Swift
+### Swift
-### 0112.路径总和
+0112.路径总和
**递归**
@@ -905,7 +1125,7 @@ func hasPathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> Bool {
guard let root = root else {
return false
}
-
+
return traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
}
@@ -913,57 +1133,59 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, _ count: Int) -> Bool {
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil && count == 0 {
return true
}
-
+
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil {
return false
}
-
+
if let leftNode = cur?.left {
if traversal(leftNode, count - leftNode.val) {
return true
}
}
-
+
if let rightNode = cur?.right {
if traversal(rightNode, count - rightNode.val) {
return true
}
}
-
+
return false
}
```
+
**迭代**
+
```swift
func hasPathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> Bool {
guard let root = root else {
return false
}
-
+
var stack = Array<(TreeNode, Int)>()
stack.append((root, root.val))
-
+
while !stack.isEmpty {
let node = stack.removeLast()
-
+
if node.0.left == nil && node.0.right == nil && targetSum == node.1 {
return true
}
-
+
if let rightNode = node.0.right {
stack.append((rightNode, node.1 + rightNode.val))
}
-
+
if let leftNode = node.0.left {
stack.append((leftNode, node.1 + leftNode.val))
}
}
-
+
return false
}
```
-### 0113.路径总和 II
+0113.路径总和 II
**递归**
@@ -989,12 +1211,12 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
result.append(path)
return
}
-
+
// 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil{
return
}
-
+
if let leftNode = cur?.left {
path.append(leftNode.val)
count -= leftNode.val
@@ -1002,7 +1224,7 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
count += leftNode.val// 回溯
path.removeLast()// 回溯
}
-
+
if let rightNode = cur?.right {
path.append(rightNode.val)
count -= rightNode.val
@@ -1014,9 +1236,12 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
}
```
-## C
-> 0112.路径总和
+### C
+
+0112.路径总和
+
递归法:
+
```c
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
// 递归结束条件:若当前节点不存在,返回false
@@ -1025,13 +1250,14 @@ bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
// 若当前节点为叶子节点,且targetSum-root的值为0。(当前路径上的节点值的和满足条件)返回true
if(!root->right && !root->left && targetSum == root->val)
return true;
-
+
// 查看左子树和右子树的所有节点是否满足条件
return hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val);
}
```
迭代法:
+
```c
// 存储一个节点以及当前的和
struct Pair {
@@ -1056,7 +1282,7 @@ bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
// 若栈顶元素为叶子节点,且和为targetSum时,返回true
if(!topPair.node->left && !topPair.node->right && topPair.sum == targetSum)
return true;
-
+
// 若当前栈顶节点有左右孩子,计算和并入栈
if(topPair.node->left) {
struct Pair newPair = {topPair.node->left, topPair.sum + topPair.node->left->val};
@@ -1070,7 +1296,9 @@ bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
return false;
}
```
-> 0113.路径总和 II
+
+0113.路径总和 II
+
```c
int** ret;
int* path;
@@ -1134,11 +1362,12 @@ int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** retur
}
```
-## Scala
+### Scala
-### 0112.路径总和
+0112.路径总和
**递归:**
+
```scala
object Solution {
def hasPathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): Boolean = {
@@ -1163,6 +1392,7 @@ object Solution {
```
**迭代:**
+
```scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
@@ -1184,9 +1414,10 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-### 0113.路径总和 II
+0113.路径总和 II
**递归:**
+
```scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
@@ -1219,9 +1450,9 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-## rust
+### Rust
-### 112.路径总和.md
+0112.路径总和
递归:
@@ -1275,7 +1506,7 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
-### 113.路径总和-ii
+0113.路径总和-ii
```rust
impl Solution {
@@ -1323,8 +1554,72 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 0112.路径总和
+// 递归
+public bool HasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum)
+{
+ if (root == null) return false;
+ if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == root.val) return true;
+ return HasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || HasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
+}
+```
+0113.路径总和:
+```csharp
+/*
+ * @lc app=leetcode id=113 lang=csharp
+ * 0113.路径总和 II
+ * [113] Path Sum II
+ * 递归法
+ */
+public class Solution {
+ private List> result = new List>();
+ private List path = new List();
+
+ // Main function to find paths with the given sum
+ public IList> PathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
+ result.Clear();
+ path.Clear();
+ if (root == null) return result.Select(list => list as IList).ToList();
+ path.Add(root.val); // Add the root node to the path
+ traversal(root, targetSum - root.val); // Start the traversal
+ return result.Select(list => list as IList).ToList();
+ }
+
+ // Recursive function to traverse the tree and find paths
+ private void traversal(TreeNode node, int count) {
+ // If a leaf node is reached and the target sum is achieved
+ if (node.left == null && node.right == null && count == 0) {
+ result.Add(new List(path)); // Add a copy of the path to the result
+ return;
+ }
+
+ // If a leaf node is reached and the target sum is not achieved, or if it's not a leaf node
+ if (node.left == null && node.right == null) return;
+
+ // Traverse the left subtree
+ if (node.left != null) {
+ path.Add(node.left.val);
+ count -= node.left.val;
+ traversal(node.left, count); // Recursive call
+ count += node.left.val; // Backtrack
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1); // Backtrack
+ }
+
+ // Traverse the right subtree
+ if (node.right != null) {
+ path.Add(node.right.val);
+ count -= node.right.val;
+ traversal(node.right, count); // Recursive call
+ count += node.right.val; // Backtrack
+ path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1); // Backtrack
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// @lc code=end
+
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index daa708bc84..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index daa708bc84..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 115.不同的子序列
@@ -14,12 +12,16 @@
题目数据保证答案符合 32 位带符号整数范围。
-
+
提示:
-0 <= s.length, t.length <= 1000
-s 和 t 由英文字母组成
+* 0 <= s.length, t.length <= 1000
+* s 和 t 由英文字母组成
+
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划之子序列,为了编辑距离做铺垫 | LeetCode:115.不同的子序列](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fG4y1m75Q/),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -68,7 +70,7 @@ dp[i][j]:以i-1为结尾的s子序列中出现以j-1为结尾的t的个数为d
从递推公式dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j]; 和 dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]; 中可以看出dp[i][j] 是从上方和左上方推导而来,如图:,那么 dp[i][0] 和dp[0][j]是一定要初始化的。
-
+
每次当初始化的时候,都要回顾一下dp[i][j]的定义,不要凭感觉初始化。
@@ -99,7 +101,7 @@ for (int j = 1; j <= t.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = 0; // 其实这行代码可以和
从递推公式dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j]; 和 dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]; 中可以看出dp[i][j]都是根据左上方和正上方推出来的。
-
+
所以遍历的时候一定是从上到下,从左到右,这样保证dp[i][j]可以根据之前计算出来的数值进行计算。
@@ -121,7 +123,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= s.size(); i++) {
以s:"baegg",t:"bag"为例,推导dp数组状态如下:
-
+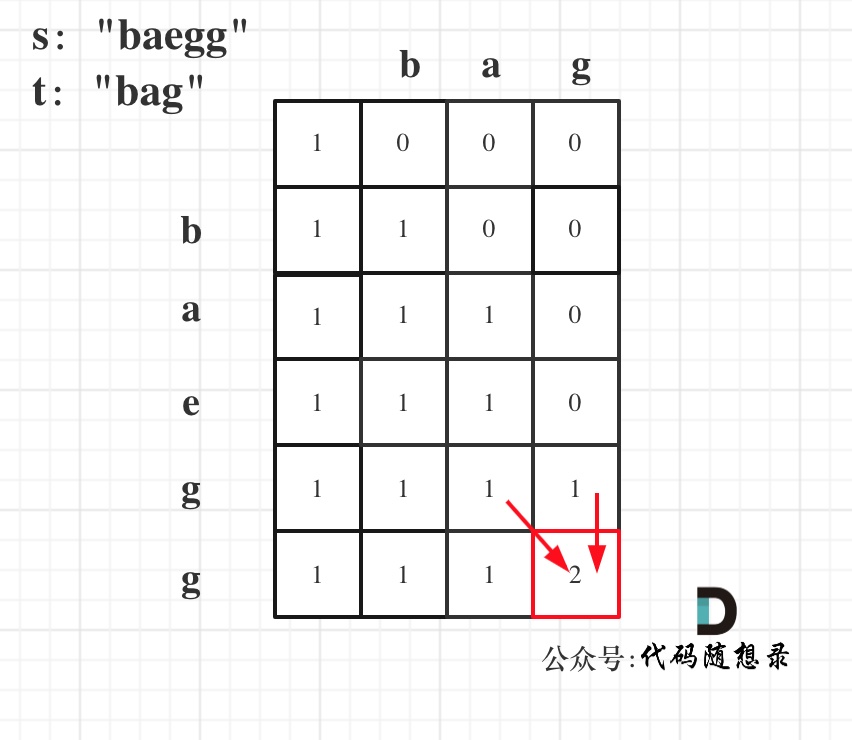
如果写出来的代码怎么改都通过不了,不妨把dp数组打印出来,看一看,是不是这样的。
@@ -149,10 +151,15 @@ public:
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n * m)
+* 空间复杂度: O(n * m)
+
+
+
## 其他语言版本
+### Java:
-Java:
```java
class Solution {
public int numDistinct(String s, String t) {
@@ -176,7 +183,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
class Solution:
def numDistinct(self, s: str, t: str) -> int:
@@ -194,7 +202,8 @@ class Solution:
return dp[-1][-1]
```
-Python3:
+### Python3:
+
```python
class SolutionDP2:
"""
@@ -228,7 +237,8 @@ class SolutionDP2:
return dp[-1]
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```go
func numDistinct(s string, t string) int {
dp:= make([][]int,len(s)+1)
@@ -253,8 +263,8 @@ func numDistinct(s string, t string) int {
}
```
+### JavaScript:
-Javascript:
```javascript
const numDistinct = (s, t) => {
let dp = Array.from(Array(s.length + 1), () => Array(t.length +1).fill(0));
@@ -277,7 +287,7 @@ const numDistinct = (s, t) => {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function numDistinct(s: string, t: string): number {
@@ -305,10 +315,62 @@ function numDistinct(s: string, t: string): number {
};
```
+### Rust:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn num_distinct(s: String, t: String) -> i32 {
+ if s.len() < t.len() {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; s.len() + 1]; t.len() + 1];
+ // i = 0, t 为空字符串,s 作为子序列的个数为 1(删除 s 所有元素)
+ dp[0] = vec![1; s.len() + 1];
+ for (i, char_t) in t.chars().enumerate() {
+ for (j, char_s) in s.chars().enumerate() {
+ if char_t == char_s {
+ // t 的前 i 个字符在 s 的前 j 个字符中作为子序列的个数
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + dp[i + 1][j];
+ continue;
+ }
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i + 1][j];
+ }
+ }
+ dp[t.len()][s.len()]
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 滚动数组
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn num_distinct(s: String, t: String) -> i32 {
+ if s.len() < t.len() {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ let (s, t) = (s.into_bytes(), t.into_bytes());
+ // 对于 t 为空字符串,s 作为子序列的个数为 1(删除 s 所有元素)
+ let mut dp = vec![1; s.len() + 1];
+ for char_t in t {
+ // dp[i - 1][j - 1],dp[j + 1] 更新之前的值
+ let mut pre = dp[0];
+ // 当开始遍历 t,s 的前 0 个字符无法包含任意子序列
+ dp[0] = 0;
+ for (j, &char_s) in s.iter().enumerate() {
+ let temp = dp[j + 1];
+ if char_t == char_s {
+ dp[j + 1] = pre + dp[j];
+ } else {
+ dp[j + 1] = dp[j];
+ }
+ pre = temp;
+ }
+ }
+ dp[s.len()]
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31bb6822cc..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31bb6822cc..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
@@ -28,9 +26,9 @@ struct Node {
* 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
* 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
-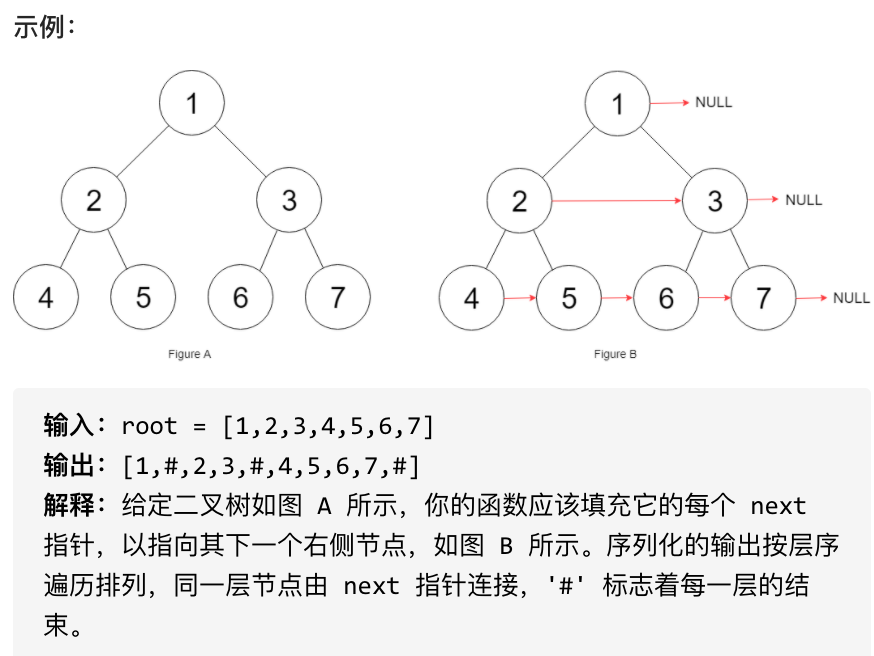
+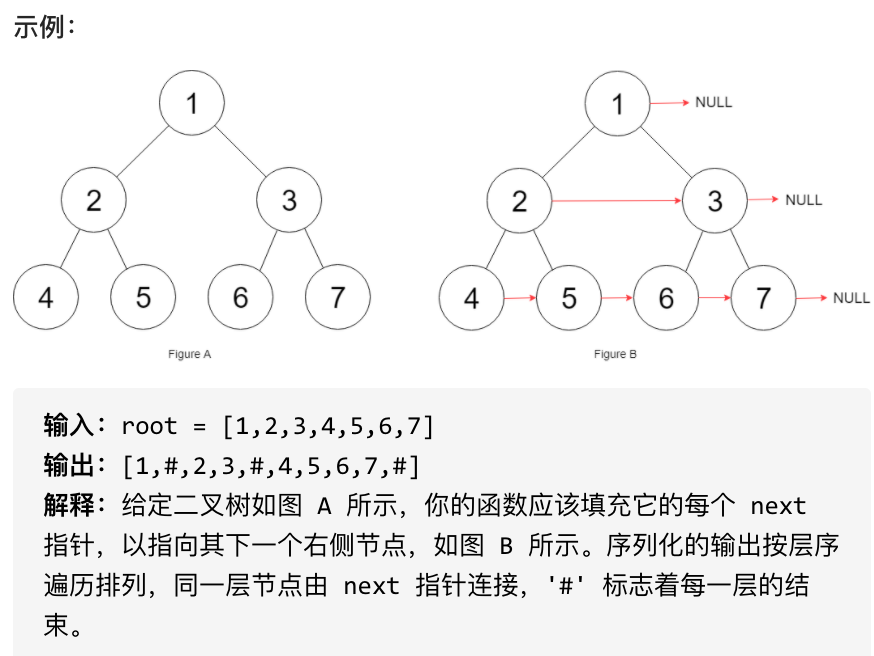
-# 思路
+## 思路
注意题目提示内容,:
* 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
@@ -38,13 +36,13 @@ struct Node {
基本上就是要求使用递归了,迭代的方式一定会用到栈或者队列。
-## 递归
+### 递归
一想用递归怎么做呢,虽然层序遍历是最直观的,但是递归的方式确实不好想。
如图,假如当前操作的节点是cur:
- +
+ 最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ public:
};
```
-## 迭代(层序遍历)
+### 迭代(层序遍历)
本题使用层序遍历是最为直观的,如果对层序遍历不了解,看这篇:[二叉树:层序遍历登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html)。
@@ -114,9 +112,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
// 递归法
@@ -169,7 +167,57 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
+
+ queue.add(root);
+
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int size = queue.size();
+
+ // 每层的第一个节点
+ Node cur = queue.poll();
+ if (cur.left != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.left);
+ }
+ if (cur.right != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.right);
+ }
+
+ // 因为已经移除了每层的第一个节点,所以将 0 改为 1
+ while (size-- > 1) {
+ Node next = queue.poll();
+
+ if (next.left != null) {
+ queue.add(next.left);
+ }
+ if (next.right != null) {
+ queue.add(next.right);
+ }
+
+ // 当前节点指向同层的下一个节点
+ cur.next = next;
+ // 更新当前节点
+ cur = next;
+ }
+
+ // 每层的最后一个节点不指向 null 在力扣也能过
+ cur.next = null;
+ }
+
+ return root;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Python
```python
# 递归法
@@ -210,7 +258,7 @@ class Solution:
nodePre.next = None # 本层最后一个节点指向None
return root
```
-## Go
+### Go
```go
// 迭代法
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
@@ -259,7 +307,7 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
const connect = root => {
@@ -287,7 +335,7 @@ const connect = root => {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
(注:命名空间‘Node’与typescript中内置类型冲突,这里改成了‘NodePro’)
@@ -358,10 +406,85 @@ function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
};
```
+```csharp
+//递归
+public class Solution {
+ public Node Connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return null;
+ }
+
+ ConnectNodes(root.left, root.right);
+
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ private void ConnectNodes(Node node1, Node node2) {
+ if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
+ return;
+ }
+
+ // 将左子节点的 next 指向右子节点
+ node1.next = node2;
+
+ // 递归连接当前节点的左右子节点
+ ConnectNodes(node1.left, node1.right);
+ ConnectNodes(node2.left, node2.right);
+
+ // 连接跨越父节点的两个子树
+ ConnectNodes(node1.right, node2.left);
+ }
+}
+
+
+// 迭代
+public class Solution
+{
+ public Node Connect(Node root)
+ {
+ Queue que = new Queue();
+
+ if (root != null)
+ {
+ que.Enqueue(root);
+ }
+
+ while (que.Count > 0)
+ {
+
+ var queSize = que.Count;
+ for (int i = 0; i < queSize; i++)
+ {
+ var cur = que.Dequeue();
+
+ // 当这个节点不是这一层的最后的节点
+ if (i != queSize - 1)
+ {
+ // 当前节点指向下一个节点
+ cur.next = que.Peek();
+ }
+ // 否则指向空
+ else
+ {
+ cur.next = null;
+ }
+
+ if (cur.left != null)
+ {
+ que.Enqueue(cur.left);
+ }
+ if (cur.right != null)
+ {
+ que.Enqueue(cur.right);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return root;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ public:
};
```
-## 迭代(层序遍历)
+### 迭代(层序遍历)
本题使用层序遍历是最为直观的,如果对层序遍历不了解,看这篇:[二叉树:层序遍历登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html)。
@@ -114,9 +112,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
// 递归法
@@ -169,7 +167,57 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
+
+ queue.add(root);
+
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int size = queue.size();
+
+ // 每层的第一个节点
+ Node cur = queue.poll();
+ if (cur.left != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.left);
+ }
+ if (cur.right != null) {
+ queue.add(cur.right);
+ }
+
+ // 因为已经移除了每层的第一个节点,所以将 0 改为 1
+ while (size-- > 1) {
+ Node next = queue.poll();
+
+ if (next.left != null) {
+ queue.add(next.left);
+ }
+ if (next.right != null) {
+ queue.add(next.right);
+ }
+
+ // 当前节点指向同层的下一个节点
+ cur.next = next;
+ // 更新当前节点
+ cur = next;
+ }
+
+ // 每层的最后一个节点不指向 null 在力扣也能过
+ cur.next = null;
+ }
+
+ return root;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Python
```python
# 递归法
@@ -210,7 +258,7 @@ class Solution:
nodePre.next = None # 本层最后一个节点指向None
return root
```
-## Go
+### Go
```go
// 迭代法
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
@@ -259,7 +307,7 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
const connect = root => {
@@ -287,7 +335,7 @@ const connect = root => {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
(注:命名空间‘Node’与typescript中内置类型冲突,这里改成了‘NodePro’)
@@ -358,10 +406,85 @@ function connect(root: NodePro | null): NodePro | null {
};
```
+```csharp
+//递归
+public class Solution {
+ public Node Connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return null;
+ }
+
+ ConnectNodes(root.left, root.right);
+
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ private void ConnectNodes(Node node1, Node node2) {
+ if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
+ return;
+ }
+
+ // 将左子节点的 next 指向右子节点
+ node1.next = node2;
+
+ // 递归连接当前节点的左右子节点
+ ConnectNodes(node1.left, node1.right);
+ ConnectNodes(node2.left, node2.right);
+
+ // 连接跨越父节点的两个子树
+ ConnectNodes(node1.right, node2.left);
+ }
+}
+
+
+// 迭代
+public class Solution
+{
+ public Node Connect(Node root)
+ {
+ Queue que = new Queue();
+
+ if (root != null)
+ {
+ que.Enqueue(root);
+ }
+
+ while (que.Count > 0)
+ {
+
+ var queSize = que.Count;
+ for (int i = 0; i < queSize; i++)
+ {
+ var cur = que.Dequeue();
+
+ // 当这个节点不是这一层的最后的节点
+ if (i != queSize - 1)
+ {
+ // 当前节点指向下一个节点
+ cur.next = que.Peek();
+ }
+ // 否则指向空
+ else
+ {
+ cur.next = null;
+ }
+
+ if (cur.left != null)
+ {
+ que.Enqueue(cur.left);
+ }
+ if (cur.right != null)
+ {
+ que.Enqueue(cur.right);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return root;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8736c9f375..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8736c9f375..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
@@ -14,16 +12,19 @@
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
-示例 1:
-输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
-输出:5
+* 示例 1:
+* 输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
+* 输出:5
解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
-示例 2:
-输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
-输出:0
+* 示例 2:
+* 输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
+* 输出:0
解释:在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划之 LeetCode:121.买卖股票的最佳时机1](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Xe4y1u77q),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
@@ -127,7 +128,8 @@ dp[0][1]表示第0天不持有股票,不持有股票那么现金就是0,所
以示例1,输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]为例,dp数组状态如下:
-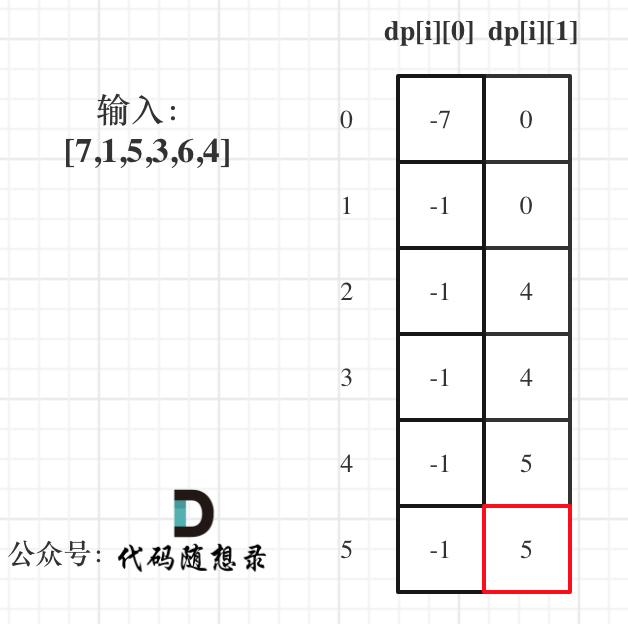
+
+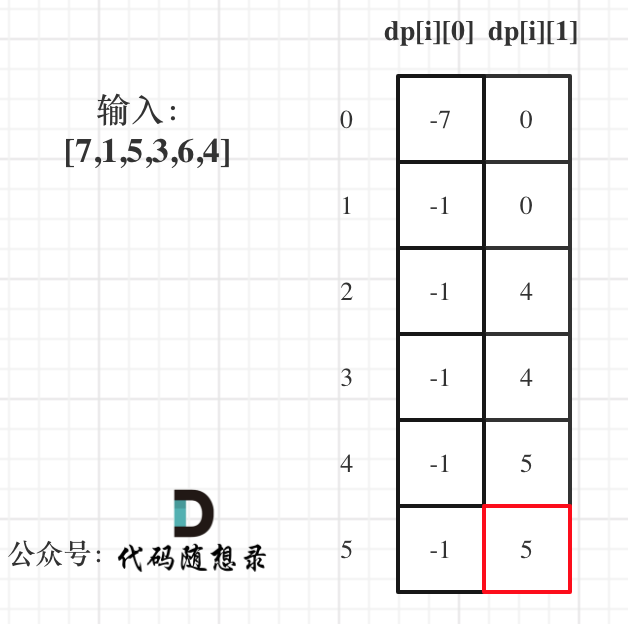
dp[5][1]就是最终结果。
@@ -196,7 +198,7 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
> 贪心法:
@@ -237,8 +239,27 @@ class Solution {
}
}
```
+> 动态规划:版本二(使用二維數組(和卡哥思路一致),下面還有使用一維滾動數組的更優化版本)
-> 动态规划:版本二
+```Java
+class Solution {
+ public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
+ int len = prices.length;
+ int dp[][] = new int[2][2];
+
+ dp[0][0] = - prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+
+ for (int i = 1; i < len; i++){
+ dp[i % 2][0] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][0], - prices[i]);
+ dp[i % 2][1] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][1], prices[i] + dp[(i - 1) % 2][0]);
+ }
+ return dp[(len - 1) % 2][1];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 动态规划:版本二(使用一維數組)
``` java
class Solution {
@@ -266,7 +287,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
> 贪心法:
```python
@@ -285,7 +306,7 @@ class Solution:
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
length = len(prices)
- if len == 0:
+ if length == 0:
return 0
dp = [[0] * 2 for _ in range(length)]
dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
@@ -322,7 +343,8 @@ class Solution:
return dp1
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
> 贪心法:
```Go
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
@@ -389,7 +411,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
> 动态规划
@@ -425,7 +447,7 @@ var maxProfit = function(prices) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
> 贪心法
@@ -442,7 +464,7 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
-> 动态规划
+> 动态规划:版本一
```typescript
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
@@ -463,7 +485,27 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
-C#:
+> 动态规划:版本二
+
+```typescript
+// dp[i][0] 表示第i天持有股票所得最多现金
+// dp[i][1] 表示第i天不持有股票所得最多现金
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ const dp:number[][] = Array(2).fill(0).map(item => Array(2));
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
+ dp[i % 2][0] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][0], -prices[i]);
+ dp[i % 2][1] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][1], dp[(i - 1) % 2][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+
+ // 返回不持有股票的最大现金
+ return dp[(prices.length-1) % 2][1];
+};
+```
+
+### C#:
> 贪心法
@@ -504,11 +546,82 @@ public class Solution
}
```
+### C:
+
+> 贪心
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ int low = INT_MIN;
+ int result = 0;
+ for(int i = 0; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ low = min(low, prices[i]);
+ result = max(result, prices[i] - low);
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+> 动态规划
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
+ if(pricesSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // dp初始化
+ int ** dp = malloc(sizeof (int *) * pricesSize);
+ for(int i = 0; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ dp[i] = malloc(sizeof (int ) * 2);
+ }
+ // 下标0表示持有股票的情况下的最大现金,下标1表示不持有股票的情况下获得的最大现金
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+ for(int i = 1; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[pricesSize - 1][1];
+}
+```
+
+### Rust:
+
+> 贪心
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let (mut low, mut res) = (i32::MAX, 0);
+ for p in prices {
+ low = p.min(low);
+ res = res.max(p - low);
+ }
+ res
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 动态规划
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![-prices[0], 0];
+ for p in prices {
+ dp[0] = dp[0].max(-p);
+ dp[1] = dp[1].max(dp[0] + p);
+ }
+ dp[1]
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d094da488e..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,46 +1,50 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d094da488e..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,46 +1,50 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
-
-# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
+# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机 II
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
-给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
+给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
-
示例 1:
-* 输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
-* 输出: 7
-* 解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 3 天(股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4。随后,在第 4 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-3 = 3 。
+
+- 输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
+- 输出: 7
+- 解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 3 天(股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4。随后,在第 4 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-3 = 3 。
示例 2:
-* 输入: [1,2,3,4,5]
-* 输出: 4
-* 解释: 在第 1 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4 。注意你不能在第 1 天和第 2 天接连购买股票,之后再将它们卖出。因为这样属于同时参与了多笔交易,你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票。
-示例 3:
-* 输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
-* 输出: 0
-* 解释: 在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
+- 输入: [1,2,3,4,5]
+- 输出: 4
+- 解释: 在第 1 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4 。注意你不能在第 1 天和第 2 天接连购买股票,之后再将它们卖出。因为这样属于同时参与了多笔交易,你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票。
+
+示例 3:
+
+- 输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
+- 输出: 0
+- 解释: 在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
提示:
-* 1 <= prices.length <= 3 * 10 ^ 4
-* 0 <= prices[i] <= 10 ^ 4
+
+- 1 <= prices.length <= 3 \* 10 ^ 4
+- 0 <= prices[i] <= 10 ^ 4
+
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[贪心算法也能解决股票问题!LeetCode:122.买卖股票最佳时机 II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ev4y1C7na),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
## 思路
本题首先要清楚两点:
-* 只有一只股票!
-* 当前只有买股票或者卖股票的操作
+- 只有一只股票!
+- 当前只有买股票或者卖股票的操作
想获得利润至少要两天为一个交易单元。
@@ -52,17 +56,17 @@
如何分解呢?
-假如第0天买入,第3天卖出,那么利润为:prices[3] - prices[0]。
+假如第 0 天买入,第 3 天卖出,那么利润为:prices[3] - prices[0]。
相当于(prices[3] - prices[2]) + (prices[2] - prices[1]) + (prices[1] - prices[0])。
-**此时就是把利润分解为每天为单位的维度,而不是从0天到第3天整体去考虑!**
+**此时就是把利润分解为每天为单位的维度,而不是从 0 天到第 3 天整体去考虑!**
-那么根据prices可以得到每天的利润序列:(prices[i] - prices[i - 1]).....(prices[1] - prices[0])。
+那么根据 prices 可以得到每天的利润序列:(prices[i] - prices[i - 1]).....(prices[1] - prices[0])。
如图:
-
+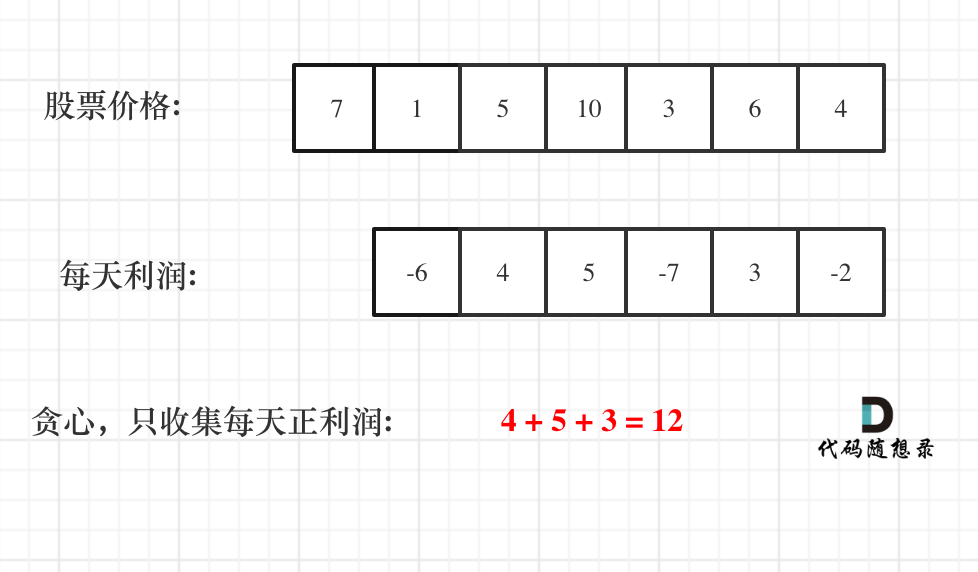
一些同学陷入:第一天怎么就没有利润呢,第一天到底算不算的困惑中。
@@ -76,7 +80,7 @@
局部最优可以推出全局最优,找不出反例,试一试贪心!
-对应C++代码如下:
+对应 C++代码如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -91,12 +95,12 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:O(n)
-* 空间复杂度:O(1)
+- 时间复杂度:O(n)
+- 空间复杂度:O(1)
### 动态规划
-动态规划将在下一个系列详细讲解,本题解先给出我的C++代码(带详细注释),感兴趣的同学可以自己先学习一下。
+动态规划将在下一个系列详细讲解,本题解先给出我的 C++代码(带详细注释),想先学习的话,可以看本篇:[122.买卖股票的最佳时机II(动态规划)](https://programmercarl.com/0122.%E4%B9%B0%E5%8D%96%E8%82%A1%E7%A5%A8%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E4%BD%B3%E6%97%B6%E6%9C%BAII%EF%BC%88%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E8%A7%84%E5%88%92%EF%BC%89.html#%E6%80%9D%E8%B7%AF)
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -118,8 +122,8 @@ public:
};
```
-* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
-* 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
+- 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
+- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
## 总结
@@ -133,9 +137,10 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-### Java:
+### Java:
贪心:
+
```java
// 贪心思路
class Solution {
@@ -150,6 +155,7 @@ class Solution {
```
动态规划:
+
```java
class Solution { // 动态规划
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
@@ -171,8 +177,10 @@ class Solution { // 动态规划
}
```
-### Python:
+### Python:
+
贪心:
+
```python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
@@ -183,6 +191,7 @@ class Solution:
```
动态规划:
+
```python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
@@ -199,6 +208,7 @@ class Solution:
### Go:
贪心算法
+
```go
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
var sum int
@@ -211,7 +221,9 @@ func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
return sum
}
```
+
动态规划
+
```go
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
dp := make([][]int, len(prices))
@@ -225,7 +237,7 @@ func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][0] - prices[i], dp[i-1][1])
}
return dp[len(prices)-1][0]
-
+
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
@@ -235,9 +247,10 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-### Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
贪心
+
```Javascript
var maxProfit = function(prices) {
let result = 0
@@ -248,54 +261,69 @@ var maxProfit = function(prices) {
};
```
-动态规划
+动态规划
+
```javascript
const maxProfit = (prices) => {
- let dp = Array.from(Array(prices.length), () => Array(2).fill(0));
- // dp[i][0] 表示第i天持有股票所得现金。
- // dp[i][1] 表示第i天不持有股票所得最多现金
- dp[0][0] = 0 - prices[0];
- dp[0][1] = 0;
- for(let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
- // 如果第i天持有股票即dp[i][0], 那么可以由两个状态推出来
- // 第i-1天就持有股票,那么就保持现状,所得现金就是昨天持有股票的所得现金 即:dp[i - 1][0]
- // 第i天买入股票,所得现金就是昨天不持有股票的所得现金减去 今天的股票价格 即:dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]
- dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1] - prices[i]);
-
- // 在来看看如果第i天不持有股票即dp[i][1]的情况, 依然可以由两个状态推出来
- // 第i-1天就不持有股票,那么就保持现状,所得现金就是昨天不持有股票的所得现金 即:dp[i - 1][1]
- // 第i天卖出股票,所得现金就是按照今天股票佳价格卖出后所得现金即:prices[i] + dp[i - 1][0]
- dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]);
- }
+ let dp = Array.from(Array(prices.length), () => Array(2).fill(0));
+ // dp[i][0] 表示第i天持有股票所得现金。
+ // dp[i][1] 表示第i天不持有股票所得最多现金
+ dp[0][0] = 0 - prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+ for (let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
+ // 如果第i天持有股票即dp[i][0], 那么可以由两个状态推出来
+ // 第i-1天就持有股票,那么就保持现状,所得现金就是昨天持有股票的所得现金 即:dp[i - 1][0]
+ // 第i天买入股票,所得现金就是昨天不持有股票的所得现金减去 今天的股票价格 即:dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]
+ dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
+
+ // 在来看看如果第i天不持有股票即dp[i][1]的情况, 依然可以由两个状态推出来
+ // 第i-1天就不持有股票,那么就保持现状,所得现金就是昨天不持有股票的所得现金 即:dp[i - 1][1]
+ // 第i天卖出股票,所得现金就是按照今天股票佳价格卖出后所得现金即:prices[i] + dp[i - 1][0]
+ dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
- return dp[prices.length -1][1];
+ return dp[prices.length - 1][1];
};
```
### TypeScript:
+贪心
```typescript
function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
- let resProfit: number = 0;
- for (let i = 1, length = prices.length; i < length; i++) {
- resProfit += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
- }
- return resProfit;
-};
+ let resProfit: number = 0;
+ for (let i = 1, length = prices.length; i < length; i++) {
+ resProfit += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
+ }
+ return resProfit;
+}
```
-### Rust
+动态规划
+```typescript
+function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
+ const dp = Array(prices.length)
+ .fill(0)
+ .map(() => Array(2).fill(0))
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
+ for (let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
+ dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i])
+ dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i])
+ }
+ return dp[prices.length - 1][1]
+}
+```
+
+### Rust:
贪心:
+
```Rust
impl Solution {
- fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
- if a > b { a } else { b }
- }
pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
let mut result = 0;
for i in 1..prices.len() {
- result += Self::max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
+ result += (prices[i] - prices[i - 1]).max(0);
}
result
}
@@ -303,26 +331,25 @@ impl Solution {
```
动态规划:
+
```Rust
impl Solution {
- fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
- if a > b { a } else { b }
- }
pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
- let n = prices.len();
- let mut dp = vec![vec![0; 2]; n];
- dp[0][0] -= prices[0];
- for i in 1..n {
- dp[i][0] = Self::max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
- dp[i][1] = Self::max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; 2]; prices.len()];
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ for i in 1..prices.len() {
+ dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0].max(dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][1].max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
}
- Self::max(dp[n - 1][0], dp[n - 1][1])
+ dp[prices.len() - 1][1]
}
}
```
### C:
+
贪心:
+
```c
int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
int result = 0;
@@ -338,6 +365,7 @@ int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
```
动态规划:
+
```c
#define max(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b))
@@ -359,9 +387,10 @@ int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
}
```
-### Scala
+### Scala:
贪心:
+
```scala
object Solution {
def maxProfit(prices: Array[Int]): Int = {
@@ -375,8 +404,20 @@ object Solution {
}
}
```
+### C#
+```csharp
+public class Solution
+{
+ public int MaxProfit(int[] prices)
+ {
+ int res = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < prices.Length - 1; i++)
+ {
+ res += Math.Max(0, prices[i + 1] - prices[i]);
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2779083d89..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2779083d89..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
@@ -15,25 +13,30 @@
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
-示例 1:
-输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
-输出: 7
+* 示例 1:
+* 输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
+* 输出: 7
解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 3 天(股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4。随后,在第 4 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-3 = 3 。
-示例 2:
-输入: [1,2,3,4,5]
-输出: 4
+* 示例 2:
+* 输入: [1,2,3,4,5]
+* 输出: 4
解释: 在第 1 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4 。注意你不能在第 1 天和第 2 天接连购买股票,之后再将它们卖出。因为这样属于同时参与了多笔交易,你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票。
-示例 3:
-输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
-输出: 0
+* 示例 3:
+* 输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
+* 输出: 0
解释: 在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
提示:
* 1 <= prices.length <= 3 * 10 ^ 4
* 0 <= prices[i] <= 10 ^ 4
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划,股票问题第二弹 | LeetCode:122.买卖股票的最佳时机II](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1D24y1Q7Ls),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+
## 思路
本题我们在讲解贪心专题的时候就已经讲解过了[贪心算法:买卖股票的最佳时机II](https://programmercarl.com/0122.买卖股票的最佳时机II.html),只不过没有深入讲解动态规划的解法,那么这次我们再好好分析一下动规的解法。
@@ -128,8 +131,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
+### Java:
-Java:
```java
// 动态规划
class Solution
@@ -149,7 +152,24 @@ class Solution
}
}
```
+```java
+//DP using 2*2 Array (下方還有使用一維滾動數組的更優化版本)
+class Solution {
+ public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
+ int dp[][] = new int [2][2];
+ //dp[i][0]: holding the stock
+ //dp[i][1]: not holding the stock
+ dp[0][0] = - prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+ for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++){
+ dp[i % 2][0] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][0], dp[(i - 1) % 2][1] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i % 2][1] = Math.max(dp[(i - 1) % 2][1], dp[(i - 1) % 2][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[(prices.length - 1) % 2][1];
+ }
+}
+```
```java
// 优化空间
class Solution {
@@ -169,7 +189,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
> 版本一:
```python
@@ -199,7 +219,8 @@ class Solution:
return dp[(length-1) % 2][1]
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```go
// 买卖股票的最佳时机Ⅱ 动态规划
// 时间复杂度:O(n) 空间复杂度:O(n)
@@ -228,7 +249,29 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-Javascript:
+```go
+// 动态规划 版本二 滚动数组
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ dp := [2][2]int{} // 注意这里只开辟了一个2 * 2大小的二维数组
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
+ dp[0][1] = 0
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
+ dp[i%2][0] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][0], dp[(i - 1) % 2][1] - prices[i])
+ dp[i%2][1] = max(dp[(i-1)%2][1], dp[(i-1)%2][0] + prices[i])
+ }
+ return dp[(len(prices)-1)%2][1]
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
// 方法一:动态规划(dp 数组)
const maxProfit = (prices) => {
@@ -268,7 +311,7 @@ const maxProfit = (prices) => {
}
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
> 动态规划
@@ -304,7 +347,7 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
-C#:
+### C#:
> 贪心法
@@ -341,10 +384,94 @@ public class Solution
}
```
+### C:
+
+> 动态规划
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){
+ int **dp = malloc(sizeof (int *) * pricesSize);
+ for (int i = 0; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ dp[i] = malloc(sizeof (int ) * 2);
+ }
+ // 0表示持有该股票所得最大,1表示不持有所得最大
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][1] = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ return dp[pricesSize - 1][1];
+}
+```
+
+> 贪心
+
+```c
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ if(pricesSize == 0){
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int result = 0;
+ for(int i = 1; i < pricesSize; i++){
+ // 如果今天股票价格大于昨天,代表有利润
+ if(prices[i] > prices[i - 1]){
+ result += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+```
+
+
+
+### Rust:
+
+> 贪心
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let mut result = 0;
+ for i in 1..prices.len() {
+ result += (prices[i] - prices[i - 1]).max(0);
+ }
+ result
+ }
+}
+```
+
+>动态规划
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; 2]; prices.len()];
+ dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
+ for i in 1..prices.len() {
+ dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0].max(dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][1].max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
+ }
+ dp[prices.len() - 1][1]
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 优化
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![-prices[0], 0];
+ for p in prices {
+ dp[0] = dp[0].max(dp[1] - p);
+ dp[1] = dp[1].max(dp[0] + p);
+ }
+ dp[1]
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cd7ab26f8..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cd7ab26f8..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III
@@ -15,23 +13,23 @@
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
-示例 1:
-输入:prices = [3,3,5,0,0,3,1,4]
-输出:6
+* 示例 1:
+* 输入:prices = [3,3,5,0,0,3,1,4]
+* 输出:6
解释:在第 4 天(股票价格 = 0)的时候买入,在第 6 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润 = 3-0 = 3 。随后,在第 7 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 8 天 (股票价格 = 4)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润 = 4-1 = 3。
-示例 2:
-输入:prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
-输出:4
+* 示例 2:
+* 输入:prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
+* 输出:4
解释:在第 1 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4。注意你不能在第 1 天和第 2 天接连购买股票,之后再将它们卖出。因为这样属于同时参与了多笔交易,你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票。
-示例 3:
-输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
-输出:0
+* 示例 3:
+* 输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
+* 输出:0
解释:在这个情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为0。
-示例 4:
-输入:prices = [1]
+* 示例 4:
+* 输入:prices = [1]
输出:0
提示:
@@ -39,6 +37,11 @@
* 1 <= prices.length <= 10^5
* 0 <= prices[i] <= 10^5
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[动态规划,股票至多买卖两次,怎么求? | LeetCode:123.买卖股票最佳时机III](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1WG411K7AR),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
+
+
## 思路
@@ -116,7 +119,8 @@ dp[i][4] = max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
以输入[1,2,3,4,5]为例
-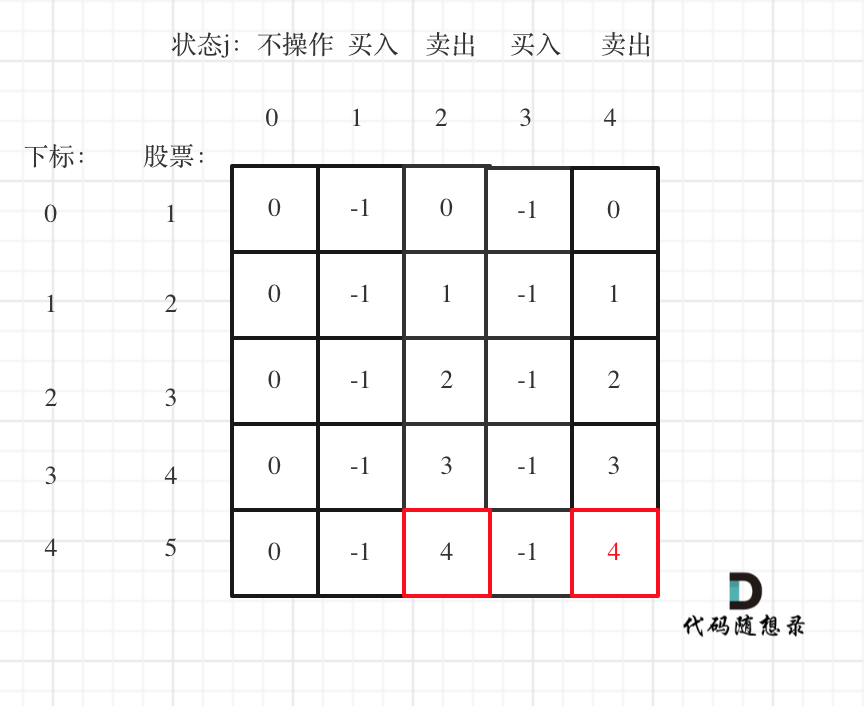
+
+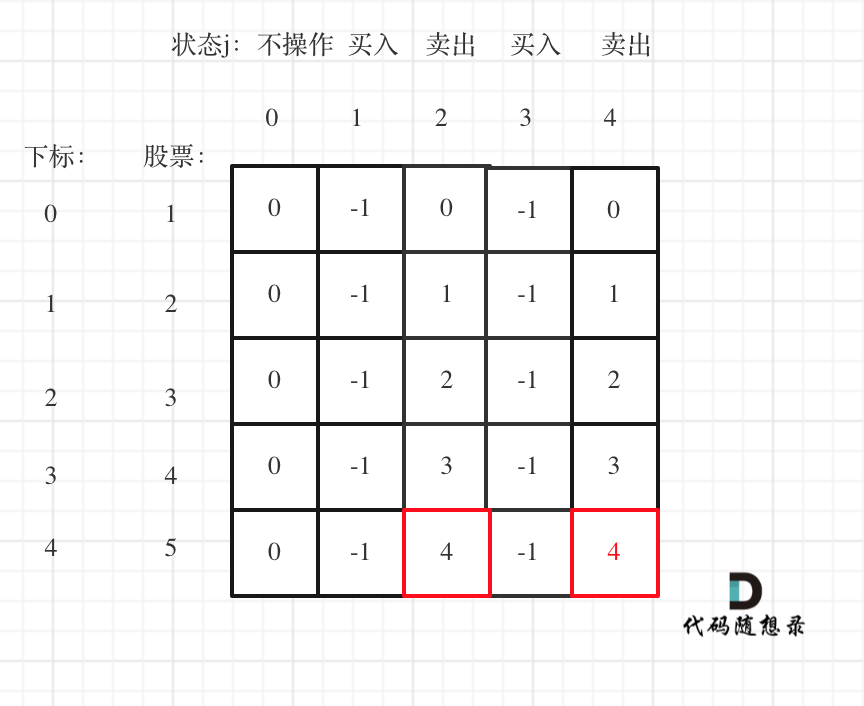
大家可以看到红色框为最后两次卖出的状态。
@@ -215,7 +219,7 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
```java
// 版本一
@@ -236,9 +240,9 @@ class Solution {
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], -prices[i]);
- dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i][1] + prices[i]);
- dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i][2] - prices[i]);
- dp[i][4] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i][3] + prices[i]);
+ dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
+ dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
+ dp[i][4] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
}
return dp[len - 1][4];
@@ -271,7 +275,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
> 版本一:
```python
@@ -308,7 +312,9 @@ class Solution:
return dp[4]
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
+> 版本一
```go
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
@@ -338,7 +344,81 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
}
```
-JavaScript:
+> 版本二
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ if len(prices) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ dp := make([]int, 5)
+ dp[1] = -prices[0]
+ dp[3] = -prices[0]
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
+ dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i])
+ dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i])
+ dp[3] = max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i])
+ dp[4] = max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i])
+ }
+ return dp[4]
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+> 版本三
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ if len(prices) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ dp := make([][5]int, len(prices))
+ dp[0][1] = -prices[0]
+ dp[0][3] = -prices[0]
+ for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
+ dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], 0 - prices[i])
+ dp[i][2] = max(dp[i-1][2], dp[i-1][1] + prices[i])
+ dp[i][3] = max(dp[i-1][3], dp[i-1][2] - prices[i])
+ dp[i][4] = max(dp[i-1][4], dp[i-1][3] + prices[i])
+ }
+ return dp[len(prices)-1][4]
+}
+
+func max(x, y int) int {
+ if x > y {
+ return x
+ }
+ return y
+}
+```
+
+> 版本四:一维 dp 易懂版本
+
+```go
+func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
+ dp := make([]int, 4)
+ dp[0] = -prices[0]
+ dp[2] = -prices[0]
+
+ for _, price := range prices[1:] {
+ dc := slices.Clone(dp) // 这句话是关键,把前一天的 dp 状态保存下来,防止被覆盖掉,后面只用它,不用 dp,逻辑简单易懂
+ dp[0] = max(dc[0], -price)
+ dp[1] = max(dc[1], dc[0] + price)
+ dp[2] = max(dc[2], dc[1] - price)
+ dp[3] = max(dc[3], dc[2] + price)
+ }
+
+ return dp[3]
+}
+```
+
+### JavaScript:
> 版本一:
@@ -377,7 +457,7 @@ const maxProfit = prices => {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
> 版本一
@@ -407,10 +487,79 @@ function maxProfit(prices: number[]): number {
};
```
+### C:
+
+```c
+#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
+#define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a))
+
+int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize) {
+ int buy1 = prices[0], buy2 = prices[0];
+ int profit1 = 0, profit2 = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < pricesSize; ++i) {
+ // 寻找最低点买入
+ buy1 = min(buy1, prices[i]);
+ // 找到第一次交易的最大盈利,并不断维护这一最大值
+ profit1 = max(profit1, prices[i] - buy1);
+
+ // 寻找第二次交易的最低投资点,并且考虑前一次交易的成本
+ // 当前价格 - 第一次操作的盈利=新的投入成本(
+ // 为了让盈利最大,要寻找最小的成本)
+ buy2 = min(buy2, prices[i] - profit1);
+ // 第二次卖出后的盈利:当前价格减去成本,不断维护这一最大的总利润
+ profit2 = max(profit2, prices[i] - buy2);
+ }
+ return profit2;
+}
+```
+
+
+### Rust:
+
+> 版本一
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
+ /*
+ * 定义 5 种状态:
+ * 0: 没有操作, 1: 第一次买入, 2: 第一次卖出, 3: 第二次买入, 4: 第二次卖出
+ */
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; 5]; prices.len()];
+ dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
+ dp[0][3] = -prices[0];
+
+ for (i, &p) in prices.iter().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ // 不操作
+ // dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0];
+ dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][1].max(-p);
+ dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][2].max(dp[i - 1][1] + p);
+ dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][3].max(dp[i - 1][2] - p);
+ dp[i][4] = dp[i - 1][4].max(dp[i - 1][3] + p);
+ }
+
+ dp[prices.len() - 1][4]
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 版本二(绕)
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_profit(prices: Vec) -> i32 {
+ let (mut one_buy, mut one_sale, mut two_buy, mut two_sale) = (-prices[0], 0, -prices[0], 0);
+
+ for p in prices {
+ one_buy = one_buy.max(-p);
+ one_sale = one_sale.max(p + one_buy);
+ two_buy = two_buy.max(one_sale - p);
+ two_sale = two_sale.max(two_buy + p);
+ }
+ two_sale
+ }
+}
+```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7ffd6a21e6..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7ffd6a21e6..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 127. 单词接龙
@@ -16,7 +14,7 @@
* 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典 wordList 中的单词。
* 给你两个单词 beginWord 和 endWord 和一个字典 wordList ,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的 最短转换序列 中的 单词数目 。如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
-
+
示例 1:
* 输入:beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
@@ -29,11 +27,11 @@
* 解释:endWord "cog" 不在字典中,所以无法进行转换。
-# 思路
+## 思路
以示例1为例,从这个图中可以看出 hit 到 cog的路线,不止一条,有三条,一条是最短的长度为5,两条长度为6。
-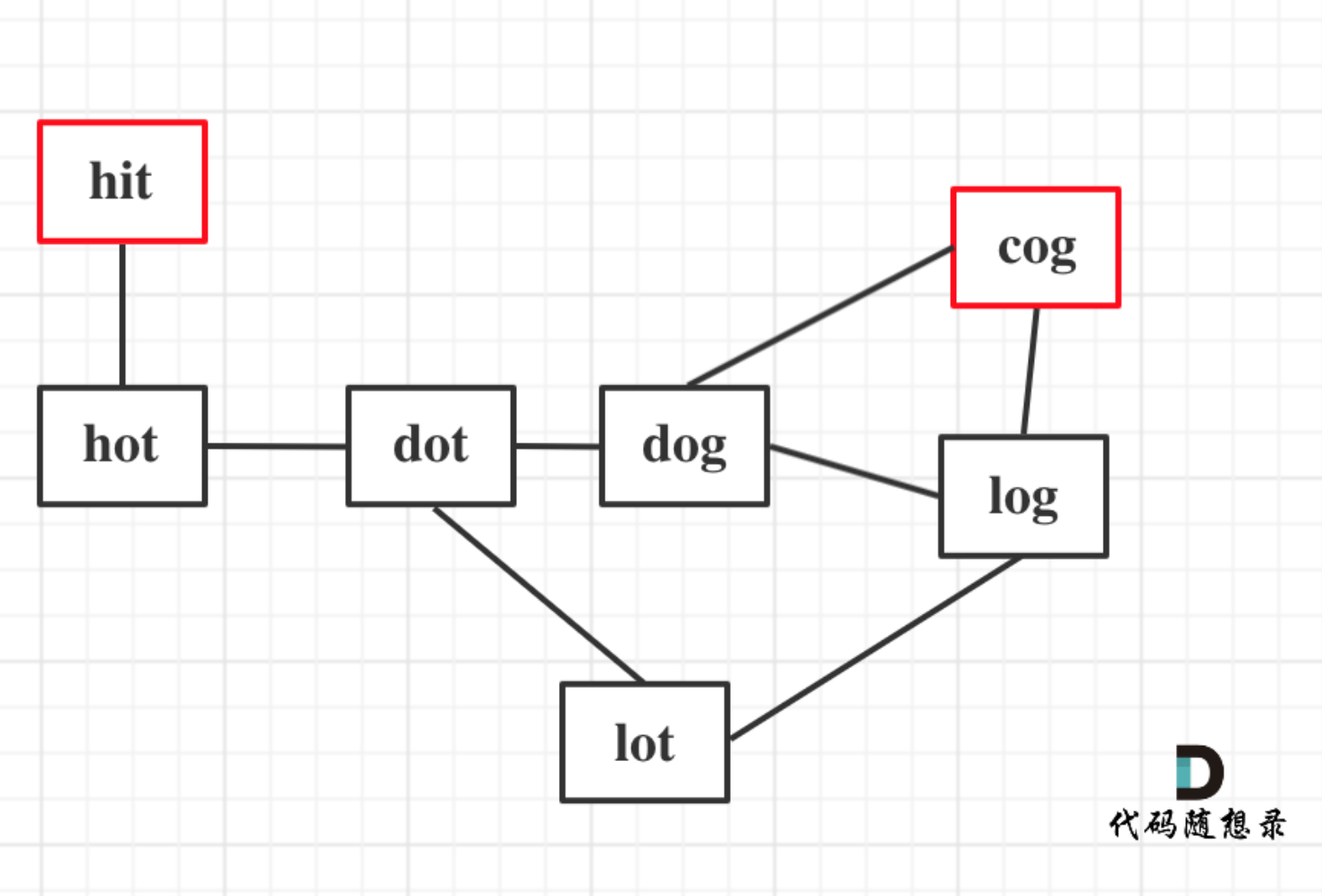
+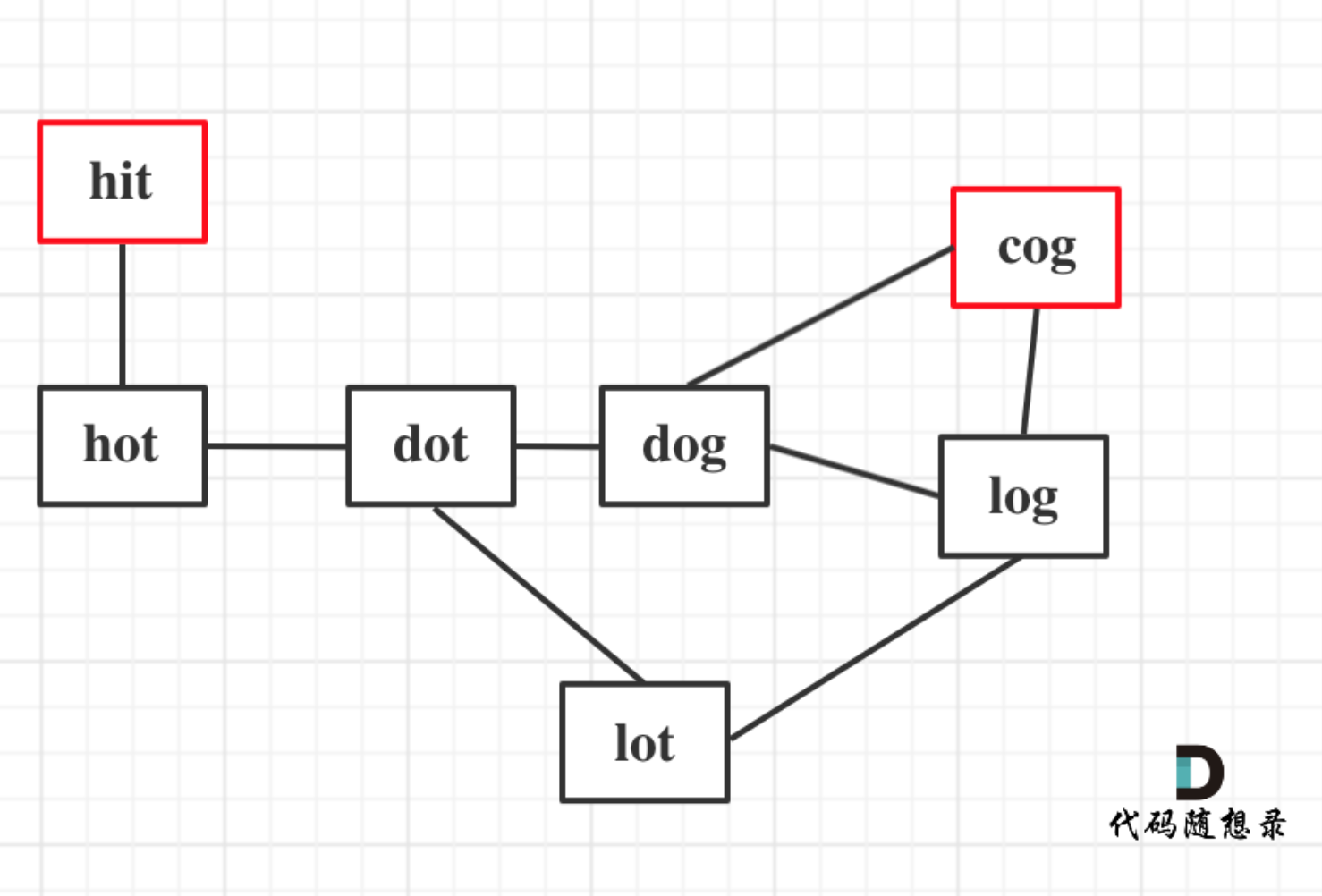
本题只需要求出最短路径的长度就可以了,不用找出路径。
@@ -97,9 +95,9 @@ public:
当然本题也可以用双向BFS,就是从头尾两端进行搜索,大家感兴趣,可以自己去实现,这里就不再做详细讲解了。
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList) {
@@ -134,8 +132,71 @@ public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList)
}
```
-## Python
+```java
+// Java 双向BFS
+class Solution {
+ // 判断单词之间是否之差了一个字母
+ public boolean isValid(String currentWord, String chooseWord) {
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < currentWord.length(); i++)
+ if (currentWord.charAt(i) != chooseWord.charAt(i)) ++count;
+ return count == 1;
+ }
+
+ public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList) {
+ if (!wordList.contains(endWord)) return 0; // 如果 endWord 不在 wordList 中,那么无法成功转换,返回 0
+
+ // ansLeft 记录从 beginWord 开始 BFS 时能组成的单词数目
+ // ansRight 记录从 endWord 开始 BFS 时能组成的单词数目
+ int ansLeft = 0, ansRight = 0;
+
+ // queueLeft 表示从 beginWord 开始 BFS 时使用的队列
+ // queueRight 表示从 endWord 开始 BFS 时使用的队列
+ Queue queueLeft = new ArrayDeque<>(), queueRight = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ queueLeft.add(beginWord);
+ queueRight.add(endWord);
+
+ // 从 beginWord 开始 BFS 时把遍历到的节点存入 hashSetLeft 中
+ // 从 endWord 开始 BFS 时把遍历到的节点存入 hashSetRight 中
+ Set hashSetLeft = new HashSet<>(), hashSetRight = new HashSet<>();
+ hashSetLeft.add(beginWord);
+ hashSetRight.add(endWord);
+
+ // 只要有一个队列为空,说明 beginWord 无法转换到 endWord
+ while (!queueLeft.isEmpty() && !queueRight.isEmpty()) {
+ ++ansLeft;
+ int size = queueLeft.size();
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
+ String currentWord = queueLeft.poll();
+ // 只要 hashSetRight 中存在 currentWord,说明从 currentWord 可以转换到 endWord
+ if (hashSetRight.contains(currentWord)) return ansRight + ansLeft;
+ for (String chooseWord : wordList) {
+ if (hashSetLeft.contains(chooseWord) || !isValid(currentWord, chooseWord)) continue;
+ hashSetLeft.add(chooseWord);
+ queueLeft.add(chooseWord);
+ }
+ }
+ ++ansRight;
+ size = queueRight.size();
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
+ String currentWord = queueRight.poll();
+ // 只要 hashSetLeft 中存在 currentWord,说明从 currentWord 可以转换到 beginWord
+ if (hashSetLeft.contains(currentWord)) return ansLeft + ansRight;
+ for (String chooseWord : wordList) {
+ if (hashSetRight.contains(chooseWord) || !isValid(currentWord, chooseWord)) continue;
+ hashSetRight.add(chooseWord);
+ queueRight.add(chooseWord);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return 0;
+ }
+}
```
+
+### Python
+
+```python
class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
wordSet = set(wordList)
@@ -158,7 +219,7 @@ class Solution:
queue.append(newWord)
return 0
```
-## Go
+### Go
```go
func ladderLength(beginWord string, endWord string, wordList []string) int {
wordMap, que, depth := getWordMap(wordList, beginWord), []string{beginWord}, 0
@@ -211,7 +272,7 @@ func getCandidates(word string) []string {
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```javascript
var ladderLength = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
// 将wordList转成Set,提高查询速度
@@ -247,7 +308,7 @@ var ladderLength = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
};
```
-## TypeScript
+### TypeScript
```typescript
function ladderLength(
beginWord: string,
@@ -297,7 +358,3 @@ function diffonechar(word1: string, word2: string): boolean {
```
-
-
-  -
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 445e108aa9..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 445e108aa9..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
@@ -10,7 +8,7 @@
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
-# 思路
+## 思路
本题和[113.路径总和II](https://programmercarl.com/0112.路径总和.html#_113-路径总和ii)是类似的思路,做完这道题,可以顺便把[113.路径总和II](https://programmercarl.com/0112.路径总和.html#_113-路径总和ii) 和 [112.路径总和](https://programmercarl.com/0112.路径总和.html#_112-路径总和) 做了。
@@ -24,7 +22,7 @@
那么先按递归三部曲来分析:
-## 递归三部曲
+### 递归三部曲
如果对递归三部曲不了解的话,可以看这里:[二叉树:前中后递归详解](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的递归遍历.html)
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ int vectorToInt(const vector& vec) {
如图:
- +
+ 代码如下:
@@ -116,7 +114,7 @@ path.pop_back(); // 回溯
```
**把回溯放在花括号外面了,世界上最遥远的距离,是你在花括号里,而我在花括号外!** 这就不对了。
-## 整体C++代码
+整体C++代码
关键逻辑分析完了,整体C++代码如下:
@@ -162,16 +160,16 @@ public:
};
```
-# 总结
+## 总结
过于简洁的代码,很容易让初学者忽视了本题中回溯的精髓,甚至作者本身都没有想清楚自己用了回溯。
**我这里提供的代码把整个回溯过程充分体现出来,希望可以帮助大家看的明明白白!**
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
```java
class Solution {
@@ -219,7 +217,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
class Solution:
def sumNumbers(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
@@ -246,7 +245,7 @@ class Solution:
backtrace(root)
return res
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
@@ -271,7 +270,8 @@ func dfs(root *TreeNode, tmpSum int, sum *int) {
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
const listToInt = path => {
@@ -315,7 +315,7 @@ var sumNumbers = function(root) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
@@ -351,7 +351,7 @@ function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
};
```
-C:
+### C:
```c
//sum记录总和
@@ -380,7 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
-
代码如下:
@@ -116,7 +114,7 @@ path.pop_back(); // 回溯
```
**把回溯放在花括号外面了,世界上最遥远的距离,是你在花括号里,而我在花括号外!** 这就不对了。
-## 整体C++代码
+整体C++代码
关键逻辑分析完了,整体C++代码如下:
@@ -162,16 +160,16 @@ public:
};
```
-# 总结
+## 总结
过于简洁的代码,很容易让初学者忽视了本题中回溯的精髓,甚至作者本身都没有想清楚自己用了回溯。
**我这里提供的代码把整个回溯过程充分体现出来,希望可以帮助大家看的明明白白!**
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
```java
class Solution {
@@ -219,7 +217,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
class Solution:
def sumNumbers(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
@@ -246,7 +245,7 @@ class Solution:
backtrace(root)
return res
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
@@ -271,7 +270,8 @@ func dfs(root *TreeNode, tmpSum int, sum *int) {
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
const listToInt = path => {
@@ -315,7 +315,7 @@ var sumNumbers = function(root) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
@@ -351,7 +351,7 @@ function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
};
```
-C:
+### C:
```c
//sum记录总和
@@ -380,7 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
-
-
-  -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c2aa569693..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c2aa569693..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
-  -
-
-
-
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
+* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
+* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
# 130. 被围绕的区域
@@ -10,7 +8,7 @@
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 board ,由若干字符 'X' 和 'O' ,找到所有被 'X' 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 'O' 用 'X' 填充。
-
+
* 输入:board = [["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","O","X"],["X","X","O","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
* 输出:[["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
@@ -18,7 +16,7 @@
## 思路
-这道题目和1020. 飞地的数量正好反过来了,[1020. 飞地的数量](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-enclaves/solution/by-carlsun-2-7lt9/)是求 地图中间的空格数,而本题是要把地图中间的'O'都改成'X'。
+这道题目和1020. 飞地的数量正好反过来了,[1020. 飞地的数量](https://programmercarl.com/1020.%E9%A3%9E%E5%9C%B0%E7%9A%84%E6%95%B0%E9%87%8F.html)是求 地图中间的空格数,而本题是要把地图中间的'O'都改成'X'。
那么两题在思路上也是差不多的。
@@ -30,11 +28,11 @@
步骤一:深搜或者广搜将地图周边的'O'全部改成'A',如图所示:
-
+
步骤二:在遍历地图,将'O'全部改成'X'(地图中间的'O'改成了'X'),将'A'改回'O'(保留的地图周边的'O'),如图所示:
-
+
整体C++代码如下,以下使用dfs实现,其实遍历方式dfs,bfs都是可以的。
@@ -84,7 +82,712 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-
-
-  -
+### Java
+
+```Java
+// 广度优先遍历
+// 使用 visited 数组进行标记
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ // rowSize:行的长度,colSize:列的长度
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
+ Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ // 从左侧边,和右侧边遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O') {
+ visited[row][0] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, 0});
+ }
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O') {
+ visited[row][colSize - 1] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1});
+ }
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O') {
+ visited[0][col] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{0, col});
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O') {
+ visited[rowSize - 1][col] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col});
+ }
+ }
+ // 广度优先遍历,把没有被 'X' 包围的 'O' 进行标记
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int[] current = queue.poll();
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int row = current[0] + pos[0], col = current[1] + pos[1];
+ // 如果范围越界、位置已被访问过、该位置的值不是 'O',就直接跳过
+ if (row < 0 || row >= rowSize || col < 0 || col >= colSize) continue;
+ if (visited[row][col] || board[row][col] != 'O') continue;
+ visited[row][col] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把没有被标记的 'O' 修改成 'X'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'O' && !visited[row][col]) board[row][col] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```Java
+// 广度优先遍历
+// 直接修改 board 的值为其他特殊值
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ // rowSize:行的长度,colSize:列的长度
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ // 从左侧边,和右侧边遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, 0});
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1});
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{0, col});
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col});
+ }
+ // 广度优先遍历,把没有被 'X' 包围的 'O' 修改成特殊值
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int[] current = queue.poll();
+ board[current[0]][current[1]] = 'A';
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int row = current[0] + pos[0], col = current[1] + pos[1];
+ // 如果范围越界、该位置的值不是 'O',就直接跳过
+ if (row < 0 || row >= rowSize || col < 0 || col >= colSize) continue;
+ if (board[row][col] != 'O') continue;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把 'O' 修改成 'X',特殊值修改成 'O'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'A') board[row][col] = 'O';
+ else if (board[row][col] == 'O') board[row][col] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```Java
+//BFS(使用helper function)
+class Solution {
+ int[][] dir ={{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ if(board[i][0] == 'O') bfs(board, i, 0);
+ if(board[i][board[0].length - 1] == 'O') bfs(board, i, board[0].length - 1);
+ }
+
+ for(int j = 1 ; j < board[0].length - 1; j++){
+ if(board[0][j] == 'O') bfs(board, 0, j);
+ if(board[board.length - 1][j] == 'O') bfs(board, board.length - 1, j);
+ }
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){
+ if(board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j] = 'X';
+ if(board[i][j] == 'A') board[i][j] = 'O';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ private void bfs(char[][] board, int x, int y){
+ Queue que = new LinkedList<>();
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ que.offer(x);
+ que.offer(y);
+
+ while(!que.isEmpty()){
+ int currX = que.poll();
+ int currY = que.poll();
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
+ int nextX = currX + dir[i][0];
+ int nextY = currY + dir[i][1];
+
+ if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= board.length || nextY >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ if(board[nextX][nextY] == 'X'|| board[nextX][nextY] == 'A')
+ continue;
+ bfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+```Java
+// 深度优先遍历
+// 使用 visited 数组进行标记
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void dfs(char[][] board, int row, int col, boolean[][] visited) {
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int nextRow = row + pos[0], nextCol = col + pos[1];
+ // 位置越界
+ if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= board.length || nextCol < 0 || nextCol >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ // 位置已被访问过、新位置值不是 'O'
+ if (visited[nextRow][nextCol] || board[nextRow][nextCol] != 'O') continue;
+ visited[nextRow][nextCol] = true;
+ dfs(board, nextRow, nextCol, visited);
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
+ // 从左侧遍、右侧遍遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O' && !visited[row][0]) {
+ visited[row][0] = true;
+ dfs(board, row, 0, visited);
+ }
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O' && !visited[row][colSize - 1]) {
+ visited[row][colSize - 1] = true;
+ dfs(board, row, colSize - 1, visited);
+ }
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O' && !visited[0][col]) {
+ visited[0][col] = true;
+ dfs(board, 0, col, visited);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O' && !visited[rowSize - 1][col]) {
+ visited[rowSize - 1][col] = true;
+ dfs(board, rowSize - 1, col, visited);
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把没有被标记的 'O' 修改成 'X'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'O' && !visited[row][col]) board[row][col] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```Java
+// 深度优先遍历
+// // 直接修改 board 的值为其他特殊值
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void dfs(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int nextRow = row + pos[0], nextCol = col + pos[1];
+ // 位置越界
+ if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= board.length || nextCol < 0 || nextCol >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ // 新位置值不是 'O'
+ if (board[nextRow][nextCol] != 'O') continue;
+ board[nextRow][nextCol] = 'A'; // 修改为特殊值
+ dfs(board, nextRow, nextCol);
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ // 从左侧遍、右侧遍遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O') {
+ board[row][0] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, row, 0);
+ }
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O') {
+ board[row][colSize - 1] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, row, colSize - 1);
+ }
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O') {
+ board[0][col] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, 0, col);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O') {
+ board[rowSize - 1][col] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, rowSize - 1, col);
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把 'O' 修改成 'X',特殊值修改成 'O'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'O') board[row][col] = 'X';
+ else if (board[row][col] == 'A') board[row][col] = 'O';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```java
+//DFS(有終止條件)
+class Solution {
+ int[][] dir ={{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ if(board[i][0] == 'O') dfs(board, i, 0);
+ if(board[i][board[0].length - 1] == 'O') dfs(board, i, board[0].length - 1);
+ }
+
+ for(int j = 1 ; j < board[0].length - 1; j++){
+ if(board[0][j] == 'O') dfs(board, 0, j);
+ if(board[board.length - 1][j] == 'O') dfs(board, board.length - 1, j);
+ }
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){
+ if(board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j] = 'X';
+ if(board[i][j] == 'A') board[i][j] = 'O';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void dfs(char[][] board, int x, int y){
+ if(board[x][y] == 'X'|| board[x][y] == 'A')
+ return;
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
+ int nextX = x + dir[i][0];
+ int nextY = y + dir[i][1];
+
+ if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= board.length || nextY >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ // if(board[nextX][nextY] == 'X'|| board[nextX][nextY] == 'A')
+ // continue;
+ dfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+### Python3
+
+```Python
+// 深度优先遍历
+class Solution:
+ dir_list = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
+ def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
+ """
+ Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
+ """
+ row_size = len(board)
+ column_size = len(board[0])
+ visited = [[False] * column_size for _ in range(row_size)]
+ # 从边缘开始,将边缘相连的O改成A。然后遍历所有,将A改成O,O改成X
+ # 第一行和最后一行
+ for i in range(column_size):
+ if board[0][i] == "O" and not visited[0][i]:
+ self.dfs(board, 0, i, visited)
+ if board[row_size-1][i] == "O" and not visited[row_size-1][i]:
+ self.dfs(board, row_size-1, i, visited)
+
+ # 第一列和最后一列
+ for i in range(1, row_size-1):
+ if board[i][0] == "O" and not visited[i][0]:
+ self.dfs(board, i, 0, visited)
+ if board[i][column_size-1] == "O" and not visited[i][column_size-1]:
+ self.dfs(board, i, column_size-1, visited)
+
+ for i in range(row_size):
+ for j in range(column_size):
+ if board[i][j] == "A":
+ board[i][j] = "O"
+ elif board[i][j] == "O":
+ board[i][j] = "X"
+
+
+ def dfs(self, board, x, y, visited):
+ if visited[x][y] or board[x][y] == "X":
+ return
+ visited[x][y] = True
+ board[x][y] = "A"
+ for i in range(4):
+ new_x = x + self.dir_list[i][0]
+ new_y = y + self.dir_list[i][1]
+ if new_x >= len(board) or new_y >= len(board[0]) or new_x < 0 or new_y < 0:
+ continue
+ self.dfs(board, new_x, new_y, visited)
+
+```
+
+### JavaScript
+```JavaScript
+/**
+ * @description 深度搜索优先
+ * @param {character[][]} board
+ * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
+ */
+function solve(board) {
+ const dir = [[-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, -1], [0, 1]];
+ const [rowSize, colSize] = [board.length, board[0].length];
+
+ function dfs(board, x, y) {
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ const nextX = dir[i][0] + x;
+ const nextY = dir[i][1] + y;
+ if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (board[nextX][nextY] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ if (board[i][0] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, i, 0);
+ }
+ if (board[i][colSize - 1] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, i, colSize - 1);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < colSize - 1; i++) {
+ if (board[0][i] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, 0, i);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][i] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, rowSize - 1, i);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
+ if (board[i][k] === 'A') {
+ board[i][k] = 'O';
+ } else if (board[i][k] === 'O') {
+ board[i][k] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+/**
+ * @description 广度搜索优先
+ * @param {character[][]} board
+ * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
+ */
+function solve(board) {
+ const dir = [[-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, -1], [0, 1]];
+ const [rowSize, colSize] = [board.length, board[0].length];
+
+ function bfs(board, x, y) {
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ const stack = [y, x];
+
+ while (stack.length !== 0) {
+ const top = [stack.pop(), stack.pop()];
+ for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ const nextX = dir[i][0] + top[0];
+ const nextY = dir[i][1] + top[1];
+
+ if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
+ continue;
+ }
+
+ if (board[nextX][nextY] === 'O') {
+ board[nextX][nextY] = 'A';
+ stack.push(nextY, nextX);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ const nextX = dir[i][0] + x;
+ const nextY = dir[i][1] + y;
+ if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (board[nextX][nextY] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ if (board[i][0] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, i, 0);
+ }
+ if (board[i][colSize - 1] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, i, colSize - 1);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < colSize - 1; i++) {
+ if (board[0][i] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, 0, i);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][i] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, rowSize - 1, i);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
+ if (board[i][k] === 'A') {
+ board[i][k] = 'O';
+ } else if (board[i][k] === 'O') {
+ board[i][k] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Go
+
+dfs:
+
+```go
+var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}}
+
+func solve(board [][]byte) {
+ rows, cols := len(board), len(board[0])
+ // 列
+ for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
+ if board[i][0] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, i, 0)
+ }
+ if board[i][cols-1] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, i, cols-1)
+ }
+ }
+ // 行
+ for j := 0; j < cols; j++ {
+ if board[0][j] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, 0, j)
+ }
+ if board[rows-1][j] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, rows-1, j)
+ }
+ }
+
+ for _, r := range board {
+ for j, c := range r {
+ if c == 'A' {
+ r[j] = 'O'
+ continue
+ }
+ if c == 'O' {
+ r[j] = 'X'
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func dfs(board [][]byte, i, j int) {
+ board[i][j] = 'A'
+ for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
+ x, y := i+d[0], j+d[1]
+ if x < 0 || x >= len(board) || y < 0 || y >= len(board[0]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if board[x][y] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, x, y)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+bfs:
+
+```go
+var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}}
+
+func solve(board [][]byte) {
+ rows, cols := len(board), len(board[0])
+ // 列
+ for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
+ if board[i][0] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, i, 0)
+ }
+ if board[i][cols-1] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, i, cols-1)
+ }
+ }
+ // 行
+ for j := 0; j < cols; j++ {
+ if board[0][j] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, 0, j)
+ }
+ if board[rows-1][j] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, rows-1, j)
+ }
+ }
+
+ for _, r := range board {
+ for j, c := range r {
+ if c == 'A' {
+ r[j] = 'O'
+ continue
+ }
+ if c == 'O' {
+ r[j] = 'X'
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func bfs(board [][]byte, i, j int) {
+ queue := [][]int{{i, j}}
+ board[i][j] = 'A'
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ cur := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
+ x, y := cur[0]+d[0], cur[1]+d[1]
+ if x < 0 || x >= len(board) || y < 0 || y >= len(board[0]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if board[x][y] == 'O' {
+ board[x][y] = 'A'
+ queue = append(queue, []int{x, y})
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Rust
+
+bfs:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ const DIRECTIONS: [(isize, isize); 4] = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)];
+ pub fn solve(board: &mut Vec
-
+### Java
+
+```Java
+// 广度优先遍历
+// 使用 visited 数组进行标记
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ // rowSize:行的长度,colSize:列的长度
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
+ Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ // 从左侧边,和右侧边遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O') {
+ visited[row][0] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, 0});
+ }
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O') {
+ visited[row][colSize - 1] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1});
+ }
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O') {
+ visited[0][col] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{0, col});
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O') {
+ visited[rowSize - 1][col] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col});
+ }
+ }
+ // 广度优先遍历,把没有被 'X' 包围的 'O' 进行标记
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int[] current = queue.poll();
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int row = current[0] + pos[0], col = current[1] + pos[1];
+ // 如果范围越界、位置已被访问过、该位置的值不是 'O',就直接跳过
+ if (row < 0 || row >= rowSize || col < 0 || col >= colSize) continue;
+ if (visited[row][col] || board[row][col] != 'O') continue;
+ visited[row][col] = true;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把没有被标记的 'O' 修改成 'X'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'O' && !visited[row][col]) board[row][col] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```Java
+// 广度优先遍历
+// 直接修改 board 的值为其他特殊值
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ // rowSize:行的长度,colSize:列的长度
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
+ // 从左侧边,和右侧边遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, 0});
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1});
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{0, col});
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O')
+ queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col});
+ }
+ // 广度优先遍历,把没有被 'X' 包围的 'O' 修改成特殊值
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ int[] current = queue.poll();
+ board[current[0]][current[1]] = 'A';
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int row = current[0] + pos[0], col = current[1] + pos[1];
+ // 如果范围越界、该位置的值不是 'O',就直接跳过
+ if (row < 0 || row >= rowSize || col < 0 || col >= colSize) continue;
+ if (board[row][col] != 'O') continue;
+ queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把 'O' 修改成 'X',特殊值修改成 'O'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'A') board[row][col] = 'O';
+ else if (board[row][col] == 'O') board[row][col] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```Java
+//BFS(使用helper function)
+class Solution {
+ int[][] dir ={{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ if(board[i][0] == 'O') bfs(board, i, 0);
+ if(board[i][board[0].length - 1] == 'O') bfs(board, i, board[0].length - 1);
+ }
+
+ for(int j = 1 ; j < board[0].length - 1; j++){
+ if(board[0][j] == 'O') bfs(board, 0, j);
+ if(board[board.length - 1][j] == 'O') bfs(board, board.length - 1, j);
+ }
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){
+ if(board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j] = 'X';
+ if(board[i][j] == 'A') board[i][j] = 'O';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ private void bfs(char[][] board, int x, int y){
+ Queue que = new LinkedList<>();
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ que.offer(x);
+ que.offer(y);
+
+ while(!que.isEmpty()){
+ int currX = que.poll();
+ int currY = que.poll();
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
+ int nextX = currX + dir[i][0];
+ int nextY = currY + dir[i][1];
+
+ if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= board.length || nextY >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ if(board[nextX][nextY] == 'X'|| board[nextX][nextY] == 'A')
+ continue;
+ bfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+```Java
+// 深度优先遍历
+// 使用 visited 数组进行标记
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void dfs(char[][] board, int row, int col, boolean[][] visited) {
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int nextRow = row + pos[0], nextCol = col + pos[1];
+ // 位置越界
+ if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= board.length || nextCol < 0 || nextCol >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ // 位置已被访问过、新位置值不是 'O'
+ if (visited[nextRow][nextCol] || board[nextRow][nextCol] != 'O') continue;
+ visited[nextRow][nextCol] = true;
+ dfs(board, nextRow, nextCol, visited);
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
+ // 从左侧遍、右侧遍遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O' && !visited[row][0]) {
+ visited[row][0] = true;
+ dfs(board, row, 0, visited);
+ }
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O' && !visited[row][colSize - 1]) {
+ visited[row][colSize - 1] = true;
+ dfs(board, row, colSize - 1, visited);
+ }
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O' && !visited[0][col]) {
+ visited[0][col] = true;
+ dfs(board, 0, col, visited);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O' && !visited[rowSize - 1][col]) {
+ visited[rowSize - 1][col] = true;
+ dfs(board, rowSize - 1, col, visited);
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把没有被标记的 'O' 修改成 'X'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'O' && !visited[row][col]) board[row][col] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```Java
+// 深度优先遍历
+// // 直接修改 board 的值为其他特殊值
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void dfs(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
+ for (int[] pos: position) {
+ int nextRow = row + pos[0], nextCol = col + pos[1];
+ // 位置越界
+ if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= board.length || nextCol < 0 || nextCol >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ // 新位置值不是 'O'
+ if (board[nextRow][nextCol] != 'O') continue;
+ board[nextRow][nextCol] = 'A'; // 修改为特殊值
+ dfs(board, nextRow, nextCol);
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ // 从左侧遍、右侧遍遍历
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ if (board[row][0] == 'O') {
+ board[row][0] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, row, 0);
+ }
+ if (board[row][colSize - 1] == 'O') {
+ board[row][colSize - 1] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, row, colSize - 1);
+ }
+ }
+ // 从上边和下边遍历,在对左侧边和右侧边遍历时我们已经遍历了矩阵的四个角
+ // 所以在遍历上边和下边时可以不用遍历四个角
+ for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
+ if (board[0][col] == 'O') {
+ board[0][col] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, 0, col);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][col] == 'O') {
+ board[rowSize - 1][col] = 'A';
+ dfs(board, rowSize - 1, col);
+ }
+ }
+ // 遍历数组,把 'O' 修改成 'X',特殊值修改成 'O'
+ for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
+ for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
+ if (board[row][col] == 'O') board[row][col] = 'X';
+ else if (board[row][col] == 'A') board[row][col] = 'O';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+```java
+//DFS(有終止條件)
+class Solution {
+ int[][] dir ={{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ if(board[i][0] == 'O') dfs(board, i, 0);
+ if(board[i][board[0].length - 1] == 'O') dfs(board, i, board[0].length - 1);
+ }
+
+ for(int j = 1 ; j < board[0].length - 1; j++){
+ if(board[0][j] == 'O') dfs(board, 0, j);
+ if(board[board.length - 1][j] == 'O') dfs(board, board.length - 1, j);
+ }
+
+ for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
+ for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){
+ if(board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j] = 'X';
+ if(board[i][j] == 'A') board[i][j] = 'O';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void dfs(char[][] board, int x, int y){
+ if(board[x][y] == 'X'|| board[x][y] == 'A')
+ return;
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
+ int nextX = x + dir[i][0];
+ int nextY = y + dir[i][1];
+
+ if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= board.length || nextY >= board[0].length)
+ continue;
+ // if(board[nextX][nextY] == 'X'|| board[nextX][nextY] == 'A')
+ // continue;
+ dfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+### Python3
+
+```Python
+// 深度优先遍历
+class Solution:
+ dir_list = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
+ def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
+ """
+ Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
+ """
+ row_size = len(board)
+ column_size = len(board[0])
+ visited = [[False] * column_size for _ in range(row_size)]
+ # 从边缘开始,将边缘相连的O改成A。然后遍历所有,将A改成O,O改成X
+ # 第一行和最后一行
+ for i in range(column_size):
+ if board[0][i] == "O" and not visited[0][i]:
+ self.dfs(board, 0, i, visited)
+ if board[row_size-1][i] == "O" and not visited[row_size-1][i]:
+ self.dfs(board, row_size-1, i, visited)
+
+ # 第一列和最后一列
+ for i in range(1, row_size-1):
+ if board[i][0] == "O" and not visited[i][0]:
+ self.dfs(board, i, 0, visited)
+ if board[i][column_size-1] == "O" and not visited[i][column_size-1]:
+ self.dfs(board, i, column_size-1, visited)
+
+ for i in range(row_size):
+ for j in range(column_size):
+ if board[i][j] == "A":
+ board[i][j] = "O"
+ elif board[i][j] == "O":
+ board[i][j] = "X"
+
+
+ def dfs(self, board, x, y, visited):
+ if visited[x][y] or board[x][y] == "X":
+ return
+ visited[x][y] = True
+ board[x][y] = "A"
+ for i in range(4):
+ new_x = x + self.dir_list[i][0]
+ new_y = y + self.dir_list[i][1]
+ if new_x >= len(board) or new_y >= len(board[0]) or new_x < 0 or new_y < 0:
+ continue
+ self.dfs(board, new_x, new_y, visited)
+
+```
+
+### JavaScript
+```JavaScript
+/**
+ * @description 深度搜索优先
+ * @param {character[][]} board
+ * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
+ */
+function solve(board) {
+ const dir = [[-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, -1], [0, 1]];
+ const [rowSize, colSize] = [board.length, board[0].length];
+
+ function dfs(board, x, y) {
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ const nextX = dir[i][0] + x;
+ const nextY = dir[i][1] + y;
+ if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (board[nextX][nextY] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ if (board[i][0] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, i, 0);
+ }
+ if (board[i][colSize - 1] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, i, colSize - 1);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < colSize - 1; i++) {
+ if (board[0][i] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, 0, i);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][i] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, rowSize - 1, i);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
+ if (board[i][k] === 'A') {
+ board[i][k] = 'O';
+ } else if (board[i][k] === 'O') {
+ board[i][k] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+/**
+ * @description 广度搜索优先
+ * @param {character[][]} board
+ * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
+ */
+function solve(board) {
+ const dir = [[-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, -1], [0, 1]];
+ const [rowSize, colSize] = [board.length, board[0].length];
+
+ function bfs(board, x, y) {
+ board[x][y] = 'A';
+ const stack = [y, x];
+
+ while (stack.length !== 0) {
+ const top = [stack.pop(), stack.pop()];
+ for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ const nextX = dir[i][0] + top[0];
+ const nextY = dir[i][1] + top[1];
+
+ if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
+ continue;
+ }
+
+ if (board[nextX][nextY] === 'O') {
+ board[nextX][nextY] = 'A';
+ stack.push(nextY, nextX);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ const nextX = dir[i][0] + x;
+ const nextY = dir[i][1] + y;
+ if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= rowSize || nextY < 0 || nextY >= colSize) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (board[nextX][nextY] === 'O') {
+ dfs(board, nextX, nextY);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ if (board[i][0] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, i, 0);
+ }
+ if (board[i][colSize - 1] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, i, colSize - 1);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 1; i < colSize - 1; i++) {
+ if (board[0][i] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, 0, i);
+ }
+ if (board[rowSize - 1][i] === 'O') {
+ bfs(board, rowSize - 1, i);
+ }
+ }
+
+ for (let i = 0; i < rowSize; i++) {
+ for (let k = 0; k < colSize; k++) {
+ if (board[i][k] === 'A') {
+ board[i][k] = 'O';
+ } else if (board[i][k] === 'O') {
+ board[i][k] = 'X';
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Go
+
+dfs:
+
+```go
+var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}}
+
+func solve(board [][]byte) {
+ rows, cols := len(board), len(board[0])
+ // 列
+ for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
+ if board[i][0] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, i, 0)
+ }
+ if board[i][cols-1] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, i, cols-1)
+ }
+ }
+ // 行
+ for j := 0; j < cols; j++ {
+ if board[0][j] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, 0, j)
+ }
+ if board[rows-1][j] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, rows-1, j)
+ }
+ }
+
+ for _, r := range board {
+ for j, c := range r {
+ if c == 'A' {
+ r[j] = 'O'
+ continue
+ }
+ if c == 'O' {
+ r[j] = 'X'
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func dfs(board [][]byte, i, j int) {
+ board[i][j] = 'A'
+ for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
+ x, y := i+d[0], j+d[1]
+ if x < 0 || x >= len(board) || y < 0 || y >= len(board[0]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if board[x][y] == 'O' {
+ dfs(board, x, y)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+bfs:
+
+```go
+var DIRECTIONS = [4][2]int{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}}
+
+func solve(board [][]byte) {
+ rows, cols := len(board), len(board[0])
+ // 列
+ for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
+ if board[i][0] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, i, 0)
+ }
+ if board[i][cols-1] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, i, cols-1)
+ }
+ }
+ // 行
+ for j := 0; j < cols; j++ {
+ if board[0][j] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, 0, j)
+ }
+ if board[rows-1][j] == 'O' {
+ bfs(board, rows-1, j)
+ }
+ }
+
+ for _, r := range board {
+ for j, c := range r {
+ if c == 'A' {
+ r[j] = 'O'
+ continue
+ }
+ if c == 'O' {
+ r[j] = 'X'
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func bfs(board [][]byte, i, j int) {
+ queue := [][]int{{i, j}}
+ board[i][j] = 'A'
+ for len(queue) > 0 {
+ cur := queue[0]
+ queue = queue[1:]
+ for _, d := range DIRECTIONS {
+ x, y := cur[0]+d[0], cur[1]+d[1]
+ if x < 0 || x >= len(board) || y < 0 || y >= len(board[0]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if board[x][y] == 'O' {
+ board[x][y] = 'A'
+ queue = append(queue, []int{x, y})
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Rust
+
+bfs:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ const DIRECTIONS: [(isize, isize); 4] = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)];
+ pub fn solve(board: &mut Vec
 -
+ 🌍 海外英文版 ·
+ 🌍🇸 英文仓库 ·
+ 🇨🇳 国内在线阅读 ·
+ 🇨 Gitee 同步
-
+ 🌍 海外英文版 ·
+ 🌍🇸 英文仓库 ·
+ 🇨🇳 国内在线阅读 ·
+ 🇨 Gitee 同步
 -
+ 🌍 海外英文版 ·
+ 🌍🇸 英文仓库 ·
+ 🇨🇳 国内在线阅读 ·
+ 🇨 Gitee 同步
-
+ 🌍 海外英文版 ·
+ 🌍🇸 英文仓库 ·
+ 🇨🇳 国内在线阅读 ·
+ 🇨 Gitee 同步

 +
+
+
+ +
+题目分类大纲如下:
+
+
+题目分类大纲如下:
+ 1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
3. [二叉树:二叉树的迭代遍历](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
4. [二叉树:二叉树的统一迭代法](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
-5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
-6. [二叉树:226.翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
+5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
+6. [二叉树:226.翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
7. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20200927二叉树周末总结.md)
8. [二叉树:101.对称二叉树](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
9. [二叉树:104.二叉树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
@@ -214,13 +210,12 @@
12. [二叉树:110.平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
13. [二叉树:257.二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
16. [二叉树:404.左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
17. [二叉树:513.找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:112.路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
19. [二叉树:106.构造二叉树](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
20. [二叉树:654.最大二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
-21. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
+21. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
22. [二叉树:617.合并两个二叉树](./problems/0617.合并二叉树.md)
23. [二叉树:700.二叉搜索树登场!](./problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md)
24. [二叉树:98.验证二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
@@ -235,12 +230,13 @@
33. [二叉树:108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](./problems/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.md)
34. [二叉树:538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树](./problems/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.md)
35. [二叉树:总结篇!(需要掌握的二叉树技能都在这里了)](./problems/二叉树总结篇.md)
+
1. [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](./problems/二叉树理论基础.md)
2. [二叉树:二叉树的递归遍历](./problems/二叉树的递归遍历.md)
3. [二叉树:二叉树的迭代遍历](./problems/二叉树的迭代遍历.md)
4. [二叉树:二叉树的统一迭代法](./problems/二叉树的统一迭代法.md)
-5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
-6. [二叉树:226.翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
+5. [二叉树:二叉树的层序遍历](./problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md)
+6. [二叉树:226.翻转二叉树](./problems/0226.翻转二叉树.md)
7. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20200927二叉树周末总结.md)
8. [二叉树:101.对称二叉树](./problems/0101.对称二叉树.md)
9. [二叉树:104.二叉树的最大深度](./problems/0104.二叉树的最大深度.md)
@@ -214,13 +210,12 @@
12. [二叉树:110.平衡二叉树](./problems/0110.平衡二叉树.md)
13. [二叉树:257.二叉树的所有路径](./problems/0257.二叉树的所有路径.md)
14. [本周总结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201003二叉树周末总结.md)
-15. [二叉树:二叉树中递归带着回溯](./problems/二叉树中递归带着回溯.md)
16. [二叉树:404.左叶子之和](./problems/0404.左叶子之和.md)
17. [二叉树:513.找树左下角的值](./problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md)
18. [二叉树:112.路径总和](./problems/0112.路径总和.md)
19. [二叉树:106.构造二叉树](./problems/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md)
20. [二叉树:654.最大二叉树](./problems/0654.最大二叉树.md)
-21. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
+21. [本周小结!(二叉树)](./problems/周总结/20201010二叉树周末总结.md)
22. [二叉树:617.合并两个二叉树](./problems/0617.合并二叉树.md)
23. [二叉树:700.二叉搜索树登场!](./problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md)
24. [二叉树:98.验证二叉搜索树](./problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md)
@@ -235,12 +230,13 @@
33. [二叉树:108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](./problems/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.md)
34. [二叉树:538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树](./problems/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.md)
35. [二叉树:总结篇!(需要掌握的二叉树技能都在这里了)](./problems/二叉树总结篇.md)
+ +
+ 1. [关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/回溯算法理论基础.md)
2. [回溯算法:77.组合](./problems/0077.组合.md)
@@ -264,13 +260,13 @@
20. [回溯算法:51.N皇后](./problems/0051.N皇后.md)
21. [回溯算法:37.解数独](./problems/0037.解数独.md)
22. [回溯算法总结篇](./problems/回溯总结.md)
+
1. [关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/回溯算法理论基础.md)
2. [回溯算法:77.组合](./problems/0077.组合.md)
@@ -264,13 +260,13 @@
20. [回溯算法:51.N皇后](./problems/0051.N皇后.md)
21. [回溯算法:37.解数独](./problems/0037.解数独.md)
22. [回溯算法总结篇](./problems/回溯总结.md)
+ +
+ 1. [关于贪心算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/贪心算法理论基础.md)
2. [贪心算法:455.分发饼干](./problems/0455.分发饼干.md)
@@ -296,12 +292,14 @@
22. [贪心算法:738.单调递增的数字](./problems/0738.单调递增的数字.md)
23. [贪心算法:968.监控二叉树](./problems/0968.监控二叉树.md)
24. [贪心算法:总结篇!(每逢总结必经典)](./problems/贪心算法总结篇.md)
+
1. [关于贪心算法,你该了解这些!](./problems/贪心算法理论基础.md)
2. [贪心算法:455.分发饼干](./problems/0455.分发饼干.md)
@@ -296,12 +292,14 @@
22. [贪心算法:738.单调递增的数字](./problems/0738.单调递增的数字.md)
23. [贪心算法:968.监控二叉树](./problems/0968.监控二叉树.md)
24. [贪心算法:总结篇!(每逢总结必经典)](./problems/贪心算法总结篇.md)
+ +
+ 1. [关于动态规划,你该了解这些!](./problems/动态规划理论基础.md)
2. [动态规划:509.斐波那契数](./problems/0509.斐波那契数.md)
3. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯](./problems/0070.爬楼梯.md)
@@ -315,27 +313,28 @@
背包问题系列:
-
1. [关于动态规划,你该了解这些!](./problems/动态规划理论基础.md)
2. [动态规划:509.斐波那契数](./problems/0509.斐波那契数.md)
3. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯](./problems/0070.爬楼梯.md)
@@ -315,27 +313,28 @@
背包问题系列:
- +
+ -11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
-12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(滚动数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
+11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
+12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
13. [动态规划:416.分割等和子集](./problems/0416.分割等和子集.md)
14. [动态规划:1049.最后一块石头的重量II](./problems/1049.最后一块石头的重量II.md)
15. [本周小结!(动态规划系列三)](./problems/周总结/20210121动规周末总结.md)
16. [动态规划:494.目标和](./problems/0494.目标和.md)
-17. [动态规划:474.一和零](./problems/0474.一和零.md)
-18. [动态规划:完全背包总结篇](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
-19. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
-20. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
-21. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
-22. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
-23. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
-24. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
-25. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
-26. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
-27. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
-28. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
+17. [动态规划:474.一和零](./problems/0474.一和零.md)
+18. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
+19. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题完全背包一维.md)
+20. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
+21. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
+22. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
+23. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
+24. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
+25. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
+26. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
+27. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
+28. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
+29. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
打家劫舍系列:
@@ -345,7 +344,7 @@
股票系列:
-
-11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
-12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(滚动数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
+11. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
+12. [动态规划:01背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
13. [动态规划:416.分割等和子集](./problems/0416.分割等和子集.md)
14. [动态规划:1049.最后一块石头的重量II](./problems/1049.最后一块石头的重量II.md)
15. [本周小结!(动态规划系列三)](./problems/周总结/20210121动规周末总结.md)
16. [动态规划:494.目标和](./problems/0494.目标和.md)
-17. [动态规划:474.一和零](./problems/0474.一和零.md)
-18. [动态规划:完全背包总结篇](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
-19. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
-20. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
-21. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
-22. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
-23. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
-24. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
-25. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
-26. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
-27. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
-28. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
+17. [动态规划:474.一和零](./problems/0474.一和零.md)
+18. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(二维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题理论基础完全背包.md)
+19. [动态规划:完全背包理论基础(一维dp数组)](./problems/背包问题完全背包一维.md)
+20. [动态规划:518.零钱兑换II](./problems/0518.零钱兑换II.md)
+21. [本周小结!(动态规划系列四)](./problems/周总结/20210128动规周末总结.md)
+22. [动态规划:377.组合总和Ⅳ](./problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md)
+23. [动态规划:70.爬楼梯(完全背包版本)](./problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md)
+24. [动态规划:322.零钱兑换](./problems/0322.零钱兑换.md)
+25. [动态规划:279.完全平方数](./problems/0279.完全平方数.md)
+26. [本周小结!(动态规划系列五)](./problems/周总结/20210204动规周末总结.md)
+27. [动态规划:139.单词拆分](./problems/0139.单词拆分.md)
+28. [动态规划:多重背包理论基础](./problems/背包问题理论基础多重背包.md)
+29. [背包问题总结篇](./problems/背包总结篇.md)
打家劫舍系列:
@@ -345,7 +344,7 @@
股票系列:
- +
+ 32. [动态规划:121.买卖股票的最佳时机](./problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md)
@@ -358,9 +357,9 @@
39. [动态规划:714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费](./problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费(动态规划).md)
40. [动态规划:股票系列总结篇](./problems/动态规划-股票问题总结篇.md)
-子序列系列:
+子序列系列:
-
32. [动态规划:121.买卖股票的最佳时机](./problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md)
@@ -358,9 +357,9 @@
39. [动态规划:714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费](./problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费(动态规划).md)
40. [动态规划:股票系列总结篇](./problems/动态规划-股票问题总结篇.md)
-子序列系列:
+子序列系列:
- +
+ 41. [动态规划:300.最长递增子序列](./problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md)
@@ -377,138 +376,103 @@
52. [动态规划:647.回文子串](./problems/0647.回文子串.md)
53. [动态规划:516.最长回文子序列](./problems/0516.最长回文子序列.md)
54. [动态规划总结篇](./problems/动态规划总结篇.md)
+
41. [动态规划:300.最长递增子序列](./problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md)
@@ -377,138 +376,103 @@
52. [动态规划:647.回文子串](./problems/0647.回文子串.md)
53. [动态规划:516.最长回文子序列](./problems/0516.最长回文子序列.md)
54. [动态规划总结篇](./problems/动态规划总结篇.md)
+
 +
+
 -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4d48f18458..05dd610a72
--- "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md" "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4d48f18458..05dd610a72
--- "a/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
+++ "b/problems/0005.\346\234\200\351\225\277\345\233\236\346\226\207\345\255\220\344\270\262.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6675e4088a..e2cb3f4612
--- "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,9 @@
-
-
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 6675e4088a..e2cb3f4612
--- "a/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0015.\344\270\211\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,9 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index df038806a5..6dcf9ee690
--- "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index df038806a5..6dcf9ee690
--- "a/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0017.\347\224\265\350\257\235\345\217\267\347\240\201\347\232\204\345\255\227\346\257\215\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8e87fcbd2f..bf7d3bd4ee
--- "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8e87fcbd2f..bf7d3bd4ee
--- "a/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0018.\345\233\233\346\225\260\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+def four_sum(nums, target)
+ #结果集
+ result = []
+ nums = nums.sort!
+
+ for i in 0..nums.size - 1
+ return result if i > 0 && nums[i] > target && nums[i] >= 0
+ #对a进行去重
+ next if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]
+
+ for j in i + 1..nums.size - 1
+ break if nums[i] + nums[j] > target && nums[i] + nums[j] >= 0
+ #对b进行去重
+ next if j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]
+ left = j + 1
+ right = nums.size - 1
+ while left < right
+ sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]
+ if sum > target
+ right -= 1
+ elsif sum < target
+ left += 1
+ else
+ result << [nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]]
+
+ #对c进行去重
+ while left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]
+ left += 1
+ end
+
+ #对d进行去重
+ while left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]
+ right -= 1
+ end
+
+ right -= 1
+ left += 1
+ end
+ end
+ end
+ end
+
+ return result
+end
+```
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0641b5f08..08f602c1c1
--- "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,11 @@
-
-
+### Ruby:
+
+```ruby
+def four_sum(nums, target)
+ #结果集
+ result = []
+ nums = nums.sort!
+
+ for i in 0..nums.size - 1
+ return result if i > 0 && nums[i] > target && nums[i] >= 0
+ #对a进行去重
+ next if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]
+
+ for j in i + 1..nums.size - 1
+ break if nums[i] + nums[j] > target && nums[i] + nums[j] >= 0
+ #对b进行去重
+ next if j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]
+ left = j + 1
+ right = nums.size - 1
+ while left < right
+ sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]
+ if sum > target
+ right -= 1
+ elsif sum < target
+ left += 1
+ else
+ result << [nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]]
+
+ #对c进行去重
+ while left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]
+ left += 1
+ end
+
+ #对d进行去重
+ while left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]
+ right -= 1
+ end
+
+ right -= 1
+ left += 1
+ end
+ end
+ end
+ end
+
+ return result
+end
+```
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0641b5f08..08f602c1c1
--- "a/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0019.\345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\347\232\204\345\200\222\346\225\260\347\254\254N\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,11 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ * fast首先走n + 1步 ,为什么是n+1呢,因为只有这样同时移动的时候slow才能指向删除节点的上一个节点(方便做删除操作),如图:
-
* fast首先走n + 1步 ,为什么是n+1呢,因为只有这样同时移动的时候slow才能指向删除节点的上一个节点(方便做删除操作),如图:
- +
+ * fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向末尾,如题:
-
* fast和slow同时移动,直到fast指向末尾,如题:
- -
+
-
+ +//图片中有错别词:应该将“只到”改为“直到”
* 删除slow指向的下一个节点,如图:
-
+//图片中有错别词:应该将“只到”改为“直到”
* 删除slow指向的下一个节点,如图:
- +
+ 此时不难写出如下C++代码:
@@ -79,67 +82,115 @@ public:
// ListNode *tmp = slow->next; C++释放内存的逻辑
// slow->next = tmp->next;
- // delete nth;
+ // delete tmp;
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(1)
+
## 其他语言版本
-java:
+### Java:
```java
-public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n){
- ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
- dummyNode.next = head;
-
- ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
- ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ //新建一个虚拟头节点指向head
+ ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
+ dummyNode.next = head;
+ //快慢指针指向虚拟头节点
+ ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
+ ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+
+ // 只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ }
+ while (fastIndex != null) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
+ }
- //只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
- for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ // 此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
+ // 具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
+ // 检查 slowIndex.next 是否为 null,以避免空指针异常
+ if (slowIndex.next != null) {
+ slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummyNode.next;
}
+}
+```
- while (fastIndex.next != null){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
- slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
- }
- //此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
- //具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
- slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
- return dummyNode.next;
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ // 创建一个新的哑节点,指向原链表头
+ ListNode s = new ListNode(-1, head);
+ // 递归调用remove方法,从哑节点开始进行删除操作
+ remove(s, n);
+ // 返回新链表的头(去掉可能的哑节点)
+ return s.next;
+ }
+
+ public int remove(ListNode p, int n) {
+ // 递归结束条件:如果当前节点为空,返回0
+ if (p == null) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // 递归深入到下一个节点
+ int net = remove(p.next, n);
+ // 如果当前节点是倒数第n个节点,进行删除操作
+ if (net == n) {
+ p.next = p.next.next;
+ }
+ // 返回当前节点的总深度
+ return net + 1;
+ }
}
```
-Python:
+
+### Python:
+
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
+
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
- head_dummy = ListNode()
- head_dummy.next = head
-
- slow, fast = head_dummy, head_dummy
- while(n!=0): #fast先往前走n步
+ # 创建一个虚拟节点,并将其下一个指针设置为链表的头部
+ dummy_head = ListNode(0, head)
+
+ # 创建两个指针,慢指针和快指针,并将它们初始化为虚拟节点
+ slow = fast = dummy_head
+
+ # 快指针比慢指针快 n+1 步
+ for i in range(n+1):
fast = fast.next
- n -= 1
- while(fast.next!=None):
+
+ # 移动两个指针,直到快速指针到达链表的末尾
+ while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
- #fast 走到结尾后,slow的下一个节点为倒数第N个节点
- slow.next = slow.next.next #删除
- return head_dummy.next
+
+ # 通过更新第 (n-1) 个节点的 next 指针删除第 n 个节点
+ slow.next = slow.next.next
+
+ return dummy_head.next
+
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
@@ -149,24 +200,21 @@ Go:
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
- dummyHead := &ListNode{}
- dummyHead.Next = head
- cur := head
- prev := dummyHead
- i := 1
- for cur != nil {
- cur = cur.Next
- if i > n {
- prev = prev.Next
- }
- i++
- }
- prev.Next = prev.Next.Next
- return dummyHead.Next
+ dummyNode := &ListNode{0, head}
+ fast, slow := dummyNode, dummyNode
+ for i := 0; i <= n; i++ { // 注意<=,否则快指针为空时,慢指针正好在倒数第n个上面
+ fast = fast.Next
+ }
+ for fast != nil {
+ fast = fast.Next
+ slow = slow.Next
+ }
+ slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
+ return dummyNode.Next
}
```
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
```js
/**
@@ -174,19 +222,21 @@ JavaScript:
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
-var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
- let ret = new ListNode(0, head),
- slow = fast = ret;
- while(n--) fast = fast.next;
- while (fast.next !== null) {
- fast = fast.next;
- slow = slow.next
- };
- slow.next = slow.next.next;
- return ret.next;
+var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
+ // 创建哨兵节点,简化解题逻辑
+ let dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
+ let fast = dummyHead;
+ let slow = dummyHead;
+ while (n--) fast = fast.next;
+ while (fast.next !== null) {
+ slow = slow.next;
+ fast = fast.next;
+ }
+ slow.next = slow.next.next;
+ return dummyHead.next;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
版本一(快慢指针法):
@@ -251,7 +301,7 @@ function removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode | null, n: number): ListNode | null {
};
```
-Kotlin:
+### Kotlin:
```Kotlin
fun removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode?, n: Int): ListNode? {
@@ -272,7 +322,8 @@ fun removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode?, n: Int): ListNode? {
}
```
-Swift:
+### Swift:
+
```swift
func removeNthFromEnd(_ head: ListNode?, _ n: Int) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil {
@@ -297,8 +348,8 @@ func removeNthFromEnd(_ head: ListNode?, _ n: Int) -> ListNode? {
}
```
+### PHP:
-PHP:
```php
function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
// 设置虚拟头节点
@@ -320,7 +371,8 @@ function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
}
```
-Scala:
+### Scala:
+
```scala
object Solution {
def removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode, n: Int): ListNode = {
@@ -344,7 +396,8 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-Rust:
+### Rust:
+
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option
此时不难写出如下C++代码:
@@ -79,67 +82,115 @@ public:
// ListNode *tmp = slow->next; C++释放内存的逻辑
// slow->next = tmp->next;
- // delete nth;
+ // delete tmp;
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
```
+* 时间复杂度: O(n)
+* 空间复杂度: O(1)
+
## 其他语言版本
-java:
+### Java:
```java
-public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n){
- ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
- dummyNode.next = head;
-
- ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
- ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ //新建一个虚拟头节点指向head
+ ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
+ dummyNode.next = head;
+ //快慢指针指向虚拟头节点
+ ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
+ ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
+
+ // 只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
+ for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ }
+ while (fastIndex != null) {
+ fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
+ }
- //只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
- for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
+ // 此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
+ // 具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
+ // 检查 slowIndex.next 是否为 null,以避免空指针异常
+ if (slowIndex.next != null) {
+ slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummyNode.next;
}
+}
+```
- while (fastIndex.next != null){
- fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
- slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
- }
- //此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
- //具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
- slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
- return dummyNode.next;
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ // 创建一个新的哑节点,指向原链表头
+ ListNode s = new ListNode(-1, head);
+ // 递归调用remove方法,从哑节点开始进行删除操作
+ remove(s, n);
+ // 返回新链表的头(去掉可能的哑节点)
+ return s.next;
+ }
+
+ public int remove(ListNode p, int n) {
+ // 递归结束条件:如果当前节点为空,返回0
+ if (p == null) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ // 递归深入到下一个节点
+ int net = remove(p.next, n);
+ // 如果当前节点是倒数第n个节点,进行删除操作
+ if (net == n) {
+ p.next = p.next.next;
+ }
+ // 返回当前节点的总深度
+ return net + 1;
+ }
}
```
-Python:
+
+### Python:
+
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
+
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
- head_dummy = ListNode()
- head_dummy.next = head
-
- slow, fast = head_dummy, head_dummy
- while(n!=0): #fast先往前走n步
+ # 创建一个虚拟节点,并将其下一个指针设置为链表的头部
+ dummy_head = ListNode(0, head)
+
+ # 创建两个指针,慢指针和快指针,并将它们初始化为虚拟节点
+ slow = fast = dummy_head
+
+ # 快指针比慢指针快 n+1 步
+ for i in range(n+1):
fast = fast.next
- n -= 1
- while(fast.next!=None):
+
+ # 移动两个指针,直到快速指针到达链表的末尾
+ while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
- #fast 走到结尾后,slow的下一个节点为倒数第N个节点
- slow.next = slow.next.next #删除
- return head_dummy.next
+
+ # 通过更新第 (n-1) 个节点的 next 指针删除第 n 个节点
+ slow.next = slow.next.next
+
+ return dummy_head.next
+
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
@@ -149,24 +200,21 @@ Go:
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
- dummyHead := &ListNode{}
- dummyHead.Next = head
- cur := head
- prev := dummyHead
- i := 1
- for cur != nil {
- cur = cur.Next
- if i > n {
- prev = prev.Next
- }
- i++
- }
- prev.Next = prev.Next.Next
- return dummyHead.Next
+ dummyNode := &ListNode{0, head}
+ fast, slow := dummyNode, dummyNode
+ for i := 0; i <= n; i++ { // 注意<=,否则快指针为空时,慢指针正好在倒数第n个上面
+ fast = fast.Next
+ }
+ for fast != nil {
+ fast = fast.Next
+ slow = slow.Next
+ }
+ slow.Next = slow.Next.Next
+ return dummyNode.Next
}
```
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
```js
/**
@@ -174,19 +222,21 @@ JavaScript:
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
-var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
- let ret = new ListNode(0, head),
- slow = fast = ret;
- while(n--) fast = fast.next;
- while (fast.next !== null) {
- fast = fast.next;
- slow = slow.next
- };
- slow.next = slow.next.next;
- return ret.next;
+var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
+ // 创建哨兵节点,简化解题逻辑
+ let dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
+ let fast = dummyHead;
+ let slow = dummyHead;
+ while (n--) fast = fast.next;
+ while (fast.next !== null) {
+ slow = slow.next;
+ fast = fast.next;
+ }
+ slow.next = slow.next.next;
+ return dummyHead.next;
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
版本一(快慢指针法):
@@ -251,7 +301,7 @@ function removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode | null, n: number): ListNode | null {
};
```
-Kotlin:
+### Kotlin:
```Kotlin
fun removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode?, n: Int): ListNode? {
@@ -272,7 +322,8 @@ fun removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode?, n: Int): ListNode? {
}
```
-Swift:
+### Swift:
+
```swift
func removeNthFromEnd(_ head: ListNode?, _ n: Int) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil {
@@ -297,8 +348,8 @@ func removeNthFromEnd(_ head: ListNode?, _ n: Int) -> ListNode? {
}
```
+### PHP:
-PHP:
```php
function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
// 设置虚拟头节点
@@ -320,7 +371,8 @@ function removeNthFromEnd($head, $n) {
}
```
-Scala:
+### Scala:
+
```scala
object Solution {
def removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode, n: Int): ListNode = {
@@ -344,7 +396,8 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-Rust:
+### Rust:
+
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn remove_nth_from_end(head: Option -
+### C#:
+
+```csharp
+public class Solution {
+ public ListNode RemoveNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ ListNode dummpHead = new ListNode(0);
+ dummpHead.next = head;
+ var fastNode = dummpHead;
+ var slowNode = dummpHead;
+ while(n-- != 0 && fastNode != null)
+ {
+ fastNode = fastNode.next;
+ }
+ while(fastNode.next != null)
+ {
+ fastNode = fastNode.next;
+ slowNode = slowNode.next;
+ }
+ slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next;
+ return dummpHead.next;
+ }
+}
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md" "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 737fab86eb..09cf997839
--- "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
+++ "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+### C#:
+
+```csharp
+public class Solution {
+ public ListNode RemoveNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
+ ListNode dummpHead = new ListNode(0);
+ dummpHead.next = head;
+ var fastNode = dummpHead;
+ var slowNode = dummpHead;
+ while(n-- != 0 && fastNode != null)
+ {
+ fastNode = fastNode.next;
+ }
+ while(fastNode.next != null)
+ {
+ fastNode = fastNode.next;
+ slowNode = slowNode.next;
+ }
+ slowNode.next = slowNode.next.next;
+ return dummpHead.next;
+ }
+}
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md" "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 737fab86eb..09cf997839
--- "a/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
+++ "b/problems/0020.\346\234\211\346\225\210\347\232\204\346\213\254\345\217\267.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4dc051aa74..14d2538f45
--- "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4dc051aa74..14d2538f45
--- "a/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
+++ "b/problems/0024.\344\270\244\344\270\244\344\272\244\346\215\242\351\223\276\350\241\250\344\270\255\347\232\204\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ -## 思路
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[帮你把链表细节学清楚! | LeetCode:24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YT411g7br),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-《代码随想录》算法公开课:[帮你把链表细节学清楚! | LeetCode:24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YT411g7br),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
+## 思路
这道题目正常模拟就可以了。
@@ -31,16 +31,16 @@
初始时,cur指向虚拟头结点,然后进行如下三步:
-
+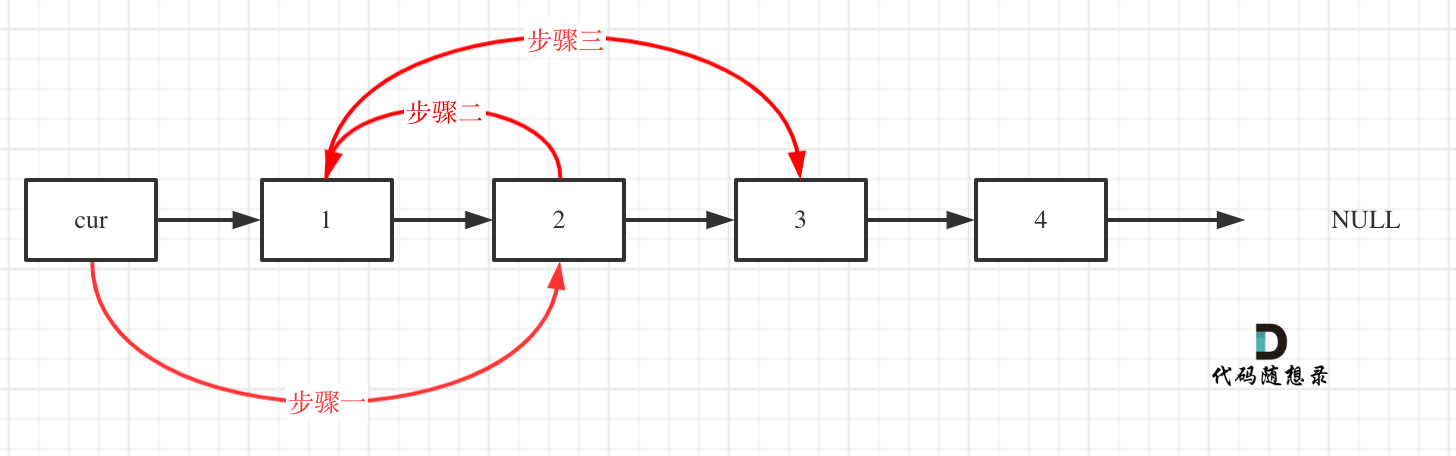
操作之后,链表如下:
-
+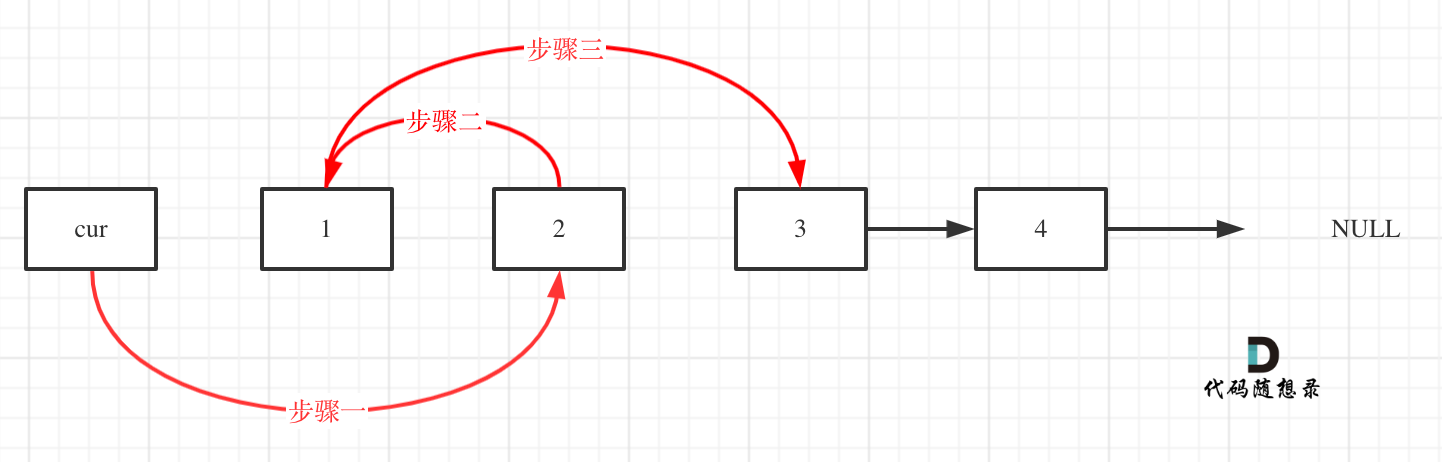
看这个可能就更直观一些了:
-
+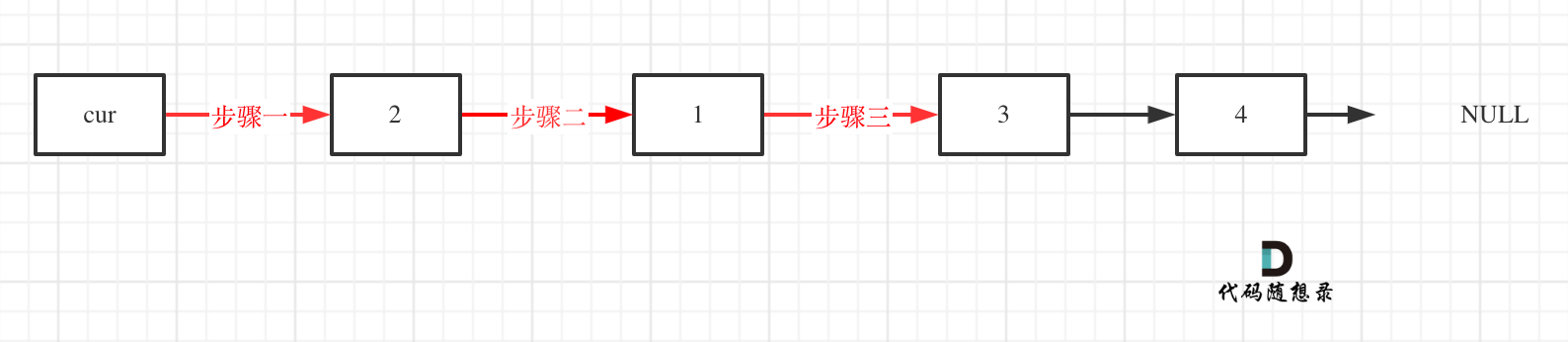
对应的C++代码实现如下: (注释中详细和如上图中的三步做对应)
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
- dummyHead->next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方面后面做删除操作
+ dummyHead->next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方便后面做删除操作
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next; // 记录临时节点
@@ -61,7 +61,9 @@ public:
cur = cur->next->next; // cur移动两位,准备下一轮交换
}
- return dummyHead->next;
+ ListNode* result = dummyHead->next;
+ delete dummyHead;
+ return result;
}
};
```
@@ -77,9 +79,9 @@ public:
上面的代码我第一次提交执行用时8ms,打败6.5%的用户,差点吓到我了。
-心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就$O(n)$的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
+心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就 $O(n)$ 的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
-
+
力扣上的统计如果两份代码是 100ms 和 300ms的耗时,其实是需要注意的。
@@ -88,7 +90,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-C:
+### C:
+
```c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
@@ -132,7 +135,7 @@ struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head){
}
```
-Java:
+### Java:
```Java
// 递归版本
@@ -157,7 +160,7 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dumyhead = new ListNode(-1); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
- dumyhead.next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方面后面做删除操作
+ dumyhead.next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方便后面做删除操作
ListNode cur = dumyhead;
ListNode temp; // 临时节点,保存两个节点后面的节点
ListNode firstnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第一个节点
@@ -176,7 +179,49 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+```java
+// 将步骤 2,3 交换顺序,这样不用定义 temp 节点
+public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
+ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
+ ListNode cur = dummy;
+ while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
+ ListNode node1 = cur.next;// 第 1 个节点
+ ListNode node2 = cur.next.next;// 第 2 个节点
+ cur.next = node2; // 步骤 1
+ node1.next = node2.next;// 步骤 3
+ node2.next = node1;// 步骤 2
+ cur = cur.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummy.next;
+}
+```
+
+### Python:
+
+```python
+# 递归版本
+# Definition for singly-linked list.
+# class ListNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.next = next
+
+class Solution:
+ def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
+ if head is None or head.next is None:
+ return head
+
+ # 待翻转的两个node分别是pre和cur
+ pre = head
+ cur = head.next
+ next = head.next.next
+
+ cur.next = pre # 交换
+ pre.next = self.swapPairs(next) # 将以next为head的后续链表两两交换
+
+ return cur
+```
+
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
@@ -186,24 +231,24 @@ Python:
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
- res = ListNode(next=head)
- pre = res
+ dummy_head = ListNode(next=head)
+ current = dummy_head
- # 必须有pre的下一个和下下个才能交换,否则说明已经交换结束了
- while pre.next and pre.next.next:
- cur = pre.next
- post = pre.next.next
+ # 必须有cur的下一个和下下个才能交换,否则说明已经交换结束了
+ while current.next and current.next.next:
+ temp = current.next # 防止节点修改
+ temp1 = current.next.next.next
- # pre,cur,post对应最左,中间的,最右边的节点
- cur.next = post.next
- post.next = cur
- pre.next = post
+ current.next = current.next.next
+ current.next.next = temp
+ temp.next = temp1
+ current = current.next.next
+ return dummy_head.next
- pre = pre.next.next
- return res.next
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```go
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{
@@ -239,7 +284,8 @@ func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
}
```
-Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
var swapPairs = function (head) {
let ret = new ListNode(0, head), temp = ret;
@@ -254,7 +300,22 @@ var swapPairs = function (head) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+```javascript
+// 递归版本
+var swapPairs = function (head) {
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) {
+ return head;
+ }
+
+ let after = head.next;
+ head.next = swapPairs(after.next);
+ after.next = head;
+
+ return after;
+};
+```
+
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
@@ -273,7 +334,7 @@ function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
};
```
-Kotlin:
+### Kotlin:
```kotlin
fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
@@ -293,7 +354,8 @@ fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
}
```
-Swift:
+### Swift:
+
```swift
func swapPairs(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil || head?.next == nil {
@@ -314,7 +376,8 @@ func swapPairs(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
return dummyHead.next
}
```
-Scala:
+### Scala:
+
```scala
// 虚拟头节点
object Solution {
@@ -338,7 +401,8 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-PHP:
+### PHP:
+
```php
//虚拟头结点
function swapPairs($head) {
@@ -381,7 +445,7 @@ function swapPairs($head)
}
```
-Rust:
+### Rust:
```rust
// 虚拟头节点
@@ -410,7 +474,7 @@ impl Solution {
// 递归
impl Solution {
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option
-## 思路
+## 算法公开课
+
+**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[帮你把链表细节学清楚! | LeetCode:24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YT411g7br),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
-《代码随想录》算法公开课:[帮你把链表细节学清楚! | LeetCode:24. 两两交换链表中的节点](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YT411g7br),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对链表的理解。
+## 思路
这道题目正常模拟就可以了。
@@ -31,16 +31,16 @@
初始时,cur指向虚拟头结点,然后进行如下三步:
-
+
操作之后,链表如下:
-
+
看这个可能就更直观一些了:
-
+
对应的C++代码实现如下: (注释中详细和如上图中的三步做对应)
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
- dummyHead->next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方面后面做删除操作
+ dummyHead->next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方便后面做删除操作
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next; // 记录临时节点
@@ -61,7 +61,9 @@ public:
cur = cur->next->next; // cur移动两位,准备下一轮交换
}
- return dummyHead->next;
+ ListNode* result = dummyHead->next;
+ delete dummyHead;
+ return result;
}
};
```
@@ -77,9 +79,9 @@ public:
上面的代码我第一次提交执行用时8ms,打败6.5%的用户,差点吓到我了。
-心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就$O(n)$的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
+心想应该没有更好的方法了吧,也就 $O(n)$ 的时间复杂度,重复提交几次,这样了:
-
+
力扣上的统计如果两份代码是 100ms 和 300ms的耗时,其实是需要注意的。
@@ -88,7 +90,8 @@ public:
## 其他语言版本
-C:
+### C:
+
```c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
@@ -132,7 +135,7 @@ struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head){
}
```
-Java:
+### Java:
```Java
// 递归版本
@@ -157,7 +160,7 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dumyhead = new ListNode(-1); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
- dumyhead.next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方面后面做删除操作
+ dumyhead.next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方便后面做删除操作
ListNode cur = dumyhead;
ListNode temp; // 临时节点,保存两个节点后面的节点
ListNode firstnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第一个节点
@@ -176,7 +179,49 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+```java
+// 将步骤 2,3 交换顺序,这样不用定义 temp 节点
+public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
+ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
+ ListNode cur = dummy;
+ while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
+ ListNode node1 = cur.next;// 第 1 个节点
+ ListNode node2 = cur.next.next;// 第 2 个节点
+ cur.next = node2; // 步骤 1
+ node1.next = node2.next;// 步骤 3
+ node2.next = node1;// 步骤 2
+ cur = cur.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummy.next;
+}
+```
+
+### Python:
+
+```python
+# 递归版本
+# Definition for singly-linked list.
+# class ListNode:
+# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
+# self.val = val
+# self.next = next
+
+class Solution:
+ def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
+ if head is None or head.next is None:
+ return head
+
+ # 待翻转的两个node分别是pre和cur
+ pre = head
+ cur = head.next
+ next = head.next.next
+
+ cur.next = pre # 交换
+ pre.next = self.swapPairs(next) # 将以next为head的后续链表两两交换
+
+ return cur
+```
+
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
@@ -186,24 +231,24 @@ Python:
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
- res = ListNode(next=head)
- pre = res
+ dummy_head = ListNode(next=head)
+ current = dummy_head
- # 必须有pre的下一个和下下个才能交换,否则说明已经交换结束了
- while pre.next and pre.next.next:
- cur = pre.next
- post = pre.next.next
+ # 必须有cur的下一个和下下个才能交换,否则说明已经交换结束了
+ while current.next and current.next.next:
+ temp = current.next # 防止节点修改
+ temp1 = current.next.next.next
- # pre,cur,post对应最左,中间的,最右边的节点
- cur.next = post.next
- post.next = cur
- pre.next = post
+ current.next = current.next.next
+ current.next.next = temp
+ temp.next = temp1
+ current = current.next.next
+ return dummy_head.next
- pre = pre.next.next
- return res.next
```
-Go:
+### Go:
+
```go
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{
@@ -239,7 +284,8 @@ func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
}
```
-Javascript:
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
var swapPairs = function (head) {
let ret = new ListNode(0, head), temp = ret;
@@ -254,7 +300,22 @@ var swapPairs = function (head) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+```javascript
+// 递归版本
+var swapPairs = function (head) {
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) {
+ return head;
+ }
+
+ let after = head.next;
+ head.next = swapPairs(after.next);
+ after.next = head;
+
+ return after;
+};
+```
+
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
@@ -273,7 +334,7 @@ function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
};
```
-Kotlin:
+### Kotlin:
```kotlin
fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
@@ -293,7 +354,8 @@ fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
}
```
-Swift:
+### Swift:
+
```swift
func swapPairs(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil || head?.next == nil {
@@ -314,7 +376,8 @@ func swapPairs(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
return dummyHead.next
}
```
-Scala:
+### Scala:
+
```scala
// 虚拟头节点
object Solution {
@@ -338,7 +401,8 @@ object Solution {
}
```
-PHP:
+### PHP:
+
```php
//虚拟头结点
function swapPairs($head) {
@@ -381,7 +445,7 @@ function swapPairs($head)
}
```
-Rust:
+### Rust:
```rust
// 虚拟头节点
@@ -410,7 +474,7 @@ impl Solution {
// 递归
impl Solution {
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option -
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 虚拟头结点
+public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
+{
+ var dummyHead = new ListNode();
+ dummyHead.next = head;
+ ListNode cur = dummyHead;
+ while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null)
+ {
+ ListNode tmp1 = cur.next;
+ ListNode tmp2 = cur.next.next.next;
+
+ cur.next = cur.next.next;
+ cur.next.next = tmp1;
+ cur.next.next.next = tmp2;
+
+ cur = cur.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummyHead.next;
+}
+```
+``` C#
+// 递归
+public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
+{
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
+ var cur = head.next;
+ head.next = SwapPairs(head.next.next);
+ cur.next = head;
+ return cur;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 91150c74b9..47e05eec6a
--- "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
-
-
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 虚拟头结点
+public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
+{
+ var dummyHead = new ListNode();
+ dummyHead.next = head;
+ ListNode cur = dummyHead;
+ while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null)
+ {
+ ListNode tmp1 = cur.next;
+ ListNode tmp2 = cur.next.next.next;
+
+ cur.next = cur.next.next;
+ cur.next.next = tmp1;
+ cur.next.next.next = tmp2;
+
+ cur = cur.next.next;
+ }
+ return dummyHead.next;
+}
+```
+``` C#
+// 递归
+public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
+{
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
+ var cur = head.next;
+ head.next = SwapPairs(head.next.next);
+ cur.next = head;
+ return cur;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md" "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 91150c74b9..47e05eec6a
--- "a/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
+++ "b/problems/0027.\347\247\273\351\231\244\345\205\203\347\264\240.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List
-
+###Dart:
+```dart
+int removeElement(List -
-
-
- +
+ 然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
-
然后就找到了下标2,指向b,继续匹配:如图:
- +
+ 以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -163,21 +161,21 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
**很多介绍KMP的文章或者视频并没有把为什么要用前缀表?这个问题说清楚,而是直接默认使用前缀表。**
-# 如何计算前缀表
+### 如何计算前缀表
接下来就要说一说怎么计算前缀表。
如图:
-
以下这句话,对于理解为什么使用前缀表可以告诉我们匹配失败之后跳到哪里重新匹配 非常重要!
@@ -163,21 +161,21 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
**很多介绍KMP的文章或者视频并没有把为什么要用前缀表?这个问题说清楚,而是直接默认使用前缀表。**
-# 如何计算前缀表
+### 如何计算前缀表
接下来就要说一说怎么计算前缀表。
如图:
- +
+ 长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
-
长度为前1个字符的子串`a`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。(注意字符串的**前缀是指不包含最后一个字符的所有以第一个字符开头的连续子串**;**后缀是指不包含第一个字符的所有以最后一个字符结尾的连续子串**。)
- +
+ 长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
-
长度为前2个字符的子串`aa`,最长相同前后缀的长度为1。
- +
+ 长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
-
长度为前3个字符的子串`aab`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
@@ -187,13 +185,13 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
长度为前6个字符的子串`aabaaf`,最长相同前后缀的长度为0。
那么把求得的最长相同前后缀的长度就是对应前缀表的元素,如图:
- +
+ 可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -205,9 +203,9 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
最后就在文本串中找到了和模式串匹配的子串了。
-# 前缀表与next数组
+### 前缀表与next数组
-很多KMP算法的时间都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
+很多KMP算法的实现都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减一(右移一位,初始位置为-1)之后作为next数组。
@@ -217,7 +215,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
后面我会提供两种不同的实现代码,大家就明白了。
-# 使用next数组来匹配
+### 使用next数组来匹配
**以下我们以前缀表统一减一之后的next数组来做演示**。
@@ -227,9 +225,9 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
-# 时间复杂度分析
+### 时间复杂度分析
其中n为文本串长度,m为模式串长度,因为在匹配的过程中,根据前缀表不断调整匹配的位置,可以看出匹配的过程是O(n),之前还要单独生成next数组,时间复杂度是O(m)。所以整个KMP算法的时间复杂度是O(n+m)的。
@@ -239,7 +237,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
都知道使用KMP算法,一定要构造next数组。
-# 构造next数组
+### 构造next数组
我们定义一个函数getNext来构建next数组,函数参数为指向next数组的指针,和一个字符串。 代码如下:
@@ -334,11 +332,11 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
-# 使用next数组来做匹配
+### 使用next数组来做匹配
在文本串s里 找是否出现过模式串t。
@@ -403,7 +401,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
此时所有逻辑的代码都已经写出来了,力扣 28.实现strStr 题目的整体代码如下:
-# 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
+### 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -425,8 +423,8 @@ public:
if (needle.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
- int next[needle.size()];
- getNext(next, needle);
+ vector
可以看出模式串与前缀表对应位置的数字表示的就是:**下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。**
再来看一下如何利用 前缀表找到 当字符不匹配的时候应该指针应该移动的位置。如动画所示:
-
+
找到的不匹配的位置, 那么此时我们要看它的前一个字符的前缀表的数值是多少。
@@ -205,9 +203,9 @@ next数组就是一个前缀表(prefix table)。
最后就在文本串中找到了和模式串匹配的子串了。
-# 前缀表与next数组
+### 前缀表与next数组
-很多KMP算法的时间都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
+很多KMP算法的实现都是使用next数组来做回退操作,那么next数组与前缀表有什么关系呢?
next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减一(右移一位,初始位置为-1)之后作为next数组。
@@ -217,7 +215,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
后面我会提供两种不同的实现代码,大家就明白了。
-# 使用next数组来匹配
+### 使用next数组来匹配
**以下我们以前缀表统一减一之后的next数组来做演示**。
@@ -227,9 +225,9 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
匹配过程动画如下:
-
+
-# 时间复杂度分析
+### 时间复杂度分析
其中n为文本串长度,m为模式串长度,因为在匹配的过程中,根据前缀表不断调整匹配的位置,可以看出匹配的过程是O(n),之前还要单独生成next数组,时间复杂度是O(m)。所以整个KMP算法的时间复杂度是O(n+m)的。
@@ -239,7 +237,7 @@ next数组就可以是前缀表,但是很多实现都是把前缀表统一减
都知道使用KMP算法,一定要构造next数组。
-# 构造next数组
+### 构造next数组
我们定义一个函数getNext来构建next数组,函数参数为指向next数组的指针,和一个字符串。 代码如下:
@@ -334,11 +332,11 @@ void getNext(int* next, const string& s){
代码构造next数组的逻辑流程动画如下:
-
+
得到了next数组之后,就要用这个来做匹配了。
-# 使用next数组来做匹配
+### 使用next数组来做匹配
在文本串s里 找是否出现过模式串t。
@@ -403,7 +401,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { // 注意i就从0开始
此时所有逻辑的代码都已经写出来了,力扣 28.实现strStr 题目的整体代码如下:
-# 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
+### 前缀表统一减一 C++代码实现
```CPP
class Solution {
@@ -425,8 +423,8 @@ public:
if (needle.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
- int next[needle.size()];
- getNext(next, needle);
+ vector -
+>前缀表统一不减一
+```csharp
+public int StrStr(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(needle))
+ return 0;
+
+ if (needle.Length > haystack.Length || string.IsNullOrEmpty(haystack))
+ return -1;
+
+ return KMP(haystack, needle);
+}
+
+public int KMP(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = GetNext(needle);
+ int i = 0, j = 0;
+ while (i < haystack.Length)
+ {
+ if (haystack[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ i++;
+ j++;
+ }
+ if (j == needle.Length)
+ return i-j;
+ else if (i < haystack.Length && haystack[i] != needle[j])
+ if (j != 0)
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+public int[] GetNext(string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = new int[needle.Length];
+ next[0] = 0;
+ int i = 1, j = 0;
+ while (i < needle.Length)
+ {
+ if (needle[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ next[i++] = ++j;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ if (j == 0)
+ {
+ next[i++] = 0;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+```
+
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 34aa1086c0..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+>前缀表统一不减一
+```csharp
+public int StrStr(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(needle))
+ return 0;
+
+ if (needle.Length > haystack.Length || string.IsNullOrEmpty(haystack))
+ return -1;
+
+ return KMP(haystack, needle);
+}
+
+public int KMP(string haystack, string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = GetNext(needle);
+ int i = 0, j = 0;
+ while (i < haystack.Length)
+ {
+ if (haystack[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ i++;
+ j++;
+ }
+ if (j == needle.Length)
+ return i-j;
+ else if (i < haystack.Length && haystack[i] != needle[j])
+ if (j != 0)
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+public int[] GetNext(string needle)
+{
+ int[] next = new int[needle.Length];
+ next[0] = 0;
+ int i = 1, j = 0;
+ while (i < needle.Length)
+ {
+ if (needle[i] == needle[j])
+ {
+ next[i++] = ++j;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ if (j == 0)
+ {
+ next[i++] = 0;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ j = next[j - 1];
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+```
+
+### C:
+
+> 前缀表统一右移和减一
+
+```c
+
+int *build_next(char* needle, int len) {
+
+ int *next = (int *)malloc(len * sizeof(int));
+ assert(next); // 确保分配成功
+
+ // 初始化next数组
+ next[0] = -1; // next[0] 设置为 -1,表示没有有效前缀匹配
+ if (len <= 1) { // 如果模式串长度小于等于 1,直接返回
+ return next;
+ }
+ next[1] = 0; // next[1] 设置为 0,表示第一个字符没有公共前后缀
+
+ // 构建next数组, i 从模式串的第三个字符开始, j 指向当前匹配的最长前缀长度
+ int i = 2, j = 0;
+ while (i < len) {
+ if (needle[i - 1] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ next[i] = j;
+ i++;
+ } else if (j > 0) {
+ // 如果不匹配且 j > 0, 回退到次长匹配前缀的长度
+ j = next[j];
+ } else {
+ next[i] = 0;
+ i++;
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+
+int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {
+
+ int needle_len = strlen(needle);
+ int haystack_len = strlen(haystack);
+
+ int *next = build_next(needle, needle_len);
+
+ int i = 0, j = 0; // i 指向主串的当前起始位置, j 指向模式串的当前匹配位置
+ while (i <= haystack_len - needle_len) {
+ if (haystack[i + j] == needle[j]) {
+ j++;
+ if (j == needle_len) {
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL
+ return i;
+ }
+ } else {
+ i += j - next[j]; // 调整主串的起始位置
+ j = j > 0 ? next[j] : 0;
+ }
+ }
+
+ free(next);
+ next = NULL;
+ return -1;
+}
+```
diff --git "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 34aa1086c0..4bbf20fbb8
--- "a/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0031.\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -92,9 +90,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -159,7 +157,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+### Python
>直接使用sorted()会开辟新的空间并返回一个新的list,故补充一个原地反转函数
```python
class Solution:
@@ -191,7 +189,7 @@ class Solution:
"""
```
-## Go
+### Go
```go
//卡尔的解法
@@ -216,7 +214,7 @@ func reverse(a []int,begin,end int){
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
//卡尔的解法(吐槽一下JavaScript的sort和其他语言的不太一样,只想到了拷贝数组去排序再替换原数组来实现nums的[i + 1, nums.length)升序排序)
@@ -268,7 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
-
对应的C++代码如下:
@@ -92,9 +90,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
class Solution {
@@ -159,7 +157,7 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+### Python
>直接使用sorted()会开辟新的空间并返回一个新的list,故补充一个原地反转函数
```python
class Solution:
@@ -191,7 +189,7 @@ class Solution:
"""
```
-## Go
+### Go
```go
//卡尔的解法
@@ -216,7 +214,7 @@ func reverse(a []int,begin,end int){
}
```
-## JavaScript
+### JavaScript
```js
//卡尔的解法(吐槽一下JavaScript的sort和其他语言的不太一样,只想到了拷贝数组去排序再替换原数组来实现nums的[i + 1, nums.length)升序排序)
@@ -268,7 +266,4 @@ var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
```
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e58a870d8..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7e58a870d8..37248e4819
--- "a/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0034.\345\234\250\346\216\222\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\344\270\255\346\237\245\346\211\276\345\205\203\347\264\240\347\232\204\347\254\254\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\222\214\346\234\200\345\220\216\344\270\200\344\270\252\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### C
+```c
+int searchLeftBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录leftBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int leftBorder = -1;
+ // 边界为[left, right]
+ while (left <= right) {
+ // 更新middle值,等同于middle = (left + right) / 2
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将左边界设为middle,并向左继续寻找左边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ leftBorder = middle;
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return leftBorder;
+}
+int searchRightBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录rightBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int rightBorder = -1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将右边界设为middle,并向右继续寻找右边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ rightBorder = middle;
+ left = middle + 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return rightBorder;
+}
+
+int* searchRange(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
+ int leftBorder = searchLeftBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+ int rightBorder = searchRightBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+
+ // 定义返回数组及数组大小
+ *returnSize = 2;
+ int *resNums = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
+ resNums[0] = leftBorder;
+ resNums[1] = rightBorder;
+ return resNums;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4d9ee74fb2..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
+### C
+```c
+int searchLeftBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录leftBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int leftBorder = -1;
+ // 边界为[left, right]
+ while (left <= right) {
+ // 更新middle值,等同于middle = (left + right) / 2
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将左边界设为middle,并向左继续寻找左边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ leftBorder = middle;
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return leftBorder;
+}
+int searchRightBorder(int *nums, int numsSize, int target) {
+ int left = 0, right = numsSize - 1;
+ // 记录rightBorder没有被赋值的情况
+ int rightBorder = -1;
+ while (left <= right) {
+ int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
+ // 若当前middle所指为target,将右边界设为middle,并向右继续寻找右边界
+ if (nums[middle] == target) {
+ rightBorder = middle;
+ left = middle + 1;
+ } else if (nums[middle] > target) {
+ right = middle - 1;
+ } else {
+ left = middle + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return rightBorder;
+}
+
+int* searchRange(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
+ int leftBorder = searchLeftBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+ int rightBorder = searchRightBorder(nums, numsSize, target);
+
+ // 定义返回数组及数组大小
+ *returnSize = 2;
+ int *resNums = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
+ resNums[0] = leftBorder;
+ resNums[1] = rightBorder;
+ return resNums;
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md" "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4d9ee74fb2..b48910eef7
--- "a/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
+++ "b/problems/0035.\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\217\222\345\205\245\344\275\215\347\275\256.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18a96d581b..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md" "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 18a96d581b..204f0cc092
--- "a/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0037.\350\247\243\346\225\260\347\213\254.md"
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a3c62c53dd..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,45 +1,47 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a3c62c53dd..d8dac0b45b
--- "a/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0039.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,45 +1,47 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 415fdb605f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md" "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 415fdb605f..0d3972662f
--- "a/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0040.\347\273\204\345\220\210\346\200\273\345\222\214II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8ea81234cc..62fbe270b7
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md" "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8ea81234cc..62fbe270b7
--- "a/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0042.\346\216\245\351\233\250\346\260\264.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d4f2e6ea78..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md" "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d4f2e6ea78..c20cdc65e6
--- "a/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0045.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217II.md"
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 86bc704d4b..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 86bc704d4b..356f51b5a8
--- "a/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0046.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3eb99948ea..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md" "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3eb99948ea..5330997a66
--- "a/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0047.\345\205\250\346\216\222\345\210\227II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 624452fd2c..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md" "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 624452fd2c..d06d7798e8
--- "a/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
+++ "b/problems/0051.N\347\232\207\345\220\216.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c88fb3c7b..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md" "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c88fb3c7b..6c6650ad00
--- "a/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0052.N\347\232\207\345\220\216II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14017f9899..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14017f9899..84bb5f6663
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 506c000fd2..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 506c000fd2..ba44a36104
--- "a/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0053.\346\234\200\345\244\247\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\222\214\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 858741d0b0..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md" "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 858741d0b0..8b700c1fe8
--- "a/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
+++ "b/problems/0054.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7b02075bdb..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md" "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7b02075bdb..513fc2e340
--- "a/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
+++ "b/problems/0055.\350\267\263\350\267\203\346\270\270\346\210\217.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3c980c2be3..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md" "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3c980c2be3..24a97f6c5a
--- "a/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
+++ "b/problems/0056.\345\220\210\345\271\266\345\214\272\351\227\264.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d9a656b9f6..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md" "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d9a656b9f6..927df1c6c1
--- "a/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0059.\350\236\272\346\227\213\347\237\251\351\230\265II.md"
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### Ruby:
+```ruby
+def generate_matrix(n)
+ result = Array.new(n) { Array.new(n, 0) }
+ #循环次数
+ loop_times = 0
+ #步长
+ step = n - 1
+ val = 1
+
+
+ while loop_times < n / 2
+ #模拟从左向右
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[loop_times][i+loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从上到下
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[i+loop_times][n-loop_times-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从右到左
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[n-loop_times-1][n-loop_times-i-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从下到上
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[n-loop_times-i-1][loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ loop_times += 1
+ step -= 2
+ end
+
+ #如果是奇数,则填充最后一个元素
+ result[n/2][n/2] = n**2 if n % 2
+
+ return result
+
+end
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40655f0c28..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
-
-
+### Ruby:
+```ruby
+def generate_matrix(n)
+ result = Array.new(n) { Array.new(n, 0) }
+ #循环次数
+ loop_times = 0
+ #步长
+ step = n - 1
+ val = 1
+
+
+ while loop_times < n / 2
+ #模拟从左向右
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[loop_times][i+loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从上到下
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[i+loop_times][n-loop_times-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从右到左
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #行数不变,列数变
+ result[n-loop_times-1][n-loop_times-i-1] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ #模拟从下到上
+ for i in 0..step - 1
+ #列数不变,行数变
+ result[n-loop_times-i-1][loop_times] = val
+ val += 1
+ end
+
+ loop_times += 1
+ step -= 2
+ end
+
+ #如果是奇数,则填充最后一个元素
+ result[n/2][n/2] = n**2 if n % 2
+
+ return result
+
+end
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md" "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 40655f0c28..ac60767dce
--- "a/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
+++ "b/problems/0062.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204.md"
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c4ce3f954f..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md" "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c4ce3f954f..f39afe8455
--- "a/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0063.\344\270\215\345\220\214\350\267\257\345\276\204II.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14aeef0142..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 14aeef0142..316fbd4f39
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3093c83325..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,33 +1,35 @@
-
-
+
+
diff --git "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md" "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3093c83325..a5435ddd71
--- "a/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
+++ "b/problems/0070.\347\210\254\346\245\274\346\242\257\345\256\214\345\205\250\350\203\214\345\214\205\347\211\210\346\234\254.md"
@@ -1,33 +1,35 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8a877d2088..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md" "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8a877d2088..c4bcbb4338
--- "a/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
+++ "b/problems/0072.\347\274\226\350\276\221\350\267\235\347\246\273.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+Rust:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; word2.len() + 1]; word1.len() + 1];
+ for i in 1..=word2.len() {
+ dp[0][i] = i;
+ }
+
+ for (j, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ v[0] = j;
+ }
+ for (i, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ for (j, char2) in word2.chars().enumerate() {
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j];
+ continue;
+ }
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].min(dp[i + 1][j]).min(dp[i][j]) + 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()][word2.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 一维 dp
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![0; word1.len() + 1];
+ for (i, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ *v = i;
+ }
+
+ for char2 in word2.chars() {
+ // 相当于 dp[i][0] 的初始化
+ let mut pre = dp[0];
+ dp[0] += 1; // j = 0, 将前 i 个字符变成空串的个数
+ for (j, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ let temp = dp[j + 1];
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[j + 1] = pre;
+ } else {
+ dp[j + 1] = dp[j + 1].min(dp[j]).min(pre) + 1;
+ }
+ pre = temp;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 77ea5e80eb..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,37 +1,32 @@
-
-
+Rust:
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![vec![0; word2.len() + 1]; word1.len() + 1];
+ for i in 1..=word2.len() {
+ dp[0][i] = i;
+ }
+
+ for (j, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ v[0] = j;
+ }
+ for (i, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ for (j, char2) in word2.chars().enumerate() {
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j];
+ continue;
+ }
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j + 1].min(dp[i + 1][j]).min(dp[i][j]) + 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()][word2.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
+> 一维 dp
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_distance(word1: String, word2: String) -> i32 {
+ let mut dp = vec![0; word1.len() + 1];
+ for (i, v) in dp.iter_mut().enumerate().skip(1) {
+ *v = i;
+ }
+
+ for char2 in word2.chars() {
+ // 相当于 dp[i][0] 的初始化
+ let mut pre = dp[0];
+ dp[0] += 1; // j = 0, 将前 i 个字符变成空串的个数
+ for (j, char1) in word1.chars().enumerate() {
+ let temp = dp[j + 1];
+ if char1 == char2 {
+ dp[j + 1] = pre;
+ } else {
+ dp[j + 1] = dp[j + 1].min(dp[j]).min(pre) + 1;
+ }
+ pre = temp;
+ }
+ }
+
+ dp[word1.len()] as i32
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md" "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 77ea5e80eb..4c9e97fd47
--- "a/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0077.\347\273\204\345\220\210.md"
@@ -1,37 +1,32 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### Ruby
+
+```ruby
+
+def combine(n, k)
+ result = []
+ path = []
+ backtracking(result, path, n, 1, k)
+ return result
+end
+
+#剪枝优化
+def backtracking(result, path, n, j, k)
+ if path.size == k
+ result << path.map {|item| item}
+ return
+ end
+
+ for i in j..(n-(k - path.size)) + 1
+ #处理节点
+ path << i
+ backtracking(result, path, n, i + 1, k)
+ #回溯,撤销处理过的节点
+ path.pop
+ end
+end
+
+```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 暴力
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList
-
+### Ruby
+
+```ruby
+
+def combine(n, k)
+ result = []
+ path = []
+ backtracking(result, path, n, 1, k)
+ return result
+end
+
+#剪枝优化
+def backtracking(result, path, n, j, k)
+ if path.size == k
+ result << path.map {|item| item}
+ return
+ end
+
+ for i in j..(n-(k - path.size)) + 1
+ #处理节点
+ path << i
+ backtracking(result, path, n, i + 1, k)
+ #回溯,撤销处理过的节点
+ path.pop
+ end
+end
+
+```
+### C#
+```csharp
+// 暴力
+public class Solution
+{
+ public IList -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0c51d4496..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md" "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b0c51d4496..844b8dc2ca
--- "a/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0078.\345\255\220\351\233\206.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb06414334..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md" "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index eb06414334..99fb1678e6
--- "a/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
+++ "b/problems/0084.\346\237\261\347\212\266\345\233\276\344\270\255\346\234\200\345\244\247\347\232\204\347\237\251\345\275\242.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a02161aa92..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md" "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index a02161aa92..2e8945c90f
--- "a/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0090.\345\255\220\351\233\206II.md"
@@ -1,9 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f99a7a5d0..b9a3e08f63
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md" "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1f99a7a5d0..b9a3e08f63
--- "a/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
+++ "b/problems/0093.\345\244\215\345\216\237IP\345\234\260\345\235\200.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 99a4b8dda3..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 99a4b8dda3..e5bc2b6b65
--- "a/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0096.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93c2272cf6..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 93c2272cf6..990d3c8413
--- "a/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0098.\351\252\214\350\257\201\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96acacf61c..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 96acacf61c..df1b55a462
--- "a/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0100.\347\233\270\345\220\214\347\232\204\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c2812fa64..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 1c2812fa64..24e9e2684e
--- "a/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0101.\345\257\271\347\247\260\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c6ce488cb..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,43 +1,45 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md" "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 5c6ce488cb..819153be97
--- "a/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
+++ "b/problems/0102.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\345\261\202\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206.md"
@@ -1,43 +1,45 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e54221db8c..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index e54221db8c..52d6d0e5fd
--- "a/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0104.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\244\247\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9c563619da..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 9c563619da..5253325835
--- "a/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0106.\344\273\216\344\270\255\345\272\217\344\270\216\345\220\216\345\272\217\351\201\215\345\216\206\345\272\217\345\210\227\346\236\204\351\200\240\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f0455a834f..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index f0455a834f..2df1c2615b
--- "a/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0108.\345\260\206\346\234\211\345\272\217\346\225\260\347\273\204\350\275\254\346\215\242\344\270\272\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\220\234\347\264\242\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 492e25d9a5..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 492e25d9a5..d5b100ae80
--- "a/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
+++ "b/problems/0110.\345\271\263\350\241\241\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbe7b7ecad..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md" "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index cbe7b7ecad..e1ee42657c
--- "a/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
+++ "b/problems/0111.\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221\347\232\204\346\234\200\345\260\217\346\267\261\345\272\246.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f0133663..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index b1f0133663..73795bcfc9
--- "a/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0112.\350\267\257\345\276\204\346\200\273\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index daa708bc84..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md" "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index daa708bc84..499bf100e2
--- "a/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
+++ "b/problems/0115.\344\270\215\345\220\214\347\232\204\345\255\220\345\272\217\345\210\227.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31bb6822cc..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md" "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 31bb6822cc..88d3abc93e
--- "a/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
+++ "b/problems/0116.\345\241\253\345\205\205\346\257\217\344\270\252\350\212\202\347\202\271\347\232\204\344\270\213\344\270\200\344\270\252\345\217\263\344\276\247\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\214\207\351\222\210.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ public:
};
```
-## 迭代(层序遍历)
+### 迭代(层序遍历)
本题使用层序遍历是最为直观的,如果对层序遍历不了解,看这篇:[二叉树:层序遍历登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html)。
@@ -114,9 +112,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
// 递归法
@@ -169,7 +167,57 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue
最关键的点是可以通过上一层递归 搭出来的线,进行本次搭线。
@@ -83,7 +81,7 @@ public:
};
```
-## 迭代(层序遍历)
+### 迭代(层序遍历)
本题使用层序遍历是最为直观的,如果对层序遍历不了解,看这篇:[二叉树:层序遍历登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html)。
@@ -114,9 +112,9 @@ public:
};
```
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-## Java
+### Java
```java
// 递归法
@@ -169,7 +167,57 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-## Python
+```Java
+// 迭代法
+class Solution {
+ public Node connect(Node root) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return root;
+ }
+
+ Queue -
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8736c9f375..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md" "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 8736c9f375..d12cbf2fe2
--- "a/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
+++ "b/problems/0121.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d094da488e..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,46 +1,50 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index d094da488e..0da4241931
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II.md"
@@ -1,46 +1,50 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2779083d89..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md" "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 2779083d89..d8cb308b7e
--- "a/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
+++ "b/problems/0122.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272II\357\274\210\345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\357\274\211.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cd7ab26f8..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md" "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 3cd7ab26f8..063477cb5a
--- "a/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
+++ "b/problems/0123.\344\271\260\345\215\226\350\202\241\347\245\250\347\232\204\346\234\200\344\275\263\346\227\266\346\234\272III.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7ffd6a21e6..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md" "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 7ffd6a21e6..0204606056
--- "a/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
+++ "b/problems/0127.\345\215\225\350\257\215\346\216\245\351\276\231.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 445e108aa9..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
diff --git "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md" "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 445e108aa9..1568a49469
--- "a/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
+++ "b/problems/0129.\346\261\202\346\240\271\345\210\260\345\217\266\345\255\220\350\212\202\347\202\271\346\225\260\345\255\227\344\271\213\345\222\214.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- +
+ 代码如下:
@@ -116,7 +114,7 @@ path.pop_back(); // 回溯
```
**把回溯放在花括号外面了,世界上最遥远的距离,是你在花括号里,而我在花括号外!** 这就不对了。
-## 整体C++代码
+整体C++代码
关键逻辑分析完了,整体C++代码如下:
@@ -162,16 +160,16 @@ public:
};
```
-# 总结
+## 总结
过于简洁的代码,很容易让初学者忽视了本题中回溯的精髓,甚至作者本身都没有想清楚自己用了回溯。
**我这里提供的代码把整个回溯过程充分体现出来,希望可以帮助大家看的明明白白!**
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
```java
class Solution {
@@ -219,7 +217,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
class Solution:
def sumNumbers(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
@@ -246,7 +245,7 @@ class Solution:
backtrace(root)
return res
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
@@ -271,7 +270,8 @@ func dfs(root *TreeNode, tmpSum int, sum *int) {
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
const listToInt = path => {
@@ -315,7 +315,7 @@ var sumNumbers = function(root) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
@@ -351,7 +351,7 @@ function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
};
```
-C:
+### C:
```c
//sum记录总和
@@ -380,7 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
-
代码如下:
@@ -116,7 +114,7 @@ path.pop_back(); // 回溯
```
**把回溯放在花括号外面了,世界上最遥远的距离,是你在花括号里,而我在花括号外!** 这就不对了。
-## 整体C++代码
+整体C++代码
关键逻辑分析完了,整体C++代码如下:
@@ -162,16 +160,16 @@ public:
};
```
-# 总结
+## 总结
过于简洁的代码,很容易让初学者忽视了本题中回溯的精髓,甚至作者本身都没有想清楚自己用了回溯。
**我这里提供的代码把整个回溯过程充分体现出来,希望可以帮助大家看的明明白白!**
-# 其他语言版本
+## 其他语言版本
-Java:
+### Java:
```java
class Solution {
@@ -219,7 +217,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
-Python:
+### Python:
+
```python
class Solution:
def sumNumbers(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
@@ -246,7 +245,7 @@ class Solution:
backtrace(root)
return res
```
-Go:
+### Go:
```go
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
@@ -271,7 +270,8 @@ func dfs(root *TreeNode, tmpSum int, sum *int) {
-JavaScript:
+### JavaScript:
+
```javascript
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
const listToInt = path => {
@@ -315,7 +315,7 @@ var sumNumbers = function(root) {
};
```
-TypeScript:
+### TypeScript:
```typescript
function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
@@ -351,7 +351,7 @@ function sumNumbers(root: TreeNode | null): number {
};
```
-C:
+### C:
```c
//sum记录总和
@@ -380,7 +380,4 @@ int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root){
}
```
- -
+
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c2aa569693..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
-
-
+
diff --git "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md" "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index c2aa569693..10d6585c4c
--- "a/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
+++ "b/problems/0130.\350\242\253\345\233\264\347\273\225\347\232\204\345\214\272\345\237\237.md"
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
- -
-
-
- -
+### Java
+
+```Java
+// 广度优先遍历
+// 使用 visited 数组进行标记
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ // rowSize:行的长度,colSize:列的长度
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
+ Queue
-
+### Java
+
+```Java
+// 广度优先遍历
+// 使用 visited 数组进行标记
+class Solution {
+ private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
+
+ public void solve(char[][] board) {
+ // rowSize:行的长度,colSize:列的长度
+ int rowSize = board.length, colSize = board[0].length;
+ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
+ Queue