Abstract
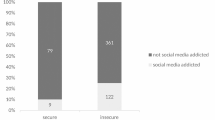
Current society is characterized by the increasing impact of online communication tools. In recent years, researchers have dedicated their efforts to the study of addictive behavior to internet and social networks as it is essential to know both the benefits and possible issues that the internet could hold for the youth and new generations. Moreover, it is fundamental to inquire about the personality traits that have influence over addictive behavior. As such the objective of this study was to measure the link between the model of five personality traits and the problematic use of social networks. In this regard, different surveys were applied online to a sample of 251 university students between the age of 18 and 24 years old. The surveys used are as follows: a questionnaire that collects socio-demographic data, the big five inventory (BFI) and the social networking addiction questionnaire (SNA). The results are: (1) a positive correlation between the neuroticism and addictive behavior to social networks, (2) a notable yet negative correlation between responsibility and kindness and (3) there was no link found between extroversion and openness to experience. In conclusion, the obtained results contribute empirical evidence of the relation between the personality and the addictive behavior to the social networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Available if required.
References
Andreassen, C. S., Griffiths, M. D., Gjertsen, S. R., Krossbakken, E., Kvam, S., & Pallesen, S. (2013). The relationships between behavioral addictions and the five-factor model of personality. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 2(2), 90–99. https://doi.org/10.1556/JBA.2.2013.003.
Arias, O., Gallego, V., Rodríguez, M., & del Pozo, M. (2012). Adicción a las nuevas tecnologías. Psicología de Las Adicciones, 1, 2–6. http://www.biblioteca.cij.gob.mx/Archivos/Materiales_de_consulta/Drogas_de_Abuso/Articulos/tratamiento%20marihuana%207.pdf#page=5.
Becerra, J. R. (2017). Conducta adictiva a redes sociales y relación con el modelo de los cinco factores de personalidad (Master dissertation). Mexico: Autonomous University of Nuevo Leon.
Biolcati, R., Mancini, G., Pupi, V., & Mugheddu, V. (2018). Facebook addiction: Onset predictors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(6), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7060118.
Buckner, J. E., Castille, C. M., & Sheets, T. L. (2012). The five factor model of personality and employees excessive use of technology computers in human behavior the five factor model of personality and employees’ excessive use of technology. Computers in Human Behavior, 28, 1947–1953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.05.014.
Davis, R. A. (2001). A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological internet use. Computers in Human Behavior, 17(2), 187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0747-5632(00)00041-8.
Escurra, M., & Salas, E. (2014). Construcción y validación del cuestionario de adicción a redes sociales (ARS). Liberabit, 20(1), 73–91. Retrieved from https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/686/68631260007.pdf.
Gámez-Guadix, M., & Villa-George, I. (2015). El modelo cognitivo-conductual de la adicción a Internet: El papel de la depresión y la impulsividad en adolescentes mexicanos. Psicología y Salud, 25(34), 111–122. https://doi.org/10.25009/pys.v25i1.1344.
Giota, K. G., & Kleftaras, G. (2013). The role of personality and depression in problematic use of social networking sites in Greece. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 7. https://doi.org/10.5817/CP2013-3-6.
Golberg, L. R. (1993). The structure of phenotypic personality traits. American Psychologist, 48(1), 26–34.
Hernangómez, L., & Fernández, C. (2012). Psicología de la personalidad y diferencial. Psicología de La Personalidad Y Diferencial (pp. 78–86). Spain: CEDE. Retrieved from https://pir.es/temasmuestra/07tema.pdf.
Herrera, M., Pacheco, M., Palomar, J., & Zavala, D. (2010). La adicción a facebook relacionada con la baja autoestima , la depresión y la falta de habilidades sociales. Psicología Iberoamericana, 18, 6–18. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/1339/133915936002.pdf.
Jafarkarimi, H., Tze, A., Sim, H., Saadatdoost, R., & Hee, J. M. (2016). Facebook addiction among malaysian students. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 6(6). https://doi.org/10.7763/IJIET.2016.V6.733.
Jasso-Medrano, J. L., & López-Rosales, F. (2018). Measuring the relationship between social media use and addictive behavior and depression and suicide ideation among university students. Computers in Human Behavior, 87, 183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.05.003.
Jasso-Medrano, J. L., López-Rosales, F., & Díaz-Loving, R. (2017). Conducta adictiva a las redes sociales y su relación con el uso problemático del móvil. Acta de Investigación Psicológica, 7(3), 2832–2838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aipprr.2017.11.001.
John, O. P., & Srivastava, S. (1999). The big-five trait taxonomy: History, measurement, and theoretical perspectives. 1999, 510. http://moityca.com.br/pdfs/bigfive_John.pdf.
Kuss, D. J., Van Rooij, A. J., Shorter, G. W., Griffiths, M. D., & van de Mheen, D. (2013). Internet addiction in adolescents: Prevalence and risk factors. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(5), 1987–1996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.04.002.
Kwon, M., Kim, D.-J., Cho, H., & Yang, S. (2013). The smartphone addiction scale: Development and validation of a short version for adolescents. PLoS One, 8(12). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083558.
Montag, C., Jurkiewicz, M., & Reuter, M. (2010). Computers in human behavior low self-directedness is a better predictor for problematic internet use than high neuroticism. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1531–1535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.05.021.
Müller, K. W., Dreier, M., Beutel, M. E., Duven, E., Giralt, S., & Wölfling, K. (2016). A hidden type of internet addiction? Intense and addictive use of social networking sites in adolescents. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.09.007.
Norman, P., Elavarasan, K., & Dhandapani, T. (2017). Facebook addiction and depression in adults [19 years-64 years ]. International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health, 4(8), 2999–3004. https://doi.org/10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20173361.
Ozer, D. J., & Bennet-Martinez, V. (2006). Personality and the prediction of consequential outcomes. Annual Review of Psychology, 57. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.57.102904.190127.
Puerta-Cortés, D. X., & Carbonell, X. (2014). El modelo de los cinco grandes factores de personalidad y el uso problemático de Internet en jóvenes colombianos. Adicciones, 26, 54–61. https://doi.org/10.20882/adicciones.131.
Reyes, E., Álvarez, C., Peredo, A., Miranda, A., & Rebolledo, I. M. (2014). Psychometric properties of the big five inventory in a Mexican sample. Salud Mental, 37(6), 491–497. https://doi.org/10.17711/SM.0185-3325.2014.059.
Rueda, J. P., & Flores, J. G. (2016). Adicción a las redes sociales en estudiantes universitarios. Tlamati Sabiduria. 7(1) 512–525. http://tlamati.uagro.mx/t7e1/48.pdf.
Ryan, T., & Xenos, S. (2011). Computers in human behavior who uses facebook? An investigation into the relationship between the Big Five, shyness, narcissism, loneliness, and Facebook usage. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(5), 1658–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2011.02.004.
Tekkanat, E., & Topaloglu, M. (2015). The Assessment of high schoolers’ internet addiction. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 205(May), 664–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.09.104.
Uribe, J. F., Contreras, F., Sánchez, O., García, A. (2008). Los cinco grandes y maquiavelismo en trabajadores mexicanos: Un estudio de personalidad y manipulación. Revista de Psicología del Trabajo y de las Organizaciones, 24(1), 61–79. http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1576-59622008000100004.
Valencia-Ortiz, R., & Cabero-Almenara, J. (2019). La adicción a las redes sociales: Validación de un instrumento en el contexto mexicano. Health & Addictions/Salud y Drogas, 19(2), 149–159. https://doi.org/10.21134/haaj.v19i2.460.
Viñas, F. (2009). Uso autoinformado de Internet en adolescentes: Perfil psicológico de un uso elevado de la red. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 1, 109–122. https://www.ijpsy.com/volumen9/num1/225/uso-autoinformado-de-internet-en-adolescentes-ES.pdf.
Zhou, Y., Li, D., Li, X., Wang, Y., & Zhao, L. (2017). Addictive behaviors big five personality and adolescent Internet addiction: The mediating role of coping style. Addictive Behaviors, 64, 42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.08.009.
Funding
This work was supported by the Support Program for Scientific and Technological Research (PAICYT) [Grant Numbers CSH024-15].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FLR, JRBG, JLJM drafted the manuscript. FLR was involved in structure, translation and submission of the manuscript. JRBG and JLJM were involved in corrections of the revised manuscript, data collection and statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The project was reviewed and approved by the research Ethics Committee of the Psychology Faculty of the Autonomous University of Nuevo Leon.
Informed Consent
First, the study objectives were informed to the participants. The participation of the people involved was voluntary and guaranteeing the privacy of each answer. If they accepted the consent to participate, they could answer and complete the survey.
Consent to Publication
The researchers involved agree to the publication of the results.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López Rosales, F., Becerra Guajardo, J.R. & Jasso Medrano, J.L. Addictive Behavior to Social Networks and Five Personality Traits in Young People. Psychol Stud 66, 92–96 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-020-00591-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-020-00591-7